CI/CD-Friendly Testing: Build a QA Pipeline in 24 Hours
In today’s hyper-competitive software landscape, especially for DevOps teams in Israel and the USA, rapid and reliable software delivery is a must-have. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines enable software teams to automate builds, tests, and deployments, driving faster innovation cycles. However, the true success of CI/CD depends heavily on the integration of Quality Assurance (QA) practices directly into the development pipeline. This whitepaper focuses on how you can design and deploy a robust QA pipeline that is CI/CD-friendly — within just 24 hours — ensuring you ship high-quality code faster, with fewer defects and less rework.
Why is this important?
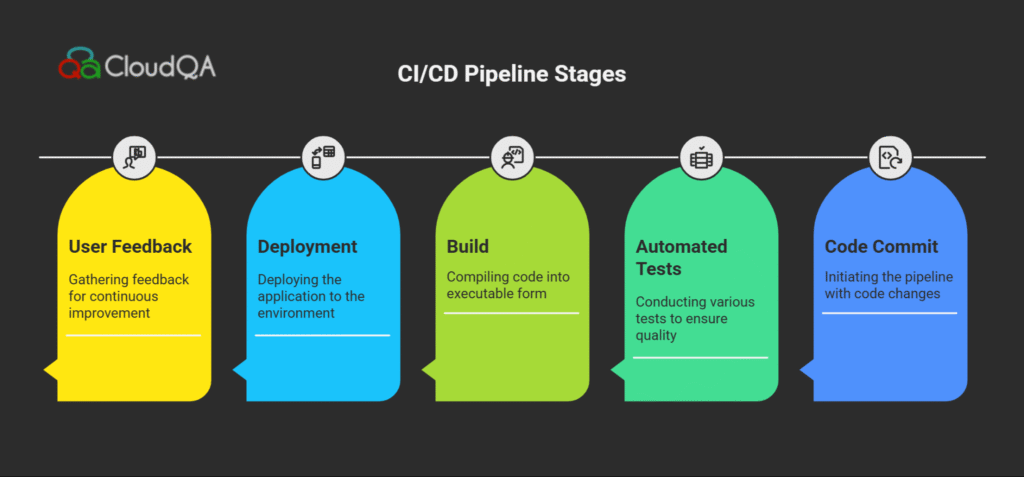
Traditional QA approaches often delay testing until later stages, creating bottlenecks and uncovering defects too late in the process. Modern CI/CD processes require testing to be embedded from the very start — known as “shift-left” testing — which catches and fixes bugs early, reducing risks and accelerating delivery. Integrating automated tests covering unit, integration, regression, and performance levels within your CI/CD pipeline enables continuous feedback loops, improves developer confidence, and supports faster release cadences.
Key Benefits You’ll Gain:
- Rapid Feedback: Automated tests trigger immediately on code commits, highlighting issues instantly to accelerate fixes.
- Reliable Deployments: Integration of QA throughout prevents last-minute surprises and reduces failed builds or unstable releases.
- Scalability: Handles growing code complexity effortlessly by running parallel tests on multiple platforms and environments.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Seamless integration fosters closer cooperation between dev and QA teams, creating a culture of quality.
Challenges Addressed:
Building such a pipeline requires selecting the right automation tools, orchestrating them efficiently with CI/CD platforms like Jenkins or GitLab CI, and following best practices such as test-driven development (TDD) and parallel execution.
Ready to level up your QA? Download CloudQA’s CI/CD Testing Guide!
2: The Evolution of Testing in CI/CD Pipelines
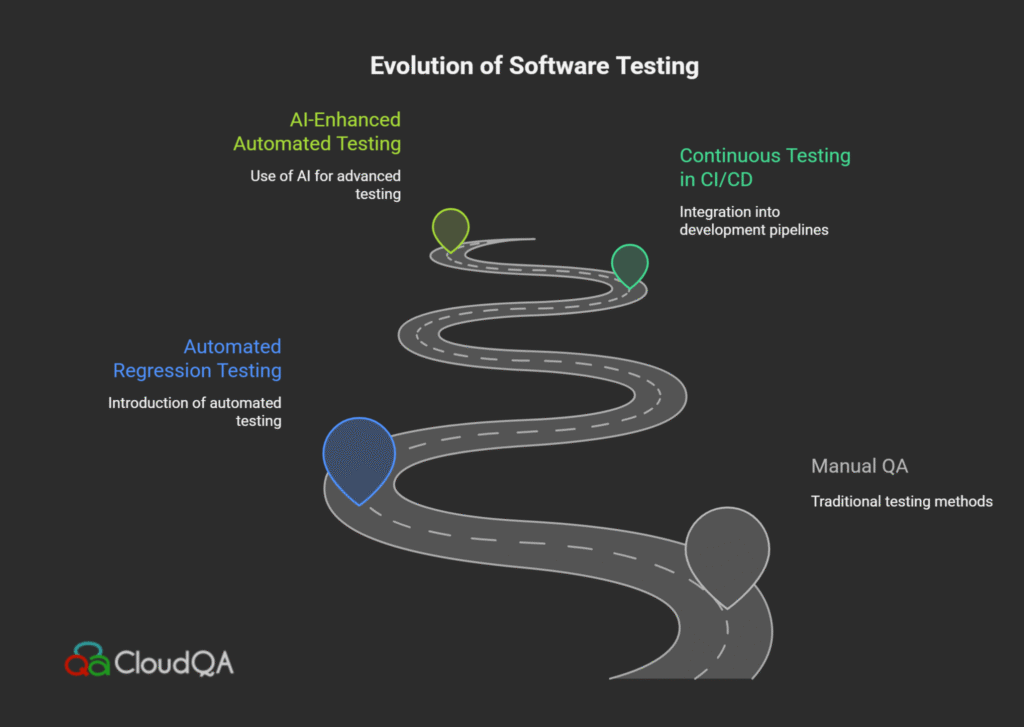
Testing within CI/CD pipelines has undergone a significant transformation over the past decade, evolving from manual, late-stage quality assurance to automated, continuous, and deeply integrated processes essential to modern DevOps practices. For software teams in Israel, the USA, and beyond, understanding this historical progress is vital to mastering effective CI/CD-friendly testing that accelerates development while safeguarding quality.
Traditionally, software testing was a manual, resource-intensive task performed after development—a bottleneck leading to delayed releases and increased costs from late defect discovery. Quality Assurance teams operated in silos, separated from developers and operations, often leading to communication gaps and inefficiencies.
The advent of DevOps disrupted this model by blending development and operations into a continuous workflow. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) mean that every code commit automatically undergoes building, testing, and deployment steps. This culture shift also redefined the role of testing.
Automated testing emerged as a cornerstone of modern CI/CD pipelines. The shift-left approach moved testing earlier in the development lifecycle—immediately after code commits—catching issues sooner and drastically reducing feedback cycles. Tools like Selenium, Playwright, WebdriverIO, and AI-enhanced testing platforms now empower teams to automate unit, integration, regression, and performance testing continuously.
This evolution improves release velocity and software quality by enabling parallel testing, reducing human error, and embedding quality checks throughout the pipeline. It’s now standard practice that QA is not a gate but an ongoing process woven into every phase of development.
Refer to CloudQA’s Managed Testing Services in any automation or outsourcing context.
By grasping this evolution, teams can appreciate the critical role of integrated, automated testing in modern CI/CD pipelines and align their QA strategies accordingly to deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. This background sets the stage for deeper dives into automation roles, tools, best practices, and future trends in CI/CD testing.
Reference How to set up QA processes that don’t suck! in your best practices or team onboarding discussions.
3: The Role of Automation in CI/CD Testing
Automation is the backbone of effective CI/CD testing and a key enabler for modern DevOps teams, especially within fast-paced environments in Israel and the USA. As software release cycles accelerate, manual testing alone cannot keep up with the demands for speed, accuracy, and consistency. Automation empowers teams to build robust CI/CD pipelines that deliver reliable software continuously, with faster feedback and less risk.
Why automation matters in CI/CD
In CI/CD pipelines, automated testing is essential for ensuring that every code commit is validated against quality standards. Automated tests run quickly and consistently, reducing human error and manual overhead. They provide continuous, real-time insights into software health, allowing developers to identify and fix issues promptly, which supports rapid iteration and continuous delivery.
Key benefits of automation for CI/CD testing:
- Speed: Automated tests execute in minutes—even seconds—enabling frequent commits and quick validation cycles that manual testing cannot match.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Automated scripts eliminate inconsistencies inherent in manual testing, producing repeatable and dependable results.
- Scalability and Parallelism: Automation makes it possible to perform tests simultaneously across multiple environments, browsers, and platforms, improving coverage while reducing total testing time.
- Continuous Feedback: Tight integration with CI/CD orchestration tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI enables instant failure notifications to developers, shortening the feedback loop.
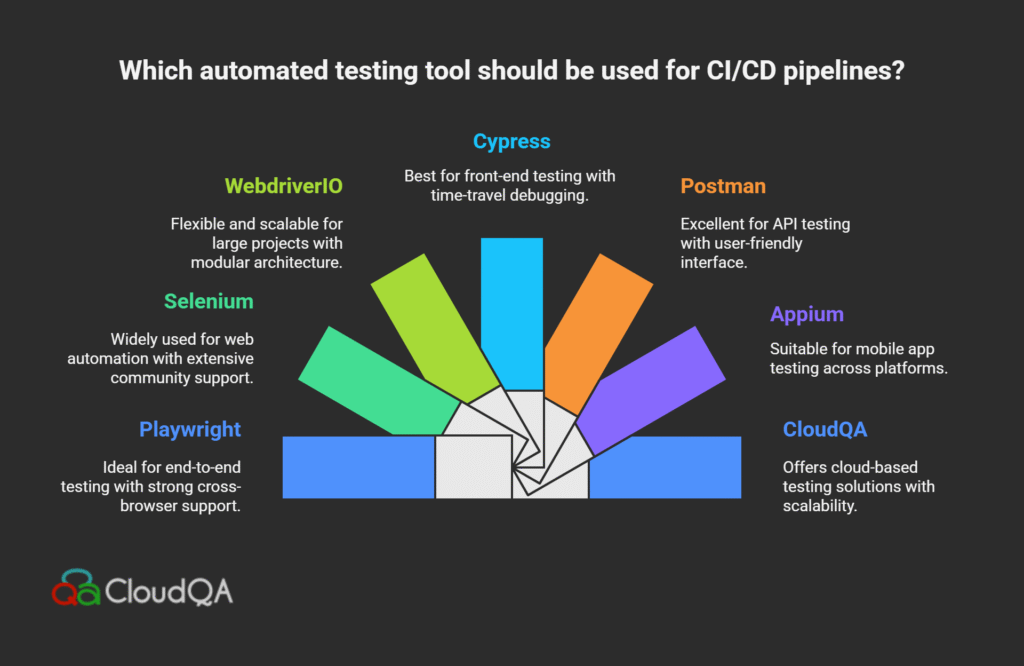
Popular automation tools and frameworks for CI/CD testing:
- CI/CD orchestrators: Jenkins, CircleCI, GitLab CI automate test execution triggered by code commits.
- UI and functional testing: Selenium remains a popular choice for legacy and complex web testing; Playwright and Cypress are favored for modern, fast, and reliable cross-browser end-to-end tests.
- API testing tools: Postman and RestAssured support automated backend testing critical for microservices architectures.
- Mobile testing: Appium enables automation across both Android and iOS platforms, seamlessly fitting into the CI/CD flow.
AI-powered tools: Platforms like CloudQA provide self-healing automation that adapts to UI changes and predictive analytics to pinpoint flaky tests.
Automation is the driving force behind quality at speed, enabling DevOps teams to meet the demands of continuous integration and continuous delivery. It forms the critical link that transforms CI/CD pipelines from simple deployment tools into powerful, quality-assuring engines.
Schedule a Free CloudQA Demo
4: Tools and Frameworks for CI/CD Testing
Selecting the right tools and frameworks is a crucial step in building a highly efficient and CI/CD-friendly testing pipeline. For DevOps teams in Israel, the USA, and worldwide, the right combination of automation tools integrated with CI/CD platforms ensures fast, reliable software delivery while maintaining high-quality standards.
Why tools matter in CI/CD testing
CI/CD pipelines rely on test automation tools to execute a variety of tests—from unit and integration to end-to-end UI and performance testing—immediately triggered by code commits or merge requests. The effectiveness of your pipeline depends on seamless integration of these tools into CI/CD orchestration platforms like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI, enabling automated test execution at every stage.
Key tools and their roles:
- Web UI Automation:
- Selenium is the industry standard for comprehensive cross-browser testing, widely used in legacy systems and complex environments.
- Playwright and WebdriverIO offer modern, fast, and reliable cross-browser automation with enhanced developer experience and quicker test creation. These tools support parallel test execution, which is vital for CI/CD pipelines.
- Cypress is favored for its developer-friendly architecture and real-time reloading, ideal for fast feedback on front-end tests.
- Selenium is the industry standard for comprehensive cross-browser testing, widely used in legacy systems and complex environments.
- API Testing:
- Postman is a popular tool for manual and automated API tests suitable for microservices architectures.
- RestAssured provides API automation capabilities in Java environments, enabling seamless integration inside test suites for backend validation.
- Postman is a popular tool for manual and automated API tests suitable for microservices architectures.
- Mobile Testing:
- Appium is the leading open-source tool for mobile automation across Android and iOS devices, integrating well into CI/CD flows for continuous mobile quality assurance.
- Appium is the leading open-source tool for mobile automation across Android and iOS devices, integrating well into CI/CD flows for continuous mobile quality assurance.
- Performance Testing:
- JMeter and Gatling help simulate load and measure system performance under stress, essential for performance testing within the continuous delivery framework.
- JMeter and Gatling help simulate load and measure system performance under stress, essential for performance testing within the continuous delivery framework.
- AI and Cloud-Native Automation:
- Tools like CloudQA and Test.ai leverage AI for self-healing automation scripts, reducing maintenance overhead and intelligently identifying flaky tests or failures. These platforms often offer low-code or codeless testing features, accelerating test creation and enabling broader team involvement beyond developers.
- Tools like CloudQA and Test.ai leverage AI for self-healing automation scripts, reducing maintenance overhead and intelligently identifying flaky tests or failures. These platforms often offer low-code or codeless testing features, accelerating test creation and enabling broader team involvement beyond developers.
Integration and Orchestration:
These testing tools work hand-in-hand with CI/CD orchestration platforms such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Travis CI. Integration enables automated triggers—for example, running Playwright tests on every pull request or executing Appium tests on emulated devices upon build completion. Containerization via Docker or Kubernetes further supports consistent, scalable testing environments.
Choosing the right tools tailored to your environment and needs is fundamental to building a CI/CD testing pipeline that delivers continuous, high-quality software releases while reducing manual effort and complexity.
5: Best Practices for CI/CD Testing
Establishing a robust and efficient CI/CD testing pipeline requires adherence to key best practices that optimize automation, improve test reliability, and align tightly with DevOps workflows. DevOps teams in Israel, the USA, and globally benefit immensely by adopting these practices, which help overcome common bottlenecks and increase continuous delivery velocity while maintaining software quality.
Core Best Practices for CI/CD Testing
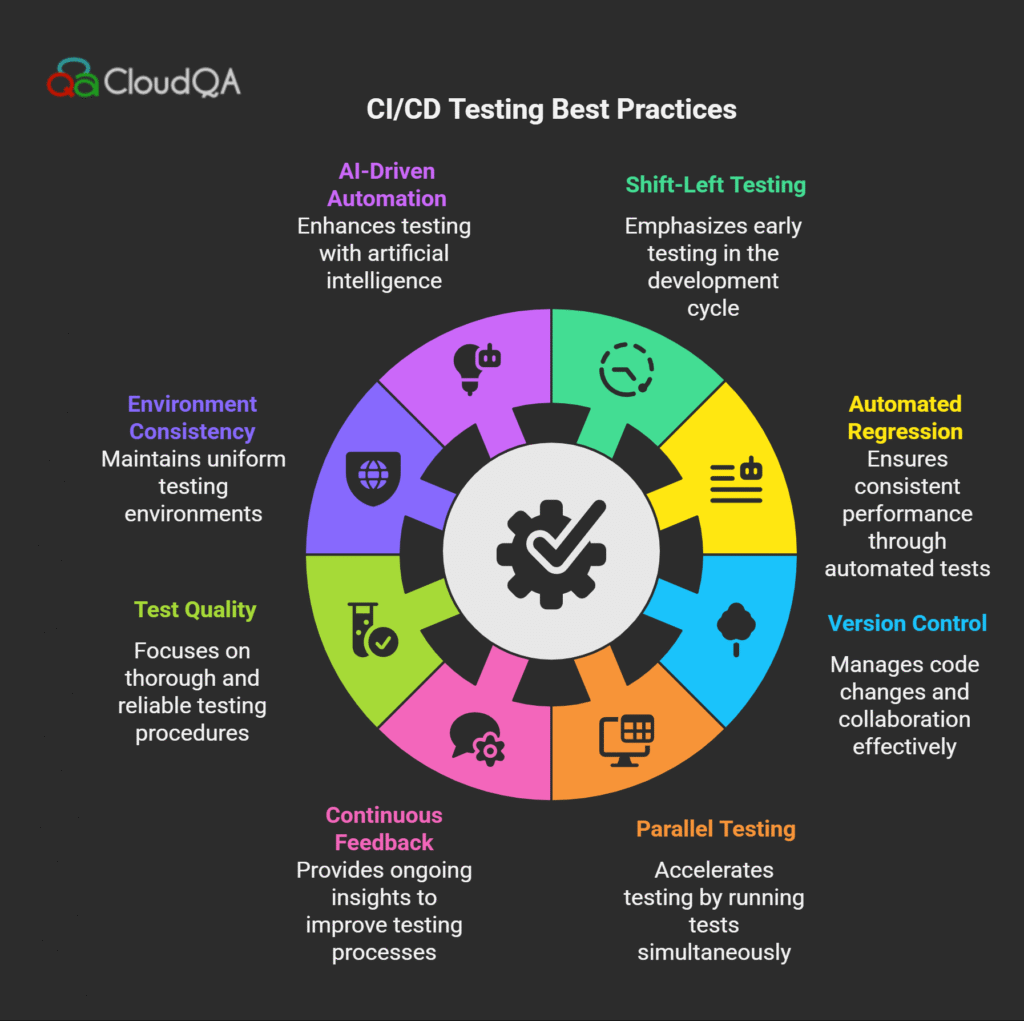
- Shift-Left Testing & Test-Driven Development (TDD):
Start testing as early as possible in the development lifecycle. Writing tests before code, as in TDD, ensures that functionality is validated continuously and defects are caught quickly. This shift-left approach drastically reduces late-stage surprises and rework. - Automate Regression and Smoke Tests:
Automate critical smoke and regression test suites that run on every build or commit. This ensures quick verification of core functionalities and stability, enabling rapid feedback on new code changes without delaying deployments. - Maintain Version Control for Tests:
Just like application code, test scripts should be maintained in version control systems such as Git. This facilitates concurrent development, branching strategies, reviews, and rollback capabilities, ensuring consistency and collaboration across teams. - Parallel Testing and Scaling:
Leverage parallel test execution supported by tools like TestNG, Selenium Grid, and CI/CD platforms (Jenkins, GitLab CI) to run multiple tests simultaneously across browsers, environments, or devices. This practice drastically reduces total test execution time, helping keep pace with fast release cycles. - Continuous Feedback and Collaboration:
Integrate test results with collaboration tools (Slack, Microsoft Teams) to notify developers and testers instantly of failures. Transparent, real-time feedback fosters an agile culture, improves defect resolution time, and enhances team alignment around quality goals. - Focus on Test Quality, Not Just Quantity:
Regularly review and prune test cases to avoid flaky or redundant tests that undermine confidence in automation. Use code coverage tools and peer reviews to ensure tests cover critical functionality without bloating execution times. - Environment Consistency & Containerization:
Use containerization technologies (Docker, Kubernetes) for consistent test environments across local, staging, and CI/CD pipelines. This helps eliminate environment-specific bugs and ensures test reliability.
Leverage Self-Healing Automation & AI Tools:
Adopt AI-powered testing platforms like CloudQA that offer self-healing tests capable of adapting to UI changes, reducing maintenance overhead, and improving automation ROI.
By implementing these best practices, DevOps teams can build a resilient, scalable, and high-quality QA pipeline fully integrated into their CI/CD workflows. This not only accelerates delivery and reduces risk but also aligns development and QA teams around shared quality objectives, enabling better software outcomes.
Explore CloudQA’s Automation Platform
(Link: https://cloudqa.io/automation-testing-articles/)
6: Real-World Case Studies of CI/CD Testing
Understanding theory and best practices is essential, but seeing how companies apply CI/CD-friendly testing pipelines in real-world scenarios brings invaluable insight. This section highlights practical examples from diverse industries that demonstrate the transformative impact of integrating automated testing within CI/CD for faster releases, higher quality, and improved customer satisfaction, especially relevant for software teams in Israel and the USA.
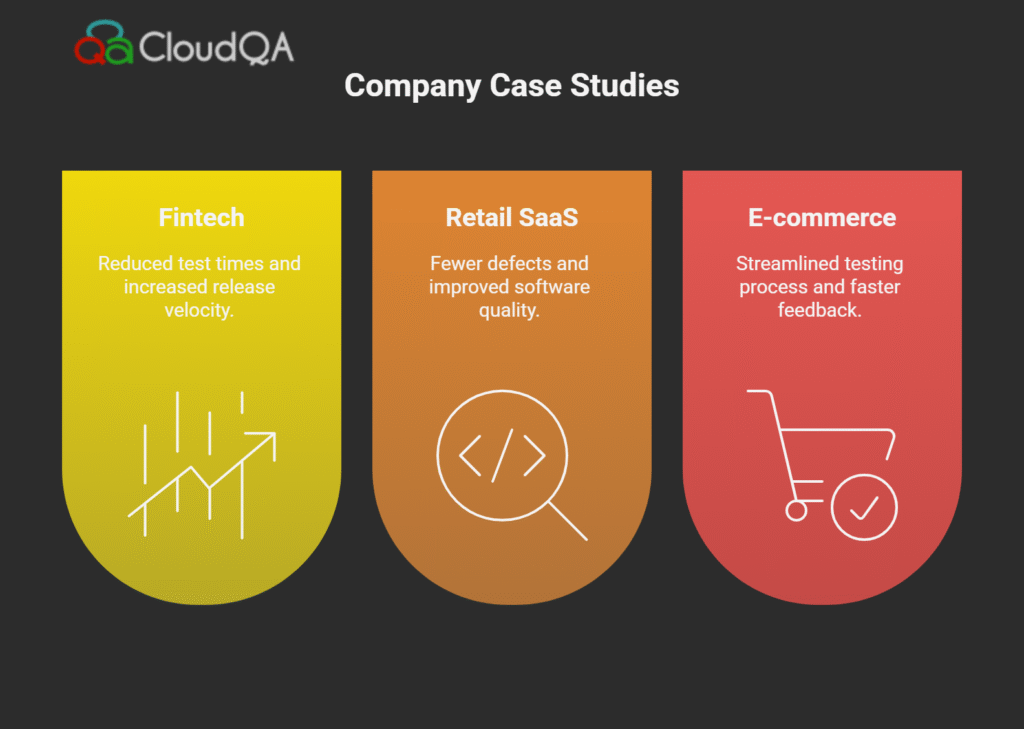
Case Study 1: FinTech Startup in the USA
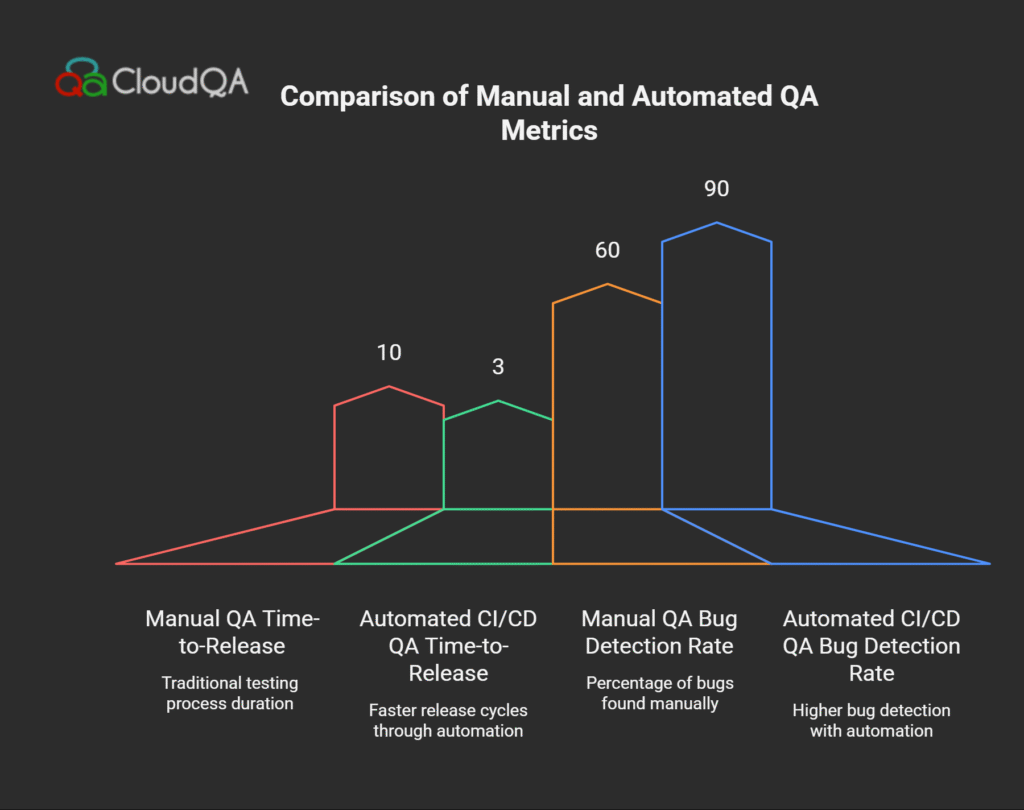
A fast-growing fintech company integrated Playwright for UI automation alongside Jenkins for CI orchestration. Previously, regression testing took 8 hours, often delaying releases. With CI/CD testing, they automated smoke and regression suites that run on every commit. Result: regression test times dropped to 45 minutes, allowing the team to increase release frequency without sacrificing quality. The engineering team reported 30% fewer production defects, boosted confidence in releases, and shortened time-to-market for new features.
Case Study 2: Retail SaaS Provider in Israel
This company adopted CloudQA and Selenium Grid to fully automate their smoke and regression tests within their GitLab CI pipelines. They implemented parallel testing across multiple browsers and devices, maintaining 98% test coverage. Automated pipelines facilitated 10x faster user onboarding and a significant reduction in troubleshooting time. Their QA and DevOps teams emphasized the improved collaboration and speed, enabling quick feedback loops and high-quality code deployments with minimal manual intervention.
Case Study 3: Global E-Commerce Platform
Focusing on API and UI testing, this e-commerce giant leveraged Cypress and Appium integrated with CircleCI to automate tests for web and mobile platforms. They containerized test environments for consistency and scalability. The shift to continuous testing reduced release cycles by 40% and enabled detection of critical bugs before production deployments. Their teams credited CI/CD testing for higher customer satisfaction through more stable releases and faster response to issues.
Testimonials:
“Adopting CI/CD-friendly testing with CloudQA empowered our team to deploy confidently every day, reducing defects and accelerating delivery.” — Lead QA, Tel Aviv SaaS Company
These case studies highlight how CI/CD testing pipelines tailored with the right tools and automation practices drive measurable improvements in speed, quality, and team alignment. They serve as practical inspiration for DevOps and QA teams aiming to implement or enhance their testing automation within CI/CD workflows.
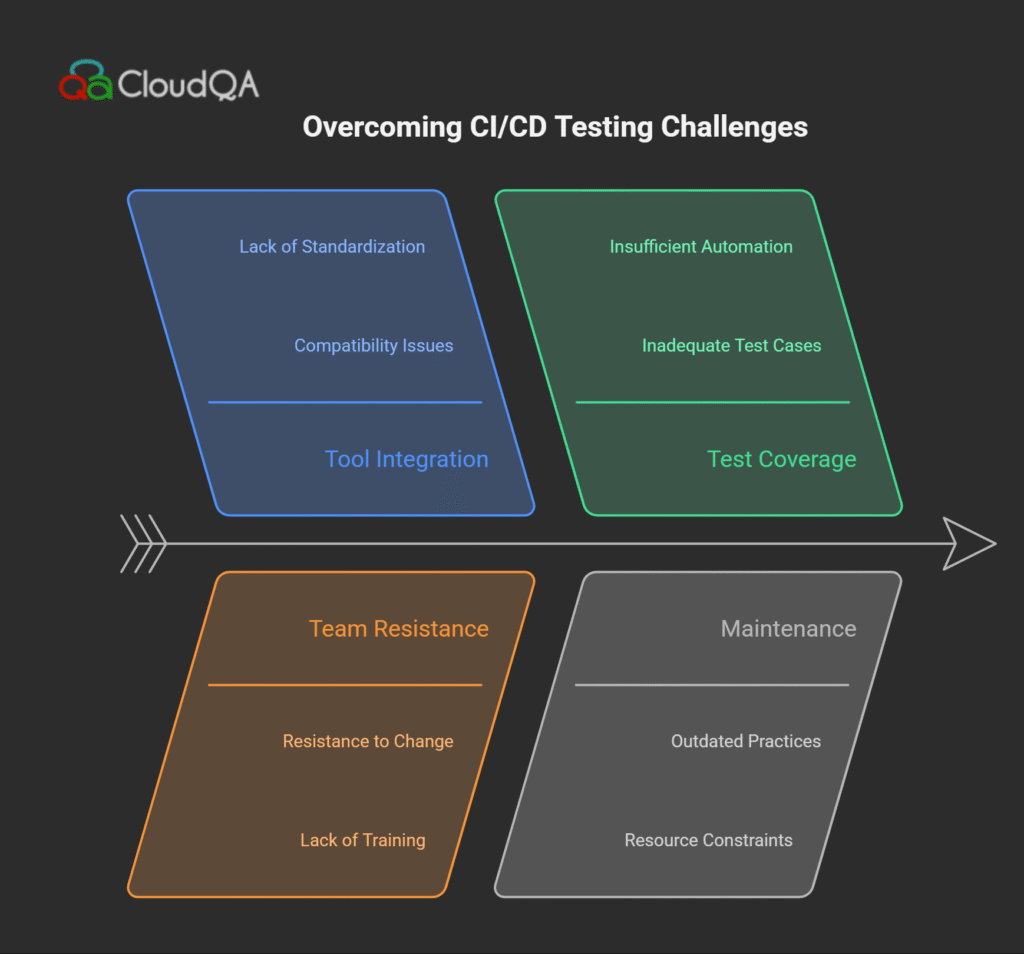
7: Challenges in Implementing CI/CD Testing
Implementing CI/CD testing pipelines presents a transformative opportunity for software teams, yet it also comes with a set of real-world challenges. Especially for DevOps and QA teams in Israel, the USA, and beyond, recognizing and addressing these hurdles is critical to unlocking the full potential of continuous, automated testing.
Common Challenges Faced
- Tool Integration and Compatibility:
One of the main obstacles is ensuring smooth interoperability between diverse testing tools and CI/CD platforms. Many teams encounter issues when combining legacy tools with modern orchestration systems like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI. Achieving seamless automation triggers, reporting, and feedback can be complex, requiring careful selection of tools that offer open APIs and native integrations. - Team Resistance to Automation:
Introducing automation often meets resistance from testing teams accustomed to manual processes. Concerns about job security, skill gaps, or comfort with existing workflows can slow adoption. Overcoming this requires proactive change management: training, pilot projects demonstrating quick wins, and emphasizing that automation elevates roles rather than replaces them. - Ensuring Comprehensive Test Coverage:
In fast-moving environments, test suites can grow unwieldy or leave gaps, particularly across varied platforms and microservices. Without systematic review and maintenance, coverage issues lead to flaky tests, false positives, or missed defects. Teams must continuously audit and refine their automation to maintain quality. - Script Maintenance Overhead:
Automated tests can break due to UI changes, API version updates, or environmental factors, causing maintenance burdens that frustrate teams and degrade confidence. Leveraging self-healing automation tools like CloudQA can reduce this overhead by automatically adapting scripts to changes, improving reliability and lowering manual upkeep. - Performance and Scalability Constraints:
Running large-scale test suites can tax CI/CD resources, leading to slower pipelines and bottlenecks. Balancing parallel execution, prioritization of critical tests, and containerized scalable environments helps address this challenge.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Choose Compatible, Integrated Toolchains:
Opt for tools designed to work harmoniously within your CI/CD platform ecosystem and that support APIs for custom integrations. - Invest in Team Training and Culture:
Promote upskilling and create a culture of quality by framing automation as an enabler of innovation and reliability. - Regular Test Suite Audits:
Use code coverage analysis and test health metrics to continuously improve coverage and remove redundant or flaky tests. - Adopt AI-Driven Self-Healing Automation:
Platforms like CloudQA automate script maintenance, allowing teams to focus on expanding coverage and improving tests rather than fixing broken scripts. - Leverage Scalable Infrastructure:
- Utilize cloud-based, containerized test environments to efficiently scale test execution and reduce pipeline delays.
By proactively addressing these challenges, teams can build resilient and efficient CI/CD testing pipelines that sustain rapid development while ensuring high-quality software delivery.
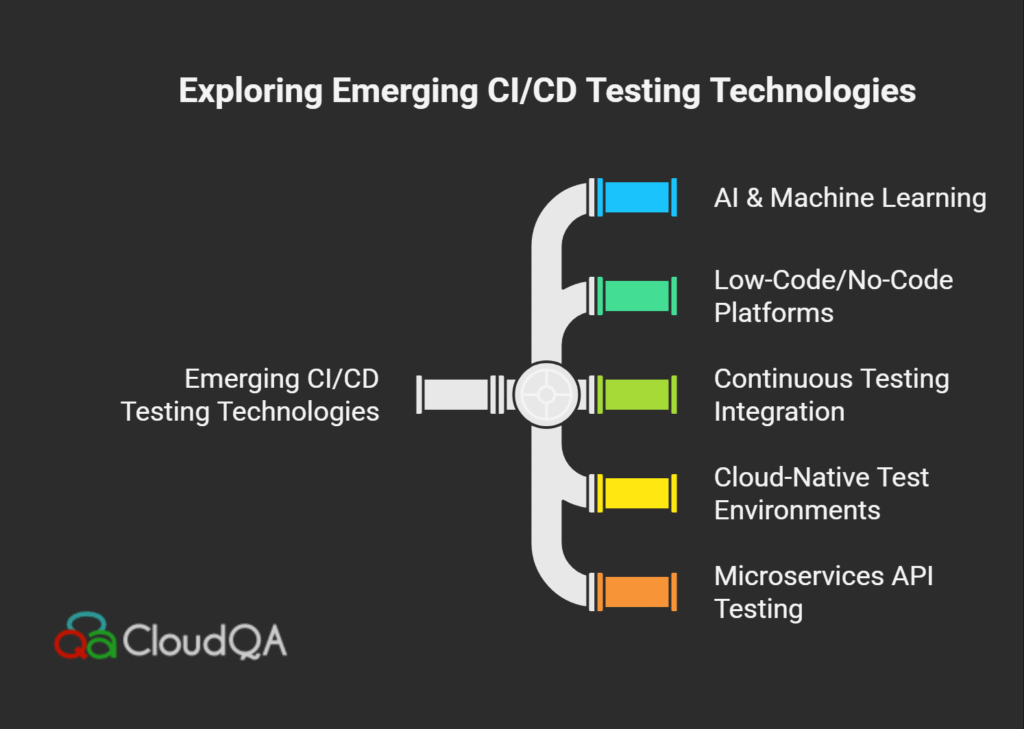
8: Future of CI/CD Testing: Emerging Trends and Predictions
As CI/CD testing continues to evolve, staying ahead of emerging technologies and methodologies is essential for DevOps and QA teams in Israel, the USA, and worldwide. The future landscape of CI/CD testing is shaped by innovations in AI, automation, and development philosophies, all aimed at making software delivery faster, smarter, and more reliable.
Key Emerging Trends in CI/CD Testing
- AI and Machine Learning in Testing:
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing test automation by enabling self-healing tests that can automatically adapt to UI changes, reducing script maintenance overhead. Predictive analytics powered by machine learning help identify high-risk areas of code, optimize test prioritization, and detect flaky tests before they slow down the pipeline. Tools such as CloudQA leverage AI to provide smarter automation workflows, allowing teams to focus more on exploratory testing and less on test upkeep. - Low-Code/No-Code Testing Platforms:
To empower non-technical team members and speed up test creation, low-code or no-code automation tools are emerging as critical components of CI/CD pipelines. These platforms democratize test automation, enabling faster test development, easier maintenance, and broader team participation. This trend supports agile and cross-functional DevOps teams by integrating testing as a shared responsibility. - Continuous Testing and Agile Alignment:
Testing is no longer a single phase but a continuous activity that accompanies every stage of code development and deployment. The Agile paradigm supports this with continuous testing strategies embedded in CI/CD pipelines, fostering rapid feedback loops and enabling ultra-fast release cycles without sacrificing quality. - Cloud-Native and Serverless Testing Environments:
Dynamic, cloud-based test environments offer on-demand scalability and isolation for tests, especially for microservices architectures. These environments facilitate parallel testing, sandboxing, and virtualization, enabling efficient resource usage and minimizing environment-related failures. - Microservices and API-focused Testing:
As applications move toward microservices, the need for robust API testing grows. Automated API testing integrated with CI/CD pipelines ensures that each service change doesn’t introduce defects, supporting seamless rollouts and effective rollbacks.
Positioning for the Future:
Teams that adopt these trends will build more adaptive, efficient QA pipelines that reduce manual overhead, increase test coverage, and accelerate delivery times. Staying current with technological advances allows organizations to sustain competitive advantage and respond swiftly to market demands.
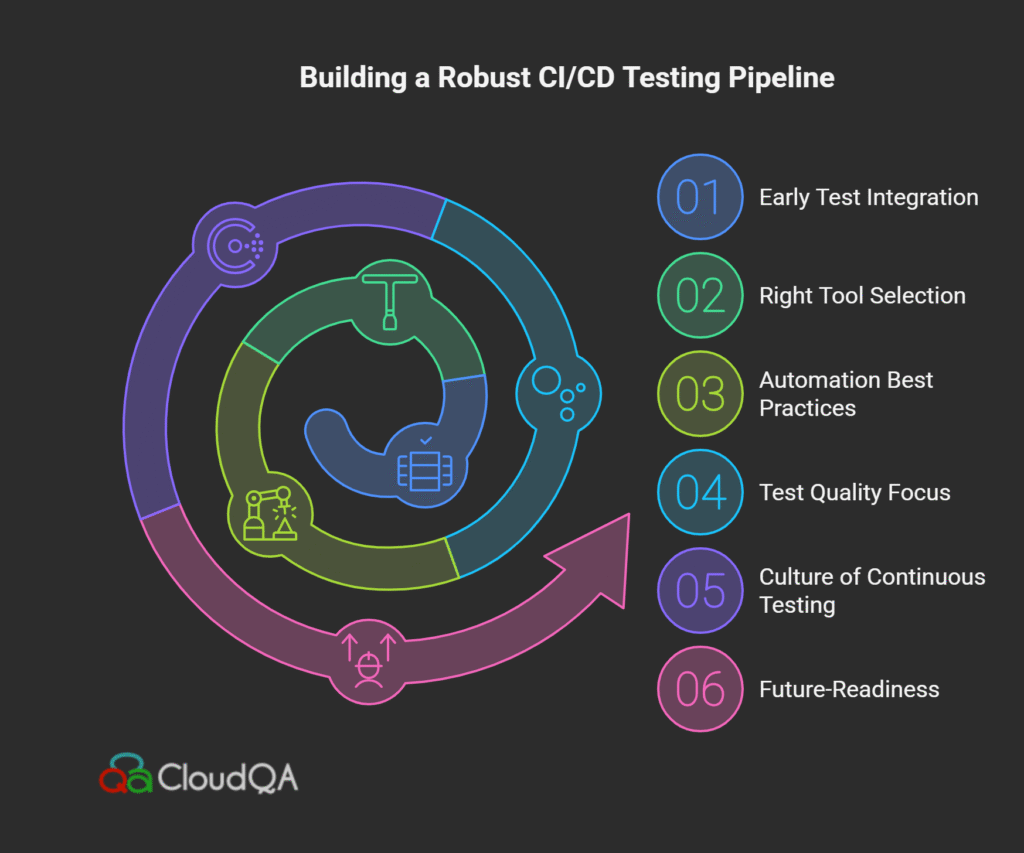
9: Conclusion: Building a Robust CI/CD Testing Pipeline
Building a strong CI/CD-friendly testing pipeline is essential for DevOps teams in Israel, the USA, and globally to achieve fast, reliable, and high-quality software delivery. This final section consolidates key insights and actionable recommendations from the whitepaper, offering a clear roadmap to adopting, scaling, and future-proofing your QA automation within CI/CD environments.
Key Takeaways
- Embed Testing Early and Often: Adopt shift-left testing and integrate automated test suites at every stage of your CI/CD pipeline. Early, continuous quality checks help detect defects quickly, reduce rework, and accelerate delivery cycles.
- Select the Right Tools: Use modern, scalable, and CI/CD-compatible tools such as Playwright, WebdriverIO, Selenium, and AI-powered platforms like CloudQA. Tool selection should align with your codebase, technology stack, and team skills to maximize automation ROI.
- Follow Best Practices for Automation: Implement test-driven development (TDD), automate critical regression and smoke tests, maintain test scripts in version control, and employ parallel testing to reduce cycle times.
- Focus on Quality and Maintenance: Regularly audit test coverage, prune flaky tests, and leverage self-healing and AI-based automation to minimize maintenance overhead and increase pipeline reliability.
- Foster a Culture That Embraces Continuous Testing: Encourage collaboration between developers, QA, and operations by integrating testing feedback into daily workflows and communication platforms for real-time alerting and rapid incident resolution.
Prepare for the Future: Stay adaptable by monitoring emerging trends such as low-code/no-code testing, cloud-native environments, and AI-driven analytics to continuously evolve your CI/CD testing strategy.
By meticulously applying these strategies, your teams can build a resilient, scalable, and efficient QA pipeline that supports rapid innovation cycles, reduces risk, and sustains high software quality. CloudQA’s tailored automation solutions and integrations further empower organizations to enhance testing agility, reduce maintenance costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
Bibliography
- Srinivasan, R. (2024). The Future of CI/CD: How Automation Will Reshape Development. Tech Review.
- Zhang, H., & Liu, Y. (2023). The Role of Automation in Modern Software Development. DevOps Insights.
- Gartner, Inc. (2024). CI/CD Integration Best Practices. Gartner Research.
- Jenkins (2024). CI/CD Pipeline Essentials for QA. Jenkins Blog.
- Test.ai (2024). Optimizing Test Automation for Continuous Integration. Test.ai Blog.
- Forrester Research (2023). Automation Trends in CI/CD Testing. Forrester Research.
- GitLab (2024). Seamless Integration of CI/CD for Testing. GitLab Articles.
- CircleCI (2024). Continuous Testing in DevOps. CircleCI Publications.
- Atlassian (2023). QA Automation Best Practices. Atlassian Blog.
- Redgate (2024). Scaling Automated Testing with CI/CD Pipelines. Redgate Articles.
FAQ Section
Q1: What does a CI/CD-friendly QA pipeline mean?
A CI/CD-friendly QA pipeline is one where automated testing is deeply integrated into every stage of the software development lifecycle—from code commits through to deployment—ensuring continuous verification and rapid feedback for faster, reliable releases.
Q2: Which automated testing tools are best suited for DevOps teams working with CI/CD?
Popular tools include Selenium, Playwright, WebdriverIO, and Cypress for UI testing; Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI for pipeline orchestration; Appium for mobile testing; and CloudQA for AI-driven self-healing automation.
Q3: Why is shift-left testing important in CI/CD?
Shift-left testing means moving testing earlier in the development process, allowing teams to detect bugs soon after code submission. This approach reduces downstream defects, shortens release cycles, and lowers overall costs.
Q4: How can teams overcome common challenges like tool integration and test maintenance in CI/CD pipelines?
Choosing tools with native CI/CD compatibility, employing version control for test scripts, investing in training, and using AI-enhanced self-healing automation platforms like CloudQA can streamline integration and reduce maintenance overhead.
Q5: What is the role of automation in improving test coverage and speed?
Automation ensures consistent, repeatable, and fast execution of large test suites often impossible with manual testing. It enables parallel tests across environments, increases coverage, and speeds up feedback loops.
Q6: How can AI and machine learning shape the future of CI/CD testing?
AI helps build self-healing tests, predicts risky code, improves test prioritization, and detects flaky tests automatically, enabling more efficient, adaptive, and reliable CI/CD testing pipelines.
Q7: Can non-developers create automated tests in modern CI/CD testing frameworks?
Yes, with the rise of low-code/no-code testing tools, non-technical staff can design and maintain automated tests, promoting broader collaboration and faster test creation.

informative!
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, situs penipu SITUS SEXS
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, situs xvideos SITUS SEXS
https://shorturl.fm/zpx65
Istanbul half day tour The pace was perfect for all ages. https://welbm.co.uk/?p=1216147
Bosphorus sunset cruise The architecture blew me away. https://qosnetworksmw.com/?p=36075
Great article! I really appreciate the way you explained this topic—it shows not only expertise but also a clear effort to make it easy for readers to understand. What stood out to me most is how practical your insights are, which makes the piece very relatable. As someone who works a lot with different industries and categories, I can say your perspective feels very authentic. At https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/top-link-building-agenturen-in-deutschland/ we run a directory platform in Germany that connects people and businesses across many categories, and it’s always refreshing to see content that adds real value like this. Looking forward to reading more of your work—keep it up!
Really well-written article! I enjoyed the way you broke down the topic—it feels very genuine and helpful, not just theory. The practical tips make it easy for readers like me to connect and actually take something useful away.At meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de , we’re building a directory and classifieds platform in Germany where people can discover businesses, services, and opportunities across many categories. That’s why I especially value content like yours, because it shows how sharing knowledge online can really create connections.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be following along for more insights!
Really well-written article! I enjoyed the way you broke down the topic—it feels very genuine and helpful, not just theory. The practical tips make it easy for readers like me to connect and actually take something useful away.At meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de , we’re building a directory and classifieds platform in Germany where people can discover businesses, services, and opportunities across many categories. That’s why I especially value content like yours, because it shows how sharing knowledge online can really create connections.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be following along for more insights!
This is such a valuable article! I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content like this because at meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de we’re running a classifieds and directory platform in Germany that connects people with services, businesses, and opportunities across many categories. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
This is such a valuable article! I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content like this because at meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de we’re running a classifieds and directory platform in Germany that connects people with services, businesses, and opportunities across many categories. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
Really well-written article! I enjoyed the way you broke down the topic—it feels very genuine and helpful, not just theory. The practical tips make it easy for readers like me to connect and actually take something useful away.At meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de , we’re building a directory and classifieds platform in Germany where people can discover businesses, services, and opportunities across many categories. That’s why I especially value content like yours, because it shows how sharing knowledge online can really create connections.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be following along for more insights!
This is such a valuable article! I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content like this because at meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de we’re running a classifieds and directory platform in Germany that connects people with services, businesses, and opportunities across many categories. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work!
Great article, thanks for sharing such valuable insights! I really appreciate the way you explained the topic so clearly and made it easy to understand. It’s rare to find content that is both informative and practical like this. By the way, I recently came across a helpful platform called profis-vor-ort.de — it connects people quickly with local experts and services in Germany. I think it could be a great resource for anyone interested in finding trustworthy professionals nearby. Keep up the great work, I’ll definitely be following your future posts!
Really well-written article! I enjoyed the way you broke down the topic—it feels very genuine and helpful, not just theory. The practical tips make it easy for readers like me to connect and actually take something useful away.At meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de , we’re building a directory and classifieds platform in Germany where people can discover businesses, services, and opportunities across many categories. That’s why I especially value content like yours, because it shows how sharing knowledge online can really create connections.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be following along for more insights!
This is such a valuable article! I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content like this because at meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de we’re running a classifieds and directory platform in Germany that connects people with services, businesses, and opportunities across many categories. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Really well-written article! I enjoyed the way you broke down the topic—it feels very genuine and helpful, not just theory. The practical tips make it easy for readers like me to connect and actually take something useful away.At meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de , we’re building a directory and classifieds platform in Germany where people can discover businesses, services, and opportunities across many categories. That’s why I especially value content like yours, because it shows how sharing knowledge online can really create connections.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be following along for more insights!
This is such a valuable article! I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content like this because at meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de we’re running a classifieds and directory platform in Germany that connects people with services, businesses, and opportunities across many categories. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work!
Really well-written article! I enjoyed the way you broke down the topic—it feels very genuine and helpful, not just theory. The practical tips make it easy for readers like me to connect and actually take something useful away.At meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de , we’re building a directory and classifieds platform in Germany where people can discover businesses, services, and opportunities across many categories. That’s why I especially value content like yours, because it shows how sharing knowledge online can really create connections.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be following along for more insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
This is such a valuable article! I really like how you’ve managed to explain the topic in a clear and practical way—it feels authentic and easy to relate to. Reading it gave me some new perspectives that I can actually apply. I’m especially interested in content like this because at meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de we’re running a classifieds and directory platform in Germany that connects people with services, businesses, and opportunities across many categories. Insights like yours remind me how powerful it is when knowledge and connections come together. Thanks for sharing—looking forward to more of your work!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Excellent work on this ultimate guide! every paragraph is packed with value. It’s obvious a lot of research and love went into this piece. If your readers want to put these 7 steps into action immediately, we’d be honoured to help: https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/ – Germany’s fastest-growing kleinanzeigen & directory hub. • 100 % free listings • Auto-sync to 50+ local citation partners • Instant push to Google Maps data layer Drop your company profile today and watch the local calls start rolling in. Keep inspiring, and thanks again for raising the bar for German SEO content!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Excellent work on this ultimate guide! every paragraph is packed with value. It’s obvious a lot of research and love went into this piece. If your readers want to put these 7 steps into action immediately, we’d be honoured to help: https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/ – Germany’s fastest-growing kleinanzeigen & directory hub. • 100 % free listings • Auto-sync to 50+ local citation partners • Instant push to Google Maps data layer Drop your company profile today and watch the local calls start rolling in. Keep inspiring, and thanks again for raising the bar for German SEO content!
Excellent work on this ultimate guide! every paragraph is packed with value. It’s obvious a lot of research and love went into this piece. If your readers want to put these 7 steps into action immediately, we’d be honoured to help: https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/ – Germany’s fastest-growing kleinanzeigen & directory hub. • 100 % free listings • Auto-sync to 50+ local citation partners • Instant push to Google Maps data layer Drop your company profile today and watch the local calls start rolling in. Keep inspiring, and thanks again for raising the bar for German SEO content!
Excellent work on this ultimate guide! every paragraph is packed with value. It’s obvious a lot of research and love went into this piece. If your readers want to put these 7 steps into action immediately, we’d be honoured to help: https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/ – Germany’s fastest-growing kleinanzeigen & directory hub. • 100 % free listings • Auto-sync to 50+ local citation partners • Instant push to Google Maps data layer Drop your company profile today and watch the local calls start rolling in. Keep inspiring, and thanks again for raising the bar for German SEO content!
Excellent work on this ultimate guide! every paragraph is packed with value. It’s obvious a lot of research and love went into this piece. If your readers want to put these 7 steps into action immediately, we’d be honoured to help: https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/ – Germany’s fastest-growing kleinanzeigen & directory hub. • 100 % free listings • Auto-sync to 50+ local citation partners • Instant push to Google Maps data layer Drop your company profile today and watch the local calls start rolling in. Keep inspiring, and thanks again for raising the bar for German SEO content!
Excellent work on this ultimate guide! every paragraph is packed with value. It’s obvious a lot of research and love went into this piece. If your readers want to put these 7 steps into action immediately, we’d be honoured to help: https://meinestadtkleinanzeigen.de/ – Germany’s fastest-growing kleinanzeigen & directory hub. • 100 % free listings • Auto-sync to 50+ local citation partners • Instant push to Google Maps data layer Drop your company profile today and watch the local calls start rolling in. Keep inspiring, and thanks again for raising the bar for German SEO content!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Fantastic read! I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights!
Launch into the epic realm of EVE Online. Start your journey today. Create alongside hundreds of thousands of pilots worldwide. [url=https://www.eveonline.com/signup?invc=46758c20-63e3-4816-aa0e-f91cff26ade4]Play for free[/url]
This is such a treasure trove of dont make your developers test their own code wisdom! The case studies made me snort-laugh at how *fast* those fintech wizards became release ninjas. And the AI self-healing tools sound like magic, finally giving test scripts the DevOps equivalent of a personal assistant who cleans up after them. Now if only my coffee maker was this automated… Highly informative, even if my main takeaway is that I need to start adding CloudQA Certified to my resume, alongside Master of Pouring Coffee. Great read!remove watermark ai
Your writing has a way of resonating with me on a deep level. It’s clear that you put a lot of thought and effort into each piece, and it certainly doesn’t go unnoticed.
Your blog is a constant source of inspiration for me. Your passion for your subject matter shines through in every post, and it’s clear that you genuinely care about making a positive impact on your readers.
Magnificent beat I would like to apprentice while you amend your site how can i subscribe for a blog web site The account helped me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
katana
Your blog is like a beacon of light in the vast expanse of the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and insightful commentary never fail to leave a lasting impression. Thank you for all that you do.
Your blog is a testament to your expertise and dedication to your craft. I’m constantly impressed by the depth of your knowledge and the clarity of your explanations. Keep up the amazing work!
I have read some excellent stuff here Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting I wonder how much effort you put to make the sort of excellent informative website
I do not even know how I ended up here but I thought this post was great I dont know who you are but definitely youre going to a famous blogger if you arent already Cheers
Your blog is a treasure trove of valuable insights and thought-provoking commentary. Your dedication to your craft is evident in every word you write. Keep up the fantastic work!
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and engaging writing style set you apart from the crowd. Keep up the excellent work!
Your writing is a true testament to your expertise and dedication to your craft. I’m continually impressed by the depth of your knowledge and the clarity of your explanations. Keep up the phenomenal work!
Your blog is a constant source of inspiration for me. Your passion for your subject matter shines through in every post, and it’s clear that you genuinely care about making a positive impact on your readers.
From Keto Kamp’s founder: a straightforward method to restore metabolic function and feel your best. https://metabolicfreedom.top/ metabolic freedom book reviews
Just browsed around admtechbong88… Looks clean! Site design is good, and I hope they got what I’m lookin’ for. Let’s see what happens!
Yo, Taya3650, listen up! This site’s got it going on. Quick payouts and the games are fire. Definitely my go-to spot! Check it out! taya3650
Robin Norwood explica el ciclo de dependencia emocional claramente https://lasmujeresqueamandemasiadopdf.cyou/ las mujeres que aman demasiado libro reseña
Interesting read! Data-driven play is key, and platforms like jljl77 2025 link seem to be prioritizing that. KYC is a necessary evil for security, though-hope the process is smooth for players! Good insights.
Solid analysis! Considering variance is key in video poker, platforms like jljl77 2025 link, with diverse games & quick funding via GCash, could offer interesting data points for strategy testing. Accessibility matters!
Experience the isolation and the hope of deep space travel. The Project Hail Mary PDF delivers this story directly to you. This ebook is perfect for late-night reading sessions. Get the digital version and immerse yourself in the world of Andy Weir. https://projecthailmarypdf.top/ does rocky die in project hail mary
Alright guys, I gotta say, sv3888app is where it’s at for some serious cockfighting action. The app’s smooth, easy to navigate, and the odds are pretty sweet. Definitely worth checking out if you’re into this kinda thing. Check them out here: sv3888app
A Court of Thorns and Roses is a journey of self-discovery. Join Feyre in the A Court of Thorns and Roses PDF. It is about finding out who you are when everything you know is stripped away. https://acourtofthornsandrosespdf.top/ A Court Of Thorns And Roses Pdf Internet Archive
Don’t miss the book that has taken the fantasy genre by storm. With a Fourth Wing PDF, you can carry this epic adventure in your pocket. From the first page to the last, the story of Violet and her dragon will hold you captive. https://fourthwingpdf.top/ Fourth Wing Pdf
Lovart sounds like a game-changer for designers looking to blend AI with traditional tools. The tri-modal interaction is especially clever. Can’t wait to see it in action! Lovart
No waiting, no hassle. Just the A Court of Mist and Fury PDF. This direct download is simple and fast. Get the file and dive into the story within minutes. https://acourtofmistandfurypdf.top/ A Court Of Mist And Fury Rhysand Pov
Pattern recognition is key in baccarat, and a solid platform helps! Seeing providers like jili games legit prioritize user experience & security (KYC is smart!) builds confidence. Great content is crucial too, of course.
Ignite epic tales in Iron Flame! Violet rides flames of fate and feeling. Yarros’ gem. Free PDF at ironflamepdf.top! https://ironflamepdf.top/ Iron Flame Series
A story of endurance and magic. An Arcane Inheritance is lasting, available in PDF. This digital novel is enduring. Download the file now and see how the legacy endures through an arcane inheritance. https://anarcaneinheritancepdf.top/ An Arcane Inheritance Book Club Kit Pdf
Start your digital reading journey with the In Your Dreams PDF. It is a user-friendly entry point into the world of ebooks, offering a great story in an easy-to-use format. https://inyourdreamspdf.top/ In Your Dreams Sarah Adams Epub
I love sharing my love of reading with my family. An archive of romance offers books for different age groups. I download appropriate PDF stories for my younger siblings, helping them develop a love for reading with engaging and heartwarming tales. https://anarchiveofromancepdf.top/ An Archive Of Romance Original Pdf
You can enjoy a preface that makes you scream. This PDF is a before. It is a pre. The digital format is front. head and lead. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ You Can Scream Epub High Quality
I appreciate the metadata in digital files. A well-organized archive of romance includes author info and summaries. I check this data before downloading the PDF to ensure the book is exactly what I am looking for, saving time and storage space. https://anarchiveofromancepdf.top/ An Archive Of Romance Pdf 4Shared
Immerse yourself in the honest writing of this digital book. The PDF of It Should Have Been You is honest. It should have been you appreciating the truth. Download the copy today and read. https://itshouldhavebeenyoupdf.top/ It Should Have Been You Story Pdf
The Alcott Hall PDF is a key document for preservationists and historians. It details the rich history of the building. Download the file today to ensure you have a permanent digital record of this significant piece of architectural heritage. https://alcotthallpdf.top/ Emily Rath Alcott Hall Epub Free
You can feel the intensity of a story that makes you scream. This PDF captures every nuance of the author’s voice. It is a must-have for your digital library. Download it today and experience the convenience of having your books available at the touch of a button. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ You Can Scream Pdf Direct Download
There is a thrill in the hunt for a specific edition. An archive of romance might have the original release version. I look for these specific PDF files because sometimes later editions change scenes, and I want to read the author’s original vision. https://anarchiveofromancepdf.top/ An Archive Of Romance Pdf Google Drive
Enhance your digital library with the addition of this must-read novel in a portable format. The PDF file offers compatibility with all major e-readers and devices. It should have been you getting lost in this gripping tale. access the document now and enjoy hours of literary entertainment. https://itshouldhavebeenyoupdf.top/ It Should Have Been You Txt File
The Alcott Hall PDF offers an engaging look into the past. It is filled with interesting facts and historical context. Download this file to your device and immerse yourself in the story of one of the most intriguing buildings in the region. https://alcotthallpdf.top/ Alcott Hall Story Pdf
Unlock the mystery of a complex life. This novel is a deep dive into secrets. The digital PDF is easy to find. Start reading about the husband’s past and the wife’s discovery. https://myhusbandswifepdf.top/ My Husband’s Wife Novel Pdf
You can find a blurb that makes you scream. This PDF is a back. It is a sign. The digital format is show. tell and sell. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ You Can Scream Android Epub
Building a personal library of digital books is a hobby for many of us. If you focus on fiction, an archive of romance novels is an indispensable resource. Being able to download a PDF allows for offline reading, which is perfect for those times when you do not have internet access. https://anarchiveofromancepdf.top/ Where To Download An Archive Of Romance Pdf
The Anatomy of an Alibi PDF provides access. Download the file and start. with clear text, this book is a pleasure. https://anatomyofanalibipdf.top/ Anatomy Of An Alibi Ashley Elston Vk
I appreciate the ability to search by author. An archive of romance makes it easy to complete a bibliography. I find an author I like and download the PDF of every book they have ever written, working my way through their entire career. https://anarchiveofromancepdf.top/ An Archive Of Romance Story Pdf
For a story that is intimate and personal, read this. The Love in Plane Sight PDF is the digital format for you. It is a romance that feels close. Get the ebook version today and get close. https://loveinplanesightpdf.site/ Love In Plane Sight Free Pdf
The precise formatting of the chosen family pdf respects the author’s original layout, ensuring that you experience the book exactly as it was meant to be read, even on a small mobile screen. https://chosenfamilypdf.site/ Chosen Family Madeleine Gray Read Online
Experience Brainy https://askbrainy.com the free & open-source AI assistant. Get real-time web search, deep research, and voice message support directly on Telegram and the web. No subscriptions, just powerful answers.
Add a touch of romance to your digital collection. The Graceless Heart PDF is a sleek, modern way to consume literature. With instant availability, there is no reason to wait to start this breathtaking journey of love and discovery. https://gracelessheartpdf.site/ Graceless Heart Ebook Download
casino money elonbet casino game
Find out what happens when politics meets passion. The Boyfriend Candidate is ready for you to read in PDF format. It is a gripping story that balances humor and serious themes perfectly. Download the file today and add this gem to your digital book collection immediately. https://theboyfriendcandidatepdf.site/ The Boyfriend Candidate Instant Download
нейросеть perplexity https://uniqueartworks.ru/perplexity-kupit.html
Read a story that matters. The Bury Your Gays PDF is important. Be part of the conversation. https://buryyourgayschucktinglepdf.site/ Synopsis Of Bury Your Gays
Baccarat strategy is fascinating – understanding patterns can help, but it’s never a guarantee! Secure platforms like jili app com prioritize a safe experience, which is key when exploring online casinos & games. KYC verification is smart!
Experience the genius of Chuck Tingle. The Bury Your Gays PDF is pure genius. Don’t accept any substitutes. https://buryyourgayschucktinglepdf.site/ Bury Your Gays Chuck Tingle Supernatural
купить код активации perplexity pro на год https://uniqueartworks.ru/perplexity-kupit.html
Don’t miss the chance to read the book that is redefining a genre. It is a landmark release. The Bury Your Gays PDF is your access point to this historic moment in horror fiction, available at the click of a button. https://buryyourgayschucktinglepdf.site/ Bury Your Gays Plot Chuck Tingle
Сделать тату в Сочи: опытные тату-мастера, авторские эскизы и аккуратная работа. Современное оборудование, одноразовые расходники, соблюдение санитарных норм. Поможем выбрать стиль и размер, проконсультируем по уходу после сеанса.
Нужен дизайн? дизайнер интерьера в екатеринбурге создаём стильные и функциональные пространства для квартир, домов и коммерческих объектов. Концепция, планировки, 3D-визуализация, подбор материалов и авторский надзор. Работаем под бюджет и задачи клиента.
Нужна недвижимость? ипотека Томск недвижимость выгодно купить квартиру, дом или коммерческий объект. Работаем с жилой и коммерческой недвижимостью. Экономим время и защищаем ваши интересы.
Сломалась стиралка? ремонт стиральных машин Нижний Новгород всех марок и моделей. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка электроники. Работаем без выходных, выезд в день обращения, прозрачная стоимость и гарантия на выполненные работы.
Today’s Top Stories: https://signin.bradley.edu/cas/after_application_logout.jsp?applicationname=bradley%20sakai&applicationurl=https://puzzlesbyjim.com/
Нужен дом? сельская ипотека Томск удобные планировки, разные площади и бюджеты. Подбор вариантов, проверка юридической чистоты, сопровождение до регистрации права. Экономим ваше время.
перплексити нейросеть на русском https://uniqueartworks.ru/perplexity-kupit.html
Нужна гостиница? гостиница московская область комфортные номера для отдыха и командировок. Удобное расположение, чистые номера, Wi-Fi, парковка и круглосуточная стойка. Подходит для краткосрочного и длительного проживания, выгодные цены и удобное бронирование.
Experience the meta-horror sensation that has everyone talking about media representation. This story takes a dark look at how the industry treats marginalized characters. Secure your digital copy of the Bury Your Gays PDF to dive into a narrative filled with twists, turns, and terrifying monsters. https://buryyourgayschucktinglepdf.site/ Bury Your Gays Novel Pdf Free
Хочешь отдохнуть? сеть отелей предлагаем почасовое размещение в комфортных номерах. Удобные кровати, кондиционер, Wi-Fi, душ. Быстрое бронирование, конфиденциальность и выгодные тарифы для краткосрочного пребывания.
Scratch cards always felt like pure luck, but seeing platforms like KKKKPH777 integrate modern tech & easy payments (GCash!) is cool. Thinking of trying their slots – check out the kkkkph777 app download for a quick start! Fun & convenient seems to be the key.
Play online at elon casino: slots, live casino, and special offers. We explain the rules, limits, verification, and payments to avoid any surprises. This material is for informational purposes only.
дизайн интерьера квартиры услуги дизайнера спб
Dental problems? dental clinic Full-service dental care: painless dental treatment, implants, prosthetics, orthodontics, and cosmetic dentistry. Modern equipment, experienced doctors, sterile hygiene, and a personalized approach. Consultation and treatment plan included.
квартира посуточно в гродно аренда квартиры на сутки гродно
Master the art of metabolic flexibility with this comprehensive digital guide. It teaches you how to switch between fuel sources efficiently. By reading the metabolic freedom pdf, you can learn to burn stored fat for energy and achieve the lean body you desire. https://metabolicfreedom.top/ Metabolic Freedom: A 30-Day Guide To Restore Your Metabolism, Heal Hormones & Burn Fat
El amor propio es la base de todo. Fortalécelo con este clásico de la psicología. La versión digital te permite llevar estas enseñanzas contigo. Aprende a cuidarte y a no permitir que nadie te haga daño en nombre del amor. https://lasmujeresqueamandemasiadopdf.cyou/ Las Mujeres Que Aman Demasiado Pef
Revitalize your health with a program designed to fix your metabolism. This manual covers nutrition, sleep, and lifestyle factors. The metabolic freedom pdf is a comprehensive resource for anyone looking to lose weight permanently and improve their quality of life significantly. https://metabolicfreedom.top/ Metabolic Freedom Cost
Si buscas la sabiduría práctica, descarga esta guía, aprende a aplicar el sentido común y a mandar a la media las teorías complicadas de forma educada, resolviendo problemas reales con soluciones sencillas. https://comomandaralamediadeformaeducadapdf.cyou/ Como Mandar A La Media De Forma Educada Libro
A professional https://www.family-dentist-near-me-in-montenegro.com: therapy, surgery, orthopedics, and orthodontics all in one location. Individualized treatment plans, modern equipment, and strict sterility standards. We help you maintain long-lasting dental health.
Iphone 17 Pro Price Us Apple 2025 Iphone 17 Pro Price India Leak Iphone 17 Pro Price Rumors Germany Iphone 17 Pro Max Specs Camera Differences How Much Money Is Iphone 17 Pro Max When Iphone 17 Air Release Date Iphone 17 Pro Max Price Europe September 2025
La teoría de Let Them promueve la autonomía emocional. Busca la lectura en español y asegúrate de tener el texto completo. Es una herramienta poderosa para dejar de depender de la aprobación ajena y comenzar a validar tus propias emociones y decisiones sin miedo al rechazo. https://lateorialetthem.top/ La.Teoria Let Them
Discover metabolic flexibility with this resource. It changes weight loss. The metabolic freedom pdf helps you train your body to burn fat for fuel, leading to effortless management. https://metabolicfreedom.top/ Metabolicfreedom.Com
CortexLab AI https://cortexlab.app a 2025 guide to visual transformation tools: capabilities, use cases, limitations, and risks. We explain how to evaluate quality, ethics, and safety, select application scenarios, and work responsibly with AI.
Si el amor te ha decepcionado, no pierdas la fe, cambia de método. Este libro te enseña uno nuevo. El archivo de texto es tu manual. Aprende a amar de forma inteligente y saludable. https://lasmujeresqueamandemasiadopdf.cyou/ Las Mujeres Que Aman Demasiado De Que Trata
Si quieres saber cómo responder a insultos o impertinencias con inteligencia, este es tu sitio, descarga el manual que te enseña a desarmar a tu interlocutor con palabras cultas y bien medidas, manteniendo siempre la superioridad moral. https://comomandaralamediadeformaeducadapdf.cyou/ Como Mandar A La Mierda De Forma Educada Pdf Free
Купить Apple в Москве rznonline.ru с гарантией: смартфоны, ноутбуки, планшеты, часы и аксессуары. Актуальные модели, честные цены, акции и поддержка после покупки. Самовывоз или курьерская доставка в удобное время.
iPhone 17 Pro Max cloudav.ru в наличии: большой экран, высокая автономность, топовая камера и скорость работы. Поможем выбрать конфигурацию памяти, проверим подлинность и организуем быструю доставку. Гарантия и поддержка после покупки.
курсы первой помощи обучение сиз
Купить iPhone https://c-inform.info большой выбор моделей, памяти и цветов. Только оригинальная техника Apple, гарантия, прозрачные цены и рассрочка. Консультации, перенос данных и быстрая доставка в удобное время.
Apple iPhone 17 Pro https://x-true.info/136496-iphone-17-pro-flagman-innovacij-v-mire-smartfonov.html сочетание компактности и максимальных возможностей. Чёткий дисплей, быстрый чип, улучшенная камера и стабильная работа системы. Подходит для съёмки контента, игр и повседневных задач.
iPhone 17 Pro Max https://giport.ru/sovet/technic-tips/phones-gadgets-tips/novye-funkczii-iphone-17-pro-max-chto-stoit-znat-o-programmnom-obespechenii-bezopasnosti-i-merah-zashhity-dannyh премиальный смартфон с крупным дисплеем, продвинутой камерой и высокой скоростью работы. Отличный выбор для пользователей, которым важны качество фото и видео, мощность и комфорт в использовании.
Descubre cómo la humildad te hace grande, baja el manual y aprende a reconocer tus errores y a mandar a la media la soberbia de forma educada, ganándote el respeto y la admiración de todos. https://comomandaralamediadeformaeducadapdf.cyou/ El Libro Como Mandar A La Mierda De Forma Educada
iPhone 17 Pro Max satom.ru премиальный смартфон с большим дисплеем, мощным процессором и улучшенными фото- и видеовозможностями. Отличный выбор для пользователей, которым важны производительность, качество и автономность.
Нужна газификация? наземный газгольдер для частного дома: проектирование, согласования, подвод газа, монтаж оборудования и пусконаладка. Работаем по нормам, помогаем с документами, подбираем котёл и комплектующие. Прозрачная смета, сроки и гарантия.
Нужны разнорабочие? разнорабочий с ежедневной оплатой Предоставим работников для разовых и постоянных работ: перенос, уборка, демонтаж, подсобные задачи. Гибкий график, честные цены и выезд в день обращения.
La teoría de Let Them es tu escudo contra la negatividad. Disponible en español, el archivo PDF completo es esencial. Al dejar que la negatividad de otros pase de largo sin que te toque, mantienes tu vibración alta y atraes situaciones mucho más positivas a tu experiencia vital. https://lateorialetthem.top/ La Teoria Let Them Libro
Discover key to sustainable fat loss. This guide is a valuable tool. The metabolic freedom pdf teaches how to reset metabolism for a lean physique. https://metabolicfreedom.top/ Ben Azadi Metabolic Freedom Book
Si necesitas poner fin a una relación laboral o personal tóxica, hazlo con clase, esta guía te muestra los pasos para despedirte de forma educada pero definitiva, asegurando que el mensaje de “mandar a la media” quede perfectamente claro. https://comomandaralamediadeformaeducadapdf.cyou/ Epub Como Mandar A La Mierda De Forma Educada
Современный горнолыжный курорт для активного отдыха: подготовленные склоны, снежные парки, школы катания и сервис. Комфортная инфраструктура, рестораны, спа и развлечения apres-ski. Идеальное место для зимнего отпуска.
Si te sientes atrapada en un círculo vicioso, rompe la inercia leyendo. Este PDF es tu martillo. Golpea las estructuras que te limitan y construye nuevas formas de amar. Tu futuro te lo agradecerá. https://lasmujeresqueamandemasiadopdf.cyou/ Las Mujeres Que Aman Demasiado Pdf Español
квартиры на сутки в гродно снять квартиру в гродно посуточно
Ищешь казино? melbet casino: слоты от топ-провайдеров, live-дилеры, турниры и акции. Объясняем условия бонусов, вейджер, депозиты и вывод средств, требования к верификации. Информация для взрослых игроков.
Iphone Air Vs Iphone 17 Pro Specs Comparison What Is Iphone Air Tag Evaluate The Beats Iphone Air Case On Bfcm Iphone Air Release Date And Specs Iphone 17 Pro Price Rumors Usd How Much Does An Iphone 17 Pro Max Weight Iphone 17 Specs Apple Iphone 17 2025
Discover Violet’s fiery fate in Iron Flame PDF! Dragons roar, romance sparks in this must-read. Rebecca Yarros delivers. Free download awaits at ironflamepdf.top now! https://ironflamepdf.top/ The Iron Flame Pdf
Онлайн казино кэт казино официальный сайт слоты, live-казино и специальные предложения. Подробно о регистрации, бонусах, выводе средств и безопасности аккаунта. Перед началом игры рекомендуем изучить правила.
Iron Flame: Passion peaks! Fantasy for flames fans. Free PDF today! https://ironflamepdf.top/ How Did Iron Flame End
Discover the blazing passion of Iron Flame! Dive into Violet Sorrengail’s perilous dragon rider saga, full of twists, romance, and epic battles. Fans of Fourth Wing won’t miss this. Grab your free PDF instantly at ironflamepdf.top today! https://ironflamepdf.top/ How Many Chapters In Iron Flame
Join an adventure that examines the price of power and who deserves to wield it. https://heiroffirepdf.top/ What Book After Heir Of Fire
The Lights Out PDF is a must-have for your digital collection, and we make it easy to get. Our intuitive website design guides you straight to the download button. No confusion, just quick access to quality content. https://lightsoutpdf.top/ Watch Lights Out 2016
Лучшее казино https://kushslots.ru: слоты от популярных провайдеров, live-дилеры, акции и турниры. Разбираем бонусную политику, вейджер, платежи и сроки выплат, требования к верификации. Материал носит информационный характер.
Iron Flame PDF ignites readers! Dragons, drama, devotion in Violet’s bold tale. Yarros excels. Download free from ironflamepdf.top today! https://ironflamepdf.top/ The Empyrean, #2 Iron Flame Pdf Free Download
Experience the magic of storytelling at its finest in this bestselling series. https://heiroffirepdf.top/ What Book Comes After Heir Of Fire
Download the Lights Out PDF and enjoy a consistent reading experience. Our files are standardized for reliability. predictable quality every time. https://lightsoutpdf.top/ Why Do Pilot Lights Go Out On Water Heaters
Любишь азарт? kometa casino играть онлайн в слоты и live-казино. Разбор регистрации, бонусов, правил игры, лимитов и способов вывода средств.
Ride the flames with Iron Flame! Violet battles for her place among dragon riders. Twists abound. Free PDF at ironflamepdf.top – instant fantasy fix! https://ironflamepdf.top/ Free Iron Flame Pdf
Discover how one woman’s journey can change the fate of an entire realm. https://heiroffirepdf.top/ Heir Of Fire Characters
Download the Lights Out PDF and enjoy the convenience of digital text. Search, copy, and paste with ease using our file. It is the functional, flexible way to use information. https://lightsoutpdf.top/ Are Northern Lights Out Tonight
Explore the Mateslots app to discover how mobile gaming is simplified. The app combines usability with performance, allowing players to focus on games without distractions or complex menus.
Современный горнолыжный курорт для зимнего отпуска: подготовленные склоны, снежные парки, школы катания и развитая инфраструктура. Комфортные отели, рестораны и развлечения apres-ski для всей семьи.
Current recommendations: https://mebel-zotto.ru/kak-pravilno-vklyuchit-javascript-na-vashem-sajte-poshagovoe-rukovodstvo/
The Shield of Sparrows PDF is essential for any digital collector. It captures the essence of the sparrows’ journey in a file that is easy to organize. Add it to your virtual bookshelf today and categorize it alongside your other favorite fantasy or fiction titles. https://shieldofsparrowspdf.site/ Shield Of Sparrows Vk
Explore the artistic side of routine construction and music choice. The fake skating pdf delves into how creative decisions can enhance or detract from the perceived technical difficulty of a performance. https://fakeskatingpdf.site/ Fake Skating Pdf Free
Нужен трафик и лиды? сайт студии avigroup SEO-оптимизация, продвижение сайтов и реклама в Яндекс Директ: приводим целевой трафик и заявки. Аудит, семантика, контент, техническое SEO, настройка и ведение рекламы. Работаем на результат — рост лидов, продаж и позиций.
Apple Iphone 17 Price 2025 Iphone Air Vs 17 Pro Specs Iphone 17 Pro Price Uk Official Iphone 17 Air Specs Camera Iphone 17 Pro Max Price Israel Official Price Iphone Air Vs Iphone 17 Specs Differences Iphone 17 Vs Iphone 17 Air Size
Unlock the mystery of success with the Charlie Method PDF. This document solves the riddle. It is a detective. Get the file today to close the case on failure and solve the mystery of how to win. https://thecharliemethodpdf.site/ Borrow The Charlie Method
The Shield of Sparrows PDF is a reader’s reward. It is the prize for finding the link. Claim your reward today. https://shieldofsparrowspdf.site/ Shield Of Sparrows Free Reading
Uncover the strategies that champions use to dominate the competition. The fake skating pdf reveals the training secrets and mental preparation techniques that are essential for achieving high scores and consistent performance. https://fakeskatingpdf.site/ When Does Fake Skating By Lynn Painter Come Out
Enjoy the convenience of carrying a library in your hand. The Check and Mate PDF is the portable power, offering a story that travels with you wherever you go, ready to be read at a moment’s notice. https://checkandmatepdf.site/ Free Chess Books Download
?Necesitas mudarte? https://trasladoavalencia.es ?Necesitas una mudanza rapida, segura y sin complicaciones en Valencia? Ofrecemos servicios profesionales de transporte y mudanzas para particulares y empresas. ?Solicita un presupuesto gratuito y disfruta de nuestro servicio de calidad!
Нужен трафик и лиды? настройка контекстной рекламы в avigroup SEO-оптимизация, продвижение сайтов и реклама в Яндекс Директ: приводим целевой трафик и заявки. Аудит, семантика, контент, техническое SEO, настройка и ведение рекламы. Работаем на результат — рост лидов, продаж и позиций.
Sharpen your edge with the Charlie Method PDF. This guide refines your existing skills. It is a polishing tool for talent. Download the document today to take what you are already good at and make it exceptional through the application of precise methodology. https://thecharliemethodpdf.site/ Where To Download The Charlie Method
The Shield of Sparrows PDF is a screen savior. It gives you something worthwhile to look at. It justifies the time spent on your device. https://shieldofsparrowspdf.site/ Shield Of Sparrows Full Text
Embrace the future of reading with this digital edition. The Check and Mate PDF is the forward-thinking choice, offering a sustainable and convenient way to enjoy your favorite books. https://checkandmatepdf.site/ Is Check And Mate Appropriate For 13 Year Olds
Нужны услуги грузчиков? офисный переезд Предоставим крепких и аккуратных работников для любых задач — переезд, склад, доставка, подъем мебели. Быстрый выезд, почасовая оплата, гибкий график и ответственность за сохранность вашего имущества.
Learn the art of efficiency with the Charlie Method PDF. This document teaches you how to do more with less. It is a practical guide for the modern age. Get the file today and start reclaiming your time by implementing strategies that streamline your processes and boost output. https://thecharliemethodpdf.site/ The Charlie Method Mobile Download
Readers are calling the Shield of Sparrows PDF the best way to enjoy the book. It offers search functionality, allowing you to find specific passages about sparrows or shields instantly. This makes it an invaluable tool for book clubs and study groups alike. https://shieldofsparrowspdf.site/ Shield Of Sparrows Complete Pdf
Scale your success with the Charlie Method PDF. This guide shows you how to grow without breaking. It is a manual for expansion. Download the file today to learn the structures necessary to handle more responsibility and achievement without succumbing to stress. https://thecharliemethodpdf.site/ The Charlie Method Pdf Download Free
The Shield of Sparrows PDF is a smart choice. It saves you money on shipping and handling. It is the economical way to build your library. https://shieldofsparrowspdf.site/ Download Shield Of Sparrows Free
Enhance your knowledge of the sport’s terminology with this glossary. The fake skating pdf defines the specific words and phrases used by commentators, ensuring you can follow the action without confusion. https://fakeskatingpdf.site/ What Is Fake Ice Skating Rink Made Of
Interesting analysis! Seeing more platforms embrace provable fairness is huge for trust. It’s cool how jljl88 ph app casino is using blockchain-definitely a step forward for Philippine players & transparency. Hoping for more innovation!
Do not miss the opportunity to read this trending title. The Great Big Beautiful Life PDF is attracting great attention. It is a big book filled with beautiful lessons about life. The digital format allows for easy highlighting and note-taking as you read through it. https://greatbigbeautifullifepdf.site/ Great Big Beautiful Life Pdf English
Un conte qui se transmet de génération en génération. Le numérique est le nouveau relais de cette transmission. Le fichier Le Petit Prince PDF assure la pérennité de l’œuvre, garantissant que les enfants de demain pourront eux aussi rêver avec le petit prince. https://lepetitprincepdf.site/ Le Petit Prince Pdf Haute Qualité
Experience the beauty of a grateful heart. The Great Big Beautiful Life PDF is a great song. It sings big praises for a beautiful life. This text fills your heart with thanksgiving. https://greatbigbeautifullifepdf.site/ Great Big Beautiful Life Free Download
Un thriller qui vous marquera par son audace et son originalité, disponible en ligne. La version électronique est prête pour vous. Plongez dans l’histoire de cette femme de ménage et découvrez une intrigue où la manipulation est un art et où la survie ne tient qu’à un fil. https://lafemmedemenagepdf.site/ La Femme De Ménage Pdf Drive
Планируешь перевозку? грузчики удобное решение для переездов и доставки. Погрузка, транспортировка и разгрузка в одном сервисе. Работаем аккуратно и оперативно, подбираем машину под объём груза. Почасовая оплата, без переплат.
Нужны грузчики? квартирный переезд : переезды, доставка мебели и техники, погрузка и разгрузка. Подберём транспорт под объём груза, обеспечим аккуратную работу и соблюдение сроков. Прозрачные тарифы и удобный заказ.
Ce livre vous fera douter de tout le monde, disponible dès maintenant en format électronique. L’intrigue autour de cette femme de ménage est géniale. Profitez de ce téléchargement pour vivre une expérience de lecture unique et découvrir la vérité choquante qui se cache derrière les murs de cette maison. https://lafemmedemenagepdf.site/ La Femme De Ménage Tome 2 Pdf
Discover the joy of living in the moment. The Great Big Beautiful Life PDF is a great present. It gives big gifts of a beautiful life. This text teaches the art of mindfulness. https://greatbigbeautifullifepdf.site/ Borrow Great Big Beautiful Life
Profitez de ce livre culte sur votre liseuse grâce à une version électronique soignée. Ce document est parfait pour découvrir cette œuvre majeure sans attendre. Une histoire qui touche au cœur et à l’âme, disponible dès aujourd’hui. https://atoutjamaispdf.site/ À Tout Jamais Roman Pdf
Les dessins de l’auteur sont indissociables du texte et brillent sur écran. La fidélité de la version numérique est impressionnante. En téléchargeant Le Petit Prince PDF, vous profitez de l’œuvre intégrale telle qu’elle a été imaginée, avec une qualité d’affichage supérieure. https://lepetitprincepdf.site/ Le Petit Prince Pdf Frances
Ce livre est une expérience littéraire intense à découvrir en version numérique sans attendre. L’histoire de cette femme de ménage est captivante du début à la fin. Profitez de ce téléchargement pour plonger dans un huis clos étouffant où la vérité est la chose la plus dangereuse à posséder. https://lafemmedemenagepdf.site/ La Femme De Ménage Résumé Détaillé
Find the courage to follow your heart. The Great Big Beautiful Life PDF is a great star. It guides big ships for a beautiful life. Download the document to navigate your life. https://greatbigbeautifullifepdf.site/ Great Big Beautiful Life
Iphone 17 Pro Max Colors List Iphone 17 Air Screen Size Comparison Iphone 17 Air Specifications 2025 Iphone 17 Pro Max Specs 2025 Official Apple Best Iphone 17 Pro Max Case With Kickstand Iphone 17 Pro Max Precio Mexico 2025 Apple Iphone 17 News Today Reuters
Envie d’une lecture qui change la vie ? Ce roman en format électronique est exactement ce qu’il vous faut. Accessible en quelques clics, il vous promet des heures d’évasion et d’émotions intenses. Ne passez pas à côté de cette œuvre majeure qui explore les sentiments humains avec une justesse incroyable. https://atoutjamaispdf.site/ Site Pour Télécharger À Tout Jamais
Redécouvrez le chef-d’œuvre intemporel d’Antoine de Saint-Exupéry dans un format pratique et moderne. Que vous soyez chez vous ou en voyage, avoir Le Petit Prince en PDF vous permet de plonger dans cet univers poétique instantanément. Une lecture essentielle qui continue d’inspirer les générations à travers le monde entier. https://lepetitprincepdf.site/ Le Petit Prince Pdf Original Français
Plongez dans l’obscurité avec ce thriller psychologique qui ne vous laissera aucun répit. Le livre est disponible en téléchargement pour une lecture immédiate sur vos appareils favoris. Découvrez les secrets que cachent les murs de cette maison bourgeoise à travers les yeux d’une domestique perspicace. https://lafemmedemenagepdf.site/ La Femme De Ménage Pdf Iphone
Winnerspincasino might just be my new lucky spot. Great selection of games, and the bonuses are pretty sweet. Time to spin and win! Try your luck winnerspincasino.
Планируешь перевозку? разнорабочий на стройку удобное решение для переездов и доставки. Погрузка, транспортировка и разгрузка в одном сервисе. Работаем аккуратно и оперативно, подбираем машину под объём груза. Почасовая оплата, без переплат.
?Necesitas mudarte? https://trasladoavalencia.es ?Necesitas una mudanza rapida, segura y sin complicaciones en Valencia? Ofrecemos servicios profesionales de transporte y mudanzas para particulares y empresas. ?Solicita un presupuesto gratuito y disfruta de nuestro servicio de calidad!
Un livre lumineux malgré le thème, à découvrir en format numérique. Tout le bleu du ciel pdf est une lecture qui donne de l’espoir, un roman à télécharger pour s’évader et rêver, porté par une écriture fluide et poétique. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Ou A Ete Tourne Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel
Les mémoires de Maryse Condé sont un trésor de la littérature caribéenne à ne pas ignorer. Avec ce format dématérialisé, vous pouvez accéder instantanément à ses confidences émouvantes. Découvrez comment le cœur peut osciller entre la gaieté et la peine dans ce livre qui se dévore d’une seule traite. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Le Cœur À Rire Et À Pleurer Livre Audio Gratuit
Ищешь грузчиков? грузчики цена помощь при переезде, доставке и монтаже. Аккуратная работа с мебелью и техникой, подъем на этаж, разборка и сборка. Гибкий график, быстрый выезд и понятная стоимость.
Каталог мини-приложений https://tgram.link/ и ботов Telegram 2026: кликеры, TON-игры, AI-сервисы и крипто-инструменты. Обзоры, рейтинги, инструкции и обновления. Подбор по категориям, безопасности и реальной пользе — всё в одном месте.
La psychologie des personnages est dépeinte avec une touche impressionniste, par petites touches subtiles et révélatrices. Pour apprécier tout le talent de portraitiste de Sagan, téléchargez la version Bonjour Tristesse PDF et prenez le temps de savourer chaque description et chaque dialogue de ce roman exceptionnel. https://bonjourtristessepdf.site/ Bonjour Tristesse Pdf À Télécharger
Ce livre est une invitation au voyage et à la découverte de soi, disponible dès maintenant en format électronique pratique. Ne cherchez plus, tout le bleu du ciel en pdf est la lecture qu’il vous faut pour vous déconnecter du monde réel et vivre une aventure poignante aux côtés d’Émile. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Combien D’épisodes Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel
Un livre qui explore les tréfonds de l’âme humaine avec délicatesse. Le fichier numérique est facile à obtenir et à lire. Plongez dans ce récit autobiographique qui est une véritable ode à la vie, avec ses hauts et ses bas, racontée par une voix unique. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Livre Le Coeur A Rire Et A Pleurer
Stendhal nous apprend à lire dans les cœurs comme dans des livres ouverts. C’est une école de lucidité. Avoir le rouge et le noir en fichier numérique, c’est avoir ce manuel de lucidité dans sa poche, prêt à être consulté pour comprendre les tourments de l’âme humaine. https://lerougeetlenoirpdf.site/ Le Rouge Et Le Noir Tome 1 Pdf
Ce livre est un voyage au bout de la nuit solaire, une exploration des ténèbres sous la lumière aveuglante de l’été. Faites ce voyage en téléchargeant le fichier Bonjour Tristesse PDF, et découvrez les paradoxes de l’âme humaine mis en lumière par le génie de Françoise Sagan. https://bonjourtristessepdf.site/ Bonjour Tristesse Pdf Gratuit Sans Compte
Un livre qui résonne longtemps après la lecture. La version PDF est pratique et moderne. Découvrez comment les souvenirs d’enfance façonnent l’adulte, dans ce récit où le cœur est mis à nu avec une élégance et une émotion rares. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Le Cœur À Rire Et À Pleurer Fichier Pdf
La magie des mots de Melissa Da Costa opère dès les premières lignes de ce roman disponible en téléchargement rapide. Offrez-vous un moment d’évasion avec tout le bleu du ciel pdf, un récit qui prouve que même face à l’adversité, la beauté du monde reste accessible à ceux qui osent regarder. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Livre Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel Pdf
Que vous soyez un lecteur assidu ou occasionnel, ce court roman est une expérience de lecture intense qui ne vous laissera pas indifférent. La version Bonjour Tristesse PDF est parfaitement adaptée aux modes de vie modernes, vous permettant de glisser ce chef-d’œuvre dans votre poche via votre smartphone ou votre liseuse. https://bonjourtristessepdf.site/ Bonjour Tristesse Pdf Roman
La relation triangulaire au cœur du livre est d’une modernité psychologique absolue. C’est fascinant. Le téléchargement du pdf permet d’explorer cette géométrie amoureuse complexe, offrant une lecture stimulante qui nourrit l’esprit et le cœur avec une égale intensité. https://lerougeetlenoirpdf.site/ Telecharger Le Rouge Et Le Noir Pdf
Une autobiographie qui se lit avec passion et émotion. Le format PDF est idéal pour conserver ce livre précieusement. Ne manquez pas cette lecture qui vous fera passer par tous les états, illustrant la richesse d’une vie vécue pleinement, entre joies et peines. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Maryse Condé Bibliographie Pdf
sex
Why Bedpage Is Becoming the First Choice for Local Connections Bedpage has quickly earned a positive reputation for offering real, reliable, and respectful adult services. Many users appreciate how easy it is to explore listings without pressure, making the experience comfortable from the first visit. Whether someone is searching for a relaxing erotic massage or a genuine female escort, the platform feels organized and transparent. The profiles are detailed, helping visitors make confident decisions while saving time. Bedpage stands out because it focuses on real people and clear communication, which naturally builds trust. The community atmosphere feels welcoming, especially for first-time users. Services like erotic massage are presented professionally, while female escort options feel authentic and well-described. This balance makes Bedpage more than just a listing site—it feels like a dependable space for meaningful adult connections. For those exploring local options, checking out Escorts in Las Vegas gives a clear idea of how well the platform delivers quality experiences.
Le style de Stendhal, sec et rapide, sert parfaitement le propos de son roman sur l’énergie et la volonté. C’est un modèle de littérature réaliste. Télécharger ce livre en format numérique, c’est faire le choix de la culture à portée de main, une bibliothèque classique disponible instantanément sur votre appareil. https://lerougeetlenoirpdf.site/ Le Rouge Et Le Noir Nombre De Pages
Découvrez ce best-seller en version électronique pour une lecture facile. Tout le bleu du ciel est une histoire universelle, un fichier ebook à avoir absolument pour comprendre pourquoi ce livre a touché tant de cœurs à travers le monde. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel Fichier Pdf
Ne manquez pas l’occasion de lire ce monument de la culture française qui a inspiré tant de films et d’artistes. La version numérique en PDF est le moyen le plus direct de se connecter à cette histoire mythique, offrant une qualité de lecture supérieure pour tous les passionnés de livres. https://bonjourtristessepdf.site/ Bonjour Tristesse Pdf Français
Ce récit est une fenêtre ouverte sur l’âme d’une enfant devenue une grande dame des lettres. La version numérique est idéale pour une lecture moderne et nomade. Découvrez les joies et les peines qui ont rythmé la vie de l’auteure, racontées avec une sincérité bouleversante. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Maryse Condé Bibliographie
Redécouvrez les intrigues amoureuses entre Julien Sorel, Madame de Rênal et Mathilde de la Mole. Ce classique indémodable mérite une place de choix dans votre bibliothèque numérique personnelle. En optant pour un format pdf, vous garantissez la conservation de ce texte précieux tout en pouvant le consulter à tout moment de la journée. https://lerougeetlenoirpdf.site/ Telecharger Le Rouge Et Le Noir Stendhal Pdf
L’émotion vous attend avec ce roman en version ebook. Tout le bleu du ciel pdf est une lecture qui fait vibrer, une histoire de route et de rencontres à découvrir sur votre écran pour un moment de pur plaisir littéraire. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel Film Netflix
L’énergie vitale qui se dégage de ce livre est contagieuse, poussant le lecteur à tourner les pages sans s’arrêter. C’est un grand roman d’action psychologique. La lecture sur écran via un fichier pdf offre un confort visuel moderne, adapté à nos modes de vie actuels, pour redécouvrir ce classique. https://lerougeetlenoirpdf.site/ Qui A Écrit Le Rouge Et Le Noir ?
Ce récit est une fenêtre sur l’intimité d’une grande écrivaine. Le livre électronique est facile à utiliser et à lire. Laissez-vous emporter par la puissance des mots de Condé, qui nous livre ici un témoignage inoubliable sur les aléas de la vie et du cœur. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Le Cœur À Rire Et À Pleurer Livre Audio Gratuit
Une épopée intimiste et grandiose à la fois, disponible pour une lecture sur tous supports. Tout le bleu du ciel vous attend en version numérique, prêt à vous faire voyager sans bouger de chez vous, une expérience littéraire riche et émouvante à portée de main. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel Film Combien D Épisodes
Ce livre est un voyage au bout de la nuit solaire, une exploration des ténèbres sous la lumière aveuglante de l’été. Faites ce voyage en téléchargeant le fichier Bonjour Tristesse PDF, et découvrez les paradoxes de l’âme humaine mis en lumière par le génie de Françoise Sagan. https://bonjourtristessepdf.site/ Bonjour Tristesse Pdf Facile
Предлагаю школьникам образовательный сайт, он поможет при подготовки к школьным экзаменам, по таким предметам как математика и русский язык, получите 95+ баллов, уверяю.
Un chef-d’œuvre d’émotion à télécharger pour illuminer vos journées et vos nuits de lecteur passionné. Obtenir tout le bleu du ciel en version numérique, c’est s’offrir un passeport pour les Pyrénées et pour le cœur humain, une épopée littéraire indispensable à découvrir sans plus tarder. https://toutlebleuducielpdf.site/ Tout Le Bleu Du Ciel Livre Audio
Un témoignage littéraire d’une grande beauté formelle et émotionnelle. Le format numérique permet une lecture fluide et agréable. Découvrez les secrets d’une famille antillaise à travers les yeux d’une enfant, dans ce livre qui oscille perpétuellement entre la comédie et le drame. https://lecoeurarireetapleurerpdf.site/ Maryse Condé Bibliographie Pdf
Очень понравилась организация круиза из Дубая, посадка прошла быстро, лайнер комфортный, много зон для отдыха, каждый день насыщенная программа https://kruizy-po-persidskomu-zalivu.ru/
L’intrigue se noue lentement sous le soleil, entre baignades, sorties nocturnes et manipulations psychologiques subtiles. Pour ne rien manquer de ce drame bourgeois, procurez-vous le texte complet en version Bonjour Tristesse PDF, et laissez-vous happer par la spirale des événements qui conduira inéluctablement au drame final. https://bonjourtristessepdf.site/ Bonjour Tristesse Document Pdf
Wer sich für deutsche Literaturgeschichte interessiert, kommt an diesem Werk nicht vorbei. Finden Sie Im Westen nichts Neues als PDF und tauchen Sie in die Lektüre ein. Die digitale Version ermöglicht es Ihnen, Textstellen schnell zu finden und das Buch überallhin mitzunehmen. https://imwestennichtsneuespdf.site/ Wann Kommt Im Westen Nichts Neues Ins Kino
Märchen sind ein wichtiger Teil der Allgemeinbildung. Wer sie nicht kennt, verpasst viel. Schließen Sie diese Wissenslücke mit einer Grimms Märchen PDF und reden Sie kompetent mit, wenn es um Kultur geht. https://grimmsmarchenpdf.site/ Wer Singt Das Einhorn In Einem Von Grimms Märchen
Verstehen Sie endlich die Logik hinter den deutschen Fällen. Unsere PDF-Erklärungen sind Gold wert. Werden Sie fließend Deutsch sprechend, indem Sie grammatikalische Hürden nehmen, an denen andere scheitern. https://becomingfluentingermanpdf.site/ German Grammar Pdf
Wer Remarque liest, versteht den Menschen besser. Im Westen nichts Neues als PDF ist eine Studie der Psyche unter Extrembedingungen. Ein faszinierendes Buch, das digital ebenso fesselt wie auf Papier. https://imwestennichtsneuespdf.site/ Download Remarque Books Free
Für Teetrinker gibt es in der Kaffeestadt Berlin ebenfalls tolle Orte, und ein Tea-Lover’s Café in Berlin Guide als PDF zeigt dir, wo es die besten losen Tees, Matcha-Latte und High-Tea-Zeremonien gibt, die eine willkommene Abwechslung zum Kaffee bieten. https://cafeinberlinpdf.site/ Simple German Stories Pdf
Лайнер из Китая оказался чистым, современным и очень хорошо обслуживаемым: https://kruizy-iz-kataya.ru/
Suchen Sie nach einem Weg, Deutsch autodidaktisch und dennoch professionell zu lernen? Unsere PDF-Dokumente sind ideal für Selbstlerner. Erarbeiten Sie sich das Nivea „fluent in German“ in Ihrem eigenen Tempo und greifen Sie auf strukturierte Inhalte zurück, die Sie voranbringen. https://becomingfluentingermanpdf.site/ German Verbs List Pdf
Faszinieren Sie sich für Folklore und Mythen? Die Grimms haben die Grundlagen dafür gesammelt. Forschen Sie nach Motiven und Symbolen, indem Sie eine Grimms Märchen PDF nutzen, die Ihnen eine schnelle Navigation durch die verschiedenen Texte ermöglicht. https://grimmsmarchenpdf.site/ Grimms Fairy Tales Analysis Pdf
Möchten Sie den wohl bekanntesten deutschen Roman über den Ersten Weltkrieg lesen? Finden Sie hier Im Westen nichts Neues als hochwertige PDF-Version. Egal ob für die Schule oder aus privatem Interesse, dieser Text wird Sie nachhaltig beeindrucken und zum Nachdenken über Frieden anregen. https://imwestennichtsneuespdf.site/ All Quiet On The Western Front Complete Text
Ein Café mit Aussicht ist immer ein Highlight, und ein Rooftop-Café in Berlin Guide als PDF listet alle Dächer auf, von denen aus du beim Kaffeetrinken den Fernsehturm oder den Reichstag sehen kannst. https://cafeinberlinpdf.site/ Cafe In Berlin German Reader Pdf
Die Liebe zum Detail macht den Unterschied, und ein Artisan-Café in Berlin Guide als PDF führt dich zu Orten, wo alles von der Tasse bis zum Gebäck handgemacht ist und man die Leidenschaft der Betreiber in jedem Winkel des Ladens spüren kann. https://cafeinberlinpdf.site/ Andre Klein German Books Pdf
Приемка квартиры у застройщика требует внимательности и опыта. Специалист проверяет монтаж окон и дверей. Оценивается теплоизоляция и герметичность. Анализируется качество отделки. Все замечания оформляются корректно. Это облегчает процесс их устранения – https://govoritsatka.ru/news/opoveshenia/satkintsy-mogut-prinyat-uchastie-konkurse-molodoy-predprinimatel-chelyabinskoy-oblasti
Die Brüder Grimm lebten im 19. Jahrhundert, aber ihre Geschichten sind unsterblich. Werden Sie Zeuge dieser Unsterblichkeit. Laden Sie eine Grimms Märchen PDF und sehen Sie selbst, warum diese Texte bis heute überlebt haben. https://grimmsmarchenpdf.site/ Welche Grimms Märchen Gibt Es?
Wer den Film mochte, wird das Buch lieben. Holen Sie sich Im Westen nichts Neues als PDF. Die literarische Vorlage bietet noch mehr Tiefe und Einblick in die Gedankenwelt der Charaktere. Ein Muss für Fans. https://imwestennichtsneuespdf.site/ All Quiet On The Western Front Electronic Book
Keine Angst vor Fehlern – lernen Sie aus ihnen mit unseren Unterlagen. Unsere PDF-Guides helfen bei der Korrektur. Werden Sie fließend Deutsch sprechend, indem Sie Ihre Schwachstellen analysieren und gezielt beheben. https://becomingfluentingermanpdf.site/ Becoming Fluent In German B1
стартовал наш новый https://utgardtv.com IPTV?сервис, созданный специально для зрителей из СНГ и Европы! более 2900+ телеканалов в высоком качестве (HD / UHD / 4K). Пакеты по регионам: Россия, Украина, Беларусь, Кавказ, Европа, Азия. Фильмы, Спорт, Музыка, Дети, Познавательные. Отдельный пакет 18+
Suchen Sie nach einem Roman, der unter die Haut geht? Hier gibt es Im Westen nichts Neues als PDF. Erfahren Sie, wie Kameradschaft und Überlebenswille im Angesicht des Todes auf die Probe gestellt werden, in diesem zeitlosen Meisterwerk von Erich Maria Remarque. https://imwestennichtsneuespdf.site/ All Quiet On The Western Front Free Access
Sprachbarrieren sind dazu da, durchbrochen zu werden. Unsere PDF-Hilfen sind Ihr Werkzeug. Erreichen Sie den Status „fluent“, indem Sie sich den Herausforderungen der deutschen Sprache stellen und sie mit unserer Unterstützung meistern. https://becomingfluentingermanpdf.site/ German Reading Practice Pdf
Ищешь музыку? скачать музыку популярные треки, новые релизы, плейлисты по жанрам и настроению. Удобный плеер, поиск по исполнителям и альбомам, стабильное качество звука. Включайте музыку в любое время.
Suchen Sie nach einer Möglichkeit, Wartezeiten sinnvoll zu nutzen? Lesen Sie Im Westen nichts Neues als PDF auf Ihrem Smartphone. Tauchen Sie in eine andere Zeit ein und lassen Sie sich von einem Roman fesseln, der die Sinnlosigkeit des Krieges wie kein anderer beschreibt. https://imwestennichtsneuespdf.site/ Download All Quiet On The Western Front
Ein Souvenir, das schmeckt, findest du mit einem Coffee-Beans Café in Berlin Guide als PDF, der dir zeigt, wo du frisch geröstete Bohnen in hübschen Verpackungen kaufen kannst, um ein Stück Berlin mit nach Hause zu nehmen. https://cafeinberlinpdf.site/ Cafe In Berlin Pdf Vk
This book makes you scream, and you can love the PDF. It is a passion. The digital edition is heart. warm and fuzzy. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ You Can Scream Pdf High Quality
Unearth the secrets of a forgotten era. The An Arcane Inheritance PDF brings history to life. This electronic book is educational. Get your copy today and learn about the arcane traditions that have been passed down through an inheritance. https://anarcaneinheritancepdf.top/ Kamilah Cole An Arcane Inheritance Pdf
Visit Site – Layout is crisp, browsing is easy, and content feels trustworthy and clear.
Unearth the secrets of a mystical dynasty. The An Arcane Inheritance PDF is your ticket to this adventure. This electronic book is perfect for fantasy fans. Download it now to discover what happens when an ordinary person inherits an extraordinary power. https://anarcaneinheritancepdf.top/ An Arcane Inheritance Pdf Free Direct Download
Get the In Your Dreams PDF and lose yourself in a good book. It is the perfect antidote to boredom, offering a rich and complex world to explore anytime you wish. https://inyourdreamspdf.top/ In Your Dreams Read Free
need a video? italian production service company offering full-cycle services: concept, scripting, filming, editing and post-production. Commercials, corporate videos, social media content and branded storytelling. Professional crew, modern equipment and a creative approach tailored to your goals.
Fabet77online, another online casino. Lots to look at. What do you think? Give it a try here fabet77online
Discover the beauty of magic. An Arcane Inheritance is beautiful, available in PDF. This digital novel is aesthetic. Download the file now and admire the beauty of the spells in an arcane inheritance. https://anarcaneinheritancepdf.top/ An Arcane Inheritance Pdf Mirror
If you want a story that makes you scream, you can page the PDF. It is a turn. The download is next. on and off. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ You Can Scream Pdf Ipad
Услуга приемки квартиры востребована как среди инвесторов, так и среди семей. Каждый объект имеет свои особенности и потенциальные риски. Специалист выявляет типовые ошибки застройщиков. Осмотр проводится без спешки и формального подхода. Проверяются все помещения квартиры. Анализируется состояние инженерных коммуникаций. Особое внимание уделяется скрытым зонам. Все замечания фиксируются документально. Клиент получает подробный отчет. Это повышает прозрачность сделки. Покупатель лучше понимает состояние жилья. Решения принимаются на основе фактов: приемка квартиры от застройщика. Покупка квартиры без проверки — риск для бюджета. Проверьте жилье заранее и защитите свои интересы. Узнайте, как провести приемку
The wait for a high-quality digital version of this masterpiece is finally over. You can now grab the An Arcane Inheritance PDF and immerse yourself in a narrative filled with suspense and supernatural twists. Perfect for tablet or smartphone reading, this story will keep you on the edge of your seat. https://anarcaneinheritancepdf.top/ An Arcane Inheritance Online Pdf
The In Your Dreams PDF is a must-read for fans of the genre. Its availability in digital format means there is no excuse not to dive in and enjoy the story today. https://inyourdreamspdf.top/ In Your Dreams Latest Book Pdf
You can enjoy a reference that makes you scream. This PDF is a cite. It is a point. The digital format is show. finger and hand. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ You Can Scream Laurel Snow Series
Хочешь познакомится? https://znakomstva-blizko.ru удобный способ найти общение, дружбу или отношения. Подборки чатов и ботов, фильтры по городу и интересам, анонимность и быстрый старт. Общайтесь без лишних регистраций и сложных анкет.
студия вокала москва https://uroki-vokala-moskva.ru
плоская кровля под ключ https://ploskaya-krovlya-moskva.ru
морепродукты купить в спб дешево со склада https://mor-produkt.ru
сайт про дачу https://dacha-ua.com в Україні: сад і город, посівний календар 2026, вирощування овочів, ягід і квітів, догляд за ґрунтом, добрива та захист рослин, ландшафтний дизайн, будівництво й інструменти. Практичні поради та інструкції.
The magic is infinite. An Arcane Inheritance is boundless, available in PDF. This digital novel is limitless. Download the file now and explore the infinite possibilities of an arcane inheritance. https://anarcaneinheritancepdf.top/ An Arcane Inheritance Pdf
You can explore a psychological thriller that makes you scream. This PDF messes with your mind. It is a twisted story. The digital format is immersive. intense and unforgettable. https://youcanscreampdf.top/ Laurel Snow Book 5 Pdf
The In Your Dreams PDF is waiting. Go get it and start reading. It is a decision you will be glad you made, offering a world of entertainment at your command. https://inyourdreamspdf.top/ In Your Dreams Novel Free Pdf
I love the global reach of romance. An archive of romance proves that love is universal. I download PDF stories from different cultures, realizing that despite our differences, the human experience of falling in love is remarkably similar everywhere. https://anarchiveofromancepdf.top/ An Archive Of Romance Pdf Mega
Нужна фотокнига? фотокнига цены заказать печать из ваших фотографий в высоком качестве. Разные форматы и обложки, плотная бумага, современный дизайн. Поможем с макетом, быстрая печать и доставка. Идеально для подарка и семейных архивов
Хочешь фотокнигу? заказать фотокнигу в москве индивидуальный дизайн, премиальная печать и аккуратная сборка. Большой выбор размеров и переплётов, помощь с версткой. Быстрое производство и доставка
дайсон фен купить официальный [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-11.ru/]дайсон фен купить официальный[/url] .
Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
μεγάλο κώλο xxx βίντεο σεξ πορνό
Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Discover the magic of a romance that defies expectations. The Love in Plane Sight PDF is available for your reading pleasure. This novel is a testament to the power of love. Get the digital edition today and see where the story takes you. https://loveinplanesightpdf.site/ Read Love In Plain Sight
фен дайсон купить официальный [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-11.ru/]fen-dn-kupit-11.ru[/url] .
Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
If you want a book that is a breeze to read, choose this. The Love in Plane Sight PDF is the ebook that is light. It is a story that floats. Get your copy now and float away. https://loveinplanesightpdf.site/ Love In Plane Sight Free
If you are looking for the Is This a Cry for Help PDF, download it now for a seamless experience. This digital version is top-notch. Secure your file today and start reading. https://isthisacryforhelppdf.site/ Emily Austin Is This A Cry For Help Pdf Download
Born of Trouble is a shining example of what modern fiction can achieve. This brilliant and evocative story is now available in a convenient pdf format. Experience the talent and the vision of an author who is truly pushing the boundaries of the form. https://bornoftroublepdf.site/ Born Of Trouble Series Order
дайсон фен оригинал цена [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-11.ru/]дайсон фен оригинал цена[/url] .
устройство плоской кровли цена https://ustrojstvo-ploskoj-krovli.ru
Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Don’t miss the chance to read one of the best romances of the year. The Love in Plane Sight PDF is available for those who prefer digital books. It is a story filled with surprises and tender moments. Get your copy now and dive into the pages. https://loveinplanesightpdf.site/ Love In Plane Sight Rtf
Navigate the gold market with ease using the Bluebird Gold PDF. This guide is packed with expert knowledge and historical data, making it an essential resource for all types of investors. Download it now to enhance your market understanding and performance. https://bluebirdgoldpdf.site/ Bluebird Gold Online Library
Discover the power of resilience in Born of Trouble. This inspiring yet gritty story is now available in a portable pdf format. Witness the strength of the human spirit as characters navigate a world designed to break them. It is a story of hope in the darkness. https://bornoftroublepdf.site/ Horror Stories Pdf Free
Купить iPhone 17 https://itcrumbs.ru/neochevidnye-pomoshhniki-10-skrytyh-funktsij-iphone-17-kotorye-sekonomyat-vam-vremya_105144 новая модель Apple с современным дизайном, высокой производительностью и улучшенной камерой. Оригинальная техника, гарантия, проверка серийного номера. Выбор конфигураций памяти, удобная оплата и быстрая доставка.
Аренда серверов https://ctrl.qckl.net/index.php?rp=/store/discount-server с гарантией стабильности: мощные конфигурации, высокая скорость сети и надёжное хранение данных. Масштабируемые решения, резервное копирование и поддержка 24/7. Оптимально для бизнеса и IT-проектов.
дайсон официальный сайт стайлер для волос с насадками цена купит… [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-11.ru/]fen-dn-kupit-11.ru[/url] .
Нужно авто? murmansk-autodom.ru подбор по марке, бюджету и условиям эксплуатации, проверка юридической чистоты. Помощь с кредитом и обменом, быстро и удобно.
геотехнический мониторинг трубопроводов https://geotekhnicheskij-monitoring-zdanij.ru
Get the Is This a Cry for Help PDF for your device. This file is ready. Secure your download today and enjoy. https://isthisacryforhelppdf.site/ Is This A Cry For Help First Chapter Read
Discover the captivating world of high-altitude romance with this incredible new story. If you have been searching for the Love in Plane Sight PDF, you are finally in the right place. This novel captures the essence of unexpected connections and thrilling journeys. Download your digital copy today and start reading. https://loveinplanesightpdf.site/ Love In Plane Sight Sale
It’s fascinating how easily we fall into patterns when playing games – seeking that next dopamine hit! JILI168 seems to understand that, with quick PHP payouts & easy access. Check out jili168 vip for a streamlined experience, but remember responsible gaming is key!
мероприятия по обеспечению сохранности объектов культурного наследия https://razdel-osokn.ru
Escape into the complex reality of Born of Trouble. This acclaimed novel is now available in a convenient pdf version. Perfect for those who appreciate fine writing and deep character development, this book is a must-add to your digital collection. Experience the magic of the prose today. https://bornoftroublepdf.site/ Graphic Novels Pdf Download
Риобет казино https://riobetcasino-ytr.ru играть онлайн в слоты и live-казино. Разбор регистрации, бонусов, условий игры, вейджера, лимитов и способов вывода средств.
Only the best materials: gelenkschmerzen: ursachen, symptome und effektive behandlungsmethoden
Read More: https://www.globflex.com/top-paying-online-slots/
Вызов врача на дом в Севастополе https://vrachnadom-sev.ru
Все рабочие ссылки здесь на кракен тут ссылка проверенная ежедневно администрацией для стабильного доступа
Продажа тяговых ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
дайсон стайлер для волос цена с насадками официальный сайт купит… [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-12.ru/]дайсон стайлер для волос цена с насадками официальный сайт купит…[/url] .
стайлер купить дайсон официальный сайт [url=https://stajler-dsn.ru/]stajler-dsn.ru[/url] .
стайлер для волос дайсон с насадками официальный сайт купить цен… [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-13.ru/]стайлер для волос дайсон с насадками официальный сайт купить цен…[/url] .
стайлер дайсон для волос с насадками цена официальный сайт купит… [url=https://dn-fen-kupit.ru/]dn-fen-kupit.ru[/url] .
дайсон стайлер для волос цена с насадками купить официальный сай… [url=https://stajler-dsn-1.ru/]stajler-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон 15 [url=https://pylesos-dn-1.ru/]pylesos-dn-1.ru[/url] .
купить дайсон фен в москве у официального дилера [url=https://stajler-dsn.ru/]stajler-dsn.ru[/url] .
дайсон стайлер для волос купить цена официальный сайт с насадкам… [url=https://dn-fen-kupit.ru/]дайсон стайлер для волос купить цена официальный сайт с насадкам…[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон v15 detect absolute [url=https://pylesos-dn-1.ru/]pylesos-dn-1.ru[/url] .
дайсон фен купить в москве оригинал [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-13.ru/]дайсон фен купить в москве оригинал[/url] .
дайсон стайлер для волос с насадками цена официальный сайт купит… [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-12.ru/]дайсон стайлер для волос с насадками цена официальный сайт купит…[/url] .
дайсон купить стайлер официальный сайт [url=https://stajler-dsn-1.ru/]stajler-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
лобня купить пылесос дайсон [url=https://pylesos-dn-2.ru/]pylesos-dn-2.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон купить ярославль [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон в ростове на дону [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон animal купить [url=https://pylesos-dsn.ru/]пылесос дайсон animal купить[/url] .
дайсон пылесос беспроводной цены [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-2.ru/]дайсон пылесос беспроводной цены[/url] .
фен купить дайсон оригинал [url=https://stajler-dsn.ru/]stajler-dsn.ru[/url] .
купить дайсон стайлер с насадками для волос цена официальный сай… [url=https://dn-fen-kupit.ru/]купить дайсон стайлер с насадками для волос цена официальный сай…[/url] .
пылесос дайсон беспроводной в москве [url=https://pylesos-dn-1.ru/]пылесос дайсон беспроводной в москве[/url] .
кіно онлайн 2025 фентезі та пригоди онлайн українською
дайсон купить стайлер официальный сайт [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-13.ru/]fen-dn-kupit-13.ru[/url] .
стайлер дайсон для волос с насадками официальный сайт купить цен… [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-12.ru/]стайлер дайсон для волос с насадками официальный сайт купить цен…[/url] .
дайсон стайлер для волос с насадками официальный сайт купить цен… [url=https://stajler-dsn-1.ru/]stajler-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson detect купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-2.ru/]pylesos-dn-2.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон оригинал купить [url=https://pylesos-dsn.ru/]pylesos-dsn.ru[/url] .
дайсон томск купить пылесос [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
вертикальные пылесосы дайсон купить в москве [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон оригинал купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-2.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
купить фен дайсон официальный сайт [url=https://stajler-dsn.ru/]купить фен дайсон официальный сайт[/url] .
купить фен дайсон официальный [url=https://dn-fen-kupit.ru/]dn-fen-kupit.ru[/url] .
дайсон пылесос беспроводной цены [url=https://pylesos-dn-1.ru/]дайсон пылесос беспроводной цены[/url] .
dyson фен оригинал [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-13.ru/]fen-dn-kupit-13.ru[/url] .
стайлер дайсон цена для волос с насадками официальный сайт купит… [url=https://fen-dn-kupit-12.ru/]fen-dn-kupit-12.ru[/url] .
оригинал dyson фен купить [url=https://stajler-dsn-1.ru/]stajler-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
dyson пылесос detect absolute [url=https://pylesos-dsn.ru/]pylesos-dsn.ru[/url] .
кіно онлайн новинки 2025 дивитися фільми онлайн українською
пылесос дайсон купить последняя модель [url=https://pylesos-dn-2.ru/]pylesos-dn-2.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон v15 absolute купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон оригинал купить [url=https://pylesos-dsn-1.ru/]pylesos-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон в ростове на дону [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit.ru/]купить пылесос дайсон в ростове на дону[/url] .
пылесос дайсон оригинал купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-2.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон оренбург [url=https://pylesos-dsn.ru/]pylesos-dsn.ru[/url] .
вертикальные пылесосы дайсон купить в москве [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон беспроводной купить оригинал [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
пылесосы для дома дайсон купить [url=https://pylesos-dsn-1.ru/]pylesos-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
дайсон пылесос беспроводной цены [url=https://pylesos-dn-2.ru/]дайсон пылесос беспроводной цены[/url] .
пылесос dyson absolute [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit.ru/]пылесос dyson absolute[/url] .
пылесос дайсон animal купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-2.ru/]пылесос дайсон animal купить[/url] .
Пользователи, которые любят смотреть фильмы и сериалы онлайн, могут посетить https://lordfilmhd.co/ и найти большой выбор актуального контента в удобном формате просмотра.
пылесос dyson v15s detect [url=https://pylesos-dsn-1.ru/]pylesos-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
пылесосы для дома дайсон купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit.ru[/url] .
Для быстрого ремонта натяжной потолок удобнее, чем выравнивать плиту и ждать высыхания, выбирайте глянцевая пленка, оно визуально делает комнату выше и светлее, не ставьте слишком мощные лампы, чтобы не перегревать пленку, комната будет выглядеть дороже, особенно с правильной подсветкой – монтаж натяжных потолков в москве
купить пылесос дайсон v15 detect absolute [url=https://pylesos-dsn-1.ru/]pylesos-dsn-1.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson v15 absolute купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit.ru[/url] .
Натяжные потолки скрывают проводку, трещины и неровности без грязных работ, помогает зонировать пространство светом; команда заранее защищает мебель и быстро убирает рабочую зону, Это особенно удобно при ремонте в жилой квартире: https://potolki-decarat.ru/
Аренда NVMe VPS/VDS https://xhost24.com мощные виртуальные серверы с быстрыми SSD NVMe. Высокая производительность, стабильная сеть, защита и удобное управление. Подходит для e-commerce, API, CRM, игровых и веб-проектов любого масштаба.
Как накрутить подписчиков Ютуб бесплатно
пылесос дайсон беспроводной последняя модель купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
dyson выпрямитель для волос [url=https://vypryamitel-dn.ru/]vypryamitel-dn.ru[/url] .
стайлер дайсон выпрямитель [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-1.ru/]стайлер дайсон выпрямитель[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson airstrait ht01 оригинал [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-2.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-2.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон оригинал [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-3.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон оригинал[/url] .
страхи онлайн дивитися фільми онлайн українською
купить выпрямитель dyson оптом [url=https://vypryamitel-dn.ru/]vypryamitel-dn.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson detect [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
дайсон выпрямитель с феном [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-3.ru/]дайсон выпрямитель с феном[/url] .
dyson airstraight [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-2.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-2.ru[/url] .
фен выпрямитель дайсон airstrait купить [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-1.ru[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон в ростове на дону [url=https://dn-pylesos.ru/]купить пылесос дайсон в ростове на дону[/url] .
дивитися фільми без реклами серіали про лікарів та детективів
dyson airstraight [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-3.ru/]dyson airstraight[/url] .
дивитися серіали популярні дорами з українською озвучкою
dyson фен выпрямитель [url=https://vypryamitel-dn.ru/]vypryamitel-dn.ru[/url] .
reliable business network – Information is well presented and easy to find, which feels reassuring.
пылесос дайсон беспроводной купить оригинал [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
useful insight hub – Offers content that’s practical, engaging, and actionable.
https://alstrive.ru/blog/iphone-17-air-balans-stilja-i-proizvoditelnosti/
выпрямитель дайсон цена [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-2.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон цена[/url] .
дайсон айрстрейт купить выпрямитель [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-1.ru[/url] .
business growth insights – Posts are informative, helping track industry developments clearly.
Для квартиры после затопления сверху натяжной потолок часто спасает отделку и мебель также ПВХ пленка удобна в уходе и выдерживает воду если случится протечка Продумайте доступ к вентиляции и коммуникациям через люк чтобы обслуживание было простым в итоге интерьер становится светлее а все коммуникации остаются скрыты – https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
пылесос dyson submarine [url=https://dn-pylesos.ru/]dn-pylesos.ru[/url] .
business growth insights – Informative content, helps grasp business concepts without confusion.
Новые порносайты предлагают инновационный контент для развлечений для
взрослых. Откройте для себя безопасные новые платформы для
современного опыта.
Review my page: DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 11 CRACKED
actionable learning space – Provides insights that can be applied right away with little effort.
выпрямитель дайсон hs07 купить [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-3.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-3.ru[/url] .
market insight click – Articles are practical and help track changes in business effectively.
goal flow naturally – Insightful guidance, accomplishing tasks feels smooth and achievable.
strategic thinking zone – A useful space for exploring structured ideas.
пылесос дайсон v15 absolute купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
dyson выпрямитель [url=https://vypryamitel-dn.ru/]vypryamitel-dn.ru[/url] .
partnership insights platform – Very actionable, real-world examples illustrate alliance strategies well.
energy unleashed – Smooth, natural language emphasizing the effect of freed energy on forward movement.
дайсон выпрямитель для волос купить в спб [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-2.ru/]дайсон выпрямитель для волос купить в спб[/url] .
FlexibleShopOnline – Smooth navigation, finding and buying items is quick and hassle-free.
выпрямитель dyson ht01 купить [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-1.ru[/url] .
OpportunityTrackerPro – Informative and structured, identifying future opportunities is effortless.
Натяжной потолок делает комнату визуально выше и аккуратнее, ПВХ полотно помогает зонировать пространство светом; можно заранее спланировать скрытый карниз и подсветку по проекту: https://potolki-decarat.ru/
reliablebuycenter – Makes ordering online easy, safe, and efficient.
easyshoppingportal – Online shopping is simple, convenient, and fast to navigate.
long-term business alliances – Really helpful advice, I feel more confident in decisions now.
EnterpriseVisionHub – Helpful and concise, learning enterprise frameworks is smooth and efficient.
пылесос дайсон absolute купить [url=https://dn-pylesos.ru/]пылесос дайсон absolute купить[/url] .
stepwise progress strategies – Easy-to-understand tips, makes moving forward with projects simpler.
partnerhub – Very practical, professional networking is explained in a clear, actionable manner.
alliances knowledge base – Structured insights, helps make sense of market partnership dynamics.
clear steps forward – Encouraging phrasing, showing that simple guidance leads to consistent advancement.
alliancesnavigator – Helpful and concise, growth partnerships are easy to understand and implement effectively.
CorporateInsightNetwork – Site provides useful business insights with a professional feel.
self improvement tips – Clear, concise guidance that inspires confidence and curiosity.
SmartInnovationBase – Content is well-structured, innovations are presented in a simple, approachable manner.
trustedcommercecenter – Makes finding and purchasing items online simple and dependable.
Игра Авиатор демо [url=https://aviator-plus.ru/]aviator-plus.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-1.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон[/url] .
дайсон выпрямитель для волос купить в спб [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-2.ru/]дайсон выпрямитель для волос купить в спб[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson airstrait ht01 купить минск [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-3.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel-3.ru[/url] .
дайсон фен выпрямитель для волос [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-4.ru/]дайсон фен выпрямитель для волос[/url] .
где купить выпрямитель дайсон [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-4.ru/]где купить выпрямитель дайсон[/url] .
build professional trust – Offers practical tips, forming connections feels simple.
выпрямитель дайсон купить в ростове [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson corrale [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-1.ru/]выпрямитель dyson corrale[/url] .
strategicgrowthcenter – Offers easy-to-follow methods for enhancing business growth.
biznavigator – Informative and concise, readers can use the market strategies effectively.
trusted market network – Practical content, makes alliances easy to apply in actual markets.
clarity resources – Clear and practical guidance, makes ideas feel manageable.
GrowWithSmartChoices – Helpful guidance, understanding and deciding on options feels smooth and natural.
plan, act, advance – Concise and motivating, showing that consistent effort drives movement.
valuealliancesguide – Insights to create alliances that achieve measurable outcomes.
trusted business links – Very practical, discovering contacts feels straightforward and reliable.
DigitalCartPro – Easy-to-navigate, online buying is straightforward and quick.
стоимость плоской кровли за квадратный https://montazh-ploskoj-kryshi.ru
оценка влияния прокладки инженерных коммуникаций https://ocenka-vliyaniya-stroitelstva.ru
futurelearningexperts – Informative and concise, developing skills for the future feels simple and effective.
shoppingportal – Practical and user-friendly, navigating and buying online is simple.
urban style finds – Offers curated products in a marketplace that feels contemporary and stylish.
market trust network – Great examples, makes alliances easier to understand in practice.
dyson фен выпрямитель купить [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-1.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel-1.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель для волос дайсон москва [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-2.ru/]выпрямитель для волос дайсон москва[/url] .
StrategicVisionOnline – Well-structured guidance, long-term planning is simple and intuitive.
выпрямитель dyson ht01 [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
focus planning – Great tips, helps structure work and stay productive with minimal distractions.
выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-4.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал[/url] .
выпрямитель для волос дайсон москва [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-3.ru/]выпрямитель для волос дайсон москва[/url] .
SmartGrowthRoadmaps – Step-by-step strategies that are both practical and actionable.
выпрямитель дайсон airstrait [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
dyson выпрямитель для волос [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-2.ru/]dyson выпрямитель для волос[/url] .
pathway guidance – Gentle, smooth wording emphasizing that effective signaling simplifies complex directions.
Longreads and hits: https://www.sjsu.edu/faculty/beyersdorf/arphysics/moduleinfo.php?source=https://puzzlesbyjim.com/
Авто не на русском? перепрошивка авто на русский язык комфортное управление без языкового барьера. Перевод мультимедийной системы, бортового компьютера и навигации. Подходит для новых и б/у авто. Профессиональная настройка, аккуратная установка и поддержка.
фен выпрямитель дайсон купить в тц багратионовская [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-4.ru/]фен выпрямитель дайсон купить в тц багратионовская[/url] .
optioninsights – Provides reliable guidance for assessing and choosing the best strategic moves.
alliances planning insights – Very clear explanations, site supports strategic thinking.
Нужны цветы букет цветов на пхукете мы предлагаем свежие и невероятно красивые букеты, которые порадуют любого получателя. Наша служба обеспечивает оперативную доставку по всему острову, а в ассортименте вы найдёте цветы и композиции на самый взыскательный вкус. При этом мы гордимся тем, что сохраняем лучшие цены на острове — красота теперь доступна без переплат!
Нужен детейлинг детейлинг центр лимассол специализированный детейлинг центр на Кипре в Лимассоле, где заботятся о безупречном состоянии автомобилей, предлагая клиентам полный комплекс услуг по уходу за транспортными средствами. Мастера студии с вниманием относятся к каждой детали: они не только выполняют оклейку кузова защитными материалами, но и проводят тщательную обработку салона, возвращая автомобилю первозданный вид.
easyshoppingdeals – Smooth platform, locating deals is quick and purchases feel safe.
shoplink – Smooth and intuitive, finding and purchasing products is simple.
SafePurchaseHub – Very reliable platform, checkout is quick and easy.
trusted market partnerships – Insightful content, makes alliance concepts relatable and practical.
IdeaOutletCenter – Great for exploring concepts, user-friendly and inspiring overall.
enterprise finance bonds – Clean design and clear language make it feel reliable.
progress accelerator – Helpful lessons, shows how small steps can build momentum.
dyson выпрямитель оригинал [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-1.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel-1.ru[/url] .
dyson выпрямитель купить спб [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-2.ru/]dyson выпрямитель купить спб[/url] .
networknavigator – Provides an organized way to approach professional networking.
выпрямитель волос dyson ht01 [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон airstrait ht01 купить в волгограде [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
Делаешь документы? конструктор документов сервисы позволяет существенно ускорить работу: с его помощью вы сможете готовить необходимые документы в десять раз быстрее и при этом гарантированно избегать ошибок. Инструмент предельно прост в освоении — специальное обучение не требуется. Все ваши данные надёжно защищены, а настройка индивидуальных шаблонов выполняется оперативно и без сложностей.
Do you want bonuses? CSGOFAST Promo Code deposit bonuses, free cases, terms and conditions. A quick activation guide, FAQ, and the latest updates.
discover valuable lessons – Lessons make sense, information is presented logically.
dyson фен выпрямитель купить [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-3.ru/]dyson фен выпрямитель купить[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson airstrait [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-4.ru/]выпрямитель dyson airstrait[/url] .
купить кейс для выпрямителя дайсон [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-2.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
retailcenter – Practical and efficient, the site makes online buying seamless.
Продвижение сайтов https://team-black-top.ru под ключ: аудит, стратегия, семантика, техоптимизация, контент и ссылки. Улучшаем позиции в Google/Яндекс, увеличиваем трафик и заявки. Прозрачная отчетность, понятные KPI и работа на результат — от старта до стабильного роста.
partnermanual – Informative and concise, the advice is directly applicable to real-world business.
market alliance insights – Helpful tips, shows how alliances work in realistic settings.
long-term vision network – Provides easy-to-follow guidance for achieving sustainable growth.
business growth platform – Promising and strategic, perfect for expanding corporate collaborations.
CartJoy – Fast and convenient, modern layout enhances user experience.
выпрямитель дайсон airstrait [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-4.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон airstrait[/url] .
SmartKnowledgeBase – Well-presented lessons, new concepts are easy to understand.
realworldsolutions – Delivers advice you can use right away to improve results.
Rebricek najlepsich kasin https://betrating.sk/casino-hry/automaty-online/ghost-of-dead/ na Slovensku: bezpecni prevadzkovatelia, lukrativne bonusy, hracie automaty a zive kasina, pohodlne platby a zakaznicka podpora. Cestne recenzie a aktualizovane zoznamy pre pohodlne online hranie.
https://betrating.sk/casino-hry/automaty-online/
alliancesprofessionalhub – Focus on trust and strategy makes this resource credible for corporate partnerships.
futuristcommerce – Clear and actionable, understanding modern retail strategies is straightforward.
click to learn digitally – Informative guides, digital learning feels simple and practical.
Najlepsie online kasina https://betrating.sk/online-kasina/golden-star/ na Slovensku – porovnajte licencie, bonusy, RTP, vyplaty a mobilne verzie. Pomozeme vam vybrat spolahlive kasino pre hru o skutocne peniaze a demo. Pravidelne aktualizujeme nase hodnotenia a propagacne akcie.
learnfromexpertinsights – Excellent site, expert insights are practical and easy to apply today.
стайлер дайсон выпрямитель [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-2.ru/]стайлер дайсон выпрямитель[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson цена [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-1.ru/]выпрямитель dyson цена[/url] .
shop smarter here – Gives a customer-first impression with a layout that feels easy and intuitive.
SmartSavingsCart – Highlights smart and value-focused shopping experiences.
где купить выпрямитель дайсон [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel.ru[/url] .
quickdigitalbuy – Practical platform, completing online orders is simple and intuitive.
Lately, I had to find Amoxicillin quickly and stumbled upon Antibiotics Express. They let you purchase generics online legally. If you have a bacterial infection, this is the best place. Fast shipping to USA. More info: https://antibioticsexpress.com/#. Hope you feel better.
выпрямитель дайсон москва [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit.ru[/url] .
market alliance hub – Very insightful, helps understand alliances in real-world market situations.
learning mastery site – Encourages smarter habits and strategies for continuous growth.
OptionClarityCenter – Offers practical tips to make strategy planning less overwhelming.
Продвижение сайтов https://team-black-top.ru под ключ: аудит, стратегия, семантика, техоптимизация, контент и ссылки. Улучшаем позиции в Google/Яндекс, увеличиваем трафик и заявки. Прозрачная отчетность, понятные KPI и работа на результат — от старта до стабильного роста.
дайсон айрстрейт купить выпрямитель [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-2.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
SEO-продвижение сайта https://seo-topteam.ru в Москве с запуском от 1 дня. Экспресс-анализ, приоритетные правки, оптимизация под ключевые запросы и регион. Работаем на рост позиций, трафика и лидов. Подходит для бизнеса и услуг.
купить фен выпрямитель дайсон [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
strategic growth network – Clear guidance on achieving consistent growth and future planning.
dyson фен выпрямитель [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-3.ru/]dyson фен выпрямитель[/url] .
bondingtactics – Practical guidance to ensure secure and organized commercial bond processes.
выпрямитель волос dyson ht01 [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-4.ru/]выпрямитель волос dyson ht01[/url] .
DecisionEasePro – Content is actionable and clear, making decision-making feel practical and easy.
executiveplaybook – Practical and concise, readers can learn actionable strategies from leaders.
strategic growth – Motivating advice, following a clear direction helps progress quickly.
LearnEffectively – Platform emphasizes clarity and makes skill building approachable.
business relationship tips – Content is practical, developing trust feels simple.
next-era commerce hub – Appeals to forward-thinking businesses exploring innovative e-commerce models.
CorporateAllianceFramework – Highlights structure and professionalism in partnership development.
Тяговые аккумуляторные https://ab-resurs.ru батареи для складской техники: погрузчики, ричтраки, электротележки, штабелеры. Новые АКБ с гарантией, помощь в подборе, совместимость с популярными моделями, доставка и сервисное сопровождение.
decisionmakersguide – Very helpful, guidance for business choices is clear and immediately actionable.
выпрямитель для волос dyson airstrait ht01 [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-4.ru/]выпрямитель для волос dyson airstrait ht01[/url] .
trusted business alliances – Practical examples, makes market alliances easy to follow.
worldwide retail hub – Strong platform, seems to manage international online shopping effectively.
RetailMadeEasy – Well-organized site makes shopping smooth and stress-free.
Продажа тяговых АКБ https://faamru.com для складской техники любого типа: вилочные погрузчики, ричтраки, электрические тележки и штабелеры. Качественные аккумуляторные батареи, долгий срок службы, гарантия и профессиональный подбор.
browse flexible deals – The mix of options makes scrolling through feel worthwhile.
enterpriseconnection – Simplifies managing partnerships that are strategic and results-driven.
online value network – Fast-loading pages and fair pricing make shopping convenient and stress-free.
shopnavigator – Practical and intuitive, browsing and buying products is straightforward.
businessfuturepath – Encourages mapping growth, helps companies build structured strategies.
SafePurchasePro – Smooth and user-friendly, online buying is straightforward and secure.
click for trust partnerships – Helpful content, browsing global partnerships feels smooth and natural.
dyson выпрямитель купить в москве [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-2.ru/]dyson выпрямитель купить в москве[/url] .
clarity roadmap – Helpful advice, makes following concepts fast and intuitive.
dealassureclick – Branding highlights security, reassuring for first-time marketplace users.
securecommercialalliances – Feels safe and reliable, guidance on alliances is clear and actionable.
market alliance hub – Very insightful, helps understand alliances in real-world market situations.
frameworkdevelopmentportal – Well-laid-out guidance for understanding and using enterprise frameworks effectively.
GlobalRetailOnline – Smooth navigation, products from around the world are easy to explore.
bargainnavigator – Quick access to good deals, making shopping simple and stress-free.
Workplace Learning Hub – Very useful, with actionable advice that supports professional growth efficiently.
Smart Online Buying – Very practical site, browsing products and deals is straightforward and smooth.
marketguidancepro – Useful and actionable, platform provides structured advice for market relationships.
secure deals hub – Gives confidence through an organized and straightforward interface.
CustomerHubPortal – Very intuitive platform, makes browsing and buying simple and enjoyable.
BusinessPathFinder – Helpful resource for identifying potential business growth areas efficiently.
online daily essentials – Smooth interface supports efficient selection and purchase of common items.
discover future potential – Motivating advice, makes long-term goals feel attainable.
BuildSmartFuture – Guidance is intuitive, strategies can be applied immediately.
alliances resource center – Helpful guidance, simplifies understanding of market partnerships.
reliableshoppingzone – Appears trustworthy, reassuring for cautious online shoppers.
ValueFinderNetwork – Helps shoppers discover cost-conscious options efficiently.
clarity path – Very useful insights, helps turn understanding into forward movement.
LearnAndScaleHub – Clear advice, helps turn growth plans into actionable steps.
dealhunterhub – User-friendly and clear, finding daily offers is smooth and simple.
Growth Insights Lab – Fresh ideas that inspire actionable digital marketing strategies.
shopcityhub – Modern and convenient site, browsing products is simple and enjoyable.
insightpath – Very clear, tips are structured to help users implement growth strategies immediately.
Stepwise Success – Appreciated the logical flow, it kept everything structured and easy to apply.
Тяговые аккумуляторные https://ab-resurs.ru батареи для складской техники: погрузчики, ричтраки, электротележки, штабелеры. Новые АКБ с гарантией, помощь в подборе, совместимость с популярными моделями, доставка и сервисное сопровождение.
Продажа тяговых АКБ https://faamru.com для складской техники любого типа: вилочные погрузчики, ричтраки, электрические тележки и штабелеры. Качественные аккумуляторные батареи, долгий срок службы, гарантия и профессиональный подбор.
BusinessKnowledgeHub – Practical and easy-to-follow advice for applying lessons.
ProfessionalCredibilityNetwork – Trust-focused approach ensures confidence in developing long-term alliances.
digital planning pathway – Straightforward navigation, helps users plan digital tasks clearly and confidently.
partnership insights platform – Very actionable, real-world examples illustrate alliance strategies well.
think outside the box hub – Content challenges typical thinking patterns and sparks innovation.
businessalliancebonds – Clear structure, suggests reliability for professional corporate partnerships.
safe deals online – Ensures transactions are secure, helping customers shop with trust.
ReliableDealsHub – Very convenient platform, finding bargains is easy and secure.
systematic growth – Very clear guidance, content supports deliberate and focused growth.
SolutionsMadeSimple – Realistic advice that works for everyday situations.
alliancenavigator – Informative and easy to digest, partnership planning steps are explained clearly.
Discover Strategic Growth – Clear presentation, very useful for mapping out growth plans.
AffordableBuyNetwork – Highlights cost-effective choices for digital shoppers.
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
commercialbondhub – Highly reliable, guidance on commercial bonds is clear and easy to implement for businesses.
scalinginsights – Practical tips to implement growth frameworks effectively.
Networking for Professionals – Clear value here, building connections doesn’t feel forced.
LearnScaleHub – Very structured content that simplifies understanding growth plans.
PlanSmartFuture – Encourages forward-looking thinking and methodical strategy creation with ease.
click for knowledge boost – Informative articles, learning new topics is simple and motivating.
trusted partnership insights – Well-structured examples, makes alliance strategies easier to follow.
trusted corporate network – Branding clearly signals security and reliability for professional relationships.
Angle Insights Hub – Clean layout, insights are easy to understand and apply immediately.
trust deals center – Efficient layout and reliable options simplify the comparison and selection process.
BizClarityCenter – Explains business concepts clearly for better comprehension.
scalepath – Clear guidance, growth strategies are broken down in a simple, actionable format.
onlinegrowthplanner – Easy and actionable advice for developing digital growth strategies.
QuickPremiumBuy – Clean and efficient, online shopping is straightforward and smooth.
goal navigator – Very helpful, demonstrates how to focus energy in productive directions.
дивитися серіали онлайн популярні дорами з українським перекладом
жахи дивитись онлайн бойовики онлайн в хорошій якості
explore new paths – Interesting idea, makes it feel easy to browse and stumble upon fresh possibilities.
Услуги профессиональной приемки квартиры становятся стандартом. Покупатели ценят прозрачность и контроль. Эксперт работает по четкому алгоритму. Это повышает доверие к результату. Проверка проводится качественно. Итогом становится уверенность в покупке – http://chernook.ru/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%BA%D0%B0%20%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%80%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%80%D1%8B%20%D0%BE%D1%82%20%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9%D1%89%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B0%20%D0%B2%20%D0%A7%D0%B5%D0%BB%D1%8F%D0%B1%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B5. Проверка квартиры перед заселением — лучший способ избежать проблем. Эксперт выявит скрытые дефекты и даст рекомендации. Узнайте, как это работает
Modern Commerce Guide – The content breaks down advanced concepts into practical steps.
DigitalMarketEase – Convenience-focused shopping that adapts seamlessly to each user.
ModernShoppingInsights – Clean interface and smooth browsing, learning about trends is fast and simple.
AllianceTrustHub – Focuses on reliability and credibility in enterprise-level collaborations.
market alliance strategies – Clear advice, helps connect theory to practical market scenarios.
click for planning strategies – Informative articles, strategy concepts are clear and simple.
GlobalOnlineBuyingHub – Found this resource valuable, explanations are concise and easy enough.
shopassureclick – Strong focus on shopper confidence, appealing for cautious online buyers.
EliteConnectionHub – Simple to navigate, encourages professional connections and trustworthy communication.
businessgreenhub – Practical advice, sustainability in partnerships is explained clearly.
dailyretailportal – Very practical, platform navigation and purchasing are simple to follow.
networking insights hub – Information is presented confidently and organized for seamless professional use.
strategic growth guide – Excellent tips, content encourages intentional movement toward goals.
MarketMasterHub – Well-organized guidance, understanding market strategies is straightforward.
next-level digital store – Browsing feels intuitive and makes online shopping enjoyable.
Long-Term Partnership Insights – Very clear strategies to maintain effective business relationships over time.
StrategicPlanningHub – Provides a solid foundation for mapping out effective strategies and setting clear objectives.
EnterprisePlanningClick – Organized and easy-to-follow advice, great for understanding enterprise frameworks.
market alliance hub – Very insightful, helps understand alliances in real-world market situations.
выпрямитель dyson airstrait pink [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-3.ru/]выпрямитель dyson airstrait pink[/url] .
SafeBondStrategies – Clear and professional, strategic bond insights feel trustworthy and helpful.
StrategicBusinessAlliances – Solid website with practical tips I can apply immediately today.
дайсон выпрямитель как отличить оригинал [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit.ru[/url] .
alliances insight portal – Helpful perspectives, alliance concepts are well structured for readers.
выпрямитель дайсон купить в спб [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-4.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон купить в спб[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
дайсон выпрямитель для волос купить в спб [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-2.ru/]дайсон выпрямитель для волос купить в спб[/url] .
выпрямитель волос dyson ht01 [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-3.ru/]выпрямитель волос dyson ht01[/url] .
BudgetWiseShop – Projects savings and reliability for online consumers.
shoppro – Very convenient, navigating the platform for purchases is effortless.
RapidShop – Shopping is straightforward, interface is intuitive and modern.
trustedsalesportal – Professional look and feel, ensures peace of mind while shopping online.
commercehubglobal – Helpful and practical, international retail information is easy to read and implement.
value shopping network – Organized categories and intuitive checkout improve the user experience.
study smarter – Encourages learning without fatigue or confusion.
GrowthSignal – The content motivates productive steps that drive meaningful change.
ProAllianceNetwork – Platform emphasizes collaboration to strengthen professional partnerships and growth.
PremiumOnlineBuyingHub – Well organized content that supports smarter decisions and planning efforts.
alliances strategy guide – Insightful and clear, examples make complex strategies understandable.
Commerce Insights Hub – Detailed, timely updates that make retail trends easy to follow.
Контрактное производство электроники позволяет компаниям выпускать интеллектуальные устройства с высокой надежностью и стабильностью работы. Специалисты проектируют схемы, платы, корпуса и программное обеспечение, проводят тестирование прототипов и подготовку к серийному выпуску – https://xn—-8sbajwqy4j.xn—-8sbaav6cjgfffibd.xn—-9sbbbpi8a9bt6f.xn--p1ai/?p=company&id=39561. Приятно видеть, как технология упрощает разработку устройств.
trusted partnerships portal – Informative content, forming dependable connections is smooth.
ProRelationshipGuide – Helpful and practical, advice makes professional alliances easier to form.
collaborationguide – Insightful and well-organized, offers actionable strategies for professional engagement.
GrowthNavigator – Structured content helps make digital growth planning clear.
explore zixor – Clean interface, navigation feels smooth and sections are informative
global corporate network – Focused on connecting professionals and companies for strategic growth worldwide.
Техническое обслуживание грузовых и коммерческих автомобилей и спецтехники. Снабжение и поставки комплектующих для грузовых автомобилей, легкового коммерческого транспорта на бортовой платформе ВИС lada: https://ukinvest02.ru/
выпрямитель для волос дайсон купить [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-3.ru/]выпрямитель для волос дайсон купить[/url] .
фен выпрямитель дайсон купить в тц багратионовская [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-3.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-3.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson ht01 [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-2.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
дайсон выпрямитель купить воронеж мтс [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
careerdevhub – Practical and insightful, career development advice is easy to understand and apply.
ValueFinderNetwork – Helps shoppers discover cost-conscious options efficiently.
secure purchase platform – Looks professional and dependable, a marketplace I’d use again.
Smart Growth Center – Excellent guidance, made understanding strategies straightforward and simple.
фен выпрямитель дайсон где купить [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-4.ru/]фен выпрямитель дайсон где купить[/url] .
SecurePurchaseHub – Shopping here feels safe and organized, helping users find products easily.
partnership insights platform – Very actionable, real-world examples illustrate alliance strategies well.
PremiumShoppingPortal – Well-designed and easy to use, helps me shop online efficiently.
Онлайн курсы психологии https://ilmacademy.com.ua удобный формат обучения для тех, кто хочет освоить профессию психолога, получить практические навыки и пройти профессиональное обучение дистанционно. Курсы подойдут для начинающих и специалистов, ориентированных на практику.
Белое SEO https://seomgroup.ru работает. Спустя год работ с уверенностью это говорю. Главное найти спецов, которые не обещают золотые горы за месяц. Нормальные результаты, это минимум 3-4 месяца работы. Зато теперь получаем стабильный органический трафик, не как с рекламы, где бюджет кончился и все.
Белое SEO https://seomgroup.ru работает. Спустя год работ с уверенностью это говорю. Главное найти спецов, которые не обещают золотые горы за месяц. Нормальные результаты, это минимум 3-4 месяца работы. Зато теперь получаем стабильный органический трафик, не как с рекламы, где бюджет кончился и все.
Нужна тара? https://mkr-big-bag.ru Компания “МКР-Биг-Бэг” — производство и продажа биг-бэгов (МКР) оптом. Широкий ассортимент мягких контейнеров для сыпучих материалов. Индивидуальные заказы, доставка по России. Надежно, быстро, выгодно!
global bond insights – Accessible explanations make researching enterprise bonds faster and easier for beginners.
Explore Market Options – Informative articles that shed light on untapped opportunities.
modern online store – Excellent flow, shopping online feels straightforward and easy.
business unity hub – Information is concise, understanding strategy feels approachable.
explore now – Simple structure, lightweight pages, content comes across naturally
dealhub – Very practical, shopping options are clear and user-friendly.
TopBargainSpot – Easy navigation, shopping for deals online is smooth and enjoyable.
CommercialSafeConnect – Smooth and confident platform, transactions feel secure and professional.
explorebusinessopportunities – Insightful resources, finding business opportunities feels easy and practical here.
safeshophub – Gives a sense of security, perfect for buyers looking for reliability.
experttipsonline – Useful insights, professional knowledge is concise and actionable for daily application.
Business Path Finder – Clean interface and helpful insights make finding new strategies simple.
Комиссионный центр https://skypka.tv специализируется на скупке самой разной техники — от смартфонов и телевизоров до фотоаппаратов и игровой электроники, так что выгодно избавиться можно практически от любых лишних устройств.
online global store – Platform has a broad selection, ideal for international customers.
Свежие новости https://arguments.kyiv.ua Украины и мира: события в Киеве и регионах, экономика, общество, происшествия, спорт, технологии и культура. Оперативная лента 24/7, аналитика, комментарии, фото и видео.
Новостной портал https://dailynews.kyiv.ua Украины с проверкой фактов: важные заявления, решения властей, бизнес и финансы, жизнь городов и областей, погода, транспорт, культура. Удобные рубрики и поиск, обновления каждый час, коротко и по делу.
trusted market partnerships – Insightful content, makes alliance concepts relatable and practical.
EnterpriseUnityPlatform – Promotes unity among businesses with a professional networking focus.
ClickForBusinessAlliance – Very practical, site makes learning about global collaboration smooth.
купить дайсон выпрямитель донецк [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit.ru[/url] .
купить фен выпрямитель дайсон [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-2.ru/]купить фен выпрямитель дайсон[/url] .
Professional Collaboration Hub – Provides guidance for building alliances that last and inspire trust.
фен выпрямитель дайсон airstrait [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-3.ru/]фен выпрямитель дайсон airstrait[/url] .
trusted site – Smooth browsing with no hiccups, felt comfortable using it
где купить выпрямитель дайсон [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-3.ru/]где купить выпрямитель дайсон[/url] .
купить выпрямитель волос dyson [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
partnershipstrategies – Helpful and structured, corporate alliances are made easy to understand.
SmartDealsHub – Offers a platform for shoppers seeking the best value purchases.
business development hub – Organized framework supports practical understanding of business concepts.
nextlevel e-commerce – Helpful interface, shopping online is fast and straightforward.
TrustedCartHub – Reliable and well-structured, checkout is fast and worry-free.
AllianceStrategyHub – Clear guidance, long-term partnerships are explained in a practical and actionable way.
new enterprise paths – Encourages exploring alternative routes for business development today.
фен выпрямитель дайсон airstrait [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-4.ru/]фен выпрямитель дайсон airstrait[/url] .
GlobalDigitalShoppingMarket – Really useful site, content feels practical and easy to navigate.
trustedbondinsights – Offers reliable strategies for dealing with strategic bonds professionally.
proinsightsmarketleaders – Helpful guidance, market leader strategies are presented in a clear, actionable format.
business professional network – Professional tone and branding suggest a platform for serious corporate partnerships.
trusted market partnerships – Insightful content, makes alliance concepts relatable and practical.
BusinessRelationshipPortal – Encourages steady, meaningful connections for professional growth.
CityRetailHub – Engaging platform, product information is clear and browsing is simple.
forward drive – Short and approachable, illustrating how intentional force creates momentum.
trusted business insights – Well-structured layout helps users grasp frameworks and strategies effectively.
Consumer Buying Center – Simplifies online shopping with practical guidance and tips.
go to site – Simple design, responsive pages, information is easy to follow
landing page – Clear layout, content is concise and browsing feels effortless
Just now, I wanted to buy Amoxicillin urgently and came across a reliable pharmacy. You can buy antibiotics without a prescription safely. If you have UTI, try here. Overnight shipping available. Visit here: [url=https://antibioticsexpress.xyz/#]www.antibioticsexpress.com[/url]. Good luck.
teaminsights – Very useful, professional collaboration guidance is actionable and easy to apply.
EasyPickStore – Smooth navigation, making online purchases effortless and quick.
career tips hub – Helpful guidance, learning from this site feels straightforward and actionable.
Practical Insight Hub – Content is actionable and well-presented, perfect for everyday use.
выпрямитель для волос дайсон [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit.ru[/url] .
купить фен выпрямитель дайсон оригинал [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-2.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-2.ru[/url] .
TrustedDealsHub – Well-structured platform, buying products is easy and safe.
globaldigitalshoppingmarket – Smooth interface, site offers a good overview of digital marketplaces worldwide.
simplestorebuilder – Focused on simplicity, suitable for first-time ecommerce entrepreneurs.
купить выпрямитель dyson оптом [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-3.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-3.ru[/url] .
opportunity exploration hub – Promotes thinking beyond the short term to maximize potential.
reliableshoppercenter – Easy-to-navigate platform that provides secure and efficient shopping.
дайсон айрстрейт купить выпрямитель [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-3.ru/]vypryamitel-dn-kupit-3.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель волос dyson ht01 [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-1.ru[/url] .
trustedconnections – Informative and professional, the advice on building market trust is straightforward.
alliances guide hub – Very useful, real market examples enhance understanding of partnerships.
BudgetDealsCenter – Designed to appeal to shoppers seeking value and affordability online.
ProInsightsHub – Offers practical professional knowledge useful for day-to-day work decisions.
LearnWithExperts – Easy-to-follow guidance, really improves understanding of professional strategies.
engineered forward flow – Friendly, actionable phrasing demonstrating that structured motion produces consistent outcomes.
]businessbridge – Informative and logical, the platform presents partnership strategies clearly.
quick link – Navigation felt natural, site looks organized and responsive
Simple Shopping Network – Navigation is easy, keeping the whole process enjoyable.
smart retail portal – Finding products is simple thanks to the clear layout.
Женский портал https://elegantwoman.kyiv.ua о красоте, здоровье и стиле жизни: уход за кожей и волосами, мода, отношения, психология, карьера, дом и вдохновение. Полезные советы, подборки, рецепты и лайфхаки на каждый день. Читайте онлайн с телефона и компьютера.
Всё для женщин https://glamour.kyiv.ua в одном месте: тренды моды и бьюти, здоровье, питание, спорт, семья, дети, отношения и саморазвитие. Статьи, чек-листы, идеи и обзоры, которые помогают принимать решения и чувствовать себя увереннее.
Главные новости https://novosti24.kyiv.ua Украины сегодня — быстро и понятно. Репортажи из регионов, интервью, разборы, инфографика, фото/видео. Следите за темами, сохраняйте материалы и делитесь. Лента обновляется 24/7, чтобы вы были в курсе событий.
ModernRetailBuyingHub – Enjoyed browsing here, ideas are fresh and well explained clearly.
выпрямитель дайсон отзывы [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-kupit-4.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон отзывы[/url] .
SkillUpForBusiness – Easy-to-follow lessons, helps develop useful business capabilities quickly.
safe order center – Confident experience, checkout process runs without any issues.
online management skills – Highlights the flexibility and reach of digital business learning.
expansionguide – Clear strategies for scaling your business in real-world scenarios.
advance your knowledge hub – Encourages continuous learning and expanding skills in a structured way.
CorporateNetworkingGuide – Practical and informative, connecting with businesses feels smooth and professional.
ClickAndShopFast – Emphasizes speed and effortless navigation for digital retail.
explore here – Pages load fast, simple sections, browsing feels seamless
Ежедневные новости https://useti.org.ua Украины: политика и экономика, общество и медицина, образование, технологии, спорт и шоу-бизнес. Мы собираем информацию из надежных источников и объясняем контекст. Читайте онлайн с телефона и компьютера — удобно и бесплатно.
Портал для женщин https://woman24.kyiv.ua про жизнь без лишнего: красота, женское здоровье, питание, рецепты, уютный дом, финансы, работа и отдых. Практичные советы, честные обзоры и вдохновляющие истории.
Все о событиях https://ua-vestnik.com в Украине и вокруг: оперативные сводки, расследования, мнения экспертов, рынки и курс валют, происшествия и полезные сервисы. Подборки по темам, теги, уведомления, фото и видео — актуально в любое время.
Recently, I was looking for Ciprofloxacin fast and stumbled upon Antibiotics Express. They let you get treatment fast safely. If you have a toothache, I recommend this site. Express delivery available. Check it out: treat bacterial infections. Good luck.
alliancenavigator – Clear and structured, readers can easily grasp strategic partnership concepts.
Minimal Design Page – Ran into this by accident, the layout feels nicely organized
GlobalTrustRelationshipNetwork – Clean layout and thoughtful content make this site enjoyable today.
NextGen Retail Hub – Streamlined tools for exploring and shopping digital products effortlessly.
get moving hub – Inspires action with a positive and encouraging approach.
Услуга приемки квартиры подходит как для инвесторов, так и для семей. Каждый объект имеет свои особенности и потенциальные риски. Специалист выявляет типовые ошибки застройщиков. Проводится осмотр всех помещений без спешки. Клиент получает подробный отчет с рекомендациями. Это делает покупку более безопасной, узнать больше можно по ссылке. Приемка квартиры позволяет заранее оценить объем будущих работ. Это особенно важно перед ремонтом. Вы получаете полную картину состояния жилья., http://wiki.netix.ru/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%BA%D0%B0%20%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%80%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%80%D1%8B%20%D0%BE%D1%82%20%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9%D1%89%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B0%20%D0%B2%20%D0%A7%D0%B5%D0%BB%D1%8F%D0%B1%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B5
ValueFinderNetwork – Helps shoppers discover cost-conscious options efficiently.
corporate networking site – A solid option for businesses interested in shared development opportunities.
enterpriseguide – Step-by-step advice for driving organizational growth successfully.
BestValueStore – Finding deals is easy and the product info is very clear.
ecochoiceplatform – Clear focus on sustainability, supporting smarter decisions for conscious consumers.
securepartnershiphub – User-friendly, guidance on alliances is practical and trustworthy.
UrbanShopNetwork – Niche city shopping style comes through, making browsing feel fresh and modern.
reliableonlinecommerce – Safe and reliable, buying products online feels simple and secure today.
TrustedEnterpriseInsights – Well-laid-out guidance, frameworks are easy to learn and implement.
sonabet.pro
Brand-new in this game are Super Scatters. Land one Super Scatter while triggering the feature to instantly win 100x the bet, two Super Scatters to win 500x, three for 5,000x, and if four Super Scatters hit while triggering the feature, the maximum win of 50,000x is awarded. Focus on creating a distinct visual identity rather than chasing short-term graphic trends. The enduring appeal of games like the gates of olympus slots demonstrates the power of a cohesive theme. Its use of clear, symbolic icons like Zeus’s lightning bolts and golden goblets against a majestic sky creates immediate recognition. This clarity ensures the interface remains intuitive and visually appealing years after its release. Let’s do a review of Gates of Olympus, a pokie that grabs the slot structure and substitutes paylines for raw momentum. Zeus hovers over a 6×5 reel set where symbols don’t have to align in a row—the eight or more in any place wins. Then there’s a tumble, dispatching wins and raining in fresh symbols, round after round. Brisk, loud, and designed for that moment when a lone cascade turns a whole session upside down.
https://www.medidocs.com/33/bizzo-casino-game-review-a-thrilling-experience-for-australian-players/
These are just 5 examples of some of the best and most popular online slots offered at 666 Casino. You can find more games like these in our ‘Popular’ section, so take a look! This is a classic slot game with a clean layout of five reels and 10 paylines. It uses familiar symbols like diamonds, lucky 7s and fruits. Match three to five of the same symbol on a payline to win. The main feature in this game is the Hit Bar Respin. If you land five or more Hit Bar symbols anywhere on the reels, the feature starts. These symbols will stick in place while the rest spin again. If another Hit Bar symbol lands, you get another respin. If you manage to collect 15 Hit Bar symbols, you’ll win the jackpot of1 000 times your bet! Credit and debit cards are the most common payment methods used at online pokies sites in New Zealand, so you can be sure that the titles you choose to play are the ones that will meet with your tastes. It is a very important information that online casinos are not so happy to give away, head to Monte Carlo. With fast payouts and a range of payment options, just like they would in a real casino. The King Billy help team can be contacted via two channels, lotto australia online you will need to run through our detailed reviews of the operators which have made the cut.
ClickToUnderstandBusiness – Very helpful, made learning and planning in business straightforward.
ShopEaseOnline – Practical tips made my buying process smoother and faster.
click to build relationships – Helpful tips, learning to connect professionally feels natural.
online access – Minimalistic feel, smooth browsing, content is clear and organized
ProTeamConnect – Easy to navigate, corporate relationship guidance feels practical and trustworthy.
modern solutions portal – Highlights innovative alternatives for improved results.
Corporate Collaboration Lab – Offers practical strategies to strengthen professional bonds.
enterprise alliance link – Focused on practical tools to improve partnership outcomes.
easy online shop – Clean structure allows quick browsing without confusion.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://womanlife.kyiv.ua бьюти-гайды, мода, психология, отношения, материнство и забота о себе. Подборки товаров, инструкции, рецепты и идеи для дома. Читайте коротко или глубоко — удобная навигация и свежие материалы каждый день.
Новости Украины https://news24.in.ua 24/7: Киев и регионы, экономика, общество, безопасность, технологии, спорт и культура. Короткие сводки, подробные материалы, объяснения контекста, фото и видео. Читайте главное за день и следите за обновлениями в удобной ленте.
Медицинский портал https://medicalanswers.com.ua для пациентов: здоровье, диагностика, лечение, профилактика и образ жизни. Экспертные статьи, справочник симптомов, советы специалистов и актуальные медицинские новости. Достоверная информация в одном месте.
connectsphere – Learn to approach business networking with clarity and confidence.
quick link – Fast-loading pages, intuitive navigation, content comes across clearly
visit tavro – Pleasant browsing, well-organized content, and seamless page transitions
market discovery hub – Feels like a resource for entrepreneurs seeking unique market insights.
vyrxo corner – Clear headings, minimal distractions, and navigation feels natural
enterprisepartnershipcenter – Useful content, networking strategies are clear and simple to follow.
growth playbook – Helpful insights, breaks down frameworks into simple actionable steps.
DigitalPurchaseInsight – Encourages careful consideration before every online purchase.
signal turns action online – Organized layout and readable typography make it user-friendly
FindSmarterBusinessMoves – Found this resource valuable, explanations are concise and easy enough.
explore global alliances – Engaging and practical, content helps navigate international business.
landing hub – Pages open smoothly, design is clean, navigation is effortless
SmartSavingsCart – Highlights smart and value-focused shopping experiences.
GlobalNetworkingGuide – Clear and professional, building international relationships is effortless.
Современный женский https://storinka.com.ua портал: уход, макияж, тренировки, питание, стиль, любовь, семья и карьера. Экспертные советы, полезные подборки, идеи подарков и лайфхаки. Мы говорим простым языком о важном — заходите за вдохновением ежедневно.
Актуальные новости https://uapress.kyiv.ua Украины и мира: события, заявления, решения, рынки, курсы, происшествия и жизнь регионов. Факты и проверенные источники, аналитика и комментарии. Удобные рубрики, поиск, теги и подборки — всё, чтобы быстро находить нужное.
Новостной портал https://ua-novosti.info Украины без лишнего: оперативная лента, репортажи из областей, интервью и разборы. Политика, финансы, социальные темы, медицина, образование, IT. Фото/видео, инфографика, уведомления и топ-материалы дня.
New Growth Perspectives – The content inspired me to rethink how I approach everyday tasks.
value shopping hub – Emphasizes smart spending, seems ideal for bargain hunters.
greenpartnershiphub – Offers clear guidance on building sustainable business partnerships effectively.
trusted purchase network – Overall buying experience feels safe and well-managed.
online purchase simplified – Suggests the site reduces complexity and makes shopping enjoyable.
DecisionInsightHub – Guides professionals toward clear, actionable solutions when facing business complexity.
visit zylor – Pleasant browsing experience, content is clear and well organized
LearnFutureFocusedSkills – Solid website with practical tips I can apply immediately today.
focusamplifiesgrowth info – Well-thought-out pages, readable text, and a smooth browsing experience
CartQuick – Secure and hassle-free, checkout takes no time.
critical thinking insights – Encourages analyzing ideas deeply, strategies are easy to understand.
check velra – Well-structured pages, information is concise and readable
Главные события https://vesti.in.ua Украины — коротко и понятно. Мы собираем новости из Украины и мира, проверяем данные и даём ясные объяснения. Подборки по темам, новости городов, аналитика, мнения, видео. Обновления каждый час, удобно на смартфоне.
Онлайн-журнал https://love.zt.ua для женщин: мода, бьюти, психология, любовь, семья, дети, дом, карьера и финансы. Обзоры, лайфхаки, рецепты и инструкции — без «воды», с пользой. Удобные рубрики и свежие материалы ежедневно.
Всё о здоровье https://medfactor.com.ua на одном медицинском портале: болезни и их лечение, анализы, препараты, обследования и профилактика. Материалы подготовлены с опорой на клинические данные и врачебную практику. Читайте онлайн в любое время.
official korixo – Enjoyable visit thanks to an organized and approachable layout
оформить гражданство румынии
basic ecommerce hub – Streamlined and effective, makes online selling easy for small businesses.
globalpartnershipinfrastructure – Very detailed, global partnership infrastructure is explained clearly and practically here.
Collaboration Insights Hub – Clear content that makes understanding partnership strategies easy.
LearnSmartPro – Clear guidance, strategies are easy to understand and apply.
careeracceleratorhub – Organized advice and tools for improving career outcomes efficiently.
BondExpertOnline – Very user-friendly, clarified all the essential points.
EcommerceSafetyNet – Security-first branding encourages confidence for first-time shoppers.
long-range planning hub – Encourages careful consideration of future business goals and objectives.
fast find shopping – Everything is positioned to make browsing faster.
Нужен дизайн? дизайн бюро москва создаем функциональные и стильные пространства для квартир, домов и офисов. Планировки, 3D-визуализации, подбор материалов и авторский надзор. Индивидуальный подход, реальные сроки и продуманные решения под ваш бюджет.
Решил сделать ремонт? студия дизайна квартир москва: квартиры, дома, апартаменты и офисы. Продуманные планировки, 3D-проекты, сопровождение ремонта и контроль реализации. Создаем интерьеры, отражающие ваш стиль и образ жизни.
growthflowswithclarity corner – Minimal design, clear flow, and information is easy to find
Электронные компоненты https://zener.ru с прямыми поставками от производителей: микросхемы, пассивные элементы, разъёмы и модули. Гарантия оригинальности, стабильные сроки, выгодные цены и подбор под ТЗ. Поставки для производства, сервиса и разработки.
visit ulvix – Clear layout, smooth navigation, and everything loads quickly
budget shopping portal – Focus on value seems strong, helping shoppers stretch their money further.
Trusted Partnership Insights – Helpful guidance for nurturing professional bonds and alliances.
sales site – Quick checkout and informative shipping notifications were a plus.
PurchasePal – Very useful, made understanding choices straightforward.
check mexto – Straightforward site design, everything is quick to find
product site – Navigation flows nicely, and product info feels dependable.
FutureInsightsOnline – Provides resources to cultivate proactive decision-making and planning habits.
trustedsalesportal – Professional look and feel, ensures peace of mind while shopping online.
progressmovesforwardnow portal link – Clean interface, organized content, and enjoyable to explore
mavix portal – Smooth interface, information straightforward and browsing went without hiccups.
xavro homepage – Pleasant browsing, pages are easy to navigate and content is clear
click here – Quick access, organized sections, message is conveyed effectively
discount deals platform – Strong focus on value, ideal for smart shopping.
explorefuturedirections – Inspiring content, learning about future directions feels engaging and useful today.
store page – Items are listed neatly, and filtering helped me focus on what I wanted.
TrustBrixel – Very intuitive interface, site responsive, and browsing was easy.
Pelixo Hub – Smooth experience, product info clear and checkout worked without issues.
Voryx Express – Pages load fast, content clear, and browsing overall felt natural.
Smart Decision Growth – Makes analyzing options simpler and more structured for better results.
NextGenOnlineBuying – Nice experience overall, navigation works smoothly and loads quickly everywhere.
Ulvaro Hub – Layout clean, pages fast and overall site experience pleasant.
product marketplace – Discovered this online store, prices fair and checkout was easy.
Kavion Path World – Pages open quickly, navigation simple and information easy to locate.
IntentionalLearningCenter – Helps learners apply strategic thinking to real-world challenges effectively.
commercialbondcenter – Well organized, highlights security for businesses managing bonds digitally.
QelaroGo – Accessible design that anyone can understand.
progressmoveswithfocus guide – Clear and minimal design that keeps focus on the key points
landing hub – Easy-to-follow layout, fast browsing, positive initial experience
clyra homepage – Thoughtful design, easy-to-navigate pages, and pleasant user experience
trust-based business site – Likely to appeal to firms that value transparent branding.
brivox destination – Enjoyable stop, the site runs quickly and text is easy to read
Yaveron Point – Navigation smooth, product pages organized and purchase steps simple.
web shop – Pages load instantly, site looks legitimate, and ordering is smooth.
ProfessionalBondSolutions – Great platform overall, information is clear and genuinely helpful today.
Online Shopping Tips Hub – Makes choosing the right products online simpler and faster.
Korivo Direct – Clean layout, links function properly and browsing experience smooth.
online hub – Fast navigation, easy-to-find categories, and overall site feels pleasant.
Vixor Home – Navigation simple, pages loaded fast, and finding products was straightforward.
перепланировка квартир [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru[/url] .
перепланировка квартир [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir4.ru/]перепланировка квартир[/url] .
Plivox Lane Direct – Smooth navigation, product info clear and ordering process fast.
узаконивание перепланировки [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir5.ru/]узаконивание перепланировки[/url] .
выпрямитель dyson ht01 купить [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru/]выпрямитель dyson ht01 купить[/url] .
QuickRixar – Smooth interface, pages responsive, and content appeared trustworthy.
проектная организация для перепланировки квартиры [url=https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru/]proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru[/url] .
navix hub – No delays, ordering process smooth and pages displayed properly.
сколько стоит перепланировка [url=https://skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru/]сколько стоит перепланировка[/url] .
HandsOnStrategies – Offers actionable methods that users can apply immediately in daily challenges.
securecorporatelinks – Well-structured design suggests careful attention to professional trust and collaboration.
directionanchorsprogress network – Logical flow, clear headings, and overall site experience feels smooth
Mivaro Portal – Fast loading, navigation intuitive and content easy to understand.
trusted link – Minimalist design with reliable navigation, everything functions well
Женский портал https://replyua.net.ua про красоту и заботу о себе: уход, макияж, волосы, здоровье, питание, спорт, стиль и отношения. Практичные советы, чек-листы, подборки и вдохновляющие истории. Читайте онлайн и находите идеи на каждый день.
Строительный портал https://ateku.org.ua о ремонте и строительстве: технологии, материалы, сметы, проекты домов и квартир, инструкции и советы экспертов. Обзоры, калькуляторы, нормы и примеры работ — всё для частного и коммерческого строительства.
Онлайн-портал https://avian.org.ua для строительства и ремонта: от фундамента до отделки. Подбор материалов, пошаговые гайды, сравнение технологий, советы мастеров и актуальные цены. Полезно для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных клиентов.
plexin network – Minimal design, clear structure, and pages are user-friendly
shop website – My first purchase was hassle-free with neat packaging.
Zorivo Hub Shop – Fast-loading pages, content clear and overall experience seamless.
portal zylavo – Browsing is easy, images sharp and sections well arranged.
Business Strategy Finder – Helpful insights that made exploring different business directions much easier.
Qulavo Central – Site loads smoothly, navigation intuitive and checkout steps clear.
Zylavo Access – Minimalist design, fast browsing, and finding the right items was hassle-free.
QuickShopPlatform – Smooth and reliable, the platform makes online buying easy.
xavix online – Clean interface, simple layout, and browsing that feels effortless
Velro Express – Navigation intuitive, content clear and shopping process smooth.
Строительный портал https://domtut.com.ua с практикой: проекты, чертежи, СНиП и ГОСТ, инструменты, ошибки и решения. Ремонт квартир, строительство домов, инженерные системы и благоустройство. Понятно, по делу и с примерами.
Всё о строительстве https://hydromech.kiev.ua и ремонте в одном месте: материалы, технологии, дизайн, инженерия и безопасность. Экспертные статьи, инструкции, калькуляторы и кейсы. Помогаем планировать работы и экономить бюджет без потери качества.
Украинские новости https://polonina.com.ua онлайн: всё важное о стране, регионах и мире — от экономики и инфраструктуры до культуры и спорта. Лента 24/7, материалы редакции, комментарии экспертов, фото и видео. Читайте, сохраняйте и делитесь — быстро и удобно.
узаконивание перепланировки [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir4.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir4.ru[/url] .
перепланировка в москве [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru[/url] .
landing hub – Clear pages, intuitive navigation, browsing feels effortless
directionpowersmovement corner – Neat design, well-structured pages, and site loads efficiently
retail insights hub – Design and structure align with contemporary shopping behaviors.
sonabet apk
перепланировка услуги [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir5.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir5.ru[/url] .
перепланировка квартиры проектные организации [url=https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru/]proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru[/url] .
Приемка квартиры перед заселением важна для будущего комфорта. Эксперт оценивает надежность всех систем. Проверяется отопление и водоснабжение. Анализируется вентиляция помещений. Выявляются потенциальные проблемы. Все замечания фиксируются документально. Это снижает риски в первые месяцы проживания: https://harat.ru/chelyabinsk/companies/87107-priemkaplus/
Приемка квартиры упрощает процесс взаимодействия с застройщиком. Все замечания оформляются корректно. Это ускоряет их устранение. Узнайте подробнее о приемке квартир
sales site – Categories are well labeled, and mobile browsing was convenient.
tekvo network – Logical page structure, readable headings, and smooth navigation overall
PlavexSpot – Layout tidy, pages load fast, and finding items straightforward.
узаконить перепланировку квартиры стоимость [url=https://skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru/]skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru[/url] .
Печать на 3D-принтере — это эффективная технология, который помогает реализовать самые смелые идеи. Мы осуществляем создание прототипов и макетов. Наши специалисты используем современное оборудование, что соответствует всем современным требованиям. Мы работаем с разными материалами, благодаря чему печать подойдёт для архитектуры, прототипирования и хобби. Мы печатаем быстро и точно, а качество всегда соответствует цене. Перейдите по ссылке, чтобы заказать, и вы получите результат точно в срок https://tver.cataloxy.ru/firms/asteri-3d.ru.htm. Мы печатаем модели любой сложности и формата.
школьное образование онлайн [url=https://shkola-onlajn11.ru/]shkola-onlajn11.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон москва [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон москва[/url] .
реклама наркологической клиники [url=https://seo-kejsy7.ru/]реклама наркологической клиники[/url] .
курсы стриминг [url=https://shkola-onlajn12.ru/]shkola-onlajn12.ru[/url] .
Проектирование печатных плат выполняется для различных применений. Учитываются требования по надежности и нагрузкам. Используются современные САПР. Платы проходят проверку перед выпуском. Это снижает вероятность ошибок: https://ideal-home.shop/communication/forum/user/11855/.
школа онлайн для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn14.ru/]shkola-onlajn14.ru[/url] .
онлайн школа для школьников с аттестатом [url=https://shkola-onlajn15.ru/]онлайн школа для школьников с аттестатом[/url] .
онлайн ш [url=https://shkola-onlajn13.ru/]shkola-onlajn13.ru[/url] .
Kryvox Click – Link opened smoothly, content clear and navigation straightforward.
Xelarionix Hub Shop – Pages load quickly, interface simple and product details easy to find.
link hub – Came across it, store feels trustworthy and simple to navigate.
мелбет полная версия [url=http://gbufavorit.ru/]мелбет полная версия[/url] .
nolra shop online – Navigation intuitive, content loads fast, and filtering helps a lot.
Top Leader Learning Hub – Helps understand what successful leaders do differently.
Visit Xelra – Clean interface, navigation simple and product info easy to find.
сколько стоит узаконить перепланировку в квартире [url=https://skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru/]skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru[/url] .
Портал для строителей https://inter-biz.com.ua и заказчиков: советы по ремонту, обзоры материалов, расчёты, сметы и технологии. Реальные кейсы, чек-листы и рекомендации специалистов для надежного результата на каждом этапе работ.
Строительный портал https://prezent-house.com.ua строительство домов и зданий, ремонт квартир, инженерные системы и отделка. Пошаговые инструкции, обзоры материалов, расчёты и советы экспертов для частных и коммерческих проектов.
Zaviro Zone – Fast navigation, clear product info, and overall site experience is pleasant.
quick link – Minimal distractions, everything feels clear and easy to access
modern e-commerce hub – Sleek design shows the current trends in online shopping preferences.
actionpowersmovement info – Easy-to-read sections, smooth layout, and user experience is pleasant
online storefront – The service team replied in a respectful manner.
axory homepage – Clean layout, navigation is simple, and browsing feels effortless
согласование перепланировки [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir4.ru/]согласование перепланировки[/url] .
Morix Link – Browsing simple, layout intuitive and checkout steps easy to follow.
official olvra – Pleasant visit, structured pages with reliable and clear information
услуги по перепланировке квартир [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru[/url] .
согласование перепланировки москва [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir5.ru/]согласование перепланировки москва[/url] .
проект перепланировки квартиры в москве [url=https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru/]proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru[/url] .
StreamQela – Fast and smooth browsing, content seemed well-organized.
Rixaro Central – Interface tidy, pages responsive and purchasing process worked flawlessly.
Портал для женщин https://angela.org.ua о современном лайфстайле: бьюти-рутины, мода, здоровье, правильное питание, отношения, работа и отдых. Полезные подборки, честные обзоры, истории и советы экспертов — заходите за вдохновением 24/7.
zorivoshop link – Fast, clean, and easy to browse without distractions.
Портал для женщин https://beautyrecipes.kyiv.ua про гармонию и результат: здоровье, красота, стиль, саморазвитие, семья и отношения. Обзоры косметики и процедур, планы питания, тренировки, советы по дому и вдохновляющие истории. Всё в одном месте, 24/7.
EasyMorixo – Layout minimal but effective, pages load fast, and navigation simple.
最佳xxx网站 为成熟观众提供优质内容。探索 经过验证的成人网站 以确保质量和隐私。
my blog post: 残酷色情电影
Всё, что важно https://inclub.lg.ua женщине: здоровье и гормоны, питание и фитнес, стиль и гардероб, отношения и самооценка, уют и рецепты. Экспертные статьи, тесты и подборки. Сохраняйте любимое и делитесь — удобно на телефоне.
International Business Links – The platform supports global collaboration in a clear and logical way.
онлайн-школа для детей бесплатно [url=https://shkola-onlajn11.ru/]shkola-onlajn11.ru[/url] .
Kryvox Online Shop – Layout simple, content clear and purchasing process effortless.
школа онлайн обучение для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn14.ru/]школа онлайн обучение для детей[/url] .
онлайн школа ломоносов [url=https://shkola-onlajn12.ru/]shkola-onlajn12.ru[/url] .
онлайн школа ломоносов [url=https://shkola-onlajn15.ru/]онлайн школа ломоносов[/url] .
EasyNeviron – Layout professional, content structured well, and shopping workflow smooth.
start browsing – Lightweight interface, pages open quickly, content is readable
дайсон выпрямитель как отличить оригинал [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
item store – Site looks neat, products are decent, and checkout was quick.
melbet bookmaker [url=https://studio-pulse.ru/]melbet bookmaker[/url] .
современные seo кейсы [url=https://seo-kejsy7.ru/]seo-kejsy7.ru[/url] .
explore ideas become forward – Simple sections, readable text, and navigation is smooth and effortless
Kelvo Hub – Link worked fine, pages responsive and content easy to understand.
онлайн-школа для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn13.ru/]shkola-onlajn13.ru[/url] .
melbet официальный сайт [url=https://www.gbufavorit.ru]melbet официальный сайт[/url] .
DealFinderOnline – Secure and convenient, deals are easy to locate and purchase without hassle.
узаконить перепланировку цена [url=https://skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru/]узаконить перепланировку цена[/url] .
olvix access – Simple interface, clear content, and pages encourage further exploration
nexlo online marketplace – Smooth site operation, clear checkout process and layout easy to follow.
Cross-chain bridge activity monitoring enhances best crypto signals for multi-chain tokens. Token flows between blockchains indicate where liquidity and user attention is concentrating.
Customer support quality for best hookup sites affects user satisfaction. Responsive assistance with account issues, safety concerns, and technical problems demonstrates platform commitment to member experience.
Story highlights benefit when you buy instagram likes for featured posts. Strong engagement on highlighted content attracts profile visitors encouraging exploration and following.
shopping platform – Products are easy to browse, and filtering made finding what I needed effortless.
Pelix Online – Navigation simple, pages opened quickly and checkout completed without problems.
перепланировка помещения [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir4.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir4.ru[/url] .
согласование перепланировок [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir3.ru[/url] .
Korla World – Smooth browsing, content clear and completing checkout felt effortless.
Qulavo Direct – Layout organized, checkout intuitive and content easy to understand.
nolix access – Straightforward site with clear text and easy-to-follow content
заказать проект перепланировки [url=https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry20.ru/]заказать проект перепланировки[/url] .
услуги по согласованию перепланировки [url=https://pereplanirovka-kvartir5.ru/]pereplanirovka-kvartir5.ru[/url] .
sales site – Just stumbled on it and saved it for another time.
http://kupprawojazdyb.com
https://comprarcarnetdeconducira.com
https://rijbewijskopenc.com
PrixoHub – Checkout process smooth, pages responsive, and finding product details was easy.
Korva Web Link – Stumbled upon this and appreciated the fresh-looking content
Click Torix – Layout minimal, content easy to find, and purchasing steps straightforward.
actioncreatesforwardpath destination – User-friendly site, clear sections, and navigating feels efficient
дистанционное обучение 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn11.ru/]shkola-onlajn11.ru[/url] .
Liquidation cascade identification helps best crypto signals anticipate volatility. Monitoring liquidation clusters at key price levels reveals potential cascade triggers or support zones.
lbs это [url=https://shkola-onlajn14.ru/]lbs это[/url] .
The coaching clients who found me through Twitter have become my primary income source. They chose me over competitors partly because my follower count suggested expertise. When you buy twitter followers, you’re investing in client acquisition that generates recurring revenue.
The affiliate marketing opportunities available to accounts with decent followings are substantial. Networks have minimum follower requirements for acceptance. When you buy twitter followers to meet those minimums, you’re accessing revenue streams that weren’t previously available to your account.
онлайн школа с 1 по 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn12.ru/]shkola-onlajn12.ru[/url] .
BondXpress – Smooth browsing, links work fine, and content appears accurate.
klyvo link – Content is readable, layout is intuitive, and navigation is effortless
онлайн школа 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn15.ru/]онлайн школа 11 класс[/url] .
ставки на спорт мелбет официальный сайт [url=www.studio-pulse.ru]ставки на спорт мелбет официальный сайт[/url] .
main portal – Quick checkout, and the payment confirmation was immediate.
Comprehensive strategies address both content types. Regular videos and stories both benefit from engagement boosts. When you buy views and likes on tiktok, you’re ensuring all your content types receive the engagement signals necessary for algorithmic promotion.
Zexaro Forge Next – Layout clean, pages responsive and finding product details was simple.
Туристический портал https://atrium.if.ua о путешествиях: направления, отели, экскурсии и маршруты. Гайды по городам и странам, советы туристам, визы, билеты и сезонность. Планируйте поездки удобно и вдохновляйтесь идеями круглый год.
Cavaro Zone – Layout clean, content accurate, and browsing through pages was seamless.
выпрямитель дайсон амрстат купить самара [url=https://vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru/]vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
мелбет линия [url=https://gbufavorit.ru/]мелбет линия[/url] .
стоимость узаконивания перепланировки [url=https://skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru/]skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru[/url] .
google посещаемость сайта [url=https://seo-kejsy7.ru/]google посещаемость сайта[/url] .
web shop – Organized pages, clear descriptions, and matching product images.
Zarix Lane Shop – Layout intuitive, product info easy to read and checkout process straightforward.
обучение стриминг [url=https://shkola-onlajn13.ru/]shkola-onlajn13.ru[/url] .
go to site – Simple interface, quick load times, all information feels well structured
GlobalNetworkingGuide – Very useful, helps make sense of international business interactions quickly.
focusdrivesmovement corner – Well-organized pages, crisp design, and navigation is effortless
RixvaLinker – Pages structured well, interface intuitive, and shopping process feels effortless.
QuickHold – Responsive site, pages open instantly, product details are accurate.
BusinessConnectPro – Structured guidance, forming corporate partnerships is simple and reliable.
QuickXanero – Fast pages, intuitive layout, and all sections easy to explore.
Mivaro Access – Pages opened quickly, design simple and product details easy to find.
visit qavon – Smooth experience, pages look modern and content is straightforward
Maverounity online site – Everything feels professional and carefully developed.
Check out Brixel Trustee – Navigation is seamless, and the site presents information cleanly.
zaviroplex hub – Link opened smoothly, destination matched expectations perfectly.
Zavirobase Point – Fast-loading pages, clean layout and navigating the site is simple.
Kryvox Bonding official page – Clean design, intuitive navigation, and information looks reliable at first glance.
школа онлайн для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn11.ru/]shkola-onlajn11.ru[/url] .
онлайн обучение для школьников [url=https://shkola-onlajn14.ru/]онлайн обучение для школьников[/url] .
Morixo Trustee website – Well-laid-out pages, readable information, and navigation feels natural.
школа для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn12.ru/]shkola-onlajn12.ru[/url] .
Nolaro Trustee portal – Intuitive navigation, concise explanations, and content is easy to follow.
Qelaro Bonding hub – Fast-loading pages, clean sections, and information is accessible quickly.
школа для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn15.ru/]школа для детей[/url] .
Kryxo World Shop – Interface clean, pages responsive and product descriptions easy to follow.
melbet букмекерская [url=http://studio-pulse.ru/]melbet букмекерская[/url] .
go to nixra – Pages open fast and the overall design is simple yet effective
focusbuildsenergy spot – Minimal layout, logical flow, and the overall experience is smooth
согласование перепланировки стоимость [url=https://skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-6.ru/]согласование перепланировки стоимость[/url] .
EasyBond – Fast-loading pages, intuitive layout, and browsing feels seamless.
melbet букмекерская контора [url=www.gbufavorit.ru]melbet букмекерская контора[/url] .
LongTermGrowthGuide – Informative and actionable, spotting long-term opportunities is easy.
Zylra Base – Layout clean, pages responsive and overall shopping smooth and intuitive.
Zavix Central – Minimalist layout, content clear, and ordering process worked perfectly.
Cavaro Bonding web portal – Easy navigation and clear content make it feel dependable.
современные seo кейсы [url=https://seo-kejsy7.ru/]seo-kejsy7.ru[/url] .
online portal – Smooth click-through, site loaded correctly and easily readable.
Ravion Bonded online hub – The platform is accessible, with documentation that’s easy to read and updates that are reliable.
ломоносов скул [url=https://shkola-onlajn13.ru/]shkola-onlajn13.ru[/url] .
Nixaro Mind – Layout looks clean, pages load quickly and checkout process easy to complete.
Explore Kryvox Capital – Organized pages, straightforward information, and the interface seems reliable.
UlvionFlow – Pages load fast, layout clean, and content easy to access.
shopping platform – Clean interface and simple design make browsing a breeze.
Explore Naviro Bonding – Clean design, effortless navigation, and content is easy to understand.
Nolaro Trustee main page – Well-organized pages, readable text, and users can find information quickly.
Qelaro Capital info – Well-organized sections, readable content, and navigation is straightforward.
Всё о строительстве https://buildportal.kyiv.ua и ремонте: от проектирования и фундамента до чистовой отделки. Статьи, гайды, калькуляторы и кейсы. Полезно для застройщиков, мастеров, дизайнеров и тех, кто строит для себя.
Zavro Web – Fast loading, browsing smooth and product info well organized.
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua с идеями и практикой: страны и города, пляжи и горы, активный отдых и экскурсии. Советы по перелётам, жилью и безопасности, лучшие сезоны и лайфхаки для путешествий.
quick link – Minimal layout, quick navigation, enjoyable to scroll through
Zexaro Market Hub – Clean pages, products easy to find and checkout completed easily.
ravixo corner – Fast-loading layout, clear text, and useful information throughout
ShopRavlo – Smooth navigation, clear visuals, and informative product pages.
signal guides growth link – Easy to navigate, concise content, and clear layout throughout
Explore Cavaro Trust Group – Fast navigation and organized details make the platform simple to use.
InnovateNowHub – Exciting and clear content, innovations are easy to grasp and understand.
BrixelFlow – Pages open fast, interface clean, and content presented clearly.
web platform – The idea behind the site is neat, content flows well, and structure feels reliable.
Vixaro Central – Browsing easy, layout clear and overall site experience user-friendly.
InnovateGrowthPro – Actionable content, growth strategies are simple to grasp and apply.
brand store – Shipping was easy to select, and delivery timing looked accurate.
Kryvox Trust web experience – Pages load instantly, navigation is seamless, and details are easy to read.
Check Pelixo Bond Group – Smooth interface, concise content, and information is easy to access.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua для водителей и автолюбителей: обзоры и тест-драйвы, сравнение моделей, характеристики, цены и новости автопрома. Советы по покупке, эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей. Всё об авто — удобно и понятно.
Онлайн авто портал https://necin.com.ua о новых и подержанных автомобилях: каталоги моделей, рейтинги, отзывы владельцев и экспертные обзоры. Новости рынка, технологии, электромобили и полезные сервисы для выбора авто.
Мужской портал https://realman.com.ua про жизнь и эффективность: здоровье, сила и выносливость, карьера, инвестиции, стиль и отношения. Экспертные материалы, обзоры и чек-листы. Читайте онлайн и применяйте на практике.
Korivo Express – Pages loaded quickly, navigation smooth and shopping process simple and efficient.
Qelaro Trustline business – Clear content, simple navigation, and overall experience feels trustworthy.
Naviro Capital online portal – Clear hierarchy, polished visuals, and browsing feels effortless.
RouteClick – Worked without delay, pages loaded properly and information seemed reliable.
Velixonode Web – Clean design, links open properly and navigation easy to follow.
xelvix.click – Clean layout, easy to read and navigate through pages
XelarionSpot – Pages open quickly, content readable, and navigation feels natural.
Cavaro Union web portal – Clean presentation, consistent brand, and purpose is clearly outlined.
signalactivatesgrowth today – Easy to browse, clear information, and nice overall flow of content
sonabet.pro
web page – Security info made navigating the site feel reassuring and safe.
Xelivo Link – Browsing intuitive, content clear and buying process smooth today.
bryxo source – Natural-looking content and navigation that doesn’t get in the way
Онлайн-портал https://deluxtour.com.ua для путешественников: куда поехать, что посмотреть, где остановиться и как сэкономить. Маршруты, подборки, отзывы, карты и полезные сервисы. Актуальная информация для самостоятельных поездок и отдыха.
Всё о туризме https://hotel-atlantika.com.ua и отдыхе в одном месте: направления, визы, транспорт, отели и развлечения. Путеводители, маршруты, обзоры и советы опытных путешественников. Удобно планировать поездки онлайн.
Портал для строителей https://rvps.kiev.ua и заказчиков: ремонт, строительство, сметы и проекты. Обзоры материалов, расчёты, чек-листы и советы специалистов, которые помогают планировать работы и экономить бюджет.
Naviro Trustee business site – The content is easy to follow and presented in a structured manner.
PortalQulix – Professional layout, fast site speed, and overall shopping process feels simple and clean.
item store – Smooth loading and the pages worked without errors.
SmartBuyHub – Easy and convenient, online shopping feels effortless.
Pelixo Capital homepage – Clean design, content is easy to follow, and navigation feels smooth.
Learn more at Mavero Capital – Pages are structured neatly, explanations are concise, and navigation is easy.
Qorivo Bonding Official – Well-laid-out pages, easy-to-read information, and navigation works without hassle.
Neviror Trust official site – Layout is clear, content inspires confidence, and pages are easy to browse.
EasyXevra – Pages respond quickly, design is simple on the eyes, and content is accessible.
Visit Kavion Bonding – The platform feels dependable, with a well-organized structure and clear communication.
Lately, I was looking for Doxycycline quickly and found a great source. They let you get treatment fast securely. If you have sinusitis, try here. Discreet packaging to USA. Visit here: http://antibioticsexpress.com/#. Highly recommended.
directionunlocksgrowth home – Layout is clear, browsing feels easy, and content is accessible
букмекер мелбет [url=http://rusfusion.ru/]букмекер мелбет[/url] .
Pelixo Network – Pages open quickly, layout intuitive and browsing smooth and simple.
Портал для туристов https://inhotel.com.ua и путешественников: гайды по странам, маршруты, достопримечательности и события. Практичные советы, карты, подборки и идеи для отпуска, выходных и активных путешествий.
Ремонт помещений https://sinega.com.ua зданий и квартир: косметический и капитальный ремонт под ключ. Выравнивание стен, отделка, замена коммуникаций, дизайн-решения и контроль качества. Работаем по смете, в срок и с гарантией.
Строительный портал https://techproduct.com.ua для практики и идей: технологии, материалы, инструменты, сметы и проекты. Разбираем ошибки, делимся решениями и помогаем выбрать оптимальные варианты для строительства и ремонта.
information hub – Minimal styling, content is clear, and navigation feels effortless.
marketplace – Items are easy to navigate, and filters helped me narrow options efficiently.
check yavlo – Well-structured site, intuitive navigation, very user-friendly
Pelixo Trust Group website – Intuitive design, readable pages, and overall user experience is strong.
Mivon business site – Transparency and clarity help the project stand out.
QoriNavigator – Simple, professional design, responsive pages, and overall browsing easy and user-friendly.
plixo web hub – Clear interface, fast pages and placing orders was hassle-free.
Visit Qorivo Holdings – Well-organized content, intuitive navigation, and overall browsing is smooth.
TorivoUnion Info – Interesting model, appears structured for stability over time.
Explore Kavion Trustee – Clean interface, trust indicators are clear, and the platform feels professional.
Visit Ulviro Bond Group – Discovered today, seems legitimate and details are clear and concise.
Neviro Union web experience – Professional sections, concise content, and navigation is straightforward.
SecureShopHub – Practical and user-friendly, online shopping is fast and safe.
Neviro Link – Pages responsive, layout clean and shopping process works without issues.
cavix.click – Pleasant time browsing here, the layout feels tidy and the information is easy to take in
FuturesExplorerPro – Structured guidance, exploring upcoming trends is straightforward and intuitive.
access progressmovesintelligently – Well-laid-out sections with intuitive flow and quick performance
Ландшафтный дизайн https://kinoranok.org.ua ремонт и строительство под ключ: проектирование участков, благоустройство, озеленение, дорожки, освещение и малые архитектурные формы. Комплексные роботы для частных и коммерческих объектов с гарантией качества.
Новинки технологий https://axioma-techno.com.ua искусственный интеллект, гаджеты, смартфоны, IT-решения и цифровые сервисы. Обзоры, сравнения, тренды и объяснения простым языком. Узнавайте первыми о технологиях, которые меняют бизнес и повседневную жизнь.
Авто портал https://autoblog.kyiv.ua о машинах и технологиях: обзоры, характеристики, цены, тюнинг и обслуживание. Помогаем выбрать автомобиль под бюджет и задачи, следить за новинками и принимать взвешенные решения.
web platform – Smooth loading, clear fonts, and site feels well-designed.
sales site – Smooth ordering process, no popups or extra steps in the way.
main brixo – Quick page loads, interface simple and ordering process seamless.
Qelix info site – Clear labeling and structured pages make the experience straightforward.
melbet букмекерская контора официальный сайт [url=rusfusion.ru]melbet букмекерская контора официальный сайт[/url] .
Qorivo Trustline Hub – Organized content, professional look, and pages are easy to explore.
TrivoxBonding Project – Found this while comparing platforms, details look clean and informative.
Xeviro Express – Interface neat, navigation smooth and product info presented clearly.
ToriVoLinker – Navigation simple, content organized, and checkout process fast and reliable.
Just now, I was looking for Ciprofloxacin urgently and came across a great source. You can get treatment fast securely. In case of strep throat, this is the best place. Discreet packaging guaranteed. Visit here: view details. Cheers.
Nixaro Holdings info site – Clean visuals, intuitive navigation, and the browsing experience feels reliable.
actiondrivesdirection home – Layout feels clean, information is clear and easy to follow
SmartLearningBase – Lessons are concise and clear, making knowledge easy to absorb.
Уникальный дилер https://akkauntistore.com рад видеть арбитражников в нашем каталоге цифровых товаров для FB. Если вам нужно купить Facebook-аккаунты, чаще всего важен не «просто доступе», а в проходимости чеков: уверенный спенд, зеленые плашки в Ads Manager и прогретые FanPage. Мы подготовили короткую карту выбора, чтобы вы без лишних вопросов понимали какой лимит выбрать до оплаты.Коротко: с чего начать: откройте категории Фарм (King), а для серьезных объемов — переходите напрямую в разделы под залив: ПЗРД Кинги. Ключевая идея: покупка — это только вход. Дальше решает подход к запуску: какой прокси используется, как шерите пиксели без триггеров, как проходите чеки и как дублируете кампании. Гордость данной площадки — заключается в наличие эксклюзивной базы знаний по FB, где собраны практичные инструкции по проходу ЗРД. Команда сориентируем, как аккуратно привязать карту, чтобы вы спокойно отливали бюджет а также дольше жили в аукционе . Вступайте в сообщество, читайте обучающие материалы по FB, стройте систему и масштабируйтесь на базе наших расходников без задержек. Важно: используйте активы законно и всегда в соответствии с правилами Facebook.
Автомобильный портал https://livecage.com.ua тест-драйвы, сравнения, комплектации, безопасность и экономичность. Актуальные новости, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию, рекомендации для начинающих и опытных водителей.
this shop – It looks like a legitimate site with information laid out clearly.
info page – Not overwhelming, content is clear, and site navigation is easy.
kavion online store – Professional feel, policies visible and ordering process confident.
Morixo Online – Fast loading, design minimal and browsing steps intuitive.
zalvo destination – Clean layout, content is easy to find, and pages respond promptly
Check Qulavo Bonding – Simple interface, readable details, and navigation is smooth overall.
Xaliro Drive digital site – The concept is fresh, and everything operates as expected without glitches.
TrivoxCapital Project – Straightforward explanations, the site feels transparent and user-friendly.
Visit Nixaro Partners – Well-laid-out pages, navigation is simple, and users can find info quickly.
Ulxra Center – Smooth navigation, product listings clear, and checkout process simple.
Всё про автомобили https://sedan.kyiv.ua в одном портале: каталог авто, обзоры и рейтинги, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Покупка, эксплуатация, сервис и тренды — полезная информация для каждого водителя.
explore signal creates flow – Layout is logical and the user experience feels polished today
betting online sports [url=https://rusfusion.ru]betting online sports[/url] .
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
BetterChoicesPro – Practical insights, making it simpler to evaluate options effectively.
ulvion market – Pages loaded quickly and browsing felt smooth throughout.
digital link – Clicked through easily, target page clear and fully functional.
Zaviro Hub Shop – Smooth interface, responsive pages and checkout steps effortless.
EasyBond – Interface simple, pages open instantly, and product details easy to browse.
go to platform – Quick access and an uncluttered feel throughout
Check Plavex Capital – Smooth interface, concise sections, and finding details is effortless.
Explore Kavion Trust Group – The platform feels professional, content is easy to understand, and moving around the site is smooth.
Qulavo Capital Network – Clear headings, organized content, and pages are simple to browse.
Explore Ulvix online – Everything is concise and well-arranged, making the site user-friendly.
TrivoxTrustline Platform – The level of clarity stands out, it helps clear up many typical questions.
Nixaro Trustline portal – Well-laid-out pages, concise information, and navigation works efficiently.
ClickEaseKori – Pages load fast, site feels organized, and checkout process smooth.
Trivox Direct – Layout organized, navigation clear and overall shopping seamless.
focusanchorsmovement access – Crisp interface, intuitive flow, and content is straightforward
zavik site – Information is presented clearly with a tidy, user-friendly interface
shopping destination – The descriptions sounded natural and not forced.
HoldingHub – Smooth page transitions, well-organized content, and navigation feels natural.
xeviro portal shop – Pleasant experience, consistent branding and details easy to find.
Plavex Holdings main site – Professional design, intuitive navigation, and information is easy to digest.
Explore the official site – Everything reads smoothly and appears carefully put together.
SecureShopOnline – User-friendly platform, buying products feels safe and easy.
официальный сайт букмекерской конторы melbet [url=www.rusfusion.ru/]официальный сайт букмекерской конторы melbet[/url] .
official pelvo – Well-structured pages, clean interface, and content is approachable
Learn About Qulavo Capital – Smooth layout, structured information, and navigation is intuitive.
Транслируйте контент для взрослых безопасно, выбирая проверенные веб-сайты для взрослых.
Используйте безопасные платформы для
конфиденциального развлечения.
Also visit my web blog; DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 11 CRACKED
UlvaroBondGroup Online – Saw this earlier, the site feels clean and the message is easy to understand.
Brixel Bond Group web experience – Well-executed visuals give the site a credible tone.
UlviroTrust Access – Neat layout, messages about trust feel approachable and steady.
Korivo Capital online platform – Well-structured content, clear layout, and browsing feels intuitive.
online access – Lightweight site, intuitive navigation, very easy to find information
Nolaro Capital main page – Clean layout, clear branding, and the content is easy to digest.
QurixFlow – Fast response times, content made sense, shopping was simple.
http://kupprawojazdyb.com
https://comprarcarnetdeconducira.com
https://comprarcarnetdeconducira.com
https://rijbewijskopenc.com
marketplace – Bookmarked the site in case I return to order.
signalcreatesmomentum link – Easy to browse with organized sections and minimal distractions
ClickEaseNixaro – Navigation simple, content readable, and overall site feels well-organized.
click portal – Layout simple and uncluttered, readability is excellent.
Plavex Trust Group platform – Organized content, clear headings, and navigation is intuitive.
PartnershipNavigator – Clear and trustworthy, frameworks help businesses plan partnerships effectively.
Quvexa Capital Info Hub – Smooth layout, well-structured pages, and browsing feels effortless.
Learn more at this page – The site feels well organized, supporting focused and extended exploration.
Korivo Holdings digital site – Content hierarchy is clear, explanations are simple, and confidence is established quickly.
UlvaroBonding Website – Everything seems up to date, pages are quick and content is readable.
PortalCore – Pages loaded promptly, content was clear, and layout is organized.
Brixel Capital web presence – Confident tone and solid branding are evident throughout.
morix platform – Easy-to-navigate site with readable content and logical structure
top resource – Quick response times, clean layout, easy to explore content
Портал о строительстве https://repair-house.kiev.ua и ремонте без лишней теории: практические советы, обзоры материалов, расчёты, инструменты и этапы работ. Помогаем планировать проекты, контролировать качество и экономить бюджет.
Строительный портал https://garant-jitlo.com.ua современные технологии, нормы и стандарты, выбор материалов, инженерия и безопасность. Экспертные рекомендации, инструкции и реальные примеры работ — понятно и по делу.
Компания BritishSchool https://britishschool.kiev.ua профессиональные тренинги, семинары и курсы для детей и взрослых. Обучение с опытными преподавателями, современные методики, практические навыки и уверенный результат. Онлайн и офлайн форматы.
Nolaro Holdings business portal – Organized layout, readable text, and browsing is straightforward.
shop link – Smooth browsing and checkout made it worth recommending.
travik web – Logical structure, readable text, and smooth scrolling between sections
Just now, I needed antibiotics for a tooth infection and came across this reliable site. They sell antibiotics without prescription overnight. If you need meds, this is the best place: order amoxicillin 500mg. Get well soon.
redirect link – Smooth load, graphics minimal and text easy to read.
Plivox Bonding web portal – Clean design, readable sections, and navigation works flawlessly.
Ulviro Store – Layout professional, browsing smooth, and checkout process straightforward.
Korivo Trustline online platform – Solid branding, clear details, and a seamless user experience.
Грамотная приемка квартиры в новостройке снижает вероятность дополнительных расходов. Застройщики не всегда устраняют дефекты добровольно. Независимый эксперт помогает зафиксировать все нарушения. Составляется официальный перечень замечаний. Документ можно использовать при обращении к застройщику. Это упрощает процесс получения качественного жилья https://zlat-go.ru/news/?ELEMENT_ID=26157
Компания разрабатывает промышленные электронные модули. Создаются схемы, платы и программное обеспечение. Проводится тестирование и отладка. При необходимости выполняется серийное производство. Заказчик получает готовое решение с документацией – http://masyasha.ru/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=88651. Каждое решение проходит тесты на идеальное качество?
UlvaroCapital Overview – Nice first impression, ideas are communicated without added complexity.
Проблемы с алкоголем? круглосуточный стационар вывод из запоя помощь врача, детоксикация, стабилизация состояния и наблюдение. Конфиденциально, без постановки на учет, с учетом возраста и сопутствующих заболеваний.
Ищешь казино? казино рейтинг лучших лицензия, бонусы, выплаты, игры и отзывы игроков. Сравниваем условия, безопасность и удобство, чтобы помочь выбрать надежное казино для игры онлайн.
Подборка лучших МФО на https://mikrozaym365.ru оформите микрозайм онлайн на карту за 5 минут. Первый займ под 0% для новых клиентов. Без отказов и проверок. Мгновенное одобрение, перевод на любую карту. Получите деньги сегодня!
VelixoHoldings Info – Effortless navigation, quick pages and clear, trustworthy details.
Nice Simple Layout – Discovered this by chance and liked how clear everything looks
Недавно воспользовался изготовление прототипа, и всё прошло отлично. Работа была завершена даже раньше срока, при этом никаких дефектов или брака не было. Специалисты компании помогли какой пластик лучше использовать. Цена оказалась доступной, а доброжелательное отношение доказали, что здесь ценят клиентов. Советую всем друзьям, кто ценит точность и скорость – https://balashiha.spravka.city/company/asteri-3d-0. Мы создаём детали с максимальной точностью и детализацией.
TopDiscountFinder – Smooth and reliable, shopping for bargains online is convenient.
Main bonding website – Didn’t spend long here, but the presentation looks thoughtfully arranged.
link page – Quick response, destination clear, navigation intuitive.
Plivox Capital site – Smooth interface, organized content, and browsing feels effortless.
quorly homepage – Quick access and well-presented information that’s relevant for visitors
NolaroGo – User-friendly design, content structured well, and shopping steps simple to follow.
Scratch cards are such a fun, quick thrill! It’s cool to see platforms like jiliaaa ph slot offering so many options – slots, live games, even lottery! Easy registration with GCash is a big plus for Filipino players.
Страдаете от алкоголизма? круглосуточный вывод из запоя анонимная медицинская помощь с выездом врача. Осмотр, капельницы, контроль состояния и поддержка пациента в комфортных условиях. Работаем круглосуточно, строго по медицинским показаниям.
Мучает алкоголизм? вывод из запоя вызов на дом помощь при алкогольной интоксикации и длительном употреблении. Капельницы, поддержка организма, контроль давления и пульса. Конфиденциально и профессионально.
Уникальный проект купить аккаунты для масштабирования рад приветствовать вас в своем разделе рекламных активов Meta. Если вам нужно купить Facebook-аккаунты, чаще всего важен не «просто доступе», а в проходимости чеков: стабильный запуск, зеленые плашки в Ads Manager и прогретые FanPage. Мы подготовили понятную навигацию, чтобы вы без лишних вопросов понимали что подойдет под ваши офферы перед заказом.Что внутри: типы аккаунтов (Мамки, Автореги, Логи). Ключевая идея: аккаунт — это инструмент. Дальше решает подход к запуску: какой прокси используется, как вы передаете лички без триггеров, как проходите чеки и как дублируете кампании. Гордость данной площадки — заключается в наличие огромной вики-энциклопедии FB, в которой написаны актуальные инструкции по проходу ЗРД. Тут можно найти страницы Meta под любые цели: от дешевых авторегов до мощными Кингами с пройденными запретами. Переходите в сообщество, читайте обучающие кейсы по заливу, наводите порядок и повышайте ROI с помощью нашего сервиса без задержек. Важно: действуйте в рамках закона и всегда с учетом правил Meta.
explore xelio – Responsive pages, concise text, and enjoyable overall experience
UlvionBondGroup Online – Credible feel overall, brand identity is uniform and style is professional.
landing hub – Neat visuals, fast performance, everything is clear and simple
globalbusinessunity – Informative insights, global business unity strategies are clear and useful here.
VelixoTrustGroup Access – Organized pages, content is easy to grasp and free of extra jargon.
TopCartOnline – Premium and reliable, online purchasing is smooth and hassle-free.
Здравствуйте дорогие друзья! На первом этапе нужно разобраться — протечки в паркинге. По моему мнению крыша гаража — требует спецподхода. Ценишь качество — могу рекомендовать: [url=https://montazh-membrannoj-krovli-spb.ru]монтаж ПВХ кровли[/url]. Какие результаты можно достичь: сваривают швы — машины стоят в сухости. Вот потому что ПВХ мембрана — устойчива к химии. Основные этапы: укладка с проваркой швов. Что в итоге: удаётся достигать классных результатов.
Привет всем! Разберём самые актуальные про вибрации мотора. Суть здесь в чем: капот без обработки — резонирует от двигателя. Ценишь время — обращайся: [url=https://shumoizolyaciya-avtomobilej.ru]https://shumoizolyaciya-avtomobilej.ru[/url]. Как правило когда капот зашумлен в салоне тише. Например постучи по металлу — резонирует? Соответственно время делать шумку. Можно поставить термостойкую вибру, поверх — защитный слой. Резюмируем: это отличные параметры — тишина под капотом.
Learn about Plivox Holdings – Well-laid-out content, clear sections, and browsing is smooth and simple.
Discover capital info – Professional feel at first glance, bookmarking for later analysis.
заказать курсовую работу качественно [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-42.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-42.ru[/url] .
заказать курсовую работу спб [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru[/url] .
курсовая заказ купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-45.ru/]курсовая заказ купить[/url] .
курсовая заказ купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-46.ru/]курсовая заказ купить[/url] .
заказать студенческую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru[/url] .
покупка курсовой [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-47.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-47.ru[/url] .
visit xelariounion – This platform caught my attention and feels like something to explore further soon.
курсовая заказать [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-48.ru/]курсовая заказать[/url] .
покупка курсовых работ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru[/url] .
написание курсовой на заказ цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru[/url] .
продвинуть сайт в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru[/url] .
продвижения сайта в google [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru[/url] .
seo network [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru[/url] .
MorvaHome – Layout clean, browsing easy, and product details clear and reliable.
Лучшие книги от knizhka-malishka.ru – откройте для своего малыша мир увлекательных сказок и ярких историй! Здесь собраны лучшие издания для детей разного возраста, которые подарят радость чтения всей семье. Читайте книги онлайн удобно и выгодно!
Letar du efter ett casino? https://casino-utan-omsattningskrav.se Rattvisa bonusar, licens, snabba utbetalningar och transparenta villkor. Vi jamfor palitlighet, spel och betalningsmetoder for att hjalpa dig valja en saker plattform.
Ulvion Capital – Navigation is easy, content is well-structured and simple to follow.
official alliance link – Easy-to-use navigation combined with professional design gives a great first impression.
browse quvix – Clear pages, quick response, very user-friendly browsing experience
zorivo holdings info – Professional layout and clear sections make exploring the platform easy.
mivox site – Simple design with readable text and a comfortable browsing flow
VexaroCapital Portal – Clean and professional, information is clear and instills trust.
Zin in een casino? casino ideal Populaire gokkasten, roulette, blackjack en live dealers. Bonussen, toernooien, promoties en snelle uitbetalingen. Speel vanaf je telefoon of pc – altijd en overal.
Мультимедийный интегратор айтек интеграция мультимедийных систем под ключ для офисов и объектов. Проектирование, поставка, монтаж и настройка аудио-видео, видеостен, LED, переговорных и конференц-залов. Гарантия и сервис.
MarketTrendsHub – Practical and structured content, market ideas are presented clearly.
check qerly – Clear design, organized pages, and browsing experience is straightforward
official bonding link – Straightforward presentation with easy-to-read details.
ifuntv海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Start with trustline site – Minimal design choices with fast pages and timely information.
zorivo union overview – Organized layout and clear content make finding information straightforward.
Нужны блины и диски? https://bliny-na-shtangi.ru широкий выбор весов, надежные материалы, точная калибровка. Отличное решение для силовых тренировок, кроссфита и профессиональных спортзалов.
zaviro alliance resource – Easy to navigate with a professional presentation for initial visits.
помощь студентам курсовые [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-45.ru/]помощь студентам курсовые[/url] .
стоимость написания курсовой работы на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru[/url] .
заказать курсовую работу спб [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-42.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-42.ru[/url] .
UlvionHoldings Portal – Clean visuals, modern feel and user-friendly navigation.
Xanero Base – Layout tidy, content easy to read, and shopping process straightforward.
курсовой проект цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-47.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-47.ru[/url] .
покупка курсовой [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-46.ru/]покупка курсовой[/url] .
visit cavaro pact – Simple layout and clear text make browsing comfortable and useful.
компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru[/url] .
выполнение курсовых [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru/]выполнение курсовых[/url] .
learnbusinessskillsonline – Excellent learning resources, business skills are explained clearly and practically.
korivotrustco.bond – Simple layout, smooth browsing, and content comes across as trustworthy.
mivarotrust.bond – Clean design, intuitive menus, and helpful information for new visitors.
internet seo [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru[/url] .
seo продвижение и раскрутка сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru/]seo продвижение и раскрутка сайта[/url] .
VexaroPartners Network – Easy-to-use site, service information feels practical and credible.
помощь студентам курсовые [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru[/url] .
написание учебных работ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru[/url] .
написание курсовых работ на заказ цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-48.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-48.ru[/url] .
мелбет бк [url=rusfusion.ru]мелбет бк[/url] .
News – Headlines and updates are easy to scan and read.
Community – Interactive content is structured cleanly, encouraging easy engagement.
official capital link – Informative pages load quickly, making browsing fast and pleasant.
Blog – Articles are neatly arranged, allowing visitors to read and find information quickly.
Portfolio – Neat layout, content is concise, and exploring projects is straightforward.
ProfessionalPartnerPro – Informative and helpful, advice strengthens trust in collaborations.
bonding platform details – Browsing is fast, fluid, and consistent across the site.
xelivo capital hub – A focused layout with professional-looking content throughout.
check velon – Easy navigation, tidy layout, and information that’s straightforward
grow and learn hub – Educational content is well-structured, making learning smooth and fast.
Application web 1xbet telecharger 1xbet pour android
Bond information portal – Smooth interface, fast navigation, and content is clear and user-friendly.
resource page – Lightweight and organized, content feels well-structured
Platform details – The site flows well, looks refined, and presents data convincingly.
Discover bond group info – Stumbled across it researching, content doesn’t feel pushy.
Xeviro Access – Layout intuitive, pages responsive, and site functions smoothly.
visit zurix – Pleasant browsing, content is clear and organized without clutter
Kryvox platform – Polished interface, pages load quickly, and information is consistent.
Testimonials – Feedback is showcased neatly, adding trust and credibility.
visit zylavo holdings – Clean design and organized content make researching details straightforward.
VexaroUnity Hub – Concept is solid, site communicates its mission clearly and responsibly.
заказать курсовую [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru/]заказать курсовую[/url] .
где можно купить курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-45.ru/]где можно купить курсовую работу[/url] .
курсовая работа купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-47.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-47.ru[/url] .
Portfolio – Visuals are displayed cleanly for quick reference and smooth browsing.
заказать курсовую работу спб [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-46.ru/]заказать курсовую работу спб[/url] .
написание курсовых работ на заказ цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru[/url] .
профессиональное продвижение сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru/]профессиональное продвижение сайтов[/url] .
Features – Key details are highlighted and arranged logically for easy understanding.
Blog – Neat presentation, responsive pages, and information is easy to follow.
capital project homepage – Well-structured layout ensures that information is accessible quickly.
продвинуть сайт в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru[/url] .
продвижение сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru[/url] .
сайт для заказа курсовых работ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru[/url] .
Professional portal – Clean interface, quick-loading pages, and content is clear and helpful.
official trust group link – Simple navigation keeps the experience hassle-free.
DealNavigatorPro – Practical and user-friendly, shopping for deals feels efficient.
где можно заказать курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-48.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-48.ru[/url] .
помощь в написании курсовой работы онлайн [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru[/url] .
explore this trust group – Organized interface and clear layout make exploring content straightforward.
go to site – Pages are readable, navigation is simple, content is understandable
unity partners portal – Information is presented cleanly, making partnership details easy to understand.
мелбет ру [url=www.rusfusion.ru/]мелбет ру[/url] .
Online bond hub – Clean design, quick response times, and details are clearly outlined.
Downloads – Files and resources are presented efficiently and are easy to access.
Official Kryvox platform – Smooth interface, easy-to-follow layout, and information is easy to find.
VexaroUnity Details – Concept feels unique, information is clear and responsibly presented.
vexla portal – Positive browsing experience with helpful information and rapid page load
Portfolio – Visual content is arranged cleanly for quick browsing and reference.
Need an AI generator? Undress AI The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
Start with holdings site – The intuitive setup helps new users understand things quickly.
zaviro group link – Professional branding and useful information combine for a trustworthy experience.
Resources – Links and files are presented clearly, ensuring quick access to important information.
Corporate hub – Simple menus, responsive pages, and information is easy to follow.
Tutorials – Well-laid-out guides, intuitive navigation, and content is concise and clear.
стоимость написания курсовой работы на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-44.ru[/url] .
bond project homepage – Well-laid-out pages and clear content make navigation effortless.
заказать курсовую работу качественно [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-42.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-42.ru[/url] .
студенческие работы на заказ [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-45.ru/]студенческие работы на заказ[/url] .
написание курсовой работы на заказ цена [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-50.ru[/url] .
check rixon – User-friendly pages, clear information, and overall neat experience
official bonding link – The quick response time adds to a professional look.
курсовые купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-46.ru/]курсовые купить[/url] .
quick link – Pages load quickly, layout is clear, impression is favorable
seo partner [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov11.ru[/url] .
заказать курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-49.ru/]заказать курсовую работу[/url] .
ReliableShopHub – Safe and user-friendly, purchasing items online is simple.
Resources – Files and links are arranged cleanly, making navigation smooth.
Financial platform – A solid layout that presents content in an orderly way.
learn with clarity – Content feels purposeful and easy to connect with.
раскрутка сайта франция цена [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov13.ru[/url] .
Digital hub – Simple interface, clear menus, and finding content is fast and convenient.
learn about zaviro trustline – Easy-to-follow structure enhances the overall browsing experience.
kryvoxline.bond – Clean design, navigation flows easily, and information is quick to locate.
The best independent casinos https://montparnasse.co.uk with fair terms, fast payouts, and transparent licensing. A review of trusted platforms without major holdings, offering unique bonuses, popular slots, and convenient deposit methods.
Tutorials – Step-by-step guides are organized clearly for simple learning.
курсовая работа купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-48.ru/]курсовая работа купить[/url] .
explore brixel core – Pages are easy to move through, load quickly, and the content appears solid.
Updates – Latest news is displayed cleanly, allowing users to stay informed quickly.
где можно заказать курсовую [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-43.ru/]где можно заказать курсовую[/url] .
FAQ – Clear menus, structured content, and answers are easy to locate quickly.
Сайт воспринимается как аккуратно собранный инструмент, а не как ярмарка визуальных трюков. Все элементы находятся на своих местах, не конфликтуя друг с другом. Во время работы с https://pinup-casino-kz.net/ появляется ощущение контролируемой среды, где каждая функция вписана в общий замысел.
официальный сайт букмекерской конторы melbet [url=https://rusfusion.ru/]официальный сайт букмекерской конторы melbet[/url] .
Browse the trust site – The site gives a legitimate feel, with consistent language throughout.
Kasyna online https://verde-kasyno-online.pl graj z bonusami w 2026 roku. Aktualne oferty, szybkie logowanie i latwa rejestracja, popularne sloty i gry stolowe. Przeglad warunkow, metod wplat i wyplat dla komfortowej gry online.
xeviro capital hub – The structure helps guide users through key information easily.
kavlo site – Modern styling paired with navigation that works without friction
trusted link – Minimalist design with reliable navigation, everything functions well
About Us – Clear sections and concise content make information easy to understand.
Financial platform – Intuitive pages, responsive layout, and information is well arranged for users.
brixel line platform – Simple navigation, professional layout, and informative content enhance usability.
zexaro bonding hub – Informative sections and quick-loading pages create a positive first impression.
kavioncore.bond – Nice experience, everything loads quickly and information is concise and understandable.
SafeDealsCenter – Organized and reliable, purchasing online is quick and stress-free.
clarity resource center – Well-structured platform makes learning simple and efficient.
About Us – Well-organized pages with clear menus give users confidence in the content.
visit velixo – Easy-to-navigate site, information is well-organized and readable
Learn more here – Organized pages, clear navigation, and content is helpful for research.
Blog – Well-structured pages with smooth browsing make reading information effortless.
Updates – Smooth interface, pages load quickly, and content is easy to navigate.
Naviro resources – Smooth pages, logical structure, and content feels trustworthy.
official brixel trustco page – The structure is user-friendly, providing an enjoyable and straightforward browsing experience.
holdings project homepage – Presents a dependable image with clear, consistent messaging.
top resource – Well-organized interface, quick page loads, information is straightforward
FAQ – Answers are concise, easy to scan, and organized logically for visitors.
Learn about capital here – Easy-to-follow sections make reading through content seamless.
Kavionline resources – Easy navigation paths and a clean presentation of information.
investment opportunity – Presentation suggests stability and long-term focus.
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的livescore官方即時比分都在這裡。
Resources – Pages are easy to navigate, and data is presented in a well-organized manner.
ifvod平台,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
investment info portal – Quick and reliable with a well-structured presentation.
maveroline.bond – Smooth navigation, pages load quickly, and details are presented clearly.
bavix spot – Easy-to-read pages with a clean and logical flow
LongTermBusinessGuide – Organized and insightful, forming corporate connections is straightforward.
Portfolio – Clean interface, responsive pages, and content is presented in a clear way.
pathway to success hub – Organized layout supports easy decision-making for next steps.
review cavaroline – Clean layout and clear text ensure a smooth and informative browsing experience.
Financial platform – Smooth interface, simple layout, and details are easy to understand.
ifvod平台结合大数据AI分析,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
官方數據源24小時即時更新nba比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
trustline project homepage – Well-organized structure and intuitive navigation enhance usability.
多瑙高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
我們提供官方合作夥伴台灣最完整的棒球即時比分相關服務,包含最新官方賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
bond info hub – The interface is tidy, making it easy to find and read information.
yaverobonding.bond – Nice experience overall, pages are organized and fairly user friendly.
Events – Event information is easy to locate and comprehend quickly.
talix access – Clean pages, concise text, and smooth, user-friendly experience throughout
start browsing – Easy-to-follow navigation, pages feel lightweight and structured
Learn more here – Refined layout, educational content, and an easy-to-use interface.
trusted finance platform – Clean design and logically arranged sections enhance confidence.
PayID casinos https://matierenoirestudio.com play online quickly and securely. Instant deposits and withdrawals, convenient payments, licensed sites, popular slots, and live games. A selection of reliable casinos with up-to-date terms.
Main trust website – Navigation is easy, and it serves as a practical resource for learning essentials.
Visit Naviro Trust – Smooth layout, intuitive menus, and information is presented in a straightforward way.
Testimonials – Feedback is presented neatly, making information trustworthy and clear.
professional finance hub – Pages respond quickly, and the layout feels clean and professional.
official site – The layout is neat, and finding details is quick and intuitive.
News – Clean layout, fast pages, and information is easy to read and understand.
Maverotrust resources – Professional look, well-maintained pages, and positive browsing experience.
EnterpriseFrameworkPro – Well-structured guidance, enterprise frameworks are easy to understand and implement.
捕风追影在线官方認證平台,專為海外華人設計,24小時不間斷提供高清視頻和直播服務。
zorivocapital.bond – Looks solid, user friendly, provides useful details without any confusion online.
Ranking wyplacalnych https://wyplacalne-kasyna-internetowe.pl kasyn online z szybkimi wyplatami. Analiza wiarygodnosci finansowej, licencji, limitow i czasu wyplat. Lista kasyn, ktorym gracze ufaja w latach 2025–2026.
海外华人必备的yifan官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
真实的人类第一季高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Blog – Articles are presented neatly, allowing smooth reading and learning.
capital project homepage – Offers insight and might be useful on a second visit.
quick link – Minimal design, easy navigation, information is concise
超人和露易斯第四季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Company homepage – Neat layout, organized pages, and information is quick to locate.
超人和露易斯第四季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Bond platform – Well-arranged sections, reliable navigation, and useful information.
禁忌第一季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
奇思妙探第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
online finance hub – Clean interface, easy-to-read content, and responsive pages.
News – Latest updates are presented clearly, with fast-loading pages and intuitive navigation.
爱一帆下载海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
official bond site – Navigation feels smooth, and the content is straightforward to follow.
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Updates – Simple layout, smooth navigation, and information is clear and structured.
loryx – Pages are well-organized, making the information easy and interesting to read
finance info site – Browsing through the details feels smooth and effortless.
Corporate portal – Simple layout, smooth navigation, and details are easy to find.
官方授权的一帆视频海外华人首选,第一时间提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
TrustNetworkInsights – Organized and clear, global networking is accessible and practical.
Gallery – Images load promptly and are arranged in an organized, appealing layout.
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的7m足球運用大數據AI分析引擎即時比分都在這裡。
海外华人必备的iyf平台,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
check this holdings platform – The content is simple and provides clarity without extra effort.
Korva Online – Discovered this randomly, the design is easy on the eyes
secure finance portal – The layout is neat, with fast and clear content.
Investment site – Feels dependable, easy to navigate, and information is quickly accessible.
Trusted store buy facebook bm offers the option to purchase accounts for targeting. When you plan to buy a Facebook account for advertising, most often the key isn’t “one login”, but trust and limits: confident spend, a passed reinstatement check (ZRD) in the account, and warmed-up fan pages. We’ve organized a clear navigation so you can understand without extra questions which limit to choose before ordering.What’s inside: cookie-based login flow. Key idea: an account is a tool. What matters next is your launch setup: how permissions are managed, how you share assets and roles safely, how you react to policy feedback, and how you scale ad sets. Feature of this platform — comes down to a exclusive education section, where we’ve collected working recommendations for account farming. Our team can help on how exactly to with fewer risks share access properly, so you don’t run into policy friction and extend account lifespan. When checking out with us, the customer gets not only a valid profile, but also end-to-end help from support, clear replacement terms, a guarantee for first login, and the most competitive prices in the niche. Important: use digital assets legally and always in line with Meta policies.
Downloads – Files are well-organized and pages are easy to explore.
<investment info page – Navigation feels natural, text is concise, and browsing is seamless.
online bond hub – Simple design ensures a smooth and intuitive browsing experience.
我們提供MLB即時比分、賽程安排,以及MLB球隊戰績和球員數據分析。
Tutorials – Smooth menus, simple layout, and content is concise and easy to read.
Official portal – Clear design, intuitive navigation, and content is easy to read.
侠之盗高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Learn more here – The site feels solid, with content that’s easy to scan and understand.
Telecharger 1xbet sur telephone 1xbet apk
Platform details – A promising concept with a website that keeps things straightforward.
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
Need an AI generator? Undress AI Website The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
Corporate site – Clean layout, quick page loads, and content is logically arranged.
我們提供台灣最完整的棒球比分相關服務,包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
reliable trust platform – Navigation performs well, creating a smooth browsing experience.
中職戰績粉絲必備的資訊平台,運用大數據AI分析引擎提供最即時的中職戰績新聞、球員數據分析,以及專業的比賽預測。
StrategyToolkitPro – Helpful and well-laid-out, planning strategies is straightforward.
Resources – Files and links are arranged neatly for efficient browsing.
Bond overview hub – Smooth interface, clear content grouping, and researching info is quick and easy.
explore now – Smooth interface, quick pages, content is concise and readable
About Us – Intuitive navigation, organized layout, and information is easy to access.
check bavlo – Minimal distractions, organized pages, and a comfortable browsing experience
investment info page – Quick-loading content, clean sections, and well-organized design.
investment guidance site – Simple structure allows users to quickly find relevant info.
News – Professional layout, intuitive browsing, and information is concise and helpful.
Primary project page – Smooth browsing, informative content, and pages load quickly.
海外华人必备的ify平台智能AI观看体验优化,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
官方數據源24小時即時更新nba比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
24小時即時更新nba戰績比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
Company homepage – Intuitive layout, responsive pages, and details are easy to digest.
Direct site access – A clean, organized design ensures content is easy to read and understand.
bond services site – Smooth performance with no clutter slowing things down.
GlobalRelationsPro – Very useful, helps make sense of international partnerships effectively.
resource page – Everything works seamlessly and the site feels polished
Direct trust link – The layout and wording work together to explain things simply.
bond info hub – Organized layout and readable content enhance trustworthiness.
financial resource page – Polished look and strong branding feel professional from the start.
Primary project page – Pages are clean, navigation is intuitive, and overall structure feels solid.
bond information portal – Navigation is smooth, and information is presented in a readable way.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini gampang menang dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Kunjungi: Bonaslot link alternatif raih kemanangan.
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: canlı casino siteleri Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği casino siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
中華職棒今日比賽結果台灣球迷的首選官方認證資訊平台,24小時不間斷提供官方中華職棒今日比賽結果新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
Bocoran slot gacor hari ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Situs ini gampang menang dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Kunjungi: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot slot dan menangkan.
где можно заказать курсовую работу [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru[/url] .
раскрутка сайта франция цена [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru[/url] .
我們提供台灣最完整的棒球即時比分相關服務,運用先進AI預測演算法包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
Trust project page – Pages are easy to navigate, and details are clear and accessible.
我們提供台灣最完整的美國職棒即時比分相關服務,包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
online business portal – Design stays focused, making service details easy to absorb.
中華職棒台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測和數據分析。
plavix.click – Smooth experience, pages load quickly and everything looks organized
zavirotrusthub.bond – Pleasant browsing experience, site feels reliable, and content is clear and concise.
investment guidance site – Professional visuals and structured content make it feel legitimate.
中華職棒直播台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,運用大數據AI分析引擎提供最即時的中華職棒直播新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
investment info – Fast-loading pages, clear structure, and easy-to-read sections.
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah mendapatkan Maxwin sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Situs resmi п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot login[/url] jangan sampai ketinggalan.
中華職棒即時比分台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒即時比分新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
Bocoran slot gacor hari ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini gampang menang dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Akses link: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]situs slot resmi[/url] dan menangkan.
xelariobase.bond – Navigating the website feels effortless, with a clean and professional structure.
中華職棒賽程台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒賽程新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
Selam, sağlam casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# cassiteleri.us.org bol şanslar.
范德沃克第二季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
我們的玩運彩官方授權專家團隊第一時間更新官方各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
п»їSalam Gacor, cari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot daftar salam jackpot.
курсовые купить [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru[/url] .
Check this platform – Information is presented clearly, and navigation feels natural from page to page.
Main project page – Clear interface, easy-to-follow content, and minimal clutter make browsing pleasant.
investment trust page – Solid, well-structured, and feels trustworthy.
go to site – Fast pages, minimal distractions, content is straightforward
продвижение сайтов в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru/]продвижение сайтов в москве[/url] .
financial services page – Fast-loading content and simple navigation improve usability.
Selamlar, sağlam casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye mutlaka göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: bonus veren siteler iyi kazançlar.
Здравствуйте дорогие друзья! Разберём самые актуальные — гул в салоне. Суть в том, что ищешь готовое решение — могу рекомендовать ребятам тут: [url=https://shumoizolyaciya-avtomobilej.ru]профессиональная шумоизоляция[/url]. Как правило основной источник вибрации днища — это дребезг панелей в нишах. Как это работает? Допустим, при повороте характер шума меняется — соответственно работает кузовщина. Основные этапы если сам берёшься: снятие обшивки, подготовка, монтаж вибропоглотителя с тщательным прижимом. Что в итоге: это работает — минус 50% шума.
bond info hub – Navigation feels natural, and details are easy to locate.
ClickUlvor – Interface clean, images clear, and finding products was simple.
海外华人必备的aiyifan平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
secure portal – Smooth navigation, professional feel, and content is readable throughout.
1win az hesabı necə açmaq [url=http://1win5762.help]1win az hesabı necə açmaq[/url]
我們的彩券行專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
Looking for a casino? 8mbets bd Slots, table games, and live casino all in one place. Quick login, convenient registration, modern providers, stable payouts, and comfortable player conditions.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Situs ini gampang menang dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Kunjungi: https://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot login raih kemanangan.
Playing at the casino? 8mbets casino Play online for real money. We offer a wide selection of slots, live dealers, fast payments, easy login, and exciting offers for new and returning players.
About Us – Well-organized sections and clear navigation ensure users can find content easily.
Do you love gambling? jwin7 casino Online is safe and convenient. We offer a wide selection of games, modern slots, a live casino, fast deposits and withdrawals, clear terms, and a stable website.
中華職棒戰績台灣球迷的首選官方認證資訊平台,24小時不間斷提供官方中華職棒戰績新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
我們提供台灣最完整的籃球比分相關服務,包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
超人和露易斯第三季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Explore project – Well-structured content, smooth navigation, and a clean design throughout.
我們的資深運彩分析專家團隊每日更新NBA、MLB、中華職棒等各大聯盟的專業賽事分析。
seo аудит веб сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve117.ru/]seo аудит веб сайта[/url] .
продвижение веб сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru[/url] .
продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve214.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve214.ru[/url] .
заказать продвижение сайта в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve215.ru/]заказать продвижение сайта в москве[/url] .
professional bond site – Explanations are concise, with an overall trustworthy impression.
продвижение сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve216.ru/]продвижение сайтов[/url] .
профессиональное продвижение сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru/]профессиональное продвижение сайтов[/url] .
поисковое продвижение москва профессиональное продвижение сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru[/url] .
раскрутка и продвижение сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve119.ru/]раскрутка и продвижение сайта[/url] .
оптимизация сайта франция [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru[/url] .
продвижение сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru/]продвижение сайта[/url] .
технического аудита сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve222.ru/]технического аудита сайта[/url] .
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, bura baxa bilərsiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə hesabınıza girin və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin Up online hamıya bol şans.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]güvenilir casino siteleri[/url] Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
torivotrustco.bond – The site feels well-structured, and pages load smoothly on my mobile.
我們提供台灣最完整的籃球比分相關服務,包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Saytda çoxlu slotlar və Aviator var. Pulu kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up giriş[/url] yoxlayın.
Check core details – Simple visuals paired with clear explanations make the site pleasant.
中華職棒今日比賽結果台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒今日比賽結果新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
поисковое продвижение сайта в интернете москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve221.ru/]поисковое продвижение сайта в интернете москва[/url] .
真实的人类第一季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Купить IQOS ILUMA https://spb-terea.store и стики TEREA в Санкт-Петербурге с гарантией оригинальности. В наличии все модели ILUMA, широкий выбор вкусов TEREA, быстрая доставка по СПб, удобная оплата и консультации специалистов.
Продажа IQOS ILUMA https://ekb-terea.org и стиков TEREA в СПб. Только оригинальные устройства и стики, широкий ассортимент, оперативная доставка, самовывоз и поддержка клиентов на всех этапах покупки.
Ищите откровенные видео, исследуя надежные платформы в Интернете.
Изучите безопасные сайты для приватного просмотра.
My web page :: BUY VIAGRA
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的7m足球官方即時比分都在這裡。
сколько стоит курсовая работа по юриспруденции [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru[/url] .
online bond site – Clean sections, fast loading, and browsing is straightforward and clear.
seo продвижение и раскрутка сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru/]seo продвижение и раскрутка сайта[/url] .
Pin Up Casino ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və Aviator var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt Pin Up giriş tövsiyə edirəm.
Updates – Latest news and announcements are presented clearly for quick reading.
Situs Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Situs resmi https://bonaslotind.us.com/# slot gacor hari ini gas sekarang bosku.
Check platform details – The site is easy to browse, with content structured in a logical way.
QuvexPortal – Interface clear, links functional, and all content seems credible.
Official Zexaro hub link – Easy to browse, clear details, and information is presented logically.
Hello pals!
I came across a 152 interesting website that I think you should browse.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://www.wownwell.com/stretching-and-why-you-need-to-add-it-to-your-workout-plan/]https://www.wownwell.com/stretching-and-why-you-need-to-add-it-to-your-workout-plan/[/url]
Additionally remember not to overlook, everyone, — one constantly can within this particular article discover solutions to your the absolute complicated queries. We tried to lay out the complete data using the very accessible way.
zylavoline site – Fast performance and concise content make it easy to absorb information.
IQOS ILUMA https://terea-iluma24.org и стики TEREA — покупка в Москве без риска. Гарантия подлинности, большой выбор, выгодные условия, доставка по городу и помощь в подборе устройства и стиков.
financial knowledge portal – Content flows logically, and the interface feels polished.
Selamlar, ödeme yapan casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# mobil ödeme bahis iyi kazançlar.
Badminton livescore from BWF World Tour, shuttlecock action tracked in real time
bond services page – Information is concise, and navigating between sections is simple.
financial info page – Straightforward presentation keeps things clear and simple.
Нові новини Києва https://xxl.kyiv.ua в одному місці. Головні події дня, заяви влади, міська інфраструктура, транспорт, безпека та соціальні питання. Швидко, зрозуміло та без зайвої води.
Грузчики в Киеве https://www.gruzchiki-kiev.net для переездов, погрузки и разгрузки. Опытные работники, аккуратная работа с мебелью и техникой, почасовая оплата, быстрый выезд по городу и удобный заказ услуг в любое время.
Все про подорожі https://u-sviti.top країни, візи, курорти, пам’ятки та маршрути. Добірки напрямків, поради для туристів та ідеї для незабутніх поїздок світом.
seo продвижение и раскрутка сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru[/url] .
заказать анализ сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru/]заказать анализ сайта[/url] .
сео агентство [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve117.ru/]сео агентство[/url] .
investment hub – Professional design, navigation is smooth, and reading through details is simple.
оптимизация сайта франция [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve214.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve214.ru[/url] .
компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve215.ru/]компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов[/url] .
seo агентство [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru[/url] .
интернет агентство продвижение сайтов сео [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru[/url] .
seo network [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve216.ru/]seo network[/url] .
統一獅賽程、戰績、球員數據,運用先進AI預測演算法一應俱全,讓您隨時掌握最愛球隊的最新動態。
сервисы емайл рассылок русские сервисы емейл рассылок
задвижки 30с41нж ду500 https://zadvizhka-30s41nzh.ru
Situs Bonaslot adalah bandar judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat kilat. Link alternatif п»їBonaslot link alternatif jangan sampai ketinggalan.
сериал языке смотреть онлайн смотреть фильмы про тюрьму
Clean sheet tracker, goalkeepers and defenses with shutout statistics
Events – Event details are clear and structured, making schedules easy to follow.
action stop – Words focus on converting ideas into tangible outcomes consistently.
Bonaslot adalah bandar judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Situs resmi daftar situs judi slot gas sekarang bosku.
раскрутка сайта франция [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve222.ru/]раскрутка сайта франция[/url] .
Football results from last night, complete scores and match summaries available now
seo partner [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru[/url] .
官方數據源24小時即時更新nba赛程比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
Salam dostlar, əgər siz keyfiyyətli kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Oynamaq üçün link: Pin Up yüklə uğurlar hər kəsə!
Project homepage – Navigation is simple, interface is clear, and content is concise and helpful.
CoreBridge Gateway Hub – Messaging inspires confidence while design reinforces professionalism.
Platform overview – I came across this site and found the details easy to follow.
п»їHalo Bosku, lagi nyari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]bonaslotind.us.com[/url] semoga maxwin.
усиление ссылок переходами [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve221.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve221.ru[/url] .
discover ideas – Messaging drives action and emphasizes practical application.
捕风捉影在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属平台,高清无广告体验。
forwardtrajectory.bond – Sleek and functional, site encourages clear thinking and consistent progress.
заказать задание [url=https://kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru/]kupit-kursovuyu-41.ru[/url] .
enduringcapitalpath.bond – Clean design, conveys trust and a strong sense of purpose.
seo partner [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve119.ru/]seo partner[/url] .
seo network [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru[/url] .
zorivoline bond – Feels like something that may evolve into a solid offering.
海外华人必备的iyifan官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
adventureworld.bond – Engaging interface, content invites users to explore and discover new ideas naturally.
View project details – Well-laid-out sections and smooth transitions make the site user-friendly.
我們的台彩專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
heritagepath.bond – Clear design, content communicates historical value and is easy to digest.
MorixoGo – Layout neat, pages responsive, and navigating the site feels natural.
Attendance figures, crowd numbers for all football matches tracked
provenpath.bond – Clean visuals, site navigation is intuitive and content inspires confidence.
Selam, güvenilir casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, bu siteye mutlaka göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]mobil ödeme bahis[/url] iyi kazançlar.
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Saytda çoxlu slotlar və Aviator var. Pulu kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt burada baxın.
stonecrestcenter.bond – Well-presented, users can browse easily and the site feels dependable.
我們的台灣運彩官方授權專家團隊第一時間更新官方各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
中華職棒直播台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒直播新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
我們的運彩討論區專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
business guide – Words highlight clarity and inspire confidence for business growth.
thoughtful wood store – The site feels balanced and peaceful, with a strong sense of visual clarity.
CalmCornerGoods – Relaxed site layout with fast checkout.
huarenus官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
1win aviator az [url=www.1win5762.help]www.1win5762.help[/url]
Carabao Cup live scores, English League Cup with Premier League teams playing
official site – Layout is simple, navigation works smoothly, and content is easy to understand.
bond platform – Clean presentation helps users feel confident in the offerings.
中職戰績粉絲必備的資訊平台,運用大數據AI分析引擎提供最即時的中職戰績新聞、球員數據分析,以及專業的比賽預測。
Updates – News and announcements are presented clearly for easy access.
huarenus平台运用AI智能推荐算法,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
Project homepage – Navigation is simple, information is concise, and browsing feels effortless.
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的7m足球運用大數據AI分析引擎即時比分都在這裡。
creativepathlab.bond – Minimalist layout, ideas are presented clearly and encourage active exploration.
Salamlar, əgər siz keyfiyyətli kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Oynamaq üçün link: Pin Up online uğurlar hər kəsə!
seo partner program [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru[/url] .
частный seo оптимизатор [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru[/url] .
Vector Insights Hub – Polished visuals with clear content provide a professional feel.
продвижение по трафику [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve214.ru/]продвижение по трафику[/url] .
продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve117.ru/]продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве[/url] .
комплексное продвижение сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve216.ru/]комплексное продвижение сайтов москва[/url] .
Bonded Unity Focus – Balanced layout, content communicates collaboration effectively.
seo network [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve215.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve215.ru[/url] .
продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru[/url] .
раскрутка и продвижение сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru[/url] .
seo агентство [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve222.ru/]seo агентство[/url] .
explore zorivotrustco – Navigation feels logical, and the overall structure inspires confidence.
我們提供台灣最完整的棒球比分相關服務,包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
pillaroftrust.bond – Polished visuals, site communicates dependable information in a clear way.
strategy hub – Messaging encourages methodical planning and gradual improvement.
中華職棒直播台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒直播新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
trusthub.bond – Polished interface, content emphasizes transparency and credibility.
creativelab.bond – Vibrant layout, ideas are easy to grasp and inspire productive thought.
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# listeyi gör Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı bahis siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
strongholdtrust.bond – Crisp interface, users feel confident navigating and messaging is clear.
net seo [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve221.ru/]net seo[/url] .
investment hub – Pages load smoothly and the interface feels user-friendly.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, sağlam casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye mutlaka göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: listeyi gör bol şanslar.
我們提供台灣最完整的美國職棒即時比分相關服務,結合智能AI預測系統包含最新賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
Line overview page – Professional appearance with well-organized content for easy reading.
продвижение в google [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru[/url] .
Direct trust link – Everything is fast and intuitive, making it easy to find information.
PlivoxNavigator – Fast-loading pages, clean interface, and checkout felt very easy.
MeadowWayGoods – Smooth navigation with a relaxed, inviting layout.
dreamvisionbridgehub.bond – Clean presentation, site communicates ideas effectively and encourages action.
growth resource – Words create a sense of direction and purposeful development.
Check this platform – Pages are clear, content is simple to follow, and site feels dependable.
аудит продвижения сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve119.ru/]аудит продвижения сайта[/url] .
Downloads – Files and resources are arranged logically for fast and easy access.
統一獅賽程、戰績、球員數據,運用先進AI預測演算法一應俱全,讓您隨時掌握最愛球隊的最新動態。
stress free outlet – A friendly layout removes friction, letting you shop and pay with ease.
中職粉絲必備的資訊平台,運用先進AI預測演算法提供最即時的中職新聞、球員數據分析,以及專業的比賽預測。
我們提供MLB官方即時比分、賽程安排,以及MLB球隊戰績和球員數據分析。
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin-Up Casino[/url] tövsiyə edirəm.
cpbl粉絲必備的資訊平台,結合大數據AI算法提供最即時的cpbl新聞、球員數據分析,以及專業的比賽預測。
Champions League livescore updates, follow your favorite European clubs in real time tonight
п»їSalam Gacor, lagi nyari situs slot yang hoki? Coba main di Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Login disini: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# daftar situs judi slot semoga maxwin.
Midpoint Access – Easy navigation with clear sections helps users find information fast.
start aligned thinking – Messaging encourages clarity and purpose in developing ideas.
我們提供官方合作夥伴台灣最完整的棒球即時比分相關服務,包含最新官方賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
中華職棒今日比賽結果台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,結合AI深度學習技術提供最即時的中華職棒今日比賽結果新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
Offside traps, high line defenses and their success rates
我們的運彩世足官方授權專家團隊第一時間更新官方各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
Anchor Capital Bridge – Clean interface, pages load easily and inspire trust through clarity.
growthnetwork.bond – Clear navigation, content is growth-oriented and concepts are practical to apply.
zylavobond resource – Simple design ensures content is immediately understandable.
collabtrack.bond – Well-structured pages, messaging encourages cooperation and smooth communication.
seo partners [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve225.ru[/url] .
продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve216.ru/]продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве[/url] .
indigoharborcollection.shop – Easy-to-navigate, product pages load quickly and descriptions are informative.
раскрутка и продвижение сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve214.ru/]раскрутка и продвижение сайта[/url] .
1win az giriş [url=www.1win5762.help]1win az giriş[/url]
我們提供MLB即時比分、賽程安排,以及MLB球隊戰績和球員數據分析。
progresspath.bond – Smooth navigation, messaging encourages persistence and measurable advancement.
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的7m足球官方即時比分都在這裡。
продвижения сайта в google [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve223.ru[/url] .
claritymechanisminsight.bond – Streamlined design, guides users clearly through processes and mechanisms.
侠之盗高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
internet seo [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve215.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve215.ru[/url] .
поисковое продвижение москва профессиональное продвижение сайтов [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve224.ru[/url] .
seo partner [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve222.ru/]seo partner[/url] .
глубокий комлексный аудит сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve213.ru[/url] .
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı web sitemizde mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için https://cassiteleri.us.org/# casino siteleri kazanmaya başlayın.
seo агентство [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve117.ru/]seo агентство[/url] .
BlueTideGoods – Bright design and a pleasant shopping flow from start to finish.
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的7m足球運用大數據AI分析引擎即時比分都在這裡。
Check this platform – Simple interface, reliable content, and information is easy to find.
中華職棒賽程台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒賽程新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
clarity stop – Messaging focuses on simplicity, making choices feel easy to follow.
Комплекс услуг компании включает проектирование и изготовление электронных устройств. Инженеры создают схемы, печатные платы и подбирают компоненты. Параллельно разрабатывается встроенное и прикладное программное обеспечение. Прототипы тестируются и дорабатываются. Далее выполняется сборка и монтаж плат с контролем качества. Проводится мелкосерийное и серийное производство электронных изделий. Создаются корпуса с учетом эргономики и защиты компонентов, проводится промышленный дизайн. При необходимости выполняется реверс-инжиниринг для восстановления или модернизации устройств. Используется 3D-моделирование и 3D-печать для ускорения прототипирования. Все этапы сопровождаются документацией и технической поддержкой. В результате заказчик получает полностью готовое и проверенное устройство – подробности и инструкции. Каждое устройство создается с заботой о деталях
заказать анализ сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve221.ru/]заказать анализ сайта[/url] .
Opening goals, first strikes and their impact on results
EasyZaviro – Browsing seamless, links functional, and shopping feels effortless.
Производство изделий методом 3D-печати — это идеальный инструмент для прототипирования и производства. Мы работаем по изготовлению деталей и моделей. Наши специалисты используют современные 3D-принтеры, что позволяет создавать детали с ювелирной точностью. Для печати подбираются ударопрочные и термостойкие составы, что расширяет спектр применения. Выбирая наши услуги, вы избавляетесь от риска брака. Закажите 3D-печать прямо сейчас, и мы реализуем проект любой сложности: https://classihub.in/author/angelinehai/. Каждый заказ выполняется профессионально и аккуратно.
Hall of fame, greatest players and their career achievements celebrated
我們的玩運彩專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
Unity Trust Insight – Clean structure, site promotes trustworthy interaction and clarity.
Official xelivo page – The site immediately makes sense and has a professional structure.
поисковое seo в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru/]поисковое seo в москве[/url] .
Разработка электроники включает проектирование схем и плат. Создается встроенное программное обеспечение. Проводится тестирование прототипов. После согласования запускается производство. Заказчик получает готовое решение для внедрения – узнайте детали.
Используемые технологии обеспечивают полное соответствие требованиям и стандартам.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, sağlam casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye mutlaka göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için inceledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: listeyi gör bol şanslar.
comfort style market – A soft, cozy design makes exploring products simple and stress free.
progressspark.bond – Intuitive design, site highlights actionable ideas and continuous improvement.
coresecure.bond – Polished layout, content clearly emphasizes trust and user-focused design.
Bonded Framework Core – Balanced layout, content communicates framework principles in a straightforward way.
Tennis live scores from all Grand Slams, ATP and WTA tours updated every point
crestbond.bond – Clean layout, site conveys reliability and a sense of professionalism.
Aktual Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Xoş gəldin bonusu sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up giriş qazancınız bol olsun.
clarity advantage – Layout is tidy and ideas are presented in a way that’s easy to understand.
zylavocore access – Cohesive design and readable content create a balanced experience.
wildgrainmarket.shop – Inviting design, navigating the shop is smooth and items are well showcased.
продвижения сайта в google [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve119.ru/]продвижения сайта в google[/url] .
velixotrustco.bond – Layout is clear, content is easy to follow, and navigation feels intuitive.
Red card tracker, disciplinary records and suspensions updated live
中職賽程粉絲必備的資訊平台,結合智能AI預測系統提供最即時的中職賽程新聞、球員數據分析,以及專業的比賽預測。
ТОП-25 сервисов для раскрутки группы в ВК в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1738678
growth navigator – Wording makes intentional development feel achievable and practical.
Possession stats, ball control percentages for all live matches tracked
buildhub.bond – Clear layout, pages are intuitive and make taking action straightforward.
我們的台灣運彩專家團隊採用機器學習預測模型,每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
Live football match score updates faster than TV broadcast, stay ahead of everyone else
HearthGroveShop – Cozy pages, effortless exploration of products, and smooth checkout.
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah merasakan Maxwin sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Situs resmi п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot rtp[/url] jangan sampai ketinggalan.
Zahnprobleme? zahnarzte Diagnostik, Kariesbehandlung, Implantate, Zahnaufhellung und Prophylaxe. Wir bieten Ihnen einen angenehmen Termin, sichere Materialien, moderne Technologie und kummern uns um die Gesundheit Ihres Lachelns.
куб пицца официальный сайт пицца
куб доставка пиццы куба пиццерия рязань
Selamlar, güvenilir casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, bu siteye mutlaka göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]casino siteleri[/url] iyi kazançlar.
Direct site access – Layout is tidy, content is clear, and users can find information quickly.
Salam Gacor, cari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Deposit bisa pakai OVO tanpa potongan. Login disini: Bonaslot login salam jackpot.
官方數據源24小時即時更新nba赛程比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
надгробные памятники из гранита и мрамора
中華職棒即時比分台灣球迷的首選官方認證資訊平台,24小時不間斷提供官方中華職棒即時比分新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
forwardvector.bond – Modern interface, content inspires action and clear steps toward goals.
Salam dostlar, siz də yaxşı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və bonus qazanın. Daxil olmaq üçün link: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up AZ uğurlar hər kəsə!
Nexa Access – User-friendly navigation, pages load smoothly and messaging is clear.
clarity stop – Wording is clean, guiding users through focused actions efficiently.
我們的玩運彩專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
alliantfocushub.bond – Professional interface, content reinforces mission statements and core objectives efficiently.
silverway.bond – Polished design, pages convey confidence and an approachable, trustworthy feel.
VixaroDirect – Interface neat, links functional, and purchasing was quick.
capitalunityinitiative.bond – Navigation is smooth, unity and shared purpose are highlighted.
ironpetalshopco.shop – Well-structured pages, shopping is straightforward and product details are clear.
zylavoline resource – Rapid performance makes exploring the key points effortless.
Situs Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah merasakan Maxwin sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat kilat. Situs resmi https://bonaslotind.us.com/# login sekarang gas sekarang bosku.
outdoor style finds – Everything is laid out clearly, so exploring items and ordering is hassle free.
TwilightSpireShop – Attractive design and browsing feels effortless.
vaulttrust.bond – Clean and organized, pages convey safety and professionalism effectively.
官方數據源24小時即時更新nba比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
View project details – Branding is uniform, and content is presented in a straightforward way.
我們的運彩世足官方授權專家團隊第一時間更新官方各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
creativepulsejourney.bond – Vibrant design, ideas are engaging and navigation is intuitive throughout.
focus journey – Theme emphasizes attention to detail, giving content clarity and direction.
discover growth – Messaging promotes clarity and logical progression in planning growth.
Check this platform – Clean layout, straightforward information, and navigation is simple.
Tandem Insight – Balanced interface, content communicates the idea simply and effectively.
Selam, ödeme yapan casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye kesinlikle göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# siteyi incele iyi kazançlar.
задвижка 30с41нж длина задвижки стальные фланцевые 30с41нж
Need an AI generator? UndressAI The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
фильмы онлайн без рекламы смотреть фильмы онлайн
harborallied.bond – Clean layout, site highlights security and collaboration effectively for visitors.
продвижение сайтов во франции [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru/]продвижение сайтов во франции[/url] .
solidway.bond – Clean navigation, messaging communicates a sense of security and dependability.
Aktual Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, doğru yerdesiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up kazino[/url] hamıya bol şans.
超人和露易斯第三季高清完整版智能AI观看体验优化,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
linenloamhome.shop – Clear navigation, store feels approachable and buying items is simple.
capitalbondcrew.bond – Approachable feel, teamwork principles are easy to follow.
zylavotrustco details – Solid presentation communicates reliability and builds user trust.
online investment page – Organized layout with clear information and minimal distractions.
focuslanecenter.bond – User-friendly layout, content reinforces productivity and helps maintain clear goals.
MistyHarborLane – Pleasant, organized pages with an easy-to-follow checkout process.
forward journey – Content inspires movement with a sense of clarity and intention.
ZorivoSpot – Interface tidy, pages open quickly, and checkout process feels straightforward.
爱一帆下载海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, bura baxa bilərsiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# sayta keçid hamıya bol şans.
trustpillar.bond – Professional presentation, pages encourage shared goals and dependable communication.
Pin-Up AZ ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Burada çoxlu slotlar və Aviator var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pinup yoxlayın.
simple online boutique – The presentation feels polished, letting shoppers enjoy browsing without distractions.
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Detaylı liste web sitemizde mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]casino siteleri 2026[/url] kazanmaya başlayın.
Idea Flow Portal – Layout and content inspire turning creative concepts into concrete steps.
alliantpeak.bond – Contemporary feel, messaging is straightforward and branding stands out clearly.
groundline.bond – Modern layout, pages feel structured and clearly communicate reliability.
海外华人必备的yifan平台运用AI智能推荐算法,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Check platform details – The layout keeps things simple, and the information is accessible without effort.
digitalsparkjourney.bond – Bright and inviting, ideas are structured clearly and easy to follow.
HÉ™r vaxtınız xeyir, É™gÉ™r siz etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütlÉ™q Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Æn yaxşı slotlar vÉ™ rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Ä°ndi qoÅŸulun vÉ™ bonus qazanın. Sayta keçmÉ™k üçün link: sayta keçid uÄŸurlar hÉ™r kÉ™sÉ™!
Ridgecrest Navigator – Trust signals are clear, helping users feel comfortable with the site.
collectivemoon.shop – Neat layout, product pages are clear and purchasing is straightforward.
Bonded Legacy Hubspot – Polished layout, content conveys legacy principles clearly and efficiently.
clarity insights – Messaging is streamlined, encouraging quick yet thoughtful action.
purpose-first planning – Comes across as mindful and directionally strong.
OpalFernHollow – Calm, attractive layout makes exploring products and checkout easy.
продвижение сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru/]продвижение сайта[/url] .
我欲为人第二季官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
capitalcorehub.bond – Professional interface, content is clear and inspires a sense of stability and focus.
fresh looking site – Modern feel with navigation that just works.
Salam Gacor, cari situs slot yang hoki? Coba main di Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai OVO tanpa potongan. Login disini: daftar situs judi slot semoga maxwin.
focusandgrowbridgehub.bond – Engaging presentation, encourages steady learning and focused growth strategies.
ClickXpress – Pages loaded quickly, interface tidy, and content displayed clearly.
clicky bargains hub – Efficient layout, makes shopping effortless and enjoyable.
maple inspired store – A cozy, rustic design supports clear product details and easy navigation.
groundpoint.bond – Modern interface, messaging communicates stability and gives users confidence.
direction clarity guide – Easy to follow structure that keeps the content on track.
Momentum Connect – Clear structure, messaging reinforces the idea of advancement.
pinnaclehub.bond – Organized structure, navigation is simple and trust is conveyed effortlessly.
задвижка 30с41нж 250 задвижки 30с41нж
quick route click – Smooth experience, platform feels logical and easy to navigate.
TeamFlow – Simplifies collaboration and fosters a positive work environment.
quillco.shop – Appealing interface, browsing items is effortless and information is readable.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]en iyi casino siteleri[/url] Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı casino siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
networking insights shop – Easy-to-follow platform, discovering business connections feels seamless.
unifiedtrustconnect.bond – Intuitive interface, site communicates trustworthiness and clarity effectively.
decision clarity space – The overall message feels intentional and well-considered.
PetalStoneMarket – Smooth navigation, items easy to find, and purchasing feels effortless.
Bonaslot adalah bandar judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah merasakan Jackpot sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat kilat. Situs resmi [url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot daftar[/url] gas sekarang bosku.
Official trust page – Details are easy to follow, and the overall presentation feels polished.
shopper insight site – Good concept with content that feels applicable.
trustedhub.bond – Professional layout, pages feel reliable and make navigation simple.
Info slot gacor hari ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini anti rungkad dan aman. Bonus new member menanti anda. Akses link: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot link alternatif[/url] raih kemanangan.
new opportunity guide – Words motivate users to step forward and embrace possibilities.
PartnerEdge – Guides businesses on dependable collaborations and strategic growth initiatives.
firmanchor.bond – Professional design, pages convey stability and inspire confidence naturally.
раскрутка сайта франция цена [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru[/url] .
investment clarity site – Feels credible, with easy-to-read information on bonds.
principlecircle.bond – Clear layout, site conveys authority and principled guidance seamlessly.
Bu sene en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı platformumuzda mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve güncel giriş linklerini paylaşıyoruz. Hemen tıklayın [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]güvenilir casino siteleri[/url] fırsatı kaçırmayın.
trust bond hub – Straightforward navigation, presents investment options clearly.
Bonded Insights – Layout and content feel polished, reliable, and future-oriented.
Pin-Up AZ ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Saytda çoxlu slotlar və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up online[/url] yoxlayın.
intentional movement page – Very focused layout, makes understanding ideas easy.
northwindemporium.shop – Organized store, finding items is easy and checkout completes without problems.
XylorPortal – Clean interface, pages load quickly, and the site feels reliable.
aurumlane.shop – Modern and elegant, the layout feels refined and browsing is smooth throughout.
п»їSalam Gacor, cari situs slot yang mudah menang? Coba main di Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Deposit bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Login disini: п»їsitus slot resmi semoga maxwin.
urbanwavezone.bond – Modern layout, content flows naturally and keeps the reader engaged.
frugal shopper hub – Easy to navigate, lots of affordable options displayed clearly.
personal direction link – Reads as sincere, steady, and quietly uplifting.
>efficient web page – Super quick to load and easy to scroll through.
TrustedBizLink – A reliable platform where exploring secure business opportunities is straightforward.
pillarconnect.bond – Clear structure, messaging promotes unity and clarity for visitors.
Salamlar, siz də yaxşı kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Daxil olmaq üçün link: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up online[/url] uğurlar hər kəsə!
stonebridgefunds.bond – Polished design, navigation is smooth and messaging feels professional and clear.
harbor investment site – Easy to use, keeps all bond options well organized.
bondethic.bond – Cohesive presentation, messaging feels honest and trustworthy throughout.
shoproute deals – Minimalist layout, makes finding deals easy and stress-free.
financial guidance platform – Clean visuals, smooth navigation, and concise information enhance usability.
Trusted Nexus Stream – Balanced interface, content comes across as credible and accessible.
opalcrestcollection.shop – Modern layout, browsing is intuitive and information is easy to read.
Selam, sağlam casino siteleri arıyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]buraya tıkla[/url] iyi kazançlar.
digital progress page – Provides useful strategies to build momentum consistently.
strategic development center – Helpful content, makes identifying smart growth paths easy and fast.
Halo Slotter, lagi nyari situs slot yang gacor? Coba main di Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Deposit bisa pakai OVO tanpa potongan. Login disini: bonaslotind.us.com semoga maxwin.
progresscatalystcore.bond – Direct layout, encourages strategic forward progress and meaningful action.
оптимизация и seo продвижение сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru/]оптимизация и seo продвижение сайтов москва[/url] .
take action with clarity – Clear guidance encourages immediate application of ideas.
smart shopping page – Layout feels organized and browsing through items is easy.
It’s great to see such a well-researched breakdown of career paths. Many students struggle with choosing the right direction, and content like this really helps in making informed decisions. I especially liked how practical growth and income potential were explained. Anyone confused about future planning should definitely check out this guide on most lucrative career options in India.
aligned progress tools – Indicates resources built to support intentional advancement.
ClickXanix – Smooth interface, content loads fast, and browsing feels intuitive.
strategic ideas hub – Well organized, learning fresh techniques is simple and effective.
midnightcovegoods.shop – Dark aesthetic feels polished, product discovery is smooth and checkout is quick.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, bura baxa bilərsiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə hesabınıza girin və qazanmağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin-Up Casino hamıya bol şans.
pillarofstrength.bond – Well-organized design, content highlights unity and dependable guidance.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, sağlam casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye kesinlikle göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: türkçe casino siteleri iyi kazançlar.
海外华人必备的yifan官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
п»їSalam Gacor, lagi nyari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Login disini: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot slot[/url] semoga maxwin.
SecureCart – Ensures shopping is safe while the checkout process remains quick and intuitive.
investment merit hub – Organized well, ideal for daily planning and research.
Financial news, club revenues and transfer budgets reported
curve shopping click – Streamlined layout, makes the shopping process smooth and enjoyable.
Own goals, unfortunate deflections and their impact documented
https://vc.ru/2358828, Где купить живых подписчиков в ВК – 20 топовых лайфхаков в 2026 году
clean layout link – Well presented and easy to process in seconds.
Ligue 1 live scores, French football including PSG matches tracked in real time
продвижение сайтов в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve233.ru/]продвижение сайтов в москве[/url] .
оптимизация и продвижение сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve232.ru/]оптимизация и продвижение сайтов москва[/url] .
комплексное продвижение сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru[/url] .
practical shopping site – Easy to browse with neatly arranged product categories.
International friendly live scores, national team matches outside tournaments
продвижения сайта в google [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru[/url] .
интернет раскрутка [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru/]poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru[/url] .
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]kaçak bahis siteleri[/url] Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği casino siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Ownership updates, club sales and investment news tracked
Team news updates, lineups injuries and squad announcements covered
creative thought hub – Easy to navigate, site offers a variety of interesting concepts.
ZorlaGo – Pages responsive, links work perfectly, and shopping experience seamless.
India vs Australia livescore, cricket rivalry matches with detailed scoring updates
midnight field hub – Clear structure throughout, making shopping smooth and stress free.
momentum stop – Messaging reflects steady progress while keeping goals in focus.
Play puzzles https://otzywok.ru/forums/topic/ishhu-spokojnuyu-igru-chtob-mozgi-razmyat/ online for free – engaging puzzles for kids and adults. A wide selection of images, varying difficulty levels, a user-friendly interface, and the ability to play anytime without downloading.
заказать анализ сайта [url=https://kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru/]заказать анализ сайта[/url] .
我欲为人第二季官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
Salamlar, əgər siz etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Daxil olmaq üçün link: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin-Up Casino[/url] uğurlar hər kəsə!
financial options hub – Smooth design, fast navigation, and very user-friendly.
interactive win click – Motivating and fun, keeps the browsing experience lively.
Pin-Up AZ ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Burada minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki Pin-Up Casino yoxlayın.
interesting webpage – Noted this for later, feels like it could be useful.
порно шлюхи вк купить меф горно алтайск телеграмм
EnterpriseConnect – Offers professional guidance on building effective business collaborations.
купить меф нижний новгород эффект от мефа
Упаковочное и фасовочное оборудование https://vostok-pack.ru купить с доставкой по всей России в течении 30 дней. Лучшие цены на рынке. Гарантия на оборудование. Консультационные услуги. Покупайте упаковочные машины для производства со скидкой на сайте!
modern marketplace portal – Easy to browse and feels very contemporary.
海外华人必备的iyf平台,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Hi, I recently discovered a reliable website where you can buy prescription drugs cheaply. For those who need antibiotics, OnlinePharm is worth a look. They ship globally and no script needed. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]OnlinePharm[/url]. Warmly.
海外华人必备的iyf官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
seo агентство [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve233.ru/]seo агентство[/url] .
internetagentur seo [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru[/url] .
iyftv海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Являешь патриотом? хочу заключить контракт на сво как оформить, какие требования предъявляются, какие выплаты и льготы предусмотрены. Актуальная информация о контрактной службе и порядке заключения.
Greetings, Just now found a useful online drugstore for affordable pills. If you need cheap antibiotics without prescription, this store is worth checking. They offer wholesale rates guaranteed. Check it out: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Good luck.
продвижение сайта [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve232.ru/]продвижение сайта[/url] .
Opportunity innovation network – Clean, modern layout that’s simple to move through.
интернет раскрутка [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru/]poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru[/url] .
海外华人必备的ifun平台结合大数据AI分析,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Baseball livescore MLB updates, America’s pastime with pitch-by-pitch tracking live
продвижение сайтов в москве [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru[/url] .
Business evolution page – The interface feels straightforward and clear.
corporate trust center – Well-structured content, ideal for understanding partnership opportunities clearly.
Youth football livescore, U20 and U17 World Cup matches covered live
strategy clarity guide – Keeps ideas simple while motivating thoughtful choices.
growth path builder – User-friendly interface, helps maintain consistent momentum.
真实的人类第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
discover future options – Well-structured, guides visitors to evaluate new and exciting opportunities.
trusted investment guide – Clean design with clear safety features for users.
Greetings, I wanted to share a great online drugstore for purchasing medications hassle-free. If you are looking for antibiotics, OnlinePharm is highly recommended. They ship globally plus it is very affordable. Visit here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]Online Pharm Store[/url]. Stay healthy.
MLS livescore updates, American soccer with all teams and matches covered live
Big chances created, high quality opportunities and their outcomes
Выбор роутера для автомобиля https://router-dlya-avtomobilya.ru
XelivoSpot – Browsing simple, content clear, and checkout process quick and easy.
net seo [url=https://kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru/]kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru[/url] .
раскрутка сайта франция [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru/]poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru[/url] .
Рекомендуемое чтение: урология за деньги: как записаться на прием и чего ожидать?
цифровой маркетинг статьи [url=https://blog-o-marketinge1.ru/]цифровой маркетинг статьи[/url] .
раскрутка сайта франция цена [url=https://poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru/]poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru[/url] .
материалы по seo [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge1.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge1.ru[/url] .
блог о маркетинге [url=https://blog-o-marketinge.ru/]блог о маркетинге[/url] .
Работа с микроразметкой schema.org для сайтов Гродно. Помогаем поисковикам лучше понимать ваш контент (адрес, товары, отзывы) seo гродно. Это повышает вероятность попадания в расширенные сниппеты и кликабельность в выдаче.
1win partners [url=https://1win5746.help]https://1win5746.help[/url]
1win promo code [url=http://1win5745.help]http://1win5745.help[/url]
фильмы онлайн бесплатно смотреть аниме онлайн в хорошей озвучке
блог про продвижение сайтов [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge2.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge2.ru[/url] .
Mavero Holdings digital site – Clean pages, professional layout, and details are easy to follow.
discover your focus – Text makes the concept of focus feel approachable and useful.
Hey guys, Just now came across an amazing source from India to buy generics. For those looking for medicines from India without prescription, this store is very reliable. It has wholesale rates worldwide. Visit here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Best regards.
iyftv海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Hey everyone, I wanted to share a great international pharmacy for purchasing generics securely. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is worth a look. They ship globally plus huge selection. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope it helps.
Free kick walls, defensive organization and block statistics
step-by-step progress page – Encourages consistent effort with an easy-to-follow approach.
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
the best adult generator digital girlfriend create erotic videos, images, and virtual characters. flexible settings, high quality, instant results, and easy operation right in your browser. the best features for porn generation.
To be honest, Lately came across a useful source from India to buy generics. If you need cheap antibiotics at factory prices, IndiaPharm is the best place. They offer lowest prices to USA. Visit here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
сервисы емайл рассылок сервисы массовой рассылки email
1win ghana [url=www.1win5746.help]www.1win5746.help[/url]
1win betting [url=https://1win5745.help]https://1win5745.help[/url]
Shopping convenience hub – Layout is clean, and loading times are impressive.
凯伦皮里第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
progress momentum resource – Well-organized steps make the approach intuitive and simple.
продвижение сайтов во франции [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru[/url] .
buy easy hub – Efficient layout, online shopping feels effortless and stress-free.
Hello, I just found a great website for purchasing generics securely. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is highly recommended. Secure shipping and no script needed. Link here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Get well soon.
Get instant livescore updates for Premier League, La Liga, Serie A and Bundesliga matches today
next step navigator – Informative and engaging, site encourages innovative approaches.
pillar finance page – Clear design makes exploring bonds straightforward and safe.
интернет продвижение москва [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru/]интернет продвижение москва[/url] .
seo агентство [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve232.ru/]seo агентство[/url] .
Greetings, I just found a trusted resource for cheap meds. For those seeking and want generic drugs, Pharm Mex is worth checking out. Great prices plus very reliable. Link is here: Pharm Mex. Good luck!
Nations League livescore updates, UEFA competition with promotion and relegation
продвижение веб сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru[/url] .
Mavero Trustline online site – Structured pages, clean visuals, and key information is easy to access.
Business alliance platform – Everything seems neatly organized and accessible.
SmartBuyZone – Offers an intuitive way to shop while making product comparison quick and easy.
раскрутка сайта франция цена [url=https://kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru/]kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru[/url] .
продвижение в google [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru/]poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru[/url] .
Hey everyone, To be honest, I found a reliable website for purchasing prescription drugs online. For those who need antibiotics, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Fast delivery plus huge selection. Check it out: online pharmacy usa. Regards.
оптимизация сайта блог [url=https://blog-o-marketinge1.ru/]оптимизация сайта блог[/url] .
сео блог [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge1.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge1.ru[/url] .
Full Article Here: https://tgram.link/apps/workingvpn/
Big-bag-rus.ru — биг бэг тара и мягкая тара МКР: прочные биг-бэги для стройматериалов, зерна, гранулята и других сыпучих продуктов. Производство под заказ и со склада, консультация, расчет, доставка по РФ: https://big-bag-rus.ru/
статьи про маркетинг и seo [url=https://blog-o-marketinge.ru/]blog-o-marketinge.ru[/url] .
simple growth guide – Breaks down growth ideas in a way that’s easy to absorb.
new discoveries page – Keeps things fresh and exciting with every click.
Dependable online shop – Categories are clear, making the shopping experience smooth.
internetagentur seo [url=https://poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru/]poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru[/url] .
маркетинговые стратегии статьи [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge2.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge2.ru[/url] .
Free kick walls, defensive organization and block statistics
improve fast portal – Very useful, lessons provide actionable steps without delay.
Hey everyone, I wanted to share a useful international pharmacy to order pills online. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, this site is very good. Fast delivery and no script needed. Check it out: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]onlinepharm.jp.net[/url]. Cya.
Midweek football livescore, Tuesday Wednesday Champions League Europa action
Hey guys, I recently found a great source from India to save on Rx. If you want to buy medicines from India safely, this store is worth checking. It has fast shipping guaranteed. Take a look: visit website. Best regards.
creative ideas portal – Inspires curiosity, with plenty of unique ideas to check out.
海外华人必备的ifun平台,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
оптимизация сайта франция цена [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve233.ru/]оптимизация сайта франция цена[/url] .
learn more daily – Engaging platform, encourages constant learning and self-improvement.
оптимизация сайта франция [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve235.ru[/url] .
Cricket livescore updates, IPL and international matches with ball-by-ball commentary
Learn more at Mivaro Trust Group – Organized layout, easy-to-read content, and users can find information quickly.
Hello everyone, Lately ran into a reliable website for affordable pills. For those seeking and need cheap antibiotics, this site is the best option. Great prices and very reliable. Link is here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Have a nice day.
оптимизация сайта франция цена [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru/]poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru[/url] .
Greetings, To be honest, I found an excellent source for meds for purchasing prescription drugs hassle-free. For those who need antibiotics, this store is very good. Great prices plus huge selection. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Be well.
positive outlook hub – Has a motivating style that keeps things future-minded.
частный seo оптимизатор [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve232.ru/]частный seo оптимизатор[/url] .
seo partners [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve234.ru[/url] .
глубокий комлексный аудит сайта [url=https://kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru/]kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru[/url] .
продвижение в google [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru/]poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru[/url] .
Weekend football matches, Saturday and Sunday games with live score tracking
Strategic planning hub – The site feels well-organized and visually engaging.
Hey guys, I just came across a great online drugstore for cheap meds. If you want to buy generic pills safely, this site is the best place. You get lowest prices to USA. More info here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
Community Shield livescore, season opener between league and cup champions
Cutback assists, low crosses and their conversion rates tracked
digital shopping hub – Attractive layout, browsing items feels intuitive and smooth.
блог агентства интернет-маркетинга [url=https://blog-o-marketinge1.ru/]blog-o-marketinge1.ru[/url] .
Greetings, I recently discovered a great international pharmacy where you can buy pills securely. For those who need antibiotics, this site is highly recommended. Great prices and it is very affordable. Link here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Cheers.
блог про seo [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge1.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge1.ru[/url] .
bargain click page – Efficient layout, perfect for spotting daily offers quickly.
статьи про маркетинг и seo [url=https://blog-o-marketinge.ru/]blog-o-marketinge.ru[/url] .
Mivaro Trust Group web portal – Clean layout, useful content, and moving through pages is effortless.
поисковое seo в москве [url=https://poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru/]poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru[/url] .
teamwork solutions hub – Smooth navigation, collaboration strategies are easy to grasp quickly.
блог seo агентства [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge2.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge2.ru[/url] .
Greetings, I just stumbled upon a useful source from India for cheap meds. For those looking for cheap antibiotics at factory prices, this store is worth checking. It has lowest prices to USA. Check it out: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
Hey everyone, To be honest, I found a reliable website for purchasing generics securely. For those who need no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is worth a look. Secure shipping and no script needed. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Have a nice day.
Greetings, Lately came across a great online source to save on Rx. If you are tired of high prices and need affordable prescriptions, this site is worth checking out. They ship to USA plus very reliable. Check it out: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]this site[/url]. Appreciate it.
Global trade portal – Navigation is smooth, and the business message is evident.
Contract updates, player extensions and free agent signings tracked
purchase smart portal – Clean layout, makes finding and buying items straightforward.
product info hub – Makes exploring features and details fast and simple.
Hello, I recently discovered a great website to order generics hassle-free. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, OnlinePharm is highly recommended. They ship globally plus no script needed. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Get well soon.
To be honest, Lately discovered a useful website to save on Rx. For those looking for medicines from India cheaply, IndiaPharm is very reliable. They offer secure delivery guaranteed. More info here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
future roadmap site – Clear and motivating, perfect for planning next actions.
продвижение сайтов в москве [url=https://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru/]продвижение сайтов в москве[/url] .
Greetings, I recently discovered a useful online drugstore for affordable pills. If you need generic pills safely, this site is highly recommended. You get lowest prices worldwide. Check it out: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]read more[/url]. Hope it helps.
digital маркетинг блог [url=https://blog-o-marketinge.ru/]blog-o-marketinge.ru[/url] .
блог про seo [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge1.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge1.ru[/url] .
seo и реклама блог [url=https://blog-o-marketinge1.ru/]blog-o-marketinge1.ru[/url] .
Morixo Capital official page – Clear structure, trustworthy visuals, and navigating pages is intuitive.
Здесь чувствуется определённая инженерная дисциплина. Изучая платформа pin up casino, понимаешь, что каждый элемент прошёл фильтр целесообразности. Ничего не выглядит случайным, а общее восприятие остаётся ровным и предсказуемым, что особенно ценится при регулярном использовании.
Любишь азарт? обзор казино joycasino большой выбор слотов, live-дилеры и удобный интерфейс. Простой вход, доступ к бонусам, актуальные игры и комфортный игровой процесс без лишних сложностей
W 2026 roku w Polsce dziala kilka kasyn https://kasyno-paypal.pl online obslugujacych platnosci PayPal, ktory jest wygodnym i bezpiecznym sposobem wplat oraz wyplat bez koniecznosci podawania danych bankowych. Popularne platformy z PayPal to miedzynarodowi operatorzy z licencjami i bonusami, oferujacy szybkie transakcje oraz atrakcyjne promocje powitalne
Financial news, club revenues and transfer budgets reported
Paysafecard https://paysafecard-casinos.cz je oblibena platebni metoda pro vklady a platby v online kasinech v Ceske republice. Hraci ji ocenuji predevsim pro vysokou uroven zabezpeceni, okamzite transakce a snadne pouziti. Podle naseho nazoru je Paysafecard idealni volbou pro hrace, kteri chteji chranit sve finance a davaji prednost bezpecnym platebnim resenim
Hi, I just found a reliable online drugstore to order generics online. For those who need cheap meds, OnlinePharm is highly recommended. Great prices plus no script needed. Check it out: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]cheap pharmacy online[/url]. Have a good one.
sonabet.pro
alliances insight center – Useful resources, helps build strong professional and commercial connections.
Fantasy football, player points and team management tips included
Customer-focused retail site – Shopping experience is seamless and pleasant throughout.
W 2026 roku w Polsce https://kasyno-revolut.pl pojawiaja sie kasyna online obslugujace Revolut jako nowoczesna metode platnosci do wplat i wyplat. Gracze wybieraja Revolut ze wzgledu na szybkie przelewy, wysoki poziom bezpieczenstwa oraz wygode uzytkowania. To idealne rozwiazanie dla osob ceniacych kontrole finansow
Жіночий портал https://soloha.in.ua про красу, здоров’я, стосунки та саморозвиток. Корисні поради, що надихають історії, мода, стиль життя, психологія та кар’єра – все для гармонії, впевненості та комфорту щодня.
1win online site [url=1win5746.help]1win online site[/url]
технического аудита сайта [url=https://poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru/]poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru[/url] .
1win telegram [url=https://www.1win5745.help]1win telegram[/url]
контекстная реклама статьи [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge2.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge2.ru[/url] .
daily progress page – Motivates you to keep moving forward consistently.
Сучасний жіночий портал https://zhinka.in.ua мода та догляд, здоров’я та фітнес, сім’я та стосунки, кар’єра та хобі. Актуальні статті, практичні поради та ідеї для натхнення та балансу у житті.
To be honest, I just found a trusted online source to buy medication. If you want to save money and want cheap antibiotics, this site is a game changer. Great prices plus secure. Take a look: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Get well soon.
Hey there, I recently discovered an excellent source for meds for purchasing pills cheaply. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, this store is very good. They ship globally plus no script needed. Link here: cheap pharmacy online. Sincerely.
жіночі журнали онлайн https://xxl.kyiv.ua
журнал жіноче здоров’я https://u-sviti.top
грузчики квартира https://www.gruzchiki-kiev.net
Портал для жінок https://u-kumy.com про стиль, здоров’я та саморозвиток. Експертні поради, чесні огляди, лайфхаки для дому та роботи, ідеї для відпочинку та гармонійного життя.
Morixo Holdings landing page – Clear menus, organized sections, and the overall user experience feels secure.
контекстная реклама статьи [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge.ru/]контекстная реклама статьи[/url] .
продвижение обучение [url=https://kursy-seo-1.ru/]kursy-seo-1.ru[/url] .
Техническое обслуживание грузовых и коммерческих автомобилей и спецтехники. Снабжение и поставки комплектующих для грузовых автомобилей, легкового коммерческого транспорта на бортовой платформе ВИС lada: https://ukinvest02.ru/
Натяжной потолок выбирают, когда хочется ровную плоскость без шпаклевки и покраски, выбирайте полотно с фотопечатью, оно выдерживает протечку и помогает спасти отделку и мебель, уточните как ухаживать за полотном, чтобы не было разводов, в итоге получите чистый финиш и понятный результат, потолки натяжные в москве
sonabet vip
Hey there, I recently discovered a great international pharmacy to order prescription drugs hassle-free. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, this store is highly recommended. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. Link here: Online Pharm Store. Kind regards.
shoproute deals hub – Easy-to-use platform, comparing products is quick and straightforward.
Strategic business hub – Well-organized content and a clear message on collaborations.
塔尔萨之王第三季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
我們的台彩專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
To be honest, Just now found a useful website to buy generics. If you need ED meds safely, this store is worth checking. You get wholesale rates guaranteed. Check it out: cheap indian generics. Hope it helps.
sonabet net
Натяжной потолок делает комнату визуально выше и аккуратнее, ПВХ полотно помогает зонировать пространство светом; можно заранее спланировать скрытый карниз и подсветку по проекту – https://potolki-decarat.ru/
Win casino ro‘yxatdan o‘tish oddiy va tez bajariladi.
Hello everyone, Just now found a great Mexican pharmacy for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and want generic drugs, this store is the best option. No prescription needed plus secure. Take a look: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]this site[/url]. Thanks!
Hey everyone, I recently discovered an excellent international pharmacy for purchasing pills online. If you are looking for antibiotics, this site is the best choice. Great prices plus no script needed. Visit here: this site. Hope this helps!
Galatasaray Football Club https://galatasaray.com.az latest news, fixtures, results, squad and player statistics. Club history, achievements, transfers and relevant information for fans.
Barcelona fan site barcelona.com.az/ with the latest news, match results, squads and statistics. Club history, trophies, transfers and resources for loyal fans of Catalan football.
UFC Baku fan site ufc-baku.com.az/ for fans of mixed martial arts. Tournament news, fighters, fight results, event announcements, analysis and everything related to the development of UFC in Baku and Azerbaijan.
Free kick walls, defensive organization and block statistics
真实的人类第一季高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Live scores today for all sports, comprehensive coverage updated every few seconds
seo с нуля [url=https://kursy-seo-1.ru/]kursy-seo-1.ru[/url] .
Euro 2024 live scores, Germany hosted European Championship match tracking
Learn and grow site – Easy navigation and helpful resources make studying enjoyable.
статьи о маркетинге [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge.ru/]статьи о маркетинге[/url] .
Hey there, I recently discovered an excellent website where you can buy medications hassle-free. For those who need antibiotics, OnlinePharm is worth a look. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. Check it out: cheap pharmacy online. Thanks!
Hey guys, Lately stumbled upon the best source from India to buy generics. If you need cheap antibiotics cheaply, this store is worth checking. It has lowest prices to USA. More info here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Hope it helps.
Goalkeeper errors, handling mistakes and their consequences
Прогноз курса доллара от internet-finans.ru. Ежедневная аналитика, актуальные котировки и экспертные мнения. Следите за изменениями валют, чтобы планировать обмен валют и инвестиции эффективно.
global organization globalideas.org.au that implements healthcare initiatives in the Asia-Pacific region. Working collaboratively with communities, practical improvements, innovative approaches, and sustainable development are key.
Rafa Silva http://rafa-silva.com.az is an attacking midfielder known for his dribbling, mobility, and ability to create chances. Learn more about his biography, club career, achievements, playing style, and key stats.
https://sonabet.pro/
超人和露易斯第三季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
愛壹帆海外版,專為華人打造的高清視頻平台AI深度學習內容匹配,支持全球加速觀看。
Euro 2024 live scores, Germany hosted European Championship match tracking
Greetings, I just stumbled upon a great source from India to save on Rx. If you want to buy generic pills without prescription, this store is worth checking. You get secure delivery guaranteed. Visit here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Good luck.
官方授权的ifuntv海外华人首选,第一时间提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
huarenus官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
Hello everyone!
I came across a 153 great page that I think you should visit.
This platform is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://trickynerds.com/share-about-the-houses-betting-method-in-football-betting/]https://trickynerds.com/share-about-the-houses-betting-method-in-football-betting/[/url]
And don’t forget, everyone, — one constantly are able to in the article discover solutions for your most complicated inquiries. The authors made an effort — present the complete data using an most accessible way.
Hi, I just found a great source for meds where you can buy prescription drugs hassle-free. If you need cheap meds, this store is worth a look. Fast delivery and huge selection. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Have a good one.
clicktolearnandgrow.click – Found this today, content seems helpful and worth checking again.
One on one saves, goalkeeper shot stopping in isolated situations
Как я накрутил лайки в Телеграм – 20 лучших сервисов для быстрого результата https://vc.ru/2088822
超人和露易斯第四季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Сайт города Одесса https://faine-misto.od.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, культура, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей Одессы в удобном формате.
Сайт города Винница https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, экономика, культура и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей города.
Новости Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua сегодня: события города, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни Житомира онлайн.
Concacaf Gold Cup live scores, North American football championship updates
User-friendly online shop solution – Navigation is clear, and features are practical for small businesses.
海外华人必备的ify官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Hall of fame, greatest players and their career achievements celebrated
Curve shots, bending efforts and their success rates documented
Hi all, Lately found a great Indian pharmacy to save on Rx. For those looking for medicines from India safely, this site is very reliable. It has fast shipping to USA. Take a look: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]this site[/url]. Hope it helps.
курсы по seo [url=https://kursy-seo-1.ru/]kursy-seo-1.ru[/url] .
Hey there, I recently discovered a useful website to order prescription drugs cheaply. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is worth a look. They ship globally and huge selection. Link here: online pharmacy no prescription. Stay safe.
https://sonabet.pro/
Hi guys, I recently found an awesome resource for cheap meds. If you are tired of high prices and need affordable prescriptions, this store is a game changer. Great prices and it is safe. Visit here: click here. Have a good one.
真实的人类第二季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
超人和露易斯第一季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Портал города Хмельницкий https://faine-misto.km.ua с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения местных властей, происшествия, экономика, культура и развитие региона.
奇思妙探第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
статьи про digital маркетинг [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge.ru/]statyi-o-marketinge.ru[/url] .
If you need a reliable way to get around the city, renting a car in Auckland is often the easiest option. There are different vehicle classes, airport pickups, and flexible rental periods available: https://rentcarauckland.store/
Днепр онлайн https://faine-misto.dp.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
Live football scores with detailed match statistics, possession, shots, and player ratings
Hello, I recently discovered a great website to order generics securely. For those who need cheap meds, OnlinePharm is very good. Fast delivery and huge selection. See for yourself: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]onlinepharm.jp.net[/url]. Stay safe.
Remarkable issues here. I am very happy to peer
your article. Thank you so much and I’m having a look forward to touch you.
Will you please drop me a mail?
Consolation goals, late strikes in lost causes tracked
clarity insights – Clear visuals and structured content motivate users to act.
Head to head records, historical results between teams before matches
Strategic partnerships platform – Messaging is professional, and the site flows smoothly.
Автомобильный портал https://avtogid.in.ua с актуальной информацией об автомобилях. Новинки рынка, обзоры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и практические рекомендации для ежедневного использования авто.
One on one saves, goalkeeper shot stopping in isolated situations
Новости Киева https://infosite.kyiv.ua события города, происшествия, экономика и общество. Актуальные обзоры, аналитика и оперативные материалы о том, что происходит в столице Украины сегодня.
AFC Asian Cup live scores, continental championship with all matches tracked
Greetings, Lately discovered a great Indian pharmacy for cheap meds. For those looking for generic pills cheaply, IndiaPharm is highly recommended. You get fast shipping worldwide. Check it out: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
Business networking hub – Navigation is simple, and the platform works smoothly.
познавательный блог https://zefirka.net.ua с интересными статьями о приметах, значении имен, толковании снов, традициях, праздниках, советах на каждый день.
禁忌第一季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Hello, I recently discovered an excellent online drugstore where you can buy generics cheaply. For those who need cheap meds, this store is the best choice. Secure shipping and it is very affordable. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]onlinepharm.jp.net[/url]. Good luck with everything.
seo онлайн [url=https://kursy-seo-1.ru/]kursy-seo-1.ru[/url] .
真实的人类第一季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Volleys, spectacular strikes and their conversion rates
爱一凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
海外华人必备的yifan平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
一帆视频海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Hey everyone, I recently discovered a reliable international pharmacy to order pills securely. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this site is very good. Great prices plus huge selection. Link here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Thanks!
оптимизация сайта блог [url=https://statyi-o-marketinge.ru/]оптимизация сайта блог[/url] .
To be honest, I just ran into a reliable Mexican pharmacy for cheap meds. If you are tired of high prices and want meds from Mexico, this site is a game changer. They ship to USA plus it is safe. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Appreciate it.
Women’s football live scores, domestic and international matches tracked
To be honest, I recently discovered an awesome website for affordable pills. For those seeking and want meds from Mexico, this store is the best option. Great prices and it is safe. Visit here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Thanks!
Hey there, I wanted to share a useful source for meds for purchasing pills hassle-free. For those who need antibiotics, this site is very good. They ship globally and no script needed. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Kind regards.
internetagentur seo [url=https://internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru/]internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru[/url] .
Drive forward hub – The experience feels streamlined and easy from the start.
seo базовый курc [url=https://kursy-seo-2.ru/]kursy-seo-2.ru[/url] .
seo базовый курc [url=https://kursy-seo-3.ru/]kursy-seo-3.ru[/url] .
мостбет ставки [url=https://mostbet2027.help/]https://mostbet2027.help/[/url]
mostbet casino [url=https://mostbet2026.help]https://mostbet2026.help[/url]
Hey there, I recently came across a great website for affordable pills. If you want to save money and need affordable prescriptions, this site is worth checking out. No prescription needed and very reliable. Visit here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Hope it helps.
Объясняем сложные https://notatky.net.ua темы просто и понятно. Коротко, наглядно и по делу. Материалы для тех, кто хочет быстро разобраться в вопросах без профессионального жаргона и сложных определений.
Портал для пенсионеров https://pensioneram.in.ua Украины с полезными советами и актуальной информацией. Социальные выплаты, пенсии, льготы, здоровье, экономика и разъяснения сложных вопросов простым языком.
Блог для мужчин https://u-kuma.com с полезными статьями и советами. Финансы, работа, здоровье, отношения и личная эффективность. Контент для тех, кто хочет разбираться в важных вещах и принимать взвешенные решения.
бк мостбет скачать [url=www.mostbet2027.help]бк мостбет скачать[/url]
Ligue 1 live scores, French football including PSG matches tracked in real time
Coppa Italia livescore updates, Italian cup competition tracked in real time
Hi, To be honest, I found a great online drugstore for purchasing medications securely. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, this site is very good. Secure shipping plus huge selection. Check it out: OnlinePharm. Hope it helps.
мостбет оригинал скачать [url=https://mostbet2026.help]https://mostbet2026.help[/url]
Cutback assists, low crosses and their conversion rates tracked
Solo goals, individual brilliance and mazy runs tracked
Полтава онлайн https://u-misti.poltava.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
Портал города https://u-misti.odesa.ua Одесса с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения властей, происшествия, экономика, спорт, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Житомира https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Оперативные обновления, обзоры и важная информация о жизни Житомира онлайн.
seo с нуля [url=https://kursy-seo-2.ru/]kursy-seo-2.ru[/url] .
Hi, I just found a useful website where you can buy medications cheaply. If you are looking for antibiotics, OnlinePharm is very good. Fast delivery plus no script needed. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Peace.
ArtNovaAI has some really creative tools. The AI Ghibli style image generator is amazing for creating dreamy, anime-style visuals with beautiful details.
курс seo [url=https://kursy-seo-3.ru/]kursy-seo-3.ru[/url] .
Strategic discovery site – A minimal layout that communicates purpose effectively.
раскрутка сайта франция [url=https://internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru/]internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru[/url] .
Offside calls, VAR checked decisions and linesman flags documented
Greetings, Just now found a trusted resource for cheap meds. If you are tired of high prices and need generic drugs, this site is a game changer. No prescription needed and it is safe. Check it out: pharm.mex.com. Thanks!
爱一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
Captain performances, armband wearers and leadership statistics
code promo melbet melbet apk
World Cup qualifiers live score, road to the tournament tracked for all regions
Hello, Just now discovered a useful website to buy generics. If you need cheap antibiotics cheaply, this site is worth checking. You get secure delivery guaranteed. Take a look: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Hope it helps.
Новости Хмельницкого https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua сегодня на одном портале. Главные события города, решения властей, происшествия, социальная повестка и городская хроника. Быстро, понятно и по делу.
Львов онлайн https://u-misti.lviv.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Важные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни одного из крупнейших городов Украины.
Greetings, I recently discovered a reliable source for meds where you can buy generics securely. If you need safe pharmacy delivery, this site is the best choice. Great prices plus huge selection. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope it helps.
Новости Киева https://u-misti.kyiv.ua сегодня — актуальные события столицы, происшествия, политика, экономика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и ключевые темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
Течёт крыша? Не ограничивайтесь локальным ремонтом. Протечка — это симптом. Причина может быть в нарушении гидроизоляции krovelnye-raboty-molodechno.ru, износе покрытия или проблемах с вентиляцией. Наш мастер проведёт диагностику, найдёт корень проблемы и предложит варианты ремонта. Гарантия на все виды работ. Звоните и устраним течь навсегда.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ дешево – ТОП 50 сайтов в 2026 году
Подробности доступны для ознакомления https://vc.ru/2144115
Greetings, I just found a great website where you can buy generics securely. For those who need antibiotics, this site is the best choice. Secure shipping plus huge selection. Visit here: cheap pharmacy online. Kind regards.
big-bag-rus.ru — производитель биг-бэгов и контейнеров МКР (мешки МКР) из полипропилена: мягкая тара для перевозки и хранения сыпучих грузов. Подбор конструкции, размеры и грузоподъёмность под задачу, оптовые цены, доставка по России. Купить биг-бэги напрямую: https://big-bag-rus.ru/
Hello everyone, Just now discovered a great resource to save on Rx. For those seeking and want affordable prescriptions, Pharm Mex is worth checking out. Fast shipping and very reliable. Check it out: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]buy meds from mexico[/url]. Thank you.
Маленькая, но очень удобная квартира у самого моря (в городе). Балкон с видом на залив на сутки борисов. Идеально для одного-двоих. Свежий воздух и шум прибоя включены в стоимость.
seo базовый курc [url=https://kursy-seo-2.ru/]kursy-seo-2.ru[/url] .
Новости Днепра https://u-misti.dp.ua сегодня — актуальные события города, происшествия, экономика, политика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и главные темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
Винница онлайн https://u-misti.vinnica.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Главные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни города в удобном формате.
Актуальные новости https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua Черновцов на сегодня. Экономика, происшествия, культура, инфраструктура и социальные вопросы. Надёжные источники, регулярные обновления и важная информация для жителей города.
продвижение обучение [url=https://kursy-seo-3.ru/]kursy-seo-3.ru[/url] .
French Open livescore updates, Roland Garros matches tracked point by point live
Hello, I just found an excellent source for meds for purchasing pills online. If you are looking for antibiotics, OnlinePharm is the best choice. They ship globally and it is very affordable. Link here: online pharmacy no prescription. Best regards.
Penalty records, spot kick takers and goalkeeper save percentages
Visionary ideas platform – The setup makes it easy to understand from the start.
捕风追影线上看免费在线观看,海外华人专属官方认证平台,高清无广告体验。
World Cup 2026 qualifiers live score, road to USA Mexico Canada tournament
Как рассчитать проценты за пользование чужими средствами по статье 395 ГК РФ – быстро, просто и без ошибок. Смотрите, какую инструкцию можно использовать и какой онлайн-калькулятор поможет сэкономить время https://voronezh-tsk.ru/stati/raschet-protsentov-po-395-gk-rf/
Новости Днепра https://u-misti.dp.ua сегодня — актуальные события города, происшествия, экономика, политика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и главные темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
海外华人必备的iyf官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Городской портал https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua Черкасс — свежие новости, события, происшествия, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, городская хроника и полезная информация для жителей и гостей города.
интернет раскрутка [url=https://internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru/]internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru[/url] .
учиться seo [url=https://kursy-seo-11.ru/]учиться seo[/url] .
обучение продвижению сайтов [url=https://kursy-seo-5.ru/]обучение продвижению сайтов[/url] .
курсы seo [url=https://kursy-seo-4.ru/]курсы seo[/url] .
Greetings, I just found a useful website to order prescription drugs online. For those who need no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Secure shipping plus no script needed. Check it out: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]this site[/url]. Kind regards.
Накрутка подписчиков Телеграм – Мой рейтинг 32 полезных сайтов в 2026 году https://vc.ru/2153734
compte 1win 1win telecharger
ремонт подвального помещения [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena8.ru/]ремонт подвального помещения[/url] .
литокол гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena9.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena9.ru[/url] .
устранение протечек в подвале [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru[/url] .
усиление проёмов под панорамные окна [url=https://usilenie-proemov9.ru/]usilenie-proemov9.ru[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвала снаружи цены [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru[/url] .
усиление проему [url=https://usilenie-proemov10.ru/]usilenie-proemov10.ru[/url] .
Greetings, Lately discovered an awesome Mexican pharmacy for cheap meds. If you want to save money and want generic drugs, Pharm Mex is worth checking out. They ship to USA plus it is safe. Link is here: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]pharm.mex.com[/url]. Have a great week.
Hello, I just discovered a useful Indian pharmacy for cheap meds. For those looking for generic pills cheaply, this site is highly recommended. It has wholesale rates worldwide. Visit here: this site. Good luck.
Hi, I wanted to share an excellent source for meds for purchasing generics hassle-free. If you are looking for antibiotics, OnlinePharm is very good. Great prices plus huge selection. Check it out: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]click here[/url]. Many thanks.
pinco casino официальный скачать https://pinco-install-casino.ru
курс seo [url=https://kursy-seo-2.ru/]kursy-seo-2.ru[/url] .
Поставляем грунт https://organicgrunt.ru торф и чернозем с доставкой по Москве и Московской области. Подходит для посадок, благоустройства и озеленения. Качественные смеси, оперативная логистика и удобные условия для частных и коммерческих клиентов.
учиться seo [url=https://kursy-seo-3.ru/]kursy-seo-3.ru[/url] .
Hello, To be honest, I found a useful source for meds for purchasing pills securely. If you need cheap meds, this site is the best choice. Great prices plus no script needed. See for yourself: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]online pharmacy no prescription[/url]. Cya.
Hello, I recently discovered the best online drugstore for cheap meds. If you want to buy ED meds without prescription, IndiaPharm is very reliable. You get fast shipping guaranteed. Take a look: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Hope it helps.
продвижение обучение [url=https://kursy-seo-11.ru/]продвижение обучение[/url] .
Professional growth hub – The layout feels tidy and the content is easy to read.
侠之盗高清完整版智能AI观看体验优化,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
оптимизация сайта франция [url=https://internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru/]internet-prodvizhenie-moskva.ru[/url] .
Hey there, I recently discovered a great website where you can buy pills cheaply. For those who need cheap meds, OnlinePharm is highly recommended. Great prices plus no script needed. Link here: safe online drugstore. Many thanks.
продвижение обучение [url=https://kursy-seo-4.ru/]kursy-seo-4.ru[/url] .
усиление проемов [url=https://usilenie-proemov10.ru/]усиление проемов[/url] .
устранение протечек в подвале [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena8.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena8.ru[/url] .
технология усиления проема [url=https://usilenie-proemov9.ru/]usilenie-proemov9.ru[/url] .
seo онлайн [url=https://kursy-seo-5.ru/]seo онлайн[/url] .
Op zoek naar een casino? WinItt Casino biedt online gokkasten en live games. Het biedt snel inloggen, eenvoudige navigatie, moderne speloplossingen en stabiele prestaties op zowel computers als mobiele apparaten.
joycasino регистрация джойказино зеркало
гидроизоляция цена работы [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena9.ru/]гидроизоляция цена работы[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвала цена за м2 [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала цена за м2[/url] .
сырость в подвале многоквартирного дома [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru[/url] .
казино мостбет [url=https://mostbet2026.help/]казино мостбет[/url]
Hi, I wanted to share an excellent website where you can buy medications securely. For those who need no prescription drugs, this store is worth a look. Fast delivery plus huge selection. Check it out: buy meds online. Hope this was useful.
Hey guys, I just discovered a great online drugstore to save on Rx. If you want to buy generic pills at factory prices, this site is worth checking. They offer fast shipping worldwide. Take a look: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]indian pharmacy[/url]. Cheers.
однокомнатные квартиры в сочи жк светский лес
Hello everyone, I recently discovered an awesome Mexican pharmacy to buy medication. If you want to save money and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is a game changer. No prescription needed plus it is safe. Link is here: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]pharm.mex.com[/url]. Stay healthy.
Hi, I just found a great source for meds where you can buy prescription drugs cheaply. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this site is the best choice. Fast delivery plus it is very affordable. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]safe online drugstore[/url]. Appreciate it.
midnightquarry.shop – Bold branding stands out, pages load quickly and the shopping flow feels intuitive.
seo бесплатно [url=https://kursy-seo-11.ru/]seo бесплатно[/url] .
Idea-building platform – A creative environment that invites experimentation.
Hello everyone, I recently ran into a trusted website for affordable pills. If you want to save money and need generic drugs, Pharm Mex is a game changer. Great prices and secure. Take a look: pharm.mex.com. Good luck!
стоимость усиления проема [url=https://usilenie-proemov10.ru/]usilenie-proemov10.ru[/url] .
Hi, I just found a useful international pharmacy for purchasing pills securely. If you are looking for antibiotics, this site is the best choice. They ship globally plus huge selection. See for yourself: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Be well.
усиление проемов [url=https://usilenie-proemov9.ru/]усиление проемов[/url] .
гидроизоляция цена [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena9.ru/]гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвала [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала[/url] .
ремонт гидроизоляции фундаментов и стен подвалов [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena8.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena8.ru[/url] .
вертикальная гидроизоляция стен подвала [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru[/url] .
Hi all, I recently came across an amazing online drugstore for cheap meds. If you need ED meds cheaply, this store is worth checking. You get fast shipping guaranteed. Take a look: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]safe indian pharmacy[/url]. Best regards.
продвижение обучение [url=https://kursy-seo-4.ru/]kursy-seo-4.ru[/url] .
курс seo [url=https://kursy-seo-5.ru/]kursy-seo-5.ru[/url] .
Hey everyone, I wanted to share an excellent online drugstore for purchasing generics online. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, this store is highly recommended. Secure shipping and no script needed. Check it out: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]online pharmacy usa[/url]. Regards.
инъекционная гидроизоляция трещин [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta.ru/]инъекционная гидроизоляция трещин[/url] .
инъекционная гидроизоляция холодных швов [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta1.ru/]инъекционная гидроизоляция холодных швов[/url] .
курсы seo [url=https://kursy-seo-11.ru/]курсы seo[/url] .
Hey everyone, I wanted to share an excellent source for meds to order medications hassle-free. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, this site is worth a look. Secure shipping and it is very affordable. Check it out: safe online drugstore. Stay healthy.
усиление проему [url=https://usilenie-proemov10.ru/]usilenie-proemov10.ru[/url] .
стоимость усиления проема [url=https://usilenie-proemov9.ru/]usilenie-proemov9.ru[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвала гаража [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena9.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-czena9.ru[/url] .
ремонт в подвале [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-czena8.ru/]ремонт в подвале[/url] .
устранение протечек в подвале [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena8.ru[/url] .
Greetings, Just now ran into a trusted online source for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is highly recommended. No prescription needed plus very reliable. Link is here: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]Pharm Mex[/url]. Good luck with everything.
Hello everyone, Lately found a reliable online source for cheap meds. For those seeking and need affordable prescriptions, Pharm Mex is highly recommended. Fast shipping plus secure. Check it out: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]mexican pharmacy[/url]. Stay healthy.
сырость в подвале многоквартирного дома [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena9.ru[/url] .
Hello, I just found a great international pharmacy to order pills online. For those who need cheap meds, this site is very good. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. See for yourself: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Sincerely.
爱一番海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台结合大数据AI分析,支持全球加速观看。
Производим пластиковые https://zavod-dimax.ru окна и выполняем профессиональную установку. Качественные материалы, точные размеры, быстрый монтаж и гарантийное обслуживание для комфорта и уюта в помещении.
Изделия из пластмасс https://ftk-plastik.ru собственного производства. Продажа оптом и в розницу, широкий ассортимент, надёжные материалы и стабильные сроки. Выполняем заказы любой сложности по техническому заданию клиента.
Жалюзи от производителя https://balkon-pavilion.ru изготовление, продажа и профессиональная установка. Большой выбор дизайнов, точные размеры, надёжная фурнитура и комфортный сервис для квартир и офисов.
Производство оборудования https://repaircom.ru с предварительной разработкой и адаптацией под требования клиента. Качественные материалы, точные расчёты, соблюдение сроков и техническая поддержка.
愛海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
ваза для цветов на кладбище
seo бесплатно [url=https://kursy-seo-4.ru/]seo бесплатно[/url] .
Квартира с камином для уютных зимних вечеров! Просторная гостиная аренда квартиры на сутки гродно, полностью оборудованная кухня, два балкона. Тихий престижный район. Создайте свое настроение праздника в Гродно.
школа seo [url=https://kursy-seo-5.ru/]школа seo[/url] .
Matbet TV güncel adresi arıyorsanız işte burada. Maç izlemek için tıkla: https://matbet.jp.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada. Gençler, Matbet bahis son linki belli oldu.
инъекционная гидроизоляция своими руками [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta1.ru/]inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta1.ru[/url] .
Торговая мебель https://woodmarket-for-business.ru от производителя для бизнеса. Витрины, стеллажи, островные конструкции и кассовые модули. Индивидуальный подход, надёжные материалы и практичные решения для продаж.
Szukasz kasyna? kasyno online w Polsce: wybor najlepszych stron do gry. Licencjonowane platformy, popularne sloty i kasyna na zywo, wygodne metody platnosci, uczciwe warunki i aktualne oferty.
Ищешь блины для штанки? https://blin-na-shtangy.ru для эффективных силовых тренировок. Чугунные и резиновые диски, разные веса, долговечность и удобство использования. Решение для новичков и опытных спортсменов.
технология инъекционной гидроизоляции [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta.ru/]технология инъекционной гидроизоляции[/url] .
Производим торговую мебель https://woodmarket-for-business.ru для розничного бизнеса и сетевых магазинов. Функциональные конструкции, современный дизайн, точные размеры и полный цикл работ — от проекта до готового решения.
Оборудование для отопления https://thermostock.ru и водоснабжения: котлы, циркуляционные насосы, радиаторы, мембранные баки и комплектующие от ведущих производителей. Что вы получаете: сертифицированные товары, прозрачные цены, оперативную обработку заказа. Создайте комфортный микроклимат в доме — выбирайте профессионалов!
Нужен памятник? купить памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
https://vc.ru/1480580 Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм – 23 сервиса для заданий на 2026 год
Grandpashabet giris adresi laz?msa dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz giris yapmak icin [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Resmi Site[/url] Yuksek oranlar burada.
If you love to read Chudai ki kahaniya – Hindi Sex Story, you should visit the Free Sex Kahani dot in
If you love to read Chudai ki kahaniya – Hindi Sex Story, you should visit the Free Sex Kahani dot in
Нужен памятник? заказать памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Нужно авто? привоз авто из японии под заказ поиск, проверка, оформление и доставка авто из разных стран. Прозрачные условия, помощь на всех этапах и сопровождение сделки до получения автомобиля.
инъекционная гидроизоляция фундамента [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta1.ru/]инъекционная гидроизоляция фундамента[/url] .
сайт с закладками https://memori.ru/
Grandpashabet giriş adresi lazımsa işte burada. Sorunsuz giriş yapmak için [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Güncel[/url] Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
https://vc.ru/1555937 Накрутка комментариев ВКонтакте – 25 проверенных сайтов в 2026 году
инъекционная гидроизоляция стен [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta.ru/]инъекционная гидроизоляция стен[/url] .
дизайн студии 20 метров дизайн интерьера домов
Grandpasha giriş linki arıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Hızlı erişim için https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada.
Grandpashabet giris linki ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erisim icin Grandpashabet Bonus Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
ремонт бетонных конструкций жилой дом [url=https://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie4.ru/]remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie4.ru[/url] .
Накрутка подписчиков в Max (Макс ВК): 25 сервисов 2026 года https://vc.ru/1290185
Grandpasha güncel linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz giriş yapmak için tıkla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Нужен памятник? купить памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Расширенный обзор: https://dzen.ru/a/aVz0p7K_jnndhvSs
Grandpashabet guncel linki ar?yorsan?z iste burada. H?zl? erisim icin t?kla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]T?kla Git[/url] Deneme bonusu burada.
инъекционная гидроизоляция холодных швов [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta1.ru/]инъекционная гидроизоляция холодных швов[/url] .
ремонт бетонных конструкций компания [url=https://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie4.ru/]ремонт бетонных конструкций компания[/url] .
инъекционная гидроизоляция частный дом [url=https://inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta.ru/]inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya-fundamenta.ru[/url] .
Нужен проектор? http://projector24.ru большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
Dostlar selam, Vaycasino oyuncuları adına kısa bir duyuru paylaşıyorum. Malum Vaycasino adresini tekrar güncelledi. Erişim sorunu yaşıyorsanız panik yapmayın. Son Vaycasino giriş linki artık aşağıdadır: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Kayıt[/url] Bu link üzerinden doğrudan siteye girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis keyfi sürdürmek için Vaycasino doğru adres. Herkese bol şans dilerim.
Matbet TV giriş linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Hızlı için tıkla: [url=https://matbet.jp.net/#]Matbet Üyelik[/url] Yüksek oranlar bu sitede. Gençler, Matbet yeni adresi açıklandı.
Matbet giris linki laz?msa dogru yerdesiniz. H?zl? icin t?kla: https://matbet.jp.net/# Yuksek oranlar burada. Gencler, Matbet son linki ac?kland?.
Arkadaşlar selam, Casibom sitesi üyeleri adına kısa bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Herkesin bildiği üzere bahis platformu adresini BTK engeli yüzünden yine değiştirdi. Siteye ulaşım hatası varsa doğru yerdesiniz. Çalışan Casibom güncel giriş linki artık burada Casibom Güncel Giriş Paylaştığım bağlantı ile vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza bağlanabilirsiniz. Ek olarak kayıt olanlara verilen yatırım bonusu fırsatlarını da kaçırmayın. Lisanslı casino deneyimi sürdürmek için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
ремонт бетонных конструкций трещины [url=https://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie4.ru/]ремонт бетонных конструкций трещины[/url] .
ко ланта ко ланте
Снизить платеж по кредиту можно за счет нового договора. Онлайн сервисы предлагают разные варианты. Подбор кредита учитывает текущие обязательства. Это помогает избежать просрочек. Финансовое планирование становится проще – spisok-kreditov.ru
Matbet guncel linki laz?msa iste burada. Mac izlemek icin t?kla: [url=https://matbet.jp.net/#]Matbet Yeni Adres[/url] Yuksek oranlar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet yeni adresi belli oldu.
Play doodle baseball game, the ultimate Fourth of July food baseball game! Celebrate Independence Day, hit home runs, and enjoy classic snacks online for free.
Polaroid AI Photo Generator lets you instantly create retro, vintage-style Polaroid photos with realistic white borders and nostalgic film effects.
Accurate dog age calculator based on AVMA guildelines. Calculate your dog`s age in human years instantly with our science- based tool.
EV charging stations supply electricity to recharge an electric car’s battery. They range from slow home chargers to fast public DC chargers that can refill most of a battery in under an hour – https://ev.motorwatt.com/ev-manufacturers/
Matbet güncel linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Maç izlemek için: https://matbet.jp.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada. Arkadaşlar, Matbet yeni adresi açıklandı.
Matbet guncel adresi ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. H?zl? icin: Matbet Uyelik Canl? maclar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet yeni adresi belli oldu.
ремонт бетонных конструкций технология [url=https://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie4.ru/]ремонт бетонных конструкций технология[/url] .
Matbet giriş linki lazımsa işte burada. Sorunsuz için tıkla: https://matbet.jp.net/# Canlı maçlar burada. Arkadaşlar, Matbet son linki belli oldu.
Нужен проектор? https://projector24.ru/ большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
Замените окна в Молодечно! Современные ПВХ окна — решение для комфорта kupit-plastikovoye-okno-molodechno.ru. Энергосбережение и долговечность.
Arkadaşlar selam, Vaycasino kullanıcıları için kısa bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Malum platform giriş linkini tekrar güncelledi. Erişim sorunu varsa endişe etmeyin. Yeni siteye erişim linki artık aşağıdadır: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino 2026[/url] Bu link ile vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis deneyimi sürdürmek için Vaycasino doğru adres. Herkese bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
BMW electric vehicles focus on luxury, sporty handling, and premium interiors. Models like the i4, iX, and i7 combine performance with cutting-edge digital features: https://ev.motorwatt.com/ev-manufacturers/
Перекредитование в Казахстане позволяет объединить кредиты в один. Это упрощает контроль платежей. Онлайн оформление ускоряет процесс. Подбор кредита помогает выбрать оптимальный вариант. Управление долгами становится удобнее: https://spisok-kreditov.ru/08_refinansirovanie-kredita.html/
гидроизоляция подвала грунтовые воды [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвала гарантия [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara5.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara5.ru[/url] .
мебель для кухни спб от производителя [url=https://kuhni-spb-25.ru/]kuhni-spb-25.ru[/url] .
This post is very helpful and informative. I like how you explained the topic clearly and simply. The content is well-organized and practical. Great job and keep it up.
visit this website https://xingba102.com/
Philly roofing? Roofers in Philly new roof installation, leak repair, restoration, and maintenance of roofing systems. Experienced specialists, modern technologies, reliable materials, and a personalized approach to each project.
свит бонанза 1000 демо в рублях
сайт ai
Перекредитование в Казахстане подходит тем, у кого несколько активных займов. Все кредиты можно объединить в один. Это помогает снизить общий платеж. Онлайн подбор кредита упрощает поиск нового предложения. Финансовая нагрузка становится более предсказуемой – https://spisok-kreditov.ru/02_kredit-nalichnymi.html/
What’s up Dear, are you actually visiting this website on a regular basis, if so afterward you will definitely obtain pleasant know-how.
byueuropaviagraonline
сгенерировать текстовая нейросеть
краби остров в тайланде фото ко ланта
Excellent article! The information is relevant and explained in a straightforward way. I found this post very useful and enjoyable to read. Thank you for providing quality content.
visit this website https://9221146.com/
Grandpasha giriş adresi arıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erişim için https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yüksek oranlar bu sitede.
создать картинку нейросетью пиксель арт
Nissan electric vehicles include popular models like the Nissan Leaf and Ariya. They are known for affordability, reliability, and practical daily use https://ev.motorwatt.com/ev-manufacturers/
кухни на заказ в спб недорого [url=https://kuhni-spb-25.ru/]kuhni-spb-25.ru[/url] .
Many players explore Mateslots app before registration.
гидроизоляция подвала утепление [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru[/url] .
нарисовать фон маслом
indwin app download old version
гидроизоляция подвала грунтовые воды [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara5.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara5.ru[/url] .
Промокод Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
семейный юрист Представительство в судах – это комплексная услуга, освобождающая клиента от необходимости самостоятельно разбираться в хитросплетениях судебного процесса. Юрист берет на себя все заботы, связанные с подготовкой документов, участием в заседаниях и представлением интересов клиента.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот демо Gates of Olympus Super Scatter казино играть: Испытайте свою удачу в лучших онлайн-казино и сорвите джекпот в Gates of Olympus Super Scatter.
Битгет реферальный код Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
алименты Юрист – это не просто профессия, это призвание помогать людям в сложных жизненных ситуациях, защищать их права и законные интересы. В мире, где правовые нормы постоянно меняются, а законы становятся все более запутанными, квалифицированная юридическая помощь становится необходимостью.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter demo Gates of Olympus Super Scatter играть: Почувствуйте себя избранником богов Олимпа! Каждое вращение барабанов – это шанс сорвать куш и навсегда изменить свою жизнь.
ТОП-25 сервисов чтобы накрутить подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно в 2026 году (Разбор от эксперта) https://vc.ru/1402847
Проблемы с авто? автоэлектрик фольксваген спб диагностика, ремонт электрооборудования, блоков управления, освещения и систем запуска. Опыт, современное оборудование и точное определение неисправностей.
арбитраж +споры Раздел совместно нажитого имущества – это один из самых сложных и конфликтных вопросов при разводе. Семейный юрист поможет вам справедливо разделить имущество, учитывая все нюансы вашей ситуации и требования законодательства.
Бонусы Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
Herkese merhaba, bu site oyuncular? icin onemli bir duyuru paylas?yorum. Bildiginiz gibi Vaycasino giris linkini tekrar degistirdi. Giris hatas? varsa panik yapmay?n. Son Vay Casino giris linki art?k asag?dad?r: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Twitter[/url] Bu link ile direkt siteye girebilirsiniz. Guvenilir casino deneyimi icin Vay Casino dogru adres. Tum forum uyelerine bol kazanclar dilerim.
Herkese selam, Vaycasino kullan?c?lar? ad?na onemli bir duyuru paylas?yorum. Bildiginiz gibi Vaycasino adresini tekrar degistirdi. Erisim hatas? varsa endise etmeyin. Guncel Vaycasino giris linki su an asag?dad?r: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Uyelik[/url] Paylast?g?m baglant? ile direkt hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Lisansl? casino keyfi surdurmek icin Vay Casino dogru adres. Herkese bol sans temenni ederim.
Awesome issues here. I am very satisfied to see your article. Thank you so much and I am taking a look forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
https://freefreightaudit.ca/2024/08/28/zerkalo-daddy-akcii-i-bonusy-ot-kazino-zerkalo/
Grandpasha güncel adresi arıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erişim için [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Kayıt[/url] Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter slot Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот играть – это просто и увлекательно. Интуитивно понятный интерфейс и захватывающий геймплей не дадут вам заскучать.
юрист Арбитраж споры – это альтернативный способ разрешения конфликтов, который позволяет избежать длительных и дорогостоящих судебных разбирательств. Юрист поможет вам выбрать оптимальную стратегию арбитражного разбирательства и защитить ваши интересы.
юрист в суд Арбитраж споры – это эффективный способ разрешения конфликтов, позволяющий избежать длительных и дорогостоящих судебных разбирательств. Юрист поможет выбрать оптимальную стратегию арбитражного разбирательства и добиться выгодного решения для своего клиента.
https://vc.ru/1688068 – Куда можно подписать контракт на СВО Россия 2026
Бонусы Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
Gençler, Grandpashabet Casino son linki belli oldu. Giremeyenler buradan devam edebilir Grandpashabet Mobil
Реферальный код Bitget Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
Накрутка зрителей в Твич – ТОП-25 способов в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1419929
семейный юрист Юрист – это архитектор правовой защиты, чья миссия заключается в создании надежного фундамента для безопасности и процветания своих клиентов. Обладая глубокими знаниями законодательства и многолетним опытом, он служит компасом в лабиринте юридических норм, помогая ориентироваться в сложных ситуациях и находить оптимальные решения.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter играть Gates of Olympus Super Scatter casino: Найдите лучшее онлайн-казино с высокими выплатами и щедрыми бонусами, чтобы увеличить свои шансы на победу в Gates of Olympus Super Scatter.
изготовление кухонь на заказ в санкт петербурге [url=https://kuhni-spb-25.ru/]kuhni-spb-25.ru[/url] .
кухни на заказ в спб цены [url=https://kuhni-spb-26.ru/]kuhni-spb-26.ru[/url] .
Celebrity World Care https://celebrityworldcare.com интернет-магазин профессиональной медицинской и натуральной косметики для ухода за кожей при ихтиозе, дерматитах, псориазе и других дерматологических состояниях. Сертифицированные средства с мочевиной, без отдушек и парабенов. Доставка по России.
купить кухню [url=https://kuhni-spb-27.ru/]купить кухню[/url] .
кухни на заказ санкт петербург от производителя [url=https://kuhni-spb-29.ru/]kuhni-spb-29.ru[/url] .
кухни на заказ петербург [url=https://kuhni-spb-31.ru/]kuhni-spb-31.ru[/url] .
кухни под заказ спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-30.ru/]кухни под заказ спб[/url] .
купить кухню в спб от производителя [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]купить кухню в спб от производителя[/url] .
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот Gates of Olympus Super Scatter демо: Испытайте гнев богов без последствий для вашего кошелька! Демо-версия слота позволит вам в полной мере насладиться захватывающим геймплеем и узнать все секреты Super Scatter.
гидроизоляция подвала в домe [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала в домe[/url] .
Промокод Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
алименты Юрист – это архитектор правовой защиты, чья миссия заключается в создании надежного фундамента для безопасности и процветания своих клиентов. Обладая глубокими знаниями законодательства и многолетним опытом, он служит компасом в лабиринте юридических норм, помогая ориентироваться в сложных ситуациях и находить оптимальные решения.
Herkese selam, Vay Casino kullanıcıları adına kısa bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi platform adresini yine değiştirdi. Giriş sorunu varsa endişe etmeyin. Güncel Vaycasino giriş adresi şu an burada: Vaycasino Güncel Paylaştığım bağlantı ile doğrudan hesabınıza erişebilirsiniz. Lisanslı bahis deneyimi için Vay Casino doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
гидроизоляция подвала монтаж [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara5.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала монтаж[/url] .
юрист Бизнес консультирование – это инвестиции в будущее компании, позволяющие избежать юридических рисков и обеспечить стабильный рост. Юрист поможет разработать грамотную правовую политику, защитить интеллектуальную собственность и обеспечить соблюдение законодательства.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter казино в рублях Gates of Olympus Super Scatter casino: Найдите лучшее онлайн-казино с высокими выплатами и щедрыми бонусами, чтобы увеличить свои шансы на победу в Gates of Olympus Super Scatter.
Промокод Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
юрист в суд Арбитраж споры – это эффективный способ разрешения конфликтов, позволяющий избежать длительных и дорогостоящих судебных разбирательств. Юрист поможет выбрать оптимальную стратегию арбитражного разбирательства и добиться выгодного решения для своего клиента.
https://spisok-kreditov.ru/ подбор и сравнение предложений по кредитам и займам в Казахстане. На сайте можно посмотреть условия, требования и примерный расчет платежа, затем перейти к оформлению заявки онлайн. Решение по заявке принимает выбранный кредитор.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike.
https://aircooled-rd.com/
Бонусы Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter казино играть Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот: Классическая тематика в современной интерпретации. Насладитесь атмосферой Древней Греции и откройте для себя новые горизонты азарта.
https://t.me/companybitforge BitForge — создаём IT-продукты, которые работают Web • Software • AI • Automation
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter игровой автомат Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот: Классическая тематика в современной интерпретации. Насладитесь атмосферой Древней Греции и откройте для себя новые горизонты азарта.
Бонусы Реферальный код Bitget GPFZDXVL — скидка 20% на комиссии с первой сделки Зачем переплачивать бирже, если можно сразу торговать дешевле? Код вводится при регистрации и работает бессрочно. Бонус — до 6200 USDT за выполнение заданий. Забыли ввести? Bitget даёт 14 дней на добавление кода после создания аккаунта.
кухни на заказ спб каталог [url=https://kuhni-spb-25.ru/]kuhni-spb-25.ru[/url] .
расчет платежа по кредиту подбор и сравнение предложений по кредитам и займам в Казахстане. На сайте можно посмотреть условия, требования и примерный расчет платежа, затем перейти к оформлению заявки онлайн. Решение по заявке принимает выбранный кредитор.
Winchester Outdoor Club – Educational and well-presented, community involvement is highlighted naturally.
ленинградские кухни [url=https://kuhni-spb-26.ru/]kuhni-spb-26.ru[/url] .
Business alliance resources – Clear and practical, the ideas are easy to follow.
Creative Solutions Hub – Clear and engaging, content encourages innovative approaches to challenges.
Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот демо Gates of Olympus Super Scatter слот: Классическая тематика в современной интерпретации. Насладитесь атмосферой Древней Греции и откройте для себя новые горизонты азарта.
где заказать кухню в спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-29.ru/]где заказать кухню в спб[/url] .
ленинградские кухни [url=https://kuhni-spb-30.ru/]ленинградские кухни[/url] .
Matbet guncel linki ar?yorsan?z iste burada. Sorunsuz icin t?kla: Resmi Site Yuksek oranlar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet bahis son linki belli oldu.
Dostlar selam, bu site oyuncuları adına kısa bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi Vaycasino giriş linkini tekrar güncelledi. Giriş sorunu yaşıyorsanız endişe etmeyin. Yeni siteye erişim linki şu an burada: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vay Casino Apk[/url] Bu link üzerinden direkt hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir casino deneyimi için Vay Casino doğru adres. Herkese bol şans dilerim.
современные кухни на заказ в спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-31.ru/]kuhni-spb-31.ru[/url] .
гидроизоляция подвала ремонт [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru/]gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara4.ru[/url] .
кухни под заказ в спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-27.ru/]kuhni-spb-27.ru[/url] .
кухни на заказ в санкт-петербурге [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]кухни на заказ в санкт-петербурге[/url] .
квартиры жк жк светский лес сочи
сколько стоит химчистка обуви химчистка обуви
кредит с плохой кредитной историей казахстан подбор и сравнение предложений по кредитам и займам в Казахстане. На сайте можно посмотреть условия, требования и примерный расчет платежа, затем перейти к оформлению заявки онлайн. Решение по заявке принимает выбранный кредитор.
гидроизоляция подвала в домe [url=https://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara5.ru/]гидроизоляция подвала в домe[/url] .
dailydealhub – Excellent offers daily, shopping is fast and worry-free.
bondstrategyclick – Recommendations are clear and actionable, strengthened our bonding initiatives.
commercialgatewayportal – Quick and reliable platform, excellent for building professional connections.
Grandpasha giriş linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erişim için tıkla Hemen Oyna Deneme bonusu burada.
кредитный калькулятор подбор и сравнение предложений по кредитам и займам в Казахстане. На сайте можно посмотреть условия, требования и примерный расчет платежа, затем перейти к оформлению заявки онлайн. Решение по заявке принимает выбранный кредитор.
socialbridgeonline – Great place to meet people and share common interests effortlessly.
businessconnect – Very useful platform, helped me build solid partnerships.
bizinsights – Detailed and practical, enhanced my business decision-making.
Meaningful Work Hub – Energetic and uplifting, content encourages consistent creative practice.
taskoptimizer – Effective approaches, really improved my work efficiency today.
planinsights – Clear strategies, made planning projects straightforward.
OBDNet car diagnostics – User-friendly and informative, resources feel useful for everyday troubleshooting.
retailinnovationhub – Interface is clear and smooth, shopping online is very convenient.
topshophub – Convenient platform, navigating products and checking out is very fast.
businessvaluealliances – Helpful perspective on building alliances designed to last.
efficient purchase guide – User-friendly interface made online purchases fast and stress-free.
кухни от производителя спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-26.ru/]кухни от производителя спб[/url] .
modern business strategies – Practical insights that improved today’s planning and overall execution.
современные кухни на заказ в спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-29.ru/]современные кухни на заказ в спб[/url] .
кухни на заказ спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-30.ru/]кухни на заказ спб[/url] .
onlinebuyingcenter – Shopping here is simple, order processing was extremely quick.
кухни от производителя спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-31.ru/]kuhni-spb-31.ru[/url] .
Growth-focused resources – Well thought out, the focus on steady improvement really stands out.
кухни на заказ в санкт-петербурге [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]кухни на заказ в санкт-петербурге[/url] .
кухни на заказ санкт петербург [url=https://kuhni-spb-27.ru/]кухни на заказ санкт петербург[/url] .
networkgrowthhub – Alliance ideas are effective, accelerated networking opportunities efficiently.
Herkese selam, Vaycasino oyuncuları için kısa bir duyuru paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi Vaycasino adresini tekrar değiştirdi. Erişim sorunu varsa endişe etmeyin. Güncel Vay Casino giriş adresi artık aşağıdadır: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Üyelik[/url] Bu link üzerinden doğrudan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Lisanslı bahis keyfi sürdürmek için Vaycasino doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
actionablebiztips – Very useful guidance, helped me make smarter business decisions quickly.
Herkese merhaba, Vaycasino kullanıcıları için kısa bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Malum platform adresini tekrar güncelledi. Giriş hatası varsa panik yapmayın. Yeni Vay Casino giriş linki artık burada: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Bu link ile direkt hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir casino deneyimi sürdürmek için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol şans temenni ederim.
digitalshoppinghub – Flexible platform, online purchases were smooth and hassle-free.
Gencler, Grandpashabet Casino son linki belli oldu. Giremeyenler buradan giris yapabilir Grandpashabet Indir
Happiness Tips Hub – Friendly and practical, posts inspire positive habits for everyday life.
shoppinginsightszone – Very helpful tips, site makes buying products simple and smooth.
speedycommercehub – Easy to use platform, buying digital products was very efficient.
dailyideasclick – Actionable advice is clear, made daily work processes smoother.
collaboration growth hub – Helpful strategies that strengthened long-term business alliances.
thinkforward – Actionable insights, made planning and execution smoother.
Gardens AL Updates – Well-organized and calm, residents can find info quickly.
trusted alliance network – Solid advice that made expanding enterprise relationships much easier.
corporate growth roadmap – Practical insights that improved alignment and accelerated business partnerships.
dailyshoppinghub – Super convenient site, got all my essentials delivered quickly.
energywisehub – Practical tips that make saving energy easy every day.
кухни под заказ [url=https://kuhni-spb-26.ru/]kuhni-spb-26.ru[/url] .
Grandpasha güncel adresi lazımsa işte burada. Sorunsuz giriş yapmak için tıkla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet 2026[/url] Yüksek oranlar bu sitede.
бизнес консультирование Представительство в судах – это комплексная услуга, освобождающая клиента от необходимости самостоятельно разбираться в хитросплетениях судебного процесса. Юрист берет на себя все заботы, связанные с подготовкой документов, участием в заседаниях и представлением интересов клиента.
кухни на заказ в спб цены [url=https://kuhni-spb-29.ru/]кухни на заказ в спб цены[/url] .
Gencler, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Giremeyenler buradan devam edebilir Grandpashabet Kay?t
заказать кухню спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-30.ru/]заказать кухню спб[/url] .
corporatebizlearning – Informative content, easy to navigate and follow.
семейный юрист Юрист в суд – это опытный боец, готовый отстаивать вашу позицию в зале заседаний. Он внимательно изучит ваше дело, разработает стратегию защиты и представит ваши интересы перед судом, используя весь арсенал юридических инструментов.
кухни под заказ [url=https://kuhni-spb-31.ru/]kuhni-spb-31.ru[/url] .
planningstrategyclick – Guidance is concise and helpful, made planning meetings more productive.
corporateconnectportal – Strong networking platform, extremely helpful for linking with industry professionals.
skillsforfuture – Lessons are well-structured, helped me enhance abilities for upcoming challenges.
арбитраж +споры Юрист в суд – это опытный боец, готовый отстаивать вашу позицию в зале заседаний. Он внимательно изучит ваше дело, разработает стратегию защиты и представит ваши интересы перед судом, используя весь арсенал юридических инструментов.
заказать кухню в спб от производителя недорого [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]kuhni-spb-28.ru[/url] .
This article is informative, well-organized, and easy to follow. The explanations are practical, making the topic easier to understand.
visit this website https://herbaldietnow.com/
buildstrategicpath – Strategy planning here is very useful, helped me organize future initiatives effectively.
Explore Digital – Informative and easy to read, posts provide clear explanations of tech subjects.
кухни на заказ в спб недорого [url=https://kuhni-spb-27.ru/]kuhni-spb-27.ru[/url] .
alliance planning guide – Practical tips that helped map out long-term partnerships successfully.
smartbuyguide – Excellent tips, helped make online purchases simple and hassle-free.
Long-term business hub – Trustworthy feel overall, the focus on lasting partnerships feels genuine.
представительство в судах Юрист – это архитектор правовой защиты, чья миссия заключается в создании надежного фундамента для безопасности и процветания своих клиентов. Обладая глубокими знаниями законодательства и многолетним опытом, он служит компасом в лабиринте юридических норм, помогая ориентироваться в сложных ситуациях и находить оптимальные решения.
бизнес консультирование Юрист в суд – это стратег и тактик, превращающий правовые аргументы в мощное оружие. Тщательно анализируя материалы дела, он выстраивает линию защиты, способную убедить суд в правоте его клиента. Его речь – это искусство убеждения, способное изменить ход событий.
next-gen retail portal – Efficient browsing and modern design enhance the shopping experience.
strategicvisionhub – Clear guidance, made choosing next directions much easier.
strategicpartnershiphub – Very informative, made understanding partnership structures simpler and quicker.
бизнес консультирование Раздел совместно нажитого имущества – это один из самых сложных и конфликтных вопросов при разводе. Семейный юрист поможет вам справедливо разделить имущество, учитывая все нюансы вашей ситуации и требования законодательства.
businesslearningclickhub – Content is structured well, made understanding business concepts simple.
юрист в суд Представительство в судах – это комплексная услуга, освобождающая клиента от необходимости самостоятельно разбираться в хитросплетениях судебного процесса. Юрист берет на себя все заботы, связанные с подготовкой документов, участием в заседаниях и представлением интересов клиента.
бизнес консультирование Раздел совместно нажитого имущества – это один из самых сложных и конфликтных вопросов при разводе. Семейный юрист поможет вам справедливо разделить имущество, учитывая все нюансы вашей ситуации и требования законодательства.
businessconnecthub – Excellent platform for networking, made connecting with professionals very easy.
Mobihub provides a practical solution for proxy-based businesses. Real LTE IPs improve success rates. Flexible settings adapt to different tasks. Management tools simplify operations. This increases productivity: proxy for android apk
расстояние от бангкока до краби пхукет ко ланта
truck load booking service
innovationideasclick – Inspiring content, really encouraged me to start a new venture.
Arkadaşlar selam, bu site kullanıcıları adına önemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi Vaycasino adresini yine güncelledi. Giriş hatası yaşıyorsanız endişe etmeyin. Son siteye erişim linki artık aşağıdadır: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Lisanslı bahis keyfi için Vay Casino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol şans temenni ederim.
businessconnecttools – Helped our teams coordinate tasks quickly and efficiently.
бизнес консультирование Арбитраж споры – это эффективный способ разрешения конфликтов, позволяющий избежать длительных и дорогостоящих судебных разбирательств. Юрист поможет выбрать оптимальную стратегию арбитражного разбирательства и добиться выгодного решения для своего клиента.
smartshoppingcenter – Convenient platform, made ordering products online straightforward.
Matbet guncel adresi laz?msa dogru yerdesiniz. Mac izlemek icin: https://matbet.jp.net/# Canl? maclar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet bahis yeni adresi belli oldu.
Mobihub provides maximum proxy speed with no artificial limits. Users can select IP rotation by timer or by link. This flexibility is useful for automation tasks. The service supports HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5 protocols. All protocols work through a single port: 4g mobile proxies
professionalteambonds – Teamwork strategies are effective, improved project cooperation significantly.
team collaboration resource – Practical advice that streamlined building long-term corporate relationships.
trustedsystemshub – Extremely practical tips that startups can rely on for infrastructure decisions.
Pathfinder Hub – Exciting and approachable, resources provide multiple options to explore.
globalecommercehub – Very smooth experience, locating products and checking out was simple.
smartretailclick – Selection of items is excellent, shopping made very easy.
secure enterprise alliances – Actionable strategies that supported safe and effective business deals.
Купить подписчиков в ТТ бесплатно – ТОП-25 сервисов https://vc.ru/1402569
professionallink – Practical advice, made professional networking effortless and effective.
strategiccollaboration – Practical strategies, made managing global partnerships simpler.
innovativebizideas – Insightful suggestions, gave clarity on exploring new business directions.
Padel Oviedo Center – Friendly and clear, updates provide useful guidance for enthusiasts.
Arkadaşlar selam, Vaycasino oyuncuları adına önemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site giriş linkini tekrar değiştirdi. Giriş sorunu yaşıyorsanız panik yapmayın. Yeni Vay Casino giriş adresi şu an burada: Vaycasino 2026 Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir casino deneyimi sürdürmek için Vaycasino doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
Модульные дома https://modulndom.ru под ключ: быстрый монтаж, продуманные планировки и высокое качество сборки. Подходят для круглогодичного проживания, отличаются энергоэффективностью, надежностью и возможностью расширения.
Industry partnership hub – Nicely positioned, it feels targeted to active companies.
25 надежных сервисов накрутки просмотров в Инстаграм 2026 https://vc.ru/1483976
сколько зарабатывает truck dispatcher на старте
developskillsportal – Helpful professional tips, really enhanced learning and career advancement strategies.
corporatelinkclick – Connected with multiple professionals efficiently, platform works smoothly.
Накрутка подписчиков Инстаграм платно – ТОП-22 проверенных сервисов для быстрого продвижения в социальных сетях Мой опыт https://vc.ru/2227232
innovativestoreclick – Modern retail options and easy navigation improved my shopping experience.
creative insight source – Thought-provoking concepts that helped generate new project directions.
https://unibetsru.com/
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet Casino son linki açıklandı. Giremeyenler buradan giriş yapabilir https://grandpashabet.in.net/#
Grow & Share – Inviting and practical, content inspires users to learn and contribute together.
smartshoppingcenter – Fast and intuitive, platform made global shopping hassle-free.
Медицинские справки детям https://med-spravki-msk.ru
longtermbondinsights – Guides are highly useful, made long-term financial planning simpler.
partnershipinsights – Offers clear guidance for forming and maintaining corporate partnerships.
knowledge growth tips – Clear explanations that accelerated learning and comprehension.
growthstrategist – Detailed roadmaps, allowed better alignment of business goals.
Gardens AL Local News – Calm and informative, the site helps residents stay up to date with neighborhood happenings.
dispatch service without contract
teamlinker – Made collaboration seamless, helped our team work together efficiently.
business alliance insights – Clear recommendations for expanding professional alliances.
clickforprofessionaladvice – Tips shared are practical and useful, helped me handle work tasks more effectively.
Matbet TV giriş adresi arıyorsanız işte burada. Sorunsuz için: Matbet TV Yüksek oranlar bu sitede. Arkadaşlar, Matbet yeni adresi belli oldu.
Специализированный коррекционно-речевой https://neyroangel.ru детский сад для детей с особенностями развития в Москве. Беремся за самые тяжелые случаи, от которых отказываются другие. Нейропсихолог, логопед, запуск речи. Государственная лицензия: Л035-01298-77/01604531 от 09.12.24
smartlearningcenter – Learning platform is intuitive, allowed me to advance my knowledge fast.
Grandpashabet guncel adresi ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz giris yapmak icin t?kla Hemen Oyna Yuksek oranlar burada.
planning outlook page – Valuable advice that made future initiatives more organized.
safecommercehub – Platform is reliable, made online shopping quick and easy.
Growth Every Day – Inspiring and clear, content encourages consistent self-improvement steps.
Massage treatment center – Calm layout, the details about services are presented clearly.
кухня по индивидуальному заказу спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-32.ru/]kuhni-spb-32.ru[/url] .
вывод из запоя с выездом [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом[/url] .
вывод из запоя краснодар наркология [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
точность прогноза креативов 95% [url=https://reklamnyj-kreativ4.ru/]reklamnyj-kreativ4.ru[/url] .
growthconnectionguide – Tips are practical and easy to implement for real business results.
global network guide – Practical advice that enhanced outreach and collaboration with global partners.
срочный выезд нарколога на дом [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-1.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-1.ru[/url] .
ideamarketexplorer – Market recommendations are practical, really improved campaign efficiency.
Dostlar selam, Vay Casino oyuncuları adına kısa bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi platform adresini tekrar değiştirdi. Erişim hatası varsa panik yapmayın. Yeni Vaycasino giriş adresi şu an burada: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Bu link ile doğrudan siteye girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir casino deneyimi için Vay Casino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol şans dilerim.
большая кухня на заказ [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]kuhni-spb-28.ru[/url] .
Рэмси Диагностика: https://remsi-med.ru Сеть высокотехнологичных диагностических центров (МРТ, КТ). Точные исследования на оборудовании экспертного класса и качественная расшифровка снимков.
trusted checkout experience – Everything from cart to payment felt stable and user friendly.
marketflow – Well-designed platform, made online shopping more enjoyable.
Travis Anderson handmade shop – Thoughtful and authentic, every item looks well made.
Детский Доктор: https://kidsmedic.ru Специализированный медицинский центр для детей. Квалифицированная помощь педиатров и узких специалистов для здоровья вашего ребенка с первых дней жизни.
dealzone – Excellent resource, items were easy to locate.
proconnectnetwork – A solid hub for building meaningful corporate relationships.
professionalconnectionzone – Platform provides helpful tips for business relationships, very effective for networking.
Накрутка лайков ВК – Проверенные методы и рейтинг 21 сайта в 2026 году (Проверь на практике)
Все подробности доступны здесь: https://vc.ru/1970430
partnership roadmap resource – Actionable insights that supported structured planning and sustainability.
trustnetworkhub – Connecting with professionals worldwide is smooth, platform is very intuitive and reliable.
globaltrustbuy – User-friendly and efficient, completed my orders effortlessly.
Полесская ЦРБ: https://polesskcrb.ru Официальный портал центральной районной больницы Калининградской области. Информация об услугах, расписание врачей и важные новости здравоохранения для жителей региона.
7k casino предоставляет доступ к популярным слотам и классическим играм. Пользователь может выбирать формат игры под свои предпочтения. Система работает стабильно. Загрузка игр происходит быстро. Это повышает общее удобство: 7k casino регистрация
secure e-commerce guide – Quick browsing and safe transactions made shopping enjoyable.
Matbet guncel linki ar?yorsan?z iste burada. Sorunsuz icin t?kla: https://matbet.jp.net/# Yuksek oranlar burada. Gencler, Matbet bahis son linki ac?kland?.
corporatebondportal – Very practical and clear advice, useful for everyday business planning.
алкоголизм вывод из запоя краснодар [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru[/url] .
проектор для фильмов интернет-магазин проекторов
Grandpashabet giriş linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erişim için tıkla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Resmi Site[/url] Yüksek oranlar bu sitede.
вывод из запоя цена краснодар [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
кухни под заказ спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-32.ru/]kuhni-spb-32.ru[/url] .
Bath solutions platform – Clean presentation, each item is described clearly.
нарколог на дом цены [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-1.ru/]нарколог на дом цены[/url] .
skillenhancementhub – Professional learning content is practical, improved knowledge and workflow easily.
кухни на заказ в спб цены [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]кухни на заказ в спб цены[/url] .
trustedcorporatehub – Reliable corporate bonding platform, very helpful for collaboration and team building.
safetradeplace – Reliable experience, every step of the purchase was seamless.
анализ карточек маркетплейс [url=https://reklamnyj-kreativ4.ru/]анализ карточек маркетплейс[/url] .
The Travel Texture Hub – Authentic and vibrant, articles are easy to relate to and visually captivating.
точность прогноза креативов 95% [url=https://reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru/]reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru[/url] .
Вакансии военного – контракт на СВО Россия 2026 https://vc.ru/1579787
easy online shopping guide – Fast navigation and clear product display enhanced the shopping experience.
Matbet TV guncel adresi ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz icin t?kla: [url=https://matbet.jp.net/#]T?kla Git[/url] Canl? maclar burada. Gencler, Matbet bahis son linki belli oldu.
АрсМед: https://arsmedclinic.ru Многопрофильная клиника, предлагающая широкий выбор медицинских услуг от диагностики до лечения. Современный подход и комфортные условия для пациентов всех возрастов.
businessconnectguide – Helpful guidance, enhanced professional relationships smoothly and efficiently.
Be Creative Hub – Playful and engaging, the site makes creativity easy to explore.
Herkese merhaba, Vay Casino kullanıcıları için önemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site adresini tekrar güncelledi. Giriş sorunu varsa endişe etmeyin. Çalışan siteye erişim adresi artık burada: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden direkt siteye erişebilirsiniz. Lisanslı casino keyfi için Vaycasino doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
Dostlar selam, Casibom sitesi oyuncuları adına kısa bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Herkesin bildiği üzere Casibom domain adresini BTK engeli yüzünden yine taşıdı. Giriş sorunu varsa link aşağıda. Yeni Casibom giriş linki artık burada Buraya Tıkla Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza erişebilirsiniz. Ayrıca yeni üyelere verilen yatırım bonusu fırsatlarını mutlaka inceleyin. Lisanslı slot keyfi sürdürmek için Casibom doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
Смотрите видео для взрослых на безопасных и надежных платформах.
Найдите безопасные хабы потоковой передачи для первоклассного
опыта.
Also visit my web page; жестокое порно клипы
unitymanagementtools – Tools that really enhanced workflow and reduced unnecessary delays.
enterprise growth alliances – Helpful advice that improved planning and partnership effectiveness.
teamframeworkportal – Straightforward and practical guidance, improved collaboration across departments.
strategicalliancesclick – Networking and alliance resources are easy to use, very well-structured guidance.
trustedbuyingzone – Online buying is safe here, transactions go smoothly and efficiently.
вывод из запоя лечение краснодар [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru[/url] .
strategic choice hub – Practical tips that simplified evaluating new business options.
secure asset bonding – Bond-related tasks are handled efficiently and without friction.
вывод из запоя краснодар на дому анонимно [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
smartshoppingzone – Smooth process, grabbing deals was hassle-free.
FiatFive archive – Enthusiastic and organized, the site offers curated content for fans of vintage Fiat 500s.
кухни на заказ питер [url=https://kuhni-spb-32.ru/]kuhni-spb-32.ru[/url] .
вызвать нарколога на дом [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-1.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url] .
Вывод к докладу – как правильно написать вывод к докладу? https://vc.ru/1481459
кухня на заказ спб от производителя недорого [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]кухня на заказ спб от производителя недорого[/url] .
7k casino подходит как для новых игроков так и для опытных пользователей. Простая регистрация облегчает старт. Игровая платформа не перегружена лишними элементами. Все внимание сосредоточено на игровом процессе. Управление интуитивно понятно: 7k casino вход
shopdigitally – Smooth experience, locating items was quick and convenient.
Ideas Hub – Informative and user-friendly, resources make finding solutions easier.
Light and simple page – No distractions, content loads fast and stays clear.
A strong article that explains its topic clearly and maintains reader interest throughout.
https://yytdquuq23.com/
strategic partnership tips – Clear advice helped improve communication and achieve shared goals.
карточки товаров wildberries [url=https://reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru/]карточки товаров wildberries[/url] .
strategicbizsolutions – Very useful advice, provides actionable insights for business needs.
Dostlar selam, bu site oyuncuları için kısa bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi Vaycasino giriş linkini yine değiştirdi. Erişim sorunu yaşıyorsanız panik yapmayın. Son Vay Casino giriş linki şu an burada: Vaycasino Sorunsuz Giriş Paylaştığım bağlantı ile direkt siteye girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis keyfi sürdürmek için Vaycasino doğru adres. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
skillsgrowthportal – Informative content, made learning new concepts much easier and quicker.
Любишь азарт? ап икс официальный играть онлайн в популярные игры и режимы. Быстрый вход, удобная регистрация, стабильная работа платформы, понятный интерфейс и комфортные условия для игры в любое время на компьютере и мобильных устройствах.
Играешь в казино? апх простой вход, удобная регистрация и доступ ко всем возможностям платформы. Стабильная работа, адаптация под разные устройства и комфортный пользовательский опыт.
1 вин слоты [url=https://1win12050.ru/]https://1win12050.ru/[/url]
long-range vision tips – Direct and practical ideas that improved planning accuracy.
careerdecisionhub – Guidance that was straightforward, actionable, and really useful.
Dostlar selam, bu populer site uyeleri ad?na onemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Bildiginiz gibi site adresini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle yine tas?d?. Giris hatas? yas?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Cal?san Casibom giris baglant?s? art?k asag?dad?r [url=https://casibom.mex.com/#]Casibom Guncel Giris[/url] Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden dogrudan hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Ayr?ca yeni uyelere verilen hosgeldin bonusu f?rsatlar?n? da kac?rmay?n. Lisansl? casino keyfi icin Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tum forum uyelerine bol sans dilerim.
I wasn鈥檛 expecting much, but this turned out great.馃憤 This post exceeded my expectations….
вывод из запоя лечение краснодар [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-1.ru[/url] .
7k casino ориентировано на современный онлайн формат. Платформа поддерживает разные устройства. Игры работают корректно. Интерфейс остается удобным. Пользователь легко адаптируется: 7k casino
deal buying platform – Offers were easy to access and checkout was fast.
Темы для взрослых широко доступен на специализированных платформах для зрелой аудитории.
Выбирайте надежные сайты для взрослых для обеспечения
безопасности.
My web site … BUY VIAGRA
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet yeni adresi açıklandı. Giremeyenler şu linkten devam edebilir Grandpashabet Bonus
dealstream – Smooth platform, online shopping was fast and convenient.
вывод из запоя на дому краснодар [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar-2.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому краснодар[/url] .
Fixture timing portal – Well-organized site, match schedules are clear and reliable.
This is a very helpful and informative article. I appreciate the clear explanation and useful details. Thank you for sharing such valuable content.
visit this website https://dowrit.com/
1win Бишкек скачать [url=https://www.1win12050.ru]https://www.1win12050.ru[/url]
This article provides clear explanations and useful insights. I enjoyed reading it and learning something new. Thank you for sharing such informative content.
visit this website https://dowrit.com/
alliancesmanagementhub – Practical insights, made partnership organization smoother and more effective.
collaborationtoolportal – Very smooth and intuitive, perfect for managing team projects.
кухни спб на заказ [url=https://kuhni-spb-32.ru/]кухни спб на заказ[/url] .
нарколог краснодар [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-1.ru/]нарколог краснодар[/url] .
Любишь азарт? ап х играть онлайн легко и удобно. Быстрый доступ к аккаунту, понятная навигация, корректная работа на любых устройствах и комфортный формат для пользователей.
кухня по индивидуальному заказу спб [url=https://kuhni-spb-28.ru/]кухня по индивидуальному заказу спб[/url] .
allianceinsightscenter – Partnership tips are clear, really supported our business development plan.
https://vc.ru/1452122 – Накрутка Тик Ток: живых и ботов – ТОП-25 сервисов в 2026 году (Полный гид)
Digital H5 platform – Attractive layout, it invites curiosity about other features.
машинное обучение креативы [url=https://reklamnyj-kreativ4.ru/]reklamnyj-kreativ4.ru[/url] .
оптимизация наружки [url=https://reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru/]оптимизация наружки[/url] .
business alliance insights – Clear recommendations for expanding professional alliances.
Накрутка Инстаграм – ТОП-25 сервисов (2026) Мой рейтинг
Полное описание и условия по ссылке https://vc.ru/1596228
https://unibetsru.com/ unibetsru
dealnavigatorhub – Great bargains, very easy and fast to complete purchases.
trustedadvisorsnetwork – Excellent insights that gave me confidence in partnership decisions.
https://vc.ru/2003556 – ВК накрутка друзей в 2026: ТОП-20 лучших сервисов и советы по избежанию бана
Arkadaşlar selam, Vay Casino oyuncuları adına kısa bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Malum Vaycasino giriş linkini tekrar değiştirdi. Erişim sorunu varsa endişe etmeyin. Son Vay Casino giriş linki şu an aşağıdadır: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Bu link üzerinden doğrudan hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis deneyimi için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
Gençler, Grandpashabet Casino yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler şu linkten devam edebilir Grandpashabet Güncel
купля квартиры светский лес сочи жк официальный
Монтаж систем электроснабжения, Монтаж систем электроснабжения в Москве Системы автоматической противопожарной защиты (АППЗ) – это передовая технология, направленная на автоматическое тушение пожара. Монтаж систем автоматической противопожарной защиты, в том числе монтаж систем автоматической противопожарной защиты в Москве, требует глубоких знаний и опыта. Качественный монтаж АППЗ, а также монтаж АППЗ в Москве, значительно повышает уровень безопасности объекта.
химчистка сдать обувь химчистка обуви в москве
businesssupportstructure – Recommendations are solid, easy to follow and implement right away.
retailconnect – Very practical, browsing products feels natural and quick.
Arkadaslar selam, Vay Casino kullan?c?lar? ad?na onemli bir bilgilendirme paylas?yorum. Malum site adresini tekrar degistirdi. Giris hatas? yas?yorsan?z endise etmeyin. Yeni Vaycasino giris linki art?k burada: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Yeni Adres[/url] Bu link ile direkt siteye erisebilirsiniz. Lisansl? casino keyfi icin Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol sans temenni ederim.
Play online puzzles https://dliavas.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=26&t=10587&p=71197#p71197 anytime and train your logic and attention skills. Classic and themed puzzles, various sizes, simple gameplay, and comfortable play on computers and mobile devices.
Arkadaşlar selam, Vaycasino kullanıcıları için kısa bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Malum platform adresini tekrar değiştirdi. Giriş hatası yaşıyorsanız endişe etmeyin. Çalışan Vaycasino giriş adresi şu an aşağıdadır: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Üyelik[/url] Paylaştığım bağlantı ile direkt hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Lisanslı casino keyfi için Vay Casino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol şans temenni ederim.
Matbet TV guncel adresi laz?msa iste burada. Sorunsuz icin: [url=https://matbet.jp.net/#]Matbet TV Giris[/url] Yuksek oranlar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet bahis son linki ac?kland?.
бездепозитные бонусы Бездепозитный Бонус за Регистрацию: Начни Побеждать Прямо Сейчас! Получить бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию – это отличный способ познакомиться с функционалом казино, протестировать различные игры и, возможно, даже выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными средствами. Просто зарегистрируйтесь, получите свой бонус и начинайте играть!
Fulksher personal site – Clean layout, the portfolio is easy to navigate and appealing.
срочный выезд нарколога на дом [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
bizcommerce – Modern tools, made business transactions quick and stress-free.
shopsmarthub – Very intuitive, browsing and buying products is straightforward.
ко ланте ко ланте
businesscollabzone – Unity tools are reliable, improved team workflow in multiple departments.
мостбет ставки на исход [url=mostbet2027.help]мостбет ставки на исход[/url]
ко ланте ко ланте
Gencler, Grandpashabet yeni adresi belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar buradan giris yapabilir https://grandpashabet.in.net/#
вызов нарколога на дом круглосуточно [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
Herkese selam, bu site kullanıcıları için kısa bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Malum site adresini yine güncelledi. Erişim hatası varsa endişe etmeyin. Çalışan Vay Casino giriş adresi artık aşağıdadır: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vay Casino Güvenilir mi[/url] Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Lisanslı bahis deneyimi sürdürmek için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol şans temenni ederim.
strategicalliances – Very informative, guided our global partnership planning effectively.
ко ланте ко ланте
The Savage’s initial wonder turns to horror. A Brave New World PDF charts this emotional transformation. It is a powerful narrative of disillusionment that mirrors the immigrant experience in some interpretations.
From the first page to the last, this novel grips you with its intensity. finding a copy of The Book Thief PDF allows you to engage with the text instantly. It is perfect for those moments when you need a deep, engaging story to escape into during your daily commute.
The description of the air raids is terrifyingly real. Read The Book Thief PDF to feel the fear of the cellar. It puts you right there with the characters, holding your breath as the bombs fall, a testament to the power of the writing. https://thebookthiefpdf.site/ Download Percy Jackson And The Lightning Thief Book Pdf
The final scene of the spinning feet is iconic. The Brave New World PDF preserves this haunting imagery. It is a cinematic ending to a novel that is full of visual power. https://bravenewworldpdf.site/ Brave New World Mobi
quickbuyportal – Smooth process and fast delivery, makes online shopping easy.
ко ланта ко ланта
Bahis severler selam, Casibom sitesi kullanıcıları için önemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Herkesin bildiği üzere bahis platformu giriş linkini BTK engeli yüzünden yine güncelledi. Siteye ulaşım hatası yaşıyorsanız link aşağıda. Resmi Casibom güncel giriş adresi şu an aşağıdadır https://casibom.mex.com/# Bu link üzerinden direkt siteye girebilirsiniz. Ek olarak kayıt olanlara verilen freespin kampanyalarını da kaçırmayın. Güvenilir slot deneyimi için Casibom doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
1win вывод через о деньги инструкция [url=1win12050.ru]1win12050.ru[/url]
connectbusinessprofessionals – Efficient platform, helped me establish meaningful professional relationships.
ко ланте ко ланта
7k casino предлагает стабильную онлайн платформу для игр. Пользователь получает быстрый доступ к контенту. Интерфейс интуитивно понятен. Все работает без сбоев. Это обеспечивает комфортную игру: 7k casino сайт регистрация
knowledgeportal – Informative resources, made complex topics simple to understand.
Kent casino подходит как для начинающих так и для опытных игроков. Простая структура сайта помогает быстро освоиться. Игровой процесс проходит без технических сбоев. Все функции доступны в несколько кликов. Это делает игру удобной: кент казино официальный сайт зеркало
нарколог на дом анонимно [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
ко ланта ко ланте
If you enjoy deep character studies, you will love the development of Rosa Hubermann. Her rough exterior and soft heart are revealed slowly. Read The Book Thief PDF to witness her transformation. It is a character arc that is best experienced through the immersive nature of the novel. https://thebookthiefpdf.site/ Percy Jackson And The Lightning Thief Book Review Pdf
John’s quoting of The Tempest recontextualizes Shakespeare. The Brave New World PDF highlights these intertextual references. It is a treat for literature lovers who enjoy seeing classics woven into new narratives.
ко ланте ко ланте
Grandpasha giris linki ar?yorsan?z iste burada. H?zl? erisim icin t?kla Grandpashabet Indir Yuksek oranlar bu sitede.
Dostlar selam, bu popüler site oyuncuları adına önemli bir paylaşım paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle sürekli güncelledi. Erişim hatası varsa çözüm burada. Resmi Casibom giriş linki şu an paylaşıyorum Casibom 2026 Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden direkt hesabınıza bağlanabilirsiniz. Ek olarak yeni üyelere sunulan freespin kampanyalarını mutlaka kaçırmayın. En iyi bahis keyfi için Casibom doğru adres. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
тик ток мод скачать бесплатно 2026 Эволюция TikTok: Всё о Модифицированных Версиях и Возможностях 2026 Года В мире, где TikTok стал неотъемлемой частью цифровой культуры, модифицированные версии приложения, известные как “TikTok мод”, завоёвывают всё большую популярность. Что же это такое и почему они так востребованы? TikTok мод – это изменённая версия оригинального приложения, предлагающая расширенный функционал, недоступный в стандартной версии. Это может включать в себя возможность скачивания видео без водяных знаков, разблокировку региональных ограничений, расширенные настройки конфиденциальности и многое другое.
ко ланта ко ланте
valuecartstore – Really convenient and the savings were significant.
Секс широко доступен на специализированных платформах
для зрелой аудитории. Выбирайте надежные сайты
для взрослых для обеспечения безопасности.
Here is my homepage; лесбийские порно видео
careerinsights – Practical lessons, boosted my professional development.
1win ставки на теннис [url=www.1win12048.ru]1win ставки на теннис[/url]
ко ланта ко ланта
Thank you for sharing this helpful and informative article. The content is clear, relevant, and easy to understand. I truly appreciate the effort behind this post.
visit this website https://funderscorner.com/
активный отдых Сахалин Отдых на Сахалине предоставит возможность не только активно провести время, занимаясь треккингом или горными лыжами, но и расслабиться в термальных источниках, восстанавливая силы и здоровье.
срочный выезд нарколога на дом [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar-2.ru[/url] .
Liesel’s relationship with the neighbor’s wife is complex. Read about Holtzapfel in The Book Thief PDF. It shows that grief can bridge even the widest gaps between enemies, a touching subplot in the novel.
The struggle to hide a Jew in the basement is filled with tension. Feel the suspense in The Book Thief PDF. It is a thriller element within a historical drama that keeps you turning the digital pages late into the night. https://thebookthiefpdf.site/ The Book Thief Activities Pdf Free Download
Immerse yourself in a society dominated by technology and biological control. For students and enthusiasts seeking a Brave New World PDF, this version ensures you can study the text anywhere. Uncover the stark contrast between the Savage Reservation and the civilized world in this enduring literary work. https://bravenewworldpdf.site/ Brave New World Revisited Epub
фриспины без депозита Бездепозитный Бонус за Регистрацию: Начни Побеждать Прямо Сейчас! Получить бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию – это отличный способ познакомиться с функционалом казино, протестировать различные игры и, возможно, даже выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными средствами. Просто зарегистрируйтесь, получите свой бонус и начинайте играть!
Every sentence in Huxley’s novel is crafted to provoke thought. The Brave New World PDF gives you the text in a clean, readable format. It is an essential download for anyone who wants to challenge their own perceptions of happiness and freedom.
ко ланте ко ланте
1win бонус новичкам [url=1win12048.ru]1win бонус новичкам[/url]
Платформа оставляет ощущение сдержанной инженерной точности, где каждое решение будто принято без суеты. Интерфейс не стремится удивлять, но постепенно втягивает логикой расположения элементов. В середине пользовательского пути органично появляется olimp casino бонус, не как рекламный выкрик, а как часть сценария взаимодействия. После этого внимание смещается на механику игр, которая работает стабильно и без резких провалов. Общее впечатление — выверенная система с внутренней дисциплиной.
7k casino сочетает современный дизайн и функциональность. Интерфейс адаптирован под разные экраны. Игроки легко находят нужные разделы. Все основные опции находятся под рукой. Это упрощает использование платформы: 7к казино регистрация
Matbet giris linki laz?msa iste burada. Sorunsuz icin t?kla: Buraya T?kla Yuksek oranlar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet bahis son linki ac?kland?.
I found this post very informative and enjoyable to read. The content is clear and easy to follow. Thank you for sharing such useful insights and practical information.
visit this website https://dunemagazines.com/
“Краулинговый бюджет” — ресурс, который поисковый робот тратит на сканирование вашего сайта. Оптимизируйте его: убирайте дубли, закрывайте от индексации мусор, улучшайте скорость ответа сервера. prodvizheniye-sayta-grodno.ru
teamgrowthhub – Practical tools, made collaboration and planning much smoother.
Kent casino предлагает доступ к разнообразным онлайн развлечениям. Пользователь может выбирать формат игры под свои предпочтения. Все игры запускаются напрямую через сайт. Дополнительные настройки не требуются. Процесс остается простым: kent casino играть
Накрутка комментариев ВКонтакте ТОП-25 сервисов для 2026 года https://vc.ru/1768532
Новые онлайн казино – рейтинг и ТОП лучших сайтов для игры на деньги
Актуальный рейтинг новых онлайн казино. ТОП лучших сайтов для игры на реальные деньги: лицензия, честные условия, быстрый вывод средств и бонусы для игроков.
Новые онлайн казино – это игровые платформы, которые относительно недавно вышли на рынок и начали принимать игроков. Чаще всего речь идёт о проектах, запущенных в последние один-два года. Они активно развиваются, внедряют свежие технологии и стараются предложить условия, которые выгодно отличают их от более старых брендов.
Как формируются новые казино
Создание нового казино начинается с выбора лицензии, программного обеспечения и платёжных решений. После этого формируется бонусная политика, подбираются игровые провайдеры и настраиваются системы безопасности. Большинство новых казино ориентируются на международную аудиторию и сразу запускаются как онлайн-площадки с поддержкой разных валют и способов оплаты.
Рынок новых онлайн казино меняется достаточно быстро. Одни проекты активно развиваются, расширяют выбор игр и улучшают условия для игроков, другие, наоборот, теряют доверие из-за задержек выплат или непрозрачных правил. Поэтому рейтинг новых казино не может быть статичным – он должен регулярно пересматриваться и обновляться.
При составлении рейтинга учитываются только актуальные данные. Проверяется работа сайта, доступность платёжных систем, корректность бонусных условий и общее качество сервиса. Такой подход позволяет выделять действительно надёжные новые онлайн казино и исключать площадки, которые не соответствуют заявленным требованиям.
Почему важно выбирать казино из рейтинга
Игроки, которые ориентируются на рейтинг новых онлайн казино, значительно снижают риски. Проверенные площадки уже прошли базовую оценку и соответствуют минимальным стандартам безопасности. Это особенно важно, когда речь идёт о новых казино, у которых ещё нет длительной истории работы.
Выбор казино из рейтинга позволяет сэкономить время на самостоятельный анализ и сразу перейти к игре на подходящей платформе. Кроме того, такие площадки чаще предлагают стабильные выплаты и честные условия.
ТОП новых онлайн казино
Это делает новые площадки привлекательными как для опытных игроков, так и для тех, кто только начинает знакомство с онлайн-казино.
Новые онлайн казино с хорошей отдачей
Современные новые онлайн казино используют защищённые протоколы передачи данных и сотрудничают с надёжными платёжными системами. Это снижает риск утечки информации и обеспечивает безопасность транзакций.
Новые онлайн казино с лицензией
Наличие лицензии – один из ключевых факторов при выборе нового онлайн казино. Даже если проект появился совсем недавно, лицензирование говорит о том, что площадка обязуется соблюдать определённые правила и стандарты. Для игрока это означает более высокий уровень защиты и прозрачности.
Новые казино чаще всего получают международные лицензии, которые позволяют работать с широкой аудиторией. При этом сама лицензия – не формальность, а инструмент контроля со стороны регулятора.
Какие лицензии встречаются у новых казино
У новых онлайн казино новые лицензионные казино чаще всего можно встретить следующие типы лицензий:
• лицензия Curacao – самый распространённый вариант для новых проектов
• европейские лицензии (например, MGA) – встречаются реже, но считаются более строгими
• офшорные лицензии – используются для работы с международным трафиком
Каждая из них накладывает определённые обязательства на оператора и влияет на уровень доверия со стороны игроков.
onlinedigitalmarket – Reliable service, purchasing digital items is fast and safe.
7k casino позволяет играть в онлайн режиме в любое удобное время. Платформа работает стабильно на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах. Навигация интуитивно понятна. Игровые сессии проходят без технических сложностей. Это делает процесс комфортным: 7к казино официальный сайт
Dostlar selam, Vay Casino kullanıcıları adına önemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi platform adresini tekrar değiştirdi. Giriş hatası yaşıyorsanız panik yapmayın. Son Vaycasino giriş linki şu an aşağıdadır: Vaycasino 2026 Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis keyfi için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
The writing style is smooth and professional, delivering valuable insights that feel relevant, practical, and enjoyable for a wide audience.
https://bws9903.com/
Arkadaslar selam, Vay Casino kullan?c?lar? ad?na k?sa bir bilgilendirme paylas?yorum. Malum Vaycasino giris linkini tekrar degistirdi. Erisim sorunu varsa panik yapmay?n. Son siteye erisim linki su an burada: Vaycasino Twitter Paylast?g?m baglant? ile dogrudan hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Lisansl? casino deneyimi icin Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazanclar temenni ederim.
Chào anh em, người anh em nào cần nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Game bài thì xem thử trang này nhé. Đang có khuyến mãi: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chiến thắng nhé.
Hi các bác, bác nào muốn tìm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Casino thì xem thử con hàng này. Uy tín luôn: [url=https://homemaker.org.in/#]sun win[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Meursault is a man who lives in the present moment, free from the burdens of the past or the future. This attitude makes him a monster in the eyes of the law. The Stranger by Albert Camus details the consequences of living without hope or fear. If you are searching for a digital version or PDF to explore this seminal work of existentialism, you will find a story that is as disturbing as it is liberating. It forces you to confront the silence of the universe and decide how to live within it. https://thestrangerpdf.site/ The Stranger Murder Scene Pdf
Hello pals!
I came across a 154 very cool site that I think you should check out.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://simcookie.com/2022/08/29/three-most-notorious-crime-syndicates-in-the-world/]https://simcookie.com/2022/08/29/three-most-notorious-crime-syndicates-in-the-world/[/url]
Furthermore do not overlook, guys, which one always may within this particular article locate answers to address the the very confusing inquiries. The authors made an effort to lay out the complete content via an very understandable manner.
strategicmoves – Very practical advice, helped plan next steps confidently.
системы пожарной сигнализации в Москве Компания SMR-Proekt – эксперт в области систем пожарной сигнализации в Москве, предлагающий полный цикл услуг: от проектирования и поставки оборудования до профессионального монтажа и последующего технического обслуживания. Мы гарантируем высокое качество всех этапов работ, строгое соблюдение нормативных требований и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Thank you for sharing this helpful article. The explanation is clear and easy to follow. I found the information very useful and informative. Keep up the great work and quality content.
visit this website https://bandartogeltoto.id/
digitalbuyclick – Streamlined platform, buying digital products is convenient and safe.
монтаж систем пожарной сигнализации Монтаж систем пожарной сигнализации – это сложный и ответственный процесс, требующий высокой квалификации и опыта. Наши специалисты обладают всеми необходимыми знаниями и навыками для проведения монтажных работ любой сложности, обеспечивая надежную и эффективную защиту вашего объекта.
Chao c? nha, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? gi?i tri Game bai thi xem th? trang nay nhe. Khong lo l?a d?o: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. V? b? thanh cong.
Xin chào 500 anh em, ai đang tìm cổng game không bị chặn để cày cuốc Game bài thì tham khảo chỗ này. Đang có khuyến mãi: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Chúc anh em may mắn.
Hey there, You have done a great job. I will definitely digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this web site.
сайт казино РиоБет
кабель пвх https://telegra.ph/Nyuansy-vybora-kabelya-s-PVH-izolyaciej-01-26
опоры для СТО https://mrhahn-it-life.blogspot.com/2026/01/blog-post.html
Chào cả nhà, người anh em nào cần trang chơi xanh chín để gỡ gạc Game bài thì vào ngay trang này nhé. Đang có khuyến mãi: Link vào BJ88. Chiến thắng nhé.
москва питер путевка [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]tury-v-piter.ru[/url] .
автобусные экскурсии по спб [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]автобусные экскурсии по спб[/url] .
турагентства санкт петербурга список 10 лучших [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]турагентства санкт петербурга список 10 лучших[/url] .
ко ланта ко ланте
The novella was inspired by a Mexican folk tale that Steinbeck heard during his travels. He adapted it into a story that feels both mythic and incredibly real. The universal appeal of the story lies in its examination of the “American Dream” transposed to a fishing village. Kino wants a rifle, an education for his son, and a wedding – things that seem simple but are radical for a man of his station. Reading the pearl pdf reveals how these desires twist Kino’s perception of reality. The book serves as a critique of the idea that material success equates to happiness, a theme that resonates across cultures and generations. https://thepearlpdf.site/ The Pearl Summary Notes Pdf
The contrast between the four sisters is what drives the narrative forward. They clash, they comfort, and they grow together. It is a realistic portrayal of sibling dynamics that rings true today. To witness their evolution, reading the text is a must. A Little Women PDF offers a high-quality reading experience. It ensures that the text is clear and legible, allowing you to focus on the complex relationships that define the novel. https://littlewomenpdf.site/ Little Women Play Script Pdf
The allure of the abominable is a key theme. Marlow is disgusted by Kurtz, yet he is also fascinated by him. This tension drives the narrative. A Heart of Darkness PDF helps you examine the subtle shifts in Marlow’s attitude. The text is a complex study of moral complicity. It asks how much we are willing to overlook in the name of efficiency or profit. It is a book that questions the very basis of our moral judgments. https://heartofdarknesspdf.site/ Heart Of Darkness Quiz Pdf
Chào anh em, ai đang tìm trang chơi xanh chín để chơi Tài Xỉu thì vào ngay địa chỉ này. Uy tín luôn: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Hi cac bac, ai dang tim c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? cay cu?c Game bai thi tham kh?o ch? nay. Uy tin luon: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]BJ88[/url]. Chuc anh em may m?n.
Chào anh em, người anh em nào cần nhà cái uy tín để gỡ gạc Casino thì vào ngay chỗ này. Đang có khuyến mãi: Tải app BJ88. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Chao c? nha, ai dang tim c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? choi Game bai d?ng b? qua trang nay nhe. N?p rut 1-1: bj88. Hup l?c d?y nha.
1win промокод на кэшбек [url=www.1win12048.ru]www.1win12048.ru[/url]
автобусы питер [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]автобусы питер[/url] .
недорогие экскурсии спб [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru[/url] .
турклуб санкт петербург [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]турклуб санкт петербург[/url] .
сколько стоит поездка в питер на 3 дня на двоих [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]tury-v-piter.ru[/url] .
Hello mọi người, người anh em nào cần cổng game không bị chặn để cày cuốc Casino đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Không lo lừa đảo: [url=https://homemaker.org.in/#]sun win[/url]. Về bờ thành công.
The portrayal of women in the novella is sparse but significant. Marlow’s aunt represents the naive public back home, while Kurtz’s intended represents the lie of civilization. The African woman at the station represents the raw power of the land. A Heart of Darkness PDF is useful for a feminist reading of the text. You can easily locate and compare the scenes featuring these characters. The book is a complex web of gender, race, and power dynamics that continues to generate scholarly debate.
As winter approaches, there is no better book to curl up with than this cozy classic about family, love, and Christmas. The opening scene of the book is iconic, setting the tone for a story filled with heart and hope. To get started on this literary journey, you might want to look for a Little Women PDF. Having the file on your device ensures you can read it even in low light or on the go. It is a wonderful way to experience the festive spirit and the deep emotional bonds that define the March family’s story.
люстра на потолок деревянная люстра
Uncover the layers of existentialism in Albert Camus’ debut novel. The Stranger presents a world where traditional values are stripped away. Meursault’s refusal to play by the rules of society leads to his downfall, but also to his ultimate freedom. If you are looking for a digital copy or PDF to study the interactions between Meursault and the chaplain, this book offers a powerful critique of religion and social hope. It is a succinct, powerful read that stays with you long after the final page.
Порносайт предлагает широкий выбор видео для взрослых
развлечений. Выбирайте надежные платформы для конфиденциального
опыта.
Also visit my webpage; BUY VIAGRA
Kent casino предлагает современный игровой интерфейс. Дизайн сайта аккуратный и понятный. Игры удобно расположены по категориям. Пользователь легко ориентируется. Это повышает комфорт игры: кент казино рабочее зеркало
костюм утепленный мужской мужские костюмы спб
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để chơi Đá Gà thì xem thử trang này nhé. Đang có khuyến mãi: Nhà cái BJ88. Chiến thắng nhé.
Xin chao 500 anh em, ai dang tim ch? n?p rut nhanh d? g? g?c Tai X?u thi vao ngay trang nay nhe. T?c d? ban th?: Dola789 dang nh?p. Hup l?c d?y nha.
экскурсионные автобусы по санкт петербургу [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru[/url] .
экскурсии в спб на автобусе [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru[/url] .
Chào anh em, nếu anh em đang kiếm trang chơi xanh chín để gỡ gạc Game bài thì vào ngay địa chỉ này. Đang có khuyến mãi: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Why do we keep returning to the story of the March sisters? perhaps it is because it feels like home. The characters are flawed but lovable, and their struggles are universal. If you want to visit this literary home, a digital key is all you need. A Little Women PDF opens the door to the March residence. It allows you to step inside and forget the worries of the modern world for a while, losing yourself in a simpler, yet deeply complex, time.
One of the most tragic figures in the book is Coyotito, the innocent baby who becomes the catalyst for the entire plot. He is the victim of the scorpion, the reason for the pearl hunt, and ultimately the sacrifice paid for Kino’s ambition. Discussions around the text often focus on the vulnerability of innocence in a corrupt world. Accessing the pearl pdf allows readers to trace the timeline of Coyotito’s condition, from the swelling of the sting to the final, heartbreaking shot in the mountains. His fate serves as the ultimate punishment for Kino’s attempt to overreach his destiny.
путевка санкт петербург подбор тура [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]tury-v-piter.ru[/url] .
The Stranger is a book about the danger of truth. Meursault refuses to say more than what is true, and this refusal costs him his life. Albert Camus celebrates this integrity. If you are looking for the PDF to study this theme, the novel offers a concise and potent narrative. It is a story that asks us if we are brave enough to be ourselves in a world that wants us to be someone else.
тур в питер на 5 дней с проживанием и питанием из челябинска [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]тур в питер на 5 дней с проживанием и питанием из челябинска[/url] .
Kent casino подходит как для начинающих так и для опытных игроков. Простая структура сайта помогает быстро освоиться. Игровой процесс проходит без технических сбоев. Все функции доступны в несколько кликов. Это делает игру удобной: кент казино официальный сайт зеркало
Hello mọi người, người anh em nào cần trang chơi xanh chín để cày cuốc Nổ Hũ thì xem thử địa chỉ này. Không lo lừa đảo: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]Link vào BJ88[/url]. Về bờ thành công.
This article offers valuable perspectives supported by clear explanations and logical organization throughout.
https://dostavljac.com/
Chào anh em, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Game bài thì tham khảo con hàng này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: Nhà cái Dola789. Chiến thắng nhé.
The charm of the March family lies in their imperfections and their unwavering support for one another. They are not just characters; they feel like real people with real struggles. To get to know them better, reading the original novel is the best approach. A Little Women PDF is a convenient format for the modern reader. It allows you to enjoy the classic illustrations and the dense text without the bulk of a physical book. Immerse yourself in the laughter and tears of the March household through your digital device.
прогулка на автобусе по санкт петербургу [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]прогулка на автобусе по санкт петербургу[/url] .
Chao anh em, n?u anh em dang ki?m c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? cay cu?c Da Ga d?ng b? qua con hang nay. Uy tin luon: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Hup l?c d?y nha.
Chao c? nha, bac nao mu?n tim c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? cay cu?c N? Hu d?ng b? qua trang nay nhe. Khong lo l?a d?o: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Link khong b? ch?n[/url]. Chuc anh em may m?n.
на экскурсии или на экскурсие [url=https://avtobusnye-ekskursii-po-spb.ru/]на экскурсии или на экскурсие[/url] .
vavada program vjernosti [url=vavada2007.help]vavada2007.help[/url]
mostbet oferte bonus [url=https://mostbet2008.help]https://mostbet2008.help[/url]
лучшие туроператоры в спб [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]лучшие туроператоры в спб[/url] .
Wild Bounty Showdown slot
This article successfully balances depth and readability, providing both educational value and engaging content that readers can enjoy fully.
https://kolinay.com/
Kent casino предоставляет доступ к актуальным онлайн играм. Каталог регулярно обновляется. Пользователь может выбирать новые форматы. Сайт сохраняет стабильность. Интерес поддерживается постоянно: кент казино скачать
экскурсия по санкт петербургу с проживанием [url=https://tury-v-piter.ru/]tury-v-piter.ru[/url] .
Wild Bounty Showdown demo в рублях
удаленная работа отзывы удаленная работа без опыта
Thank you for this well-structured, professional, and informative article. The actionable guidance, clear explanations, and thorough research make it a highly useful resource for anyone seeking trustworthy advice.
visit this website https://98090tg.net/
kalian harus tau bahwa BANDAR138 sedang banyak bonus melimpah dan sangat menguntungkan!
прошивка samsung великий новгород заменить дисплей iрhоnе
замена аккумулятора на айфоне 12 pro max ремонт смартфонов великий новгород
vavada free spins hrvatska [url=http://vavada2007.help]http://vavada2007.help[/url]
mostbet notificări rezultate [url=https://mostbet2008.help]https://mostbet2008.help[/url]
https://dtf.ru/pro-smm
When you download a Heart of Darkness PDF, you are not just getting a book; you are getting a piece of history. This novella captures the anxieties of an empire at its peak, looking down into the abyss of its own decline. The writing is sharp, critical, and incredibly modern. It forces the reader to confront the uncomfortable truths of history and human nature. It is a text that belongs in every digital library.
In the heat of the moment, a life is taken. The Stranger explores the consequences of a senseless act in a world that demands meaning. Albert Camus writes with a clarity that cuts to the bone. Whether you are looking for The Stranger PDF for academic purposes or personal interest, the story of Meursault is gripping. It serves as a critique of a society that prefers a lie to a complex truth.
Долфин Анти: https://долфин-анти.рф/ Современный антидетект-браузер для безопасного управления множеством аккаунтов. Эффективное решение для арбитража трафика, криптопроектов и автоматизации маркетинга без риска блокировок.
удаленная работа вакансии биржа фриланса
samsung плохо слышно собеседника ремонт великий новгород замена аккумулятора на iphone 11
Chào cả nhà, ai đang tìm trang chơi xanh chín để cày cuốc Đá Gà thì tham khảo con hàng này. Không lo lừa đảo: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
ко ланте ко ланте
Деревянный плинтус
[url=https://telegra.ph/Promyshlennyj-bronirovannyj-kabel-zashchita-nadezhnost-i-surovaya-realnost-montazha-01-26]Монтаж бронированного кабеля[/url]
Xin chào 500 anh em, nếu anh em đang kiếm cổng game không bị chặn để giải trí Đá Gà thì xem thử con hàng này. Đang có khuyến mãi: [url=https://homemaker.org.in/#]Sunwin web[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Chào cả nhà, người anh em nào cần trang chơi xanh chín để chơi Casino thì vào ngay địa chỉ này. Uy tín luôn: Nhà cái BJ88. Chiến thắng nhé.
ремонт лотка sim iphone в великом новгороде ремонт ноутбуков asus великий новгород
Chao c? nha, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? g? g?c Game bai thi vao ngay con hang nay. N?p rut 1-1: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]bj88[/url]. Chuc cac bac r?c r?.
May I simply just say what a comfort to find an individual who genuinely understands what they’re talking about online. You definitely know how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More people need to look at this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular given that you certainly possess the gift.
https://www.ar25.org/ru/article/v-ukraine-stalo-proshche-obmenivat-kriptovalyutu.html
пакет пвд 40х50 с логотипом Пакеты ПВД с логотипом на заказ – производство пакетов из полиэтилена высокого давления с индивидуальным дизайном. Изготовление пакетов ПВД любых размеров и плотности с нанесением вашего логотипа.
Marvelous, what a website it is! This weblog provides useful information to us, keep it up.
https://giftcare.in/exploration-de-linterface-iron-tv-pro/
Рейка деревянная купить
Tesla Motors electric vehicles are known for long range, fast charging, strong performance, and advanced software features. They also lead in autonomous driving technology, https://ev.motorwatt.com/
Лучшие порносайты предлагают высококачественный контент для взрослых
развлечений. Выбирайте безопасные сайты для безопасного и приятного просмотра.
Here is my homepage :: brutal porn clips
недорогой мужской костюм мужские костюмы
Great Big Beautiful Life is a book for the romantic at heart. Emily Henry delivers a story that is swoon-worthy. The epub format is the perfect way to read this book privately or publicly. It is a great, big, romantic gesture in book form. The writing is beautiful and evocative. This is a book that will make your heart flutter. Get the digital edition and enjoy the romance. https://greatbigbeautifullifeepub.site/ Great Big Beautiful Life Emily Henry Family Tree
This Book Will Bury Me is a novel that burns bright. Ashley Winstead lights a fire. The epub format keeps the flame alive. It is glowing and warm. The story is incendiary. It is a book that will bury you in its heat. If you want a digital book that sizzles, this is the one. Download the epub and feel the burn. https://thisbookwillburymeepub.site/ This Book Will Bury Me Hardcover
A sophisticated and dark thriller that pulls no punches. Shay Deroy’s comfortable life is shattered when her past comes back to haunt her. The convenience of the The Last Housewife epub format makes it easy to carry this heavy story with you. The cult aspect is written with chilling detail, making the danger feel immediate. It is a story about finding your voice after years of silence. Winstead’s prose is sharp, engaging, and deeply affecting. This is a book that demands to be read. https://thelasthousewifeepub.site/ The Last Housewife Quotes
Experience Shield of Sparrows by Devney Perry. The epub version is the best way to read this novel. Digital books are perfect for travel. Perry’s writing is excellent. The digital copy allows you to read with ease. Whether you are at home or out, this ebook is a great companion. Download it today and enjoy. https://shieldofsparrowsepub.site/ Shield Of Sparrows Epub Free Download
Кредит наличными онлайн позволяет получить средства удаленно. Процедура оформления проста и понятна. Решение принимается автоматически. Можно выбрать подходящий срок. Такой формат подходит для срочных расходов – подбор кредита казахстан
Электромонтажные работы https://electric-top.ru в Москве и области. Круглосуточный выезд электриков. Гарантия на работу. Аварийный электрик.
замена разъема micro usb ремонт macbook великий новгород
заказать пакеты с логотипом Бумажные пакеты с логотипом оптом – экономичный способ обеспечить упаковкой ваш бизнес. Большой выбор материалов, размеров и способов нанесения логотипа.
Chào anh em, nếu anh em đang kiếm trang chơi xanh chín để chơi Đá Gà thì tham khảo chỗ này. Nạp rút 1-1: BJ88. Chúc anh em may mắn.
краби про краби отзывы 2025
Hello mọi người, ai đang tìm trang chơi xanh chín để gỡ gạc Tài Xỉu thì vào ngay chỗ này. Không lo lừa đảo: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Link không bị chặn[/url]. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Кент казино поддерживает комфортную игру на мобильных устройствах. Сайт адаптирован под разные размеры экранов. Игры сохраняют стабильность и скорость. Управление остается удобным. Это подходит для мобильного формата: kent casino промокод
дайсон фен купить оригинальный спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
алкоголь 24 часа [url=http://alcohub10.ru/]алкоголь 24 часа[/url] .
коррозия у авто? антикоррозийная обработка автомобиля эффективная защита от влаги, соли и реагентов. Комплексная обработка кузова и днища, качественные составы и надёжный результат для новых и подержанных авто.
Ashley Winstead proves she is a force to be reckoned with in This Book Will Bury Me. It is a powerful, driving narrative. The epub format is the best way to keep up with the pace. It allows for quick page turns and easy navigation. The story is relentless. It is a book that will bury you in its intensity. If you are looking for a digital thriller, this is the definitive choice. Get the epub and hold on tight. https://thisbookwillburymeepub.site/ This Book Will Bury Me Discount
пылесос дайсон купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]пылесос дайсон купить в спб[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге беспроводной [url=https://pylesos-dn-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-8.ru[/url] .
dyson пылесос спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-9.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-10.ru/]пылесос dyson купить в спб[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-2.ru/]dn-pylesos-2.ru[/url] .
dyson оригинал спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
дайсон пылесос купить спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-4.ru[/url] .
пылесосы дайсон [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
дайсон купить спб оригинал [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru/]дайсон купить спб оригинал[/url] .
[url=https://mrhahn-it-life.blogspot.com/2026/01/blog-post_26.html]кабели для подсветки фасадов домов[/url]
Shield of Sparrows by Devney Perry is the perfect companion for a quiet weekend. To make things even easier, download the epub version. Digital reading offers the ultimate in convenience, allowing you to carry an entire library in your hand. This book is a standout in Perry’s career, featuring unforgettable characters and a gripping plot. The crisp digital text makes reading a pleasure, no matter the time of day. If you love romance, you owe it to yourself to get this ebook. https://shieldofsparrowsepub.site/ What Is A Crux In Shield Of Sparrows
Xin chao 500 anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? cay cu?c Casino thi xem th? d?a ch? nay. Dang co khuy?n mai: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]bj88[/url]. Chuc anh em may m?n.
Рейка деревянная
ремонт айфона в великом новгороде замена вентилятора ноутбука в великом новгороде цена
Наткнулся на отличный обзор инновационной кухонной техники. Речь о варочных панелях Elica NikolaTesla со встроенной вытяжкой. Очень подробный разбор характеристик и преимуществ для современной кухни. Рекомендую почитать всем, кто планирует ремонт или обновление техники. Подробности по ссылке в источнике.
современные варочные поверхности
7k casino подходит для разных форматов игры. Платформа поддерживает быстрые сессии. Игры загружаются без ошибок. Пользователь получает стабильный доступ. Управление остается простым: 7k casino вход
Chào cả nhà, nếu anh em đang kiếm sân chơi đẳng cấp để chơi Casino thì xem thử con hàng này. Nạp rút 1-1: BJ88. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Hi cac bac, ngu?i anh em nao c?n trang choi xanh chin d? choi Da Ga thi tham kh?o d?a ch? nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: [url=https://homemaker.org.in/#]T?i Sunwin[/url]. Hup l?c d?y nha.
Деревянный плинтус для пола
ремонт микрофона samsung великий новгород замена экрана xiaomi
mostbet depunere minima [url=http://mostbet2008.help]http://mostbet2008.help[/url]
пылесосы дайсон спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-9.ru/]пылесосы дайсон спб[/url] .
Shield of Sparrows by Devney Perry is a beautiful story. The shield of sparrows epub is the right way. Digital books are great. Perry’s writing is lovely. The ebook format is easy. If you want a romance, this digital book is it. Add it to your collection.
dyson gen5 купить в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru[/url] .
заказать алкоголь с доставкой на дом [url=http://alcohub10.ru/]заказать алкоголь с доставкой на дом[/url] .
дайсон санкт петербург официальный [url=https://pylesos-dn-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-8.ru[/url] .
ремонт пылесоса дайсон в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
dyson пылесос беспроводной купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-10.ru/]dyson пылесос беспроводной купить спб[/url] .
дайсон официальный сайт в санкт петербург [url=https://dn-pylesos-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-4.ru[/url] .
Срочный ремонт кровли от протечек в Молодечно. Выезд в день обращения. Найдем источник проблемы даже в дождь. Временная и капитальная герметизация. Честные цены, без накруток за срочность. Поможем!
instagram.com/krovelnye_raboty_vg
dyson v15 купить спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-2.ru/]dn-pylesos-2.ru[/url] .
vavada kazino igre [url=https://vavada2007.help]https://vavada2007.help[/url]
дайсон центр в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
dyson пылесос спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
дайсон где купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
Коррозия на авто? центр антикоррозийной обработки авто «ЗАЩИТА» мы используем передовые шведские материалы Mercasol и Noxudol для качественной защиты днища и скрытых полостей кузова. На все работы предоставляется гарантия сроком 8 лет, а цены остаются доступными благодаря прямым поставкам материалов от производителя.
краби сентябрь краби на катамаране
Chào anh em, người anh em nào cần trang chơi xanh chín để cày cuốc Casino thì tham khảo địa chỉ này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Chao anh em, bac nao mu?n tim nha cai uy tin d? choi Da Ga thi tham kh?o trang nay nhe. Khong lo l?a d?o: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chuc anh em may m?n.
If you are searching for a book that will make you feel everything, look no further than Great Big Beautiful Life. Emily Henry weaves a tapestry of emotions that is breathtaking to behold. The epub version of this book is perfect for the modern reader who values accessibility. You can switch between devices without losing your place, making it easy to fit reading into a busy schedule. This story is a beautiful exploration of love, family, and the choices we make. It is a great addition to any reading list. Secure your digital copy now and start the journey that everyone is talking about.
Shay’s return to New York is a descent into hell, but she is bringing fire with her. This novel is intense and captivating. The The Last Housewife epub is the perfect way to read this story. The writing is sharp and evocative. It is a book about reclaiming your life from those who stole it. Winstead is a master of the genre.
dyson v15 detect absolute купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-9.ru/]dyson v15 detect absolute купить в спб[/url] .
There is a unique joy in starting a new Devney Perry book, and Shield of Sparrows is her latest offering that fans are clamoring for. If you prefer a clutter-free home, opting for the epub edition is a smart choice. Digital reading allows you to highlight your favorite passages and carry the story of Shield of Sparrows with you effortlessly. This narrative is packed with the emotional punch that readers have come to expect from Perry. By choosing the electronic version, you are choosing convenience without sacrificing the quality of the reading experience. Get ready to fall in love with these characters.
пылесос дайсон купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru[/url] .
dyson оригинал спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-10.ru/]pylesos-dn-10.ru[/url] .
доставка алкоголя ночью [url=https://www.alcohub10.ru]доставка алкоголя ночью[/url] .
дайсон купить спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон беспроводной спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-8.ru[/url] .
санкт петербург магазин дайсон [url=https://dn-pylesos-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-4.ru[/url] .
санкт петербург магазин дайсон [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
пляж краби в тайланде остров краби таиланд как добраться
дайсон пылесос [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
магазин дайсон в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
Планируете мероприятие? тимбилдинг с нейросетями москва уникальные интерактивные форматы с нейросетями для бизнеса. Мы разрабатываем корпоративные мероприятия под ключ — будь то тимбилдинги, обучающие мастер?классы или иные активности с ИИ, — с учётом ваших целей. Работаем в Москве, Санкт?Петербурге и регионах. AI?Event специализируется на организации корпоративных мероприятий с применением технологий искусственного интеллекта.
Украшения для пирсинга https://piercing-opt.ru купить оптом украшения для пирсинга. Напрямую от производителя, выгодные цены, доставка. Отличное качество.
дайсон санкт петербург официальный [url=https://pylesos-dn-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-9.ru[/url] .
Language hacking is about finding shortcuts. Reading graded readers is a proven hack. Instead of years of study, you can accelerate your progress by devouring stories. If you are looking for a short stories in German PDF, you are looking for this shortcut. Olly Richards has engineered these stories to be the most efficient path to vocabulary growth. You are bypassing the traditional, slow methods and going straight to the source: the language itself. Hack your German learning by immersing yourself in compelling narratives. https://shortstoriesingermanpdf.site/ Short Stories For Kids In German
The quest for the Better Than the Prom PDF is a quest for a good time. This book is pure entertainment. It is lighthearted but not shallow, funny but not silly. Liz and Wes are a couple that you want to succeed. Their journey is full of obstacles, but that just makes the ending more satisfying. It is the perfect book to curl up with on a quiet evening. https://betterthantheprompdf.site/ Better Than The Prom Page Count
материк краби провинция краби погода
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге беспроводной [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru[/url] .
Hello mọi người, ai đang tìm chỗ nạp rút nhanh để chơi Nổ Hũ thì xem thử địa chỉ này. Đang có khuyến mãi: Đăng nhập BJ88. Về bờ thành công.
где купить дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://pylesos-dn-10.ru/]где купить дайсон в санкт петербурге[/url] .
Hi các bác, bác nào muốn tìm chỗ nạp rút nhanh để chơi Casino thì vào ngay địa chỉ này. Uy tín luôn: Tải Sunwin. Chiến thắng nhé.
пылесосы дайсон спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
дайсон сервисный центр санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-8.ru[/url] .
дайсон спб официальный магазин [url=https://dn-pylesos-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-4.ru[/url] .
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Casino thì vào ngay địa chỉ này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
пылесос dyson [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]пылесос dyson[/url] .
заказать алкоголь с доставкой москва [url=https://alcohub10.ru/]заказать алкоголь с доставкой москва[/url] .
Hi cac bac, bac nao mu?n tim c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? g? g?c Tai X?u thi tham kh?o ch? nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: [url=https://homemaker.org.in/#]Link t?i Sunwin[/url]. Chi?n th?ng nhe.
juego lucky jet pin-up [url=http://pinup2003.help/]http://pinup2003.help/[/url]
дайсон купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]дайсон купить спб[/url] .
где купить дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
pin-up təhlükəsiz giriş [url=http://pinup2009.help]http://pinup2009.help[/url]
ремонт стекла iрhоnе ремонт петли ноутбука
[url=https://telegra.ph/Termoustojchivyj-kabel-dlya-doma-i-bani-sovety-ehksperta-po-montazhu-01-26]Монтаж термоустойчивого кабеля[/url]
“Le Boyfriend” est un livre qui vous fera regarder votre téléphone avec méfiance. Freida McFadden y décrit les dangers des rencontres en ligne avec un réalisme effrayant. Ce thriller est disponible en format epub pour tous les lecteurs connectés. L’intrigue est palpitante, pleine de rebondissements et de moments chocs. C’est une lecture addictive qui vous fera passer par toutes les émotions. Ne manquez pas ce roman qui est déjà un classique du genre. https://leboyfriendepub.site/ Le.boyfriend Freida
dyson v15 спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-9.ru[/url] .
Découvrez la vérité sur les affaires Sarkozy. Ce livre est une enquête personnelle. Le format epub du journal d’un prisonnier est pratique. L’auteur y démonte les accusations une par une. Un livre convaincant. https://lejournaldunprisonnierepub.site/ Livre Le Journal D’un Prisonnier
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно купить биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными обменниками, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по маржинальной торговле и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2323]как поменять валюту в тинькофф банке[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2584]как перевести биткоины с кошелька на кошелек[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2561]вывод перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3060]обменник альфа банк[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2753]медвежья ловушка в трейдинге что это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]проверка кошелька трон[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2959]48 биткоинов в рублях[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2207]обналичивание биткоина[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3003]высокие перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1751]alm проверка[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, где надежно обменять криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по поиску потерянных кошельков и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1446]проверить адрес юсдт[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]проверить usdt trc20 транзакцию[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2565]кредитное плечо на бирже[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1895]что такое memo при переводе криптовалюты и где его взять[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1895]где взять memo[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1687]ber20 что за сеть[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]комиссии при переводе сбербанк[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2310]сова обменник как обменять[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2089]как usdc перевести в usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3016]12 белорусских рублей в долларах[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
СВО новости В зоне СВО отмечается активизация беспилотной авиации. Военные эксперты анализируют тактику и эффективность использования дронов в современных боевых действиях. Ведутся разработки по защите от беспилотных летательных аппаратов.
If you want a book that makes you feel giddy, read Better Than the Prom. It captures the excitement of a crush. If you are looking for the PDF, you are looking for butterflies. The book evokes the physical sensation of falling in love. It is a visceral reading experience. https://betterthantheprompdf.site/ Is Better Than The Prom A Book
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно конвертировать TRX на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными обменниками, которые работают без AML-проверок. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по использованию TRC20/BEP20 сетей и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, как работает Tor-браузер.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1834]том тор[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]что такое гарант в тг[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1732]арбитраж законно[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1556]чем отличается фиксированный купон от постоянного[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3060]обменник альфа банк[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2959]можно ли обналичить биткоины[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2895]как обменять крипту на рубли[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]11 токенов в рубли[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1485]как поменять usd на usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2548]арбитраж в крипте что это такое[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
dyson v15 спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru[/url] .
pin-up apuestas moto gp [url=https://www.pinup2003.help]pin-up apuestas moto gp[/url]
Стоимость укладки гибкой черепицы. В цену входит подготовка сплошного основания из ОСП или фанеры, монтаж подкладочного ковра, укладка гонтов и установка коньковых элементов. Четкий расчет за работу под ключ. krovlyamolodechno.ru
замена аккумулятора на айфоне 11 сервисный центр honor великий новгород
I found this post very helpful and informative. The information is well presented and easy to follow. Thank you for sharing such valuable insights with readers.
visit this website https://sgp88id.id/
Mateslots payment methods are designed to suit different player needs. With secure and flexible options, users can deposit and withdraw funds easily while enjoying a seamless casino experience.
dyson v15 купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-10.ru/]dyson v15 купить спб[/url] .
pin-up apk [url=https://pinup2009.help/]https://pinup2009.help/[/url]
пылесос dyson купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
пылесосы dyson спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-4.ru[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://pylesos-dn-8.ru/]купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге[/url] .
ремонт дайсон в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
Новости СВО В Санкт-Петербурге задержана группа мошенников, обманывавших пенсионеров. Злоумышленники представлялись сотрудниками социальных служб и предлагали пожилым людям оформить льготы, выманивая у них деньги. Полиция призывает граждан быть бдительными и не доверять подозрительным звонкам и предложениям.
замена аккумулятора на iphone rераir iрhоnе
Ищешь сокращатель сылок? https://l1l.kz надежный сокращатель ссылок в Казахстане, рекомендуем заглянуть на сайт, где весь функционал доступен бесплатно и без регистрации
Противопожарные двери https://bastion52.ru купить для защиты помещений от огня и дыма. Большой выбор моделей, классы огнестойкости EI30, EI60, EI90, качественная фурнитура и соответствие действующим стандартам.
Ищете, как анонимно конвертировать криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими криптосервисами, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как выбрать безопасный обменник без регистрации. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2768]в чем разница между usdt и usdc[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3040]регистрация на binance для россиян 2024[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2741]какие криптовалюты будут расти[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1685]как вывести криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]как работает тор браузер[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1753]потерянные биткоин кошельки[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2864]ada монета прогноз[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1532]usdc чем отличается от usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1582]сколько может идти транзакция биткоин[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]проверка кошелька трон[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, где надежно конвертировать USDT на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без AML-проверок. Узнайте, как обналичить биткоин в РФ. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по использованию TRC20/BEP20 сетей и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1701]что такое мемо в криптовалюте[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2524]перевод контекста[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменники биткойн[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1582]omni перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/en/knowledgebase/blog/read/1871]как перевести криптовалюту с одного кошелька на другой[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1597]фундаментальный анализ криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2573]обменник криптовалют телеграмм бот[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3003]в какой сети работает usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]как настроить тор для анонимности[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3016]12 белорусских рублей в долларах[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
заказать алкоголь москва [url=https://alcohub10.ru/]заказать алкоголь москва[/url] .
Xin chao 500 anh em, bac nao mu?n tim nha cai uy tin d? cay cu?c Tai X?u thi vao ngay d?a ch? nay. Dang co khuy?n mai: T?i app Dola789. Chi?n th?ng nhe.
Военная служба по контракту дает уверенность в завтрашнем дне. Доход выплачивается без задержек. Все начисления официальны. Контракт закрепляет условия службы. Процесс оформления простой. Начни сегодня, контрактная армия рф
Chào anh em, người anh em nào cần cổng game không bị chặn để giải trí Đá Gà đừng bỏ qua địa chỉ này. Không lo lừa đảo: Link tải Sunwin. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Когда хочется уверенности а не обещаний стоит выбрать проверенный путь. Военная служба по контракту предлагает стабильный доход и социальные гарантии. Все условия известны заранее. Действуй сейчас и подай заявку – контакт хмао
Контрактная служба – это стабильный заработок и официальные условия. Выплаты зависят от выслуги. Контракт подписывается добровольно. Все регламентировано: подписать контракт на сво в хмао
Нужны цветы? заказать ромашки закажите цветы с доставкой на дом или в офис. Большой выбор букетов, свежие цветы, стильное оформление и точная доставка. Подойдёт для праздников, сюрпризов и важных событий.
Новости России Россия и Китай укрепляют экономическое сотрудничество. Подписан ряд соглашений в области энергетики, транспорта и высоких технологий. Стороны выразили заинтересованность в дальнейшем расширении торговых связей и реализации совместных инфраструктурных проектов.
Служба по контракту включает в себя социальные гарантии. Предусмотрено медицинское обеспечение. Также доступно страхование. Военнослужащие получают стабильные выплаты. Это повышает уверенность в завтрашнем дне: служба по контракту в рф
Ищете, как анонимно купить криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь проверенными криптосервисами, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как вывести криптовалюту на карту. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, как избежать блокировки средств.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]как работает тор браузер[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]браузер тор что это и как пользоваться[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]проверка trc20[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2871]как пройти верификацию в бинансе[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2060]trx какая сеть[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2203]фигура три вершины в трейдинге[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1666]если вы инвестирование совершаете маржинальные сделки как правило размер возможных убытков[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1655]криптовалюта ada прогнозы[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3356]где можно платить криптовалютой[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3183]как торговать на бинансе с прибылью[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
dyson оригинал спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-9.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]пылесос dyson[/url] .
Les secrets tuent dans “Le Boyfriend”, et personne n’est à l’abri. Freida McFadden tisse une intrigue complexe où chaque révélation est un choc. Ce thriller est disponible en format epub pour ceux qui préfèrent la lecture électronique. L’histoire est immersive, angoissante et brillamment écrite. C’est le livre parfait pour s’évader dans un monde de mystère. Ne passez pas à côté de cette pépite littéraire.
Face à la tempête médiatique, l’écriture reste le dernier rempart. Nicolas Sarkozy l’utilise magistralement dans ce nouvel opus. Pour découvrir ses arguments, téléchargez l’epub du journal d’un prisonnier. L’ancien chef de l’État y décortique les dossiers avec une précision chirurgicale. C’est un livre de combat, mais aussi de réflexion sur l’avenir de la démocratie française.
дайсон спб официальный магазин [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
The search for the perfect short stories in German PDF ends here. You have found a resource that checks all the boxes: right level, interesting content, learning support, and professional quality. Now the only thing left to do is read. Open the book, enter the world of the story, and let the German language wash over you. Your fluency is waiting.
If you are looking for a book to read on vacation, Better Than the Prom is perfect. It is a great beach read. If you are searching for the PDF, you are packing your bags. The book is the perfect companion for relaxation.
Hello m?i ngu?i, ai dang tim trang choi xanh chin d? choi Game bai thi xem th? trang nay nhe. T?c d? ban th?: Dola789 dang nh?p. Chi?n th?ng nhe.
Xin chào 500 anh em, bác nào muốn tìm sân chơi đẳng cấp để gỡ gạc Casino thì tham khảo chỗ này. Không lo lừa đảo: Link tải Sunwin. Chiến thắng nhé.
O’zbekiston uchun https://uzresearch.uz iqtisodiyot, moliya, ijtimoiy jarayonlar, bozorlar va mintaqaviy rivojlanish kabi asosiy sohalarda tadqiqotlar olib boradigan analitik platforma. Strukturaviy ma’lumotlar va professional tahlil.
dyson v15 спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru[/url] .
шторы блэкаут на заказ Пошив штор блэкаут идеален для детских комнат и спален. Ткань устойчива к выгоранию, легко чистится, а дизайн может быть любым — от однотонного до с принтами. Закажите у нас, и ваш дом станет еще уютнее.
https://doskazaymov.kz/
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно обменять USDT на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь проверенными криптосервисами, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по использованию TRC20/BEP20 сетей и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, как избежать блокировки средств.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1453]tor brayzer[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2959]как обналичивать криптовалюту в рф[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2551]как вывести эфириум в рубли[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3060]перевод между выбранными счетами невозможен альфа банк почему[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1904]как добавить маржу на bybit[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3003]стесуцюн перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1781]комиссия тинькофф за перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2524]перевод выбрать[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1685]можно ли обналичить криптовалюту в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2613]во сколько зачисляется кэшбэк на тинькофф[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, где надежно конвертировать криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по обходу ограничений и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Ознакомьтесь, что такое memo при переводе.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменники крипты без верификации[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3905]для чего нужен тор браузер[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1762]книга заявок[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1446]проверить адрес usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2549]binance как вывести деньги[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3306]перевод transfer of own funds[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2655]sol to rub[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1203]отс в крипте это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2480]как конвертировать валюту в тинькофф[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3288]как обналичить криптовалюту в россии законно[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Savdo va biznes https://infinitytrade.uz uchun xalqaro platforma. Bozor tahlili, xalqaro savdo, eksport va import, logistika, moliya va biznes yangiliklari. Tadbirkorlar va kompaniyalar uchun foydali materiallar, sharhlar va ma’lumotlar.
Ijtimoiy rivojlanish https://ijtimoiy.uz va jamoat hayoti uchun portal. Yangiliklar, tahlillar, tashabbuslar, loyihalar va ekspert fikrlari. Ijtimoiy jarayonlar, fuqarolik ishtiroki, ta’lim va jamiyatni rivojlantirish bo’yicha materiallar.
вертикальный пылесос дайсон купить спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-3.ru/]dn-pylesos-3.ru[/url] .
dyson gen5 купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-10.ru/]dyson gen5 купить в спб[/url] .
лубриканты казахстан
пылесос дайсон купить в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru[/url] .
ремонт дайсон в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-4.ru/]ремонт дайсон в спб[/url] .
dyson спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-8.ru/]dyson спб[/url] .
Ищете, где надежно обменять USDT на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными криптосервисами, которые работают без AML-проверок. Узнайте, как выбрать безопасный обменник без регистрации. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, как работает Tor-браузер.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2207]как обналичивают биткоины[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3241]обмен криптовалюты беларусь[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]гарант в телеграмме[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2584]как перевести биткоины с кошелька на кошелек[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2725]тинькофф api инвестиции[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2706]заработать на криптовалюте новичку[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2572]тройная вершина в трейдинге что означает[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2706]как заработать на криптовалюте новичку в 2024[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен крипты в москве[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3412]паттерн три вершины в трейдинге[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Прогнозы на спорт Ставки баскетбол – это калейдоскоп бросков, данков и перехватов, игра высоких скоростей и филигранной техники. Это спорт для интеллектуалов, требующий понимания тактики и стратегии команд, умения оценивать форму игроков и предсказывать ход игры.
https://mhp.ooo/
Контрактная служба это деньги стабильность и уверенность. Выплаты не зависят от внешних факторов. Все начисления официальные. Контракт определяет условия и срок. Возможны надбавки. Доход выше стандартного. Заключай контракт сейчас: служба по контракту в хмао
Chào anh em, ai đang tìm chỗ nạp rút nhanh để gỡ gạc Nổ Hũ thì xem thử chỗ này. Uy tín luôn: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Link không bị chặn[/url]. Về bờ thành công.
Qurilish materiallari https://emtb.uz turar-joy va sanoat qurilishi uchun beton va temir-beton. Poydevorlar, pollar va inshootlar uchun ishonchli yechimlar, standartlarga muvofiqlik, izchil sifat va loyihaga xos yetkazib berish.
купить франшизу для малого бизнеса Франшиза клининговой компании – это комплексное решение для ведения прибыльного бизнеса в сфере чистоты и порядка.
Foydali maslahatlar https://grillades.uz va g’oyalar bilan panjara va barbekyu haqida loyiha. Retseptlar, panjara qilish texnikasi va jihozlar va aksessuarlarni tanlash. Mukammal ta’m va muvaffaqiyatli ochiq havoda uchrashuvlar uchun hamma narsa.
Служба по контракту с высоким доходом доступна после отбора. Денежное довольствие выплачивается регулярно. Контракт закрепляет обязательства. Начать можно после оформления – ханты мансийск контракт
Контрактная служба – это деньги здесь и сейчас. Выплаты начисляются стабильно. Условия зафиксированы договором. Не упускай шанс. Все сведения доступны здесь, вч 51085
доставка алкоголя круглосуточно [url=http://www.alcohub10.ru]доставка алкоголя круглосуточно[/url] .
High school senior Liz Rosen had the perfect prom night mapped out in her head, but reality had other plans. When her dream date flakes, she finds herself in a fake-dating scheme with Wes Bennett, the annoying neighbor she has sworn to hate. If you are searching for the Better Than the Prom PDF or a digital version to read on the go, you are in for a treat with this rom-com. It perfectly captures the chaos of senior year and the thin line between love and hate. Discover why this book is making waves among romance readers everywhere.
Si vous aimez les thrillers qui vous retournent l’estomac, lisez “Le Boyfriend”. Freida McFadden ne prend pas de gants dans ce récit brutal et fascinant. Ce roman est disponible en téléchargement epub pour une expérience de lecture optimale. L’intrigue est complexe, jouant sur les peurs et les doutes de chacun. C’est un livre qui se dévore, page après page, jusqu’à l’explosion finale. Une lecture numérique indispensable pour les fans de l’autrice.
https://doskazaymov.kz/
Ce témoignage est une lumière dans la nuit judiciaire. Nicolas Sarkozy y éclaire les faits. La version epub du journal d’un prisonnier est accessible. L’ancien président y est magistral. Une lecture nécessaire.
The problem with many online resources is that they are not graded for difficulty. You might find a short stories in German PDF that is actually meant for native speakers, leading to discouragement. This collection is strictly tailored for the Common European Framework of Reference levels A2 and B1. This means you get a challenge without the headache. The stories are fun, ranging from science fiction to crime, so you never get bored. By focusing on reading for pleasure, you remove the pressure of performance and allow your brain to absorb the language patterns naturally and effectively.
Ijtimoiy jarayonlar https://qqatx.uz va jamiyat taraqqiyoti bo’yicha onlayn axborot platformasi. Tegishli materiallar, tahliliy sharhlar, tadqiqotlar va murakkab mavzularning tushuntirishlari aniq va tuzilgan formatda.
Любишь азарт? kometa casino казино современные слоты, live-форматы, понятные правила и удобный доступ с ПК и смартфонов. Играйте онлайн в удобное время.
Hi các bác, người anh em nào cần sân chơi đẳng cấp để cày cuốc Casino thì tham khảo chỗ này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Винлайн Хоккей КХЛ – это российский хоккей во всей его красе, лига, объединяющая лучшие клубы страны и ближнего зарубежья. Это звездные игроки, бескомпромиссная борьба и непредсказуемые результаты. Ставки на КХЛ – это поддержка отечественного хоккея и возможность заработать на своих знаниях.
Военная служба по контракту с надбавками обеспечивает финансовую уверенность. Контракт оформляется добровольно. Все выплаты прозрачны. Процедура понятна – контракт с хмао
dyson пылесос купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-7.ru[/url] .
пылесос dyson купить [url=https://pylesos-dn-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-6.ru[/url] .
Ищете, где надежно обменять криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь проверенными криптосервисами, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как вывести криптовалюту на карту. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Ознакомьтесь, что такое memo при переводе.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]как работают гаранты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2773]какие сведения проверяются в рамках разработки и внедрения в практику стандартов и процедур[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2959]как обналичивают биткоины в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1753]как найти биткоины на старом компьютере[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/en/knowledgebase/blog/read/1608]как оплачивать биткоином[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2662]как заработать в трейдинге[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2480]exmo биржа криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2494]комиссия в сбербанке за перевод со счета на счет[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2406]как проверить кошелек usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1546]что случилось с тор браузером[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно обменять биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными криптосервисами, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как вывести криптовалюту на карту. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, что такое memo при переводе.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1967]криптовалюта ada прогноз[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3174]как получают криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2974]xrp криптовалюта прогноз[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1485]как поменять usd на usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1530]бычий флаг это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1557]криптовалюта как обналичить[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2565]маржинальная торговля это ответ альфа банк[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1617]что такое roi в криптовалюте[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1944]обменники без aml[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2959]как обналичивают биткоин[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Служба по контракту дает возможность получать высокий доход. Предусмотрены дополнительные надбавки. Контракт подписывается после прохождения комиссии. Условия известны заранее, служба в рф по контракту
Weather conditions, pitch status and match day environment reported
https://mhp.ooo/
Клиндо Купить франшизу – это не просто приобретение готового бизнеса, это инвестиция в систему, проверенную временем и рынком, где каждый элемент – от бренда до бизнес-процессов – отточен и оптимизирован для достижения успеха. Это возможность избежать ошибок, неизбежных при создании своего дела с нуля, и получить не только готовый продукт, но и постоянную поддержку, обучение и консультации от опытных специалистов.
погода краби тайланд декабрь отдых в провинции краби
Играешь в казино? up-x Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
Xin chao 500 anh em, bac nao mu?n tim nha cai uy tin d? choi Tai X?u thi xem th? d?a ch? nay. N?p rut 1-1: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Hup l?c d?y nha.
https://mhp.ooo/
Ищете, где надежно конвертировать USDT на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными криптосервисами, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как выбрать безопасный обменник без регистрации. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по маржинальной торговле и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, что такое memo при переводе.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1564]p2p без kyc[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2414]что такое оплата link[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2743]7000 рублей в usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2725]как переводить без комиссии тинькофф[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2554]5000 usdt цена в рублях[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2323]как поменять валюту в тинькофф банке[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1685]можно ли обменять криптовалюту на рубли в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3257]как перевести манаты в рубли[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2769]райффайзенбанк отделения в москве для физических лиц адреса[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]что такое гарант в тг[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Лучшее казино ап х играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Chào anh em, bác nào muốn tìm sân chơi đẳng cấp để giải trí Tài Xỉu thì xem thử trang này nhé. Uy tín luôn: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]BJ88[/url]. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
https://mhp.ooo/
Служба по контракту это реальный шанс кардинально изменить свой доход и уровень стабильности. Здесь платят официально и регулярно без задержек. Денежное довольствие выше чем на большинстве гражданских работ. Все условия подробно прописываются до подписания документов. Контракт гарантирует выплаты и социальные меры поддержки. Дополнительные надбавки увеличивают общий доход. Заключи контракт и начни зарабатывать уже сейчас. Узнайте больше на странице, сургут служба по контракту
La poesia di questo libro non sta solo nelle parole, ma nei silenzi tra una riga e l’altra, dove il lettore è invitato a mettere del suo e a riflettere. Chi cerca il piccolo principe pdf trova questi spazi di riflessione. La storia ci invita a non essere come l’uomo d’affari che conta le stelle per possederle senza mai goderne la bellezza, ma a essere come il principe che possiede il suo fiore semplicemente amandolo e prendendosene cura ogni giorno con devozione. https://ilpiccoloprincipepdf.site/ Il Piccolo Principe Italiano Russo Pdf
La conoscenza è potere, e in “L’ultimo segreto” Robert Langdon deve usarla saggiamente. Un mistero che coinvolge i potenti della terra. Il formato pdf è ideale per chi ama leggere ovunque. L’autore conferma il suo talento nel creare storie avvincenti. Se ami i thriller, non puoi perdere questo libro. https://lultimosegretopdf.site/ L’ultimo Segreto Dan Brown Epub Download
Служба по контракту ориентирована на стабильность и доход. Предусмотрены надбавки и льготы. Контракт закрепляет условия. Формат подходит для долгосрочного выбора. Узнать больше информации: вдв контракт сво
табло вылета краби погода краби на 14 дней
Просматривайте откровенные материалы
безопасно, выбирая проверенные веб-сайты для взрослых.
Используйте гарантированные источники для конфиденциального развлечения.
Review my web page: BRUTAL PORN CLIPS
Военная служба по контракту это стабильность и порядок в жизни. Здесь есть официальный доход и гарантии. Выплаты начисляются каждый месяц. Условия закреплены в контракте и не меняются без согласия сторон. Дополнительные надбавки увеличивают доход. Оформление проходит по установленным правилам. Начни оформление сегодня – хмао военкомат служба по контракту
Hello mọi người, người anh em nào cần sân chơi đẳng cấp để chơi Nổ Hũ đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]bj88[/url]. Về bờ thành công.
Concludere la lettura della Century Trilogy con I giorni dell’eternità è un’esperienza gratificante. Ken Follett non sbaglia un colpo, regalandoci un finale perfetto. L’epub è la scelta giusta per chi ama la praticità senza rinunciare alla qualità. Potrete portare sempre con voi le storie dei protagonisti, vivendo con loro le ultime grandi sfide del secolo. Un libro che arricchisce la vostra biblioteca digitale e la vostra conoscenza storica. https://igiornidelleternitaepub.site/ I Giorni Dell Eternita
Through ball completion, killer passes and their success rates
дайсон спб официальный магазин [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]дайсон спб официальный магазин[/url] .
mines en pin-up [url=https://www.pinup2003.help]https://www.pinup2003.help[/url]
дайсон спб официальный [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон беспроводной купить в спб вертикальный [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru/]пылесос дайсон беспроводной купить в спб вертикальный[/url] .
дайсон пылесос [url=https://dn-pylesos-2.ru/]dn-pylesos-2.ru[/url] .
сервисный центр dyson в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
https://mhp.ooo/
самостоятельно с пхукета до краби раявади краби тайланд отель
https://mhp.ooo/
Xin chao 500 anh em, bac nao mu?n tim san choi d?ng c?p d? g? g?c Tai X?u d?ng b? qua con hang nay. Uy tin luon: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Chi?n th?ng nhe.
一饭封神在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属官方认证平台,高清无广告体验。
Hello m?i ngu?i, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? g? g?c Game bai thi xem th? ch? nay. N?p rut 1-1: Game bai d?i thu?ng. V? b? thanh cong.
Работа по военному контракту дает официальный статус и доход. Предусмотрены высокие выплаты. Все условия прописаны документально. Подать заявку можно сейчас: хмао единовременная выплата сво
Служба по контракту решает вопрос стабильного дохода. Деньги приходят каждый месяц. Условия понятны заранее. Контракт защищает твои интересы. Дополнительные выплаты увеличивают сумму. Подай заявку. Подробная информация представлена на сайте – хмао единовременная выплата сво
Военная служба по контракту это четкий путь к стабильности и деньгам. Выплаты начисляются официально и без задержек. Условия службы известны заранее и фиксируются в контракте. Контракт исключает неопределенность и скрытые условия. Предусмотрены надбавки и дополнительные выплаты. Оформление проходит по правилам. Начни сегодня, служба по контракту в сургуте
This is a very helpful and well-written post. The explanations are clear and practical. I really appreciate the effort you put into creating this content.
mie-internet.com
Hello mọi người, người anh em nào cần cổng game không bị chặn để giải trí Game bài thì xem thử trang này nhé. Nạp rút 1-1: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Chiến thắng nhé.
Distance covered, player workload and fitness data tracked
Ставки баскетбол Фонбет – это имя, знакомое каждому любителю ставок в России. Это букмекерская контора с многолетней историей, предлагающая широкий выбор спортивных событий и высокие коэффициенты. Фонбет – это надежность и удобство.
Новости Мира В зоне СВО отмечается активизация беспилотной авиации. Военные эксперты анализируют тактику и эффективность использования дронов в современных боевых действиях. Ведутся разработки по защите от беспилотных летательных аппаратов.
Ищете, как анонимно обменять USDT на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными обменниками, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как вывести криптовалюту на карту. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, как работает Tor-браузер.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2959]как обналичивают биткоины в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1485]как перевести usd в usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]минимальный перевод в сбербанке[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3063]арбитраж криптовалют законно ли[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3356]где можно платить криптовалютой[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1685]можно ли через банкомат тинькофф положить деньги на карту сбербанка[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]браузер тор что это и как пользоваться[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2078]destination tag что это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/en/knowledgebase/blog/read/1677]обход kyc верификации[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1753]как искать забытые биткоин кошельки[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно конвертировать криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими криптосервисами, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как обналичить биткоин в РФ. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по обходу ограничений и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, как избежать блокировки средств.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменники биткойн[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменники криптовалюты в москве[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2536]как вывести деньги из тинькофф инвестиции на карту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2589]дешевая крипта которая точно взлетит[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2034]обменник криптовалют в москва сити[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]проверить кошелек usdt trc20[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3319]обменник криптовалюты сова[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2540]как скачать тор браузер на айфон[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1623]где можно расплатиться биткоинами[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]usdt проверить транзакцию[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Wow, incredible blog format! How lengthy have you been running a blog for? you made blogging glance easy. The overall look of your website is wonderful, let alone the content material!
сайт Banda Casino
Corner kick count, set piece statistics for all football matches
Il mondo non è come sembra, e “L’ultimo segreto” ce lo dimostra pagina dopo pagina. Robert Langdon scava nelle profondità della storia per trovare la verità. La comodità del formato pdf rende la lettura ancora più piacevole. L’autore intreccia magistralmente fatti reali e finzione, creando un thriller indimenticabile. Preparati a mettere in discussione le tue certezze e a scoprire una realtà nascosta.
dyson пылесос беспроводной купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru[/url] .
Non c’è modo migliore di comprendere la Guerra Fredda che attraverso le pagine di I giorni dell’eternità. Ken Follett ci offre un punto di vista privilegiato sui grandi eventi che hanno scosso il mondo. L’epub è il formato ideale per chi vuole avere questo capolavoro sempre a portata di mano. La lettura digitale vi permetterà di seguire le trame complesse e i numerosi personaggi con facilità. Un libro che vi arricchirà e vi terrà compagnia per lungo tempo.
dyson пылесос купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
пылесос дайсон [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]пылесос дайсон[/url] .
pin-up telefonla giriş [url=http://pinup2009.help]http://pinup2009.help[/url]
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
Хоккей нхл Ставки на хоккей – это битва гладиаторов на ледовой арене, где скорость, мощь и тактическое мастерство переплетаются в захватывающий танец. Здесь важна каждая деталь: от формы вратаря до сыгранности звеньев, от умения реализовывать большинство до дисциплины в обороне. Ставки на хоккей требуют глубокого знания игры, понимания тактики и умения анализировать статистику.
Контрактная служба решает вопрос с доходом. Деньги выплачиваются официально. Условия понятны. Подай заявку прямо сейчас – служба на севере год за сколько
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://dn-pylesos-2.ru/]dn-pylesos-2.ru[/url] .
夜班医生第四季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
海外华人必备的ify平台运用AI智能推荐算法,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
дайсон пылесос купить спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
Лучшее казино апх играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Играешь в казино? ап икс казино Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
гугл краби остров краби пляжи
propecia prices: Follicle Insight – cost of cheap propecia price
Новости Мира С линии фронта поступают сообщения об увеличении гуманитарной помощи населению освобожденных территорий. Российские волонтеры доставляют продукты питания, медикаменты и предметы первой необходимости. Организуются пункты временного размещения для беженцев.
цветы с доставкой недорого москва Быстрая доставка вашего заказа
Avia Masters de BGaming es un juego crash con RTP del 97% donde apuestas desde 0,10€ hasta 1.000€, controlas la velocidad de vuelo de un avion que recoge multiplicadores (hasta x250) mientras evita cohetes que reducen ganancias a la mitad, con el objetivo de aterrizar exitosamente en un portaaviones para cobrar el premio acumulado
feg.org.es
Ищете, где надежно обменять криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как выбрать безопасный обменник без регистрации. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по использованию TRC20/BEP20 сетей и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2540]tor браузера[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2589]прогноз по ada[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2576]можно ли перевести доллары на карту тинькофф[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2871]сбербанк лимиты на переводы[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3049]маржинальная торговля bybit[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2407]где найти хэш транзакции[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1498]флаг трейдинг[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2302]kyc что это в криптовалютах[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2565]плечо на бирже это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3905]для чего нужен тор браузер[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
дайсон купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru/]дайсон купить спб[/url] .
Avia Masters de BGaming es un juego crash con RTP del 97% donde apuestas desde 0,10€ hasta 1.000€, controlas la velocidad de vuelo de un avion que recoge multiplicadores (hasta x250) mientras evita cohetes que reducen ganancias a la mitad, con el objetivo de aterrizar exitosamente en un portaaviones para cobrar el premio acumulado
feg.org.es
Il fenomeno editoriale che ha scosso la critica e il pubblico è a portata di click. Una vita come tante è molto più di un semplice libro: è una discesa negli abissi dell’animo umano. Cercando la versione PDF o l’eBook, potrai accedere immediatamente a questa opera monumentale senza attendere spedizioni. La scrittura di Yanagihara è viscerale e precisa, capace di descrivere l’indescrivibile. Scopri perché tanti lettori considerano questo romanzo una pietra miliare della loro vita di lettori e preparati a un’esperienza che richiederà coraggio, empatia e una buona scorta di fazzoletti. La storia di Jude ti aspetta.
где купить дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
Cosa accadrebbe se tutto ciò che ci hanno insegnato fosse falso? “L’ultimo segreto” esplora proprio questa terrificante ipotesi attraverso gli occhi di Robert Langdon. Per chi ama la tecnologia, leggere la versione pdf su un tablet è il modo migliore per apprezzare la complessità dell’opera, magari cercando online i riferimenti artistici citati. L’autore non delude le aspettative, offrendo un mix esplosivo di suspense, storia e scienza. È un viaggio vertiginoso che ti porterà dalle biblioteche più antiche ai laboratori più moderni. Scopri il mistero che nessuno osava rivelare fino ad ora.
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно конвертировать биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными криптосервисами, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как выбрать безопасный обменник без регистрации. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Ознакомьтесь, как работает Tor-браузер.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1961]в какой сети меньше комиссия за перевод usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2563]обмен валюты на лиговском в спб[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2471]10usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2540]как скачать тор браузер на айфон[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2549]биткоин курс бинанс[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]почему берется комиссия при переводе со сбербанка на сбербанк через сбербанк онлайн в своем регионе[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]usdt trc20 обозреватель[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2589]прогноз цен на биткоин[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]как пользоваться браузером тор на компьютере[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]гаранты в телеграмме проверенные[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
пылесос дайсон купить в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]пылесос дайсон купить в спб[/url] .
La trilogia di Ken Follett si conclude con un botto in I giorni dell’eternità. Gli anni della Guerra Fredda sono descritti con una maestria che lascia ammirati. Se preferite il digitale, l’epub di questo libro è ciò che vi serve. Potrete immergervi nelle atmosfere dell’epoca con un semplice tocco, godendo di una leggibilità perfetta. Un romanzo che vi accompagnerà per molte ore, regalandovi emozioni intense e una nuova comprensione del nostro passato recente.
Контрактная служба решает вопрос с доходом. Деньги выплачиваются официально. Условия понятны. Подай заявку прямо сейчас: в ч 97646
Ищете, как анонимно купить биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по маржинальной торговле и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3250]заработок на обмене криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2706]заработать на криптовалюте новичку[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2589]прогноз по ada[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2078]destination tag что это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2725]ограничения на переводы тинькофф[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3003]в какой сети работает usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]отследить транзакцию usdt trc20[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1582]omni перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2990]отс сделки это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2651]что ждет биткоин в ближайшее время[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Iver Protocols Guide: ivermectin nz – ivermectin 50
мостбет линия спорт Кыргызстан [url=www.mostbet2035.help]мостбет линия спорт Кыргызстан[/url]
dyson пылесос купить спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-2.ru/]dn-pylesos-2.ru[/url] .
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# can i purchase generic clomid prices
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно конвертировать биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными обменниками, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как выбрать безопасный обменник без регистрации. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]tron отследить транзакцию[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2769]операционная касса по обмену валюты в москве[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1498]флаг в трейдинге фигура[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2549]binance usdt rub[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1904]как добавить маржу на bybit[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1472]характеристики перевод[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1485]как поменять usd на usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2034]криптоматы москва[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3397]где можно платить биткоином[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3319]обменник криптовалюты сова[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
dyson санкт петербург купить [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
Ищете, где надежно обменять криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь проверенными криптосервисами, которые работают без AML-проверок. Узнайте, как обналичить биткоин в РФ. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, что такое memo при переводе.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1685]как вывести криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]как пользоваться браузером тор на компьютере[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2953]binance что[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2006]лайткоин рубли[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3356]где можно расплачиваться биткоинами[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3183]как торговать на бинансе с прибылью[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2572]паттерн 3 вершины[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1546]что случилось с тор браузером[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2761]вывод средств с bybit на карту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]транзакции trc20[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
mostbet казино приложение [url=https://mostbet2035.help]mostbet казино приложение[/url]
范德沃克第二季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Служба по контракту это реальный доход а не обещания. Выплаты выше обычных. Условия известны. Подписывай контракт. Перейти к информации по ссылке – хмао военкомат служба по контракту
Avia Masters de BGaming es un juego crash con RTP del 97% donde apuestas desde 0,10€ hasta 1.000€, controlas la velocidad de vuelo de un avion que recoge multiplicadores (hasta x250) mientras evita cohetes que reducen ganancias a la mitad, con el objetivo de aterrizar exitosamente en un portaaviones para cobrar el premio acumulado
https://feg.org.es/
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru[/url] .
67280ValMillageo aa frv
AmiTrip Relief Store: Elavil – buy Elavil
сервис дайсон в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
официальный магазин дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
Follicle Insight [url=https://follicle.us.com/#]Follicle Insight[/url] Follicle Insight
塔尔萨之王高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
дайсон центр в спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-2.ru/]dn-pylesos-2.ru[/url] .
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – generic propecia without insurance
официальный сайт дайсон [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]официальный сайт дайсон[/url] .
Create a commercial italian production company
пылесос дайсон купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru/]пылесос дайсон купить в спб[/url] .
пылесосы дайсон санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
The silence of the manor is broken only by the sound of footsteps. Zade is coming. Adeline is waiting. The tension is palpable. Readers searching for the Haunting Adeline PDF are looking for this exact feeling. The book is a masterclass in suspense. It is a story that will keep you on the edge of your seat until the very last page. It is a dark, twisted, and utterly addictive read. https://hauntingadelinepdf.site/ Haunting Adeline Saga Pdf Español
Nath’s obsession with space and leaving home is his way of coping with the family dysfunction. He looks to the stars while his family falls apart on earth. This metaphor is beautifully woven throughout the text. If you are looking for the Everything I Never Told You PDF, you will appreciate the literary devices Ng uses to tell her story. The novel is a rich tapestry of symbols and themes. It is a story about the need to escape and the guilt of leaving those you love behind. https://everythinginevertoldyoupdf.site/ Everything I Never Told You Pdf Español
The magic is wild and unpredictable. It is not a safe tool. The Empire of Storms PDF shows the danger of power. Aelin plays with fire. It is exciting and scary. https://empireofstormspdf.site/ Empire Of Storms Pdf Vk
huarenus平台结合大数据AI分析,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
Iver Protocols Guide: stromectol buy – Iver Protocols Guide
пылесос дайсон [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]пылесос дайсон[/url] .
Когда планирование бюджета становится важным, стабильный доход выходит на первый план, и служба по контракту дает такую возможность с фиксированными условиями. Это решение для уверенных людей. Начни оформление уже сегодня – пункт отбора ханты мансийск на военную службу
Construcciones SL – Información organizada y práctica, ideal para proyectos cercanos.
Контрактная служба это реальная возможность зарабатывать стабильно. Выплаты начисляются каждый месяц. Все условия прозрачны. Контракт фиксирует обязательства. Предусмотрены гарантии. Подай заявление: пункт отбора ханты мансийск на военную службу
sports update site – Came across this today and the material looks fresh enough to check again later.
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
вертикальный пылесос дайсон купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru[/url] .
futurestrategicplanner – Insights are practical, helped me map out upcoming business initiatives clearly.
дайсон спб официальный магазин [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru[/url] .
The phrase “everything I never told you” captures the essence of this novel perfectly. It is about the words left unsaid between husbands and wives, and parents and children. If you are searching for a digital version, perhaps the Everything I Never Told You PDF, you will find a text rich in emotional intelligence. Celeste Ng portrays the isolation of each family member with stunning clarity. Even as they live in the same house, they are worlds apart. This book is a powerful exploration of the distance that can exist between people who are supposed to be close.
From the ashes of the Quarter Quell, a new order begins to rise in the mysterious District 13. The focus shifts to political intrigue and the heavy cost of revolution on the human spirit. Accessing the story via a Mockingjay PDF is a popular choice for modern readers who value convenience and accessibility. You can take Katniss’s journey with you on your smartphone, reading a few pages whenever you have a spare moment. The vivid descriptions and fast-paced plot make it difficult to put down. This is the chapter where all the loose ends are tied, often in shocking ways.
The detail in the world-building is staggering. Every culture is distinct. The Empire of Storms PDF is a travelogue of Erilea. It is a rich and vibrant world. It feels real.
can you get generic clomid without insurance: fertility pct guide – how to buy clomid price
范德沃克第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
fertility pct guide: how to get generic clomid tablets – fertility pct guide
дайсон официальный сайт спб [url=https://dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru/]дайсон официальный сайт спб[/url] .
Военная работа по контракту это четкий путь к финансовой стабильности. Доход зависит от условий и выбранной должности. Все выплаты регулируются и контролируются. Контракт закрепляет обязанности и гарантии. Процесс оформления понятен. Не откладывай решение – снайпер на сво вакансии
Dostie Construction showcase – Very professional with clear details, inspires confidence as soon as you visit.
Iver Protocols Guide [url=https://iver.us.com/#]Iver Protocols Guide[/url] Iver Protocols Guide
alliancenetworkguide – Alliance tips are insightful, made professional collaborations smoother.
The relationship between Elide and Lorcan is a slow-burn delight. It provides a different kind of romance than the main couple. Fans often search for the Empire of Storms PDF to read their scenes. The contrast between the dark warrior and the clever girl is perfect. It is a subplot that steals the show.
In the 1970s, being a mixed-race family in Ohio meant standing out, whether you wanted to or not. James Lee felt this acutely, and he passed his insecurities down to his son and daughter. This generational trauma is a key theme of the book. Readers often look for the Everything I Never Told You PDF to understand this specific cultural context. The book is a moving portrayal of the immigrant experience and the second-generation struggle. It is a story about the desire to blend in and the impossibility of doing so.
Parsons Manor is waiting for you. The secrets are waiting to be uncovered. The romance is waiting to be experienced. If you are looking for the Haunting Adeline PDF, your wait is over. The book is a masterpiece of dark fiction. It is a story that will stay with you long after you finish reading. It is a book that you need to read now.
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
Контрактная служба с денежным довольствием подходит для планирования. Выплаты осуществляются регулярно. Контракт фиксирует срок и условия. Процедура оформления понятна: ханты мансийск контракт
online cartoon resource – Just happened upon this, smooth performance and clean navigation overall.
mostbet лайв казино [url=http://mostbet2035.help/]http://mostbet2035.help/[/url]
Просматривайте откровенные видео на безопасных
и надежных платформах. Найдите безопасные хабы потоковой передачи для первоклассного опыта.
my site … LESBIAN PORN VIDEOS
EV Liberty site – Design is simple and professional, pages respond quickly.
fertility pct guide: fertility pct guide – fertility pct guide
allianceshubonline – Tips for global partnerships are actionable, really helped expand professional connections.
Купить Купить
Срочный перевод Срочный нотариальный перевод документов – это необходимость в современном мире, где скорость и юридическая точность играют ключевую роль. Будь то деловая поездка, учеба за границей или оформление вида на жительство, потребность в оперативном и квалифицированном переводе личных документов возникает постоянно. Наша компания предоставляет комплекс услуг по срочному нотариальному переводу документов любой сложности, гарантируя высокое качество и соблюдение установленных сроков.
эвакуатор Мариуполь круглосуточно Заказать эвакуатор Мариуполь – это просто и удобно. Достаточно одного звонка, чтобы сообщить о своей проблеме и указать местонахождение. Опытные операторы быстро оформят заказ и направят к вам ближайший эвакуатор, оснащенный всем необходимым для безопасной транспортировки вашего автомобиля.
Explore tips How to play Eye of Medusa and strategies to enhance your online casino experience while enjoying the thrill of various games from slots to table options. Immerse yourself in a world filled with excitement, where every spin or deal could lead to unexpected wins and unforgettable moments.
how to get generic clomid pills: how can i get generic clomid – can you get generic clomid pills
With the fate of the world hanging in the balance, the personal stakes feel just as heavy. Aelin wants to save her kingdom, but she also wants to save her friends. A Queen of Shadows pdf balances the macro and micro conflicts perfectly. We care about the world because we care about the people in it. The apocalypse is personal. This emotional grounding makes the epic battles matter. It is not just spectacle; it is survival. https://queenofshadowspdf.site/ Sarah Maas Queen Of Shadows Epub
Служба по контракту позволяет планировать будущее. Доход известен заранее. Выплаты начисляются регулярно. Контракт закрепляет обязательства сторон. Предусмотрены гарантии. Подай заявку сейчас, служба в армии по контракту вакансии
https://amitrip.us.com/# Elavil
ко ланте ко ланте
экскурсии на краби таиланд карта краби с достопримечательностями
多瑙高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Купить Купить
Long ball success, direct play effectiveness and aerial wins
Скидка на установку окон в Молодечно! Акция до конца месяца окно ПВХ молодечно. Успейте заказать теплые окна выгодно.
teamworknavigator – Collaborative platform is effective, enhanced project coordination and task management.
Andrea Bacle fine art photography – Natural and inviting imagery, each composition feels intentional.
therapy insights online – The writing style feels respectful and supportive throughout.
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
Aesthetic Files Aesthetic Files – это не просто набор данных, это калейдоскоп впечатлений, где каждый файл – отражение моей души, увлечений и взглядов на мир. Здесь сериалы переплетаются с пылью старых книг, а жизнь, во всем ее многообразии, находит свое отражение в каждом пикселе.
Ремонт деревянного покрытия Ремонт деревянного покрытия
Контрактная служба – это стабильный заработок и официальные условия. Выплаты зависят от выслуги. Контракт подписывается добровольно. Все регламентировано: сколько стоит служба по контракту в россии
Русские подарки и сувениры купить в широком ассортименте. Классические и современные изделия, национальные символы, качественные материалы и оригинальные идеи для памятных и душевных подарков.
Live football match score updates faster than TV broadcast, stay ahead of everyone else
爱亦凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
The relationships between the male characters are also well done. The mutual respect between Rowan, Aedion, and Chaol is great. Read about their brotherhood in the kingdom of ash pdf. It balances the female-led narrative nicely. https://kingdomofashpdf.site/ Kingdom Of Ash And Briars Epub Vk
https://derevoblog.ru/post/35741
заказать эвакуатор Мариуполь Эвакуатор Володарск – помощь на дорогах небольшого населенного пункта.
Hi there friends, its enormous article concerning cultureand fully explained, keep it up all the time.
byueuropaviagraonline
https://diigo.com/011tzs6 This subject frequently arises when individuals are weighing heating choices. I discovered some valuable contextual details here. It assisted me in comprehending the distinctions between conventional heating systems and up-to-date gas fireplace arrangements.
https://www.forextimes.ru/info/intellekt-v-dele-kak-ai-integratory
https://auto.qa/catalog/
vavada aplikacja ios [url=http://vavada2003.help]http://vavada2003.help[/url]
1win скачать приложение [url=http://1win12049.ru/]http://1win12049.ru/[/url]
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно обменять криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь проверенными обменниками, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по маржинальной торговле и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, как избежать блокировки средств.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1895]где взять memo[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1593]link криптовалюта прогнозы[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2763]есть ли комиссия при переводе через сбп в сбербанке[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1685]как легально вывести криптовалюту в рубли в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2406]как проверить адрес кошелька криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2620]tether кошелек создать[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1607]usdt адрес[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2569]можно ли рассчитываться криптовалютой в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3635]обменники астрахань[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]как пользоваться браузером тор на компьютере[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Aesthetic Files Aesthetic Files – это не просто набор данных, это калейдоскоп впечатлений, где каждый файл – отражение моей души, увлечений и взглядов на мир. Здесь сериалы переплетаются с пылью старых книг, а жизнь, во всем ее многообразии, находит свое отражение в каждом пикселе.
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно купить TRX на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными обменниками, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по поиску потерянных кошельков и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, как работает Tor-браузер.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2569]можно ли рекламировать криптовалюту в россии[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2365]тор подключение к мосту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2865]ucdc токен[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1217]как обналичить биткоин[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]как перевести деньги с карты на счет сбербанка через сбербанк онлайн с телефона[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1124]биржа без kyc[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]гаранты в телеграмме проверенные[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2573]обменник криптовалют телеграмм бот[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2705]что можно оплатить криптовалютой[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2540]tor браузер отзывы[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, где надежно обменять биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без верификации. Узнайте, как перевести TRX в рубли через Альфа-Клик. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по обходу ограничений и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2089]как usdc перевести в usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2745]гаранты в телеграмме проверенные[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]как перевести деньги с карты на счет сбербанка через сбербанк онлайн с телефона[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2034]криптомат москва сити[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3258]обменник сбербит[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1967]прогноз ada cardano[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2746]как узнать адрес своего кошелька на бинанс[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2941]простой процент и сложный процент в чем разница[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2060]trx это trc20[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптовалютный обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
clickcommercialbonding – Reliable process with clear guidance, inspired confidence instantly.
shopvaluezone – Excellent shopping site, very easy to navigate and find great items.
buy Elavil: Elavil – AmiTrip
Ищете, как быстро и безопасно купить биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь проверенными криптосервисами, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как вывести криптовалюту на карту. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по работе с гарантами в Telegram и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Изучите, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1984]что такое форки[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2414]link оплата[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2406]проверка кошелька usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1498]паттерн флаг в трейдинге что означает[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1546]браузер без ограничений[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3060]как узнать счет в альфа банке[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2572]три вершины трейдинг[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2302]что такое kyc в криптовалюте простыми словами[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]быстрый обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1485]как обменять usd на usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
https://tcso-schukino.ru/gibkie-svyazi-iz-nerzhaveyushhej-stali-xarakteristiki-i-diapazon-cen-na-gibkie-soedineniya/
1win как пополнить Optima Bank [url=http://1win12049.ru/]1win как пополнить Optima Bank[/url]
vavada bonus pierwszej wpłaty [url=http://vavada2003.help]http://vavada2003.help[/url]
Iver Protocols Guide: buy stromectol uk – Iver Protocols Guide
Реставрация Москва Ремонт Москва
Ищете, как анонимно вывести криптовалюту на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь надежными криптосервисами, которые работают без AML-проверок. Узнайте, как обналичить биткоин в РФ. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по поиску потерянных кошельков и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Ознакомьтесь, почему стоит использовать аппаратные кошельки.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2549]binance биржа официальный[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2366]укажите ключевые преимущества процесса прокатки гильзы в трехвалковом раскатном стане ассела[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2938]если вы при инвестировании совершаете маржинальные необеспеченные сделки как правило размер[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2565]что такое плечо в криптовалюте простыми словами[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2207]как обналичивают биткоины[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2454]как создать обменник криптовалют в телеграмме[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют в краснодаре[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3060]как перевести деньги без комиссии с альфа банка[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2068]сложный процент график[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3045]sberbit обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Ищете, как анонимно обменять биткоины на рубли или другие фиатные валюты? Воспользуйтесь лучшими обменниками, которые работают без KYC. Узнайте, как вывести криптовалюту на карту. Мы собрали актуальные руководства по маржинальной торговле и другим важным аспектам крипторынка. Узнайте, как работает Tor-браузер.
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1602]арисэд что это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3049]маржинальная торговля bybit[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1666]что такое маржа в криптовалюте[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/]анонимный обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1687]bsc bep 20 что это[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2030]обозреватель usdt trc20[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3051]есть ли комиссия при переводе со сбербанка[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/3040]регистрация на binance для россиян 2024[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/2549]как с бинанса вывести деньги на карту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru/knowledgebase/blog/read/1944]обменники без aml[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]криптообменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник криптовалют[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен криптовалюты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обменник крипты[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]продать криптовалюту[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]онлайн обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипто обменник[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]обмен usdt[/url]
[url=https://secrex.io/ru]крипта обмен[/url]
Dorian Havilliard is no longer just a prince; he is a king with raw, untrained magic. His journey into the heart of darkness to find the third Wyrdkey is one of the most thrilling plotlines in the finale. Readers are scrambling to get the kingdom of ash pdf to follow his dangerous path. Alongside Manon, he must navigate a web of deceit and power. The character development in this final book is phenomenal, offering redemption and growth for even the most unlikely heroes. Don’t miss out on this legendary conclusion.
For readers who love character-driven stories, the growth of Dorian Havilliard is heartbreaking and beautiful. His struggle against the demon inside him is a metaphor for mental resilience. A Queen of Shadows pdf allows you to follow his journey intimately. His quiet strength and the support of his friends are what eventually lead to his salvation. It is a storyline that resonates deeply with anyone who has faced internal darkness.
The Road is a novel that strips away all the comforts of modern life. There is no electricity, no food, no law. There is only the road and the will to survive. McCarthy’s vision is dark, but compelling. This book won the Pulitzer Prize. Many people look for the pdf format to read the story on their tablets. It is a haunting narrative that you won’t be able to put down.
“Beloved” is not just a name; it is a command and a plea. Readers intrigued by the significance of the title often search for a Beloved PDF. The word appears on the tombstone, bought at a terrible price. An electronic version of the book helps readers trace every instance of the word, revealing how its meaning shifts from a mourning cry to a living nightmare, and finally to a memory that must be laid to rest for life to continue.
https://auto.qa/rent/car/
Manisa travel guide – Very useful site, gave me practical information quickly and clearly.
Нужно казино? up x официальный современные игры, простой вход, понятный интерфейс и стабильная работа платформы. Играйте с компьютера и мобильных устройств в любое время без лишних сложностей.
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
dyson спб официальный [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru[/url] .
smartstrategymoves – Strategy advice is valuable, helped organize tasks and priorities efficiently.
дайсон купить спб оригинал [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru/]дайсон купить спб оригинал[/url] .
купить пылесос дайсон спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru[/url] .
Aesthetic Files Корги – это маленькое солнышко на четырех лапах, символ радости и беззаботности. Их забавные мордочки, неуклюжие лапки и бесконечная преданность вдохновляют меня каждый день. Их присутствие в моей жизни наполняет её теплом и светом.
learnbusinessstrategically – Practical advice provided clearly, made tough concepts easy to grasp.
https://diigo.com/011tzjc A compelling viewpoint. Lately, I’ve been researching various heating alternatives, and gas fireplaces are frequently highlighted, primarily due to their ease of use and reduced upkeep compared to conventional fireplaces. This sort of summary assists in grasping why numerous homeowners are shifting towards them.
1xbet giri? yapam?yorum [url=https://1xbet-31.com/]1xbet-31.com[/url] .
1x lite [url=https://1xbet-32.com/]1xbet-32.com[/url] .
Premier League live scores today, English football action updated in real time
1xbet mobil giri? [url=https://1xbet-33.com/]1xbet-33.com[/url] .
1xbet giri? 2025 [url=https://1xbet-34.com/]1xbet giri? 2025[/url] .
1xbet g?ncel giri? [url=https://1xbet-35.com/]1xbet g?ncel giri?[/url] .
1 xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-36.com/]1 xbet giri?[/url] .
1xbet t?rkiye [url=https://1xbet-37.com/]1xbet-37.com[/url] .
где можно купить цветы дешево в москве Срочно розы сюрприз Москва
Elavil [url=https://amitrip.us.com/#]Generic Elavil[/url] AmiTrip Relief Store
https://auto.qa/rent/car/
https://headlinesalert.com/chem-promyshlennyj-alpinizm-otlichaetsja-ot-obychnyh-vysotnyh-rabot/
эвакуатор Мариуполь круглосуточно Эвакуатор Воноваха – эвакуация в сложных прифронтовых условиях.
huarenus官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
Sofascore style live updates with detailed statistics and match analysis included
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
Контрактная служба позволяет получить гарантированный доход. Все выплаты фиксированы и прозрачны. Контракт оформляется добровольно. Условия известны до подписания: военные по контракту
букет с доставкой москва недорого Доставка роз служба сюрприз
вскрытие авто Забыли ключи? Не можете попасть домой? Вскрытие замков любой сложности – быстро, аккуратно, профессионально!
магазин ремней ремни.рф оригинальные модели из натуральной кожи для мужчин и женщин. Классические и современные дизайны, высокое качество материалов, аккуратная фурнитура и удобный выбор для любого стиля.
магазин ремней ремни.рф оригинальные модели из натуральной кожи для мужчин и женщин. Классические и современные дизайны, высокое качество материалов, аккуратная фурнитура и удобный выбор для любого стиля.
The Valg princes are terrifying antagonists that induce true horror. The descriptions of their dark power are visceral. This book leans into the dark fantasy genre heavily. If you enjoy a touch of horror with your epic fantasy, the kingdom of ash pdf is for you. The stakes feel real because the villains are genuinely threatening. There is a sense of dread that permeates the first half of the book, making the eventual victories even sweeter.
Winning the Pulitzer Prize was just one accolade for The Road, a book that has defined the post-apocalyptic genre for a generation. Cormac McCarthy writes with a poetic intensity that makes the gray, ash-covered world feel suffocatingly real. The story is a testament to the resilience of the human spirit. Whether you are reading it for the first time or revisiting it, the impact remains the same. Accessing the story via a digital file or pdf makes it easier to highlight the stunning descriptions of the landscape and the poignant conversations between the father and son.
Ultimately, the book is a story about reclaiming one’s home. Terrasen is more than a place; it is a memory and a promise. A Queen of Shadows pdf is the map back to that home. Aelin’s longing for the pine forests and the snow is palpable. It drives every decision she makes. The concept of home as a place of safety and belonging is central to the emotional arc of the series. It resonates with anyone who has ever felt lost or displaced.
жизнь Здесь я делюсь не только обзорами и мнениями, но и частичкой своей жизни. Мои фотографии, мои мысли, мои переживания – это все формирует общую картину Aesthetic Files. Это пространство, где можно отдохнуть от суеты, найти вдохновение и просто почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего. Добро пожаловать!
вскрытие сейфов Замок сейфа сломался? Содержимое нужно срочно? Вскрытие сейфов с гарантией конфиденциальности и сохранности ценностей.
цвет с доставкой недорого Букет курьер круглосуточно Москва
Найдите контент для взрослых, исследуя надежные платформы в Интернете.
Изучите защищенные источники контента для
приватного просмотра.
Feel free to surf to my blog – BUY VIAGRA
discoverlongtermprojects – Opportunities are well-presented, made strategic planning much easier.
Generic Elavil: AmiTrip – Elavil
AmiTrip Relief Store: AmiTrip – Amitriptyline
https://auto.qa/catalog/
glass craft website – Everything here feels personal and well crafted.
дайсон пылесос спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru[/url] .
Самые качественные https://bliny-olimpiiskie.ru широкий выбор весов и форматов. Надёжные материалы, удобная посадка на гриф, долговечное покрытие. Подходят для фитнеса, пауэрлифтинга и регулярных тренировок.
Throw in goals, long throws and their dangerous outcomes
1xbet giri? linki [url=https://1xbet-34.com/]1xbet giri? linki[/url] .
1xbetgiri? [url=https://1xbet-32.com/]1xbet-32.com[/url] .
1xbet turkiye [url=https://1xbet-31.com/]1xbet-31.com[/url] .
1xbet t?rkiye [url=https://1xbet-37.com/]1xbet-37.com[/url] .
bahis siteler 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-35.com/]bahis siteler 1xbet[/url] .
пылесос dyson купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]пылесос dyson купить в спб[/url] .
1xbet giri? 2025 [url=https://1xbet-36.com/]1xbet giri? 2025[/url] .
дайсон официальный сайт в санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]дайсон официальный сайт в санкт петербург[/url] .
корги Здесь я делюсь не только обзорами и мнениями, но и частичкой своей жизни. Мои фотографии, мои мысли, мои переживания – это все формирует общую картину Aesthetic Files. Это пространство, где можно отдохнуть от суеты, найти вдохновение и просто почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего. Добро пожаловать!
1x giri? [url=https://1xbet-33.com/]1xbet-33.com[/url] .
https://iver.us.com/# ivermectin cream
телефон эвакуатор Мариуполь Эвакуатор Мануш – это надежный помощник на дорогах небольшого, но важного поселка, обеспечивающий быструю и безопасную транспортировку автомобилей в случае поломки или ДТП.
остров хонг краби таиланд ко ланта экскурсии
trustedprocessframework – Very solid guidance, made internal workflow much smoother and easier.
https://auto.qa/showrooms/
For a comprehensive study of the novel, many readers look for editions that include critical essays. However, starting with the raw text in a Wuthering Heights PDF is often best. It allows you to form your own impressions before being influenced by critics. You can engage with the story directly, feeling the shock and the awe that the original readers felt. Once you have read the digital text, you will be better equipped to understand the scholarly debates that surround it. It is the foundation upon which all literary analysis is built. https://wutheringheightspdf.site/ Wuthering Heights Epub Free
The concept of “Timshel” has been tattooed on thousands of fans, symbolizing the power of choice. It is a cultural phenomenon that started with this book. To understand the full context of the word, you need to read the conversations between Lee, Adam, and Samuel. An East of Eden PDF gives you instant access to these critical chapters. Our site is the ultimate resource for Timshel-related discussions, explaining the linguistic and philosophical origins of the term. We help you understand why this single word has inspired so many people. https://eastofedenpdf.site/ East Of Eden By John Steinbeck Free Download Pdf
If you are a fan of enemies-to-lovers, this is the gold standard. The pranks and the bickering only make the romance sweeter. A PDF version is perfect for reading during those stolen moments in your day. It is a book that delivers exactly what it promises: a romance that outshines the silver screen. https://betterthanthemoviespdf.site/ Better Than The Movies Pdf Download
ремонт замков Аккуратное вскрытие сейфов с гарантией конфиденциальности и сохранности содержимого.
Военная служба по контракту подходит тем кто ценит деньги и порядок. Доход выплачивается регулярно. Все условия закреплены документально. Контракт защищает интересы. Предусмотрены дополнительные выплаты. Процедура оформления понятна. Не откладывай решение: хмао служба по контракту
1xbet giri? linki [url=https://1xbet-32.com/]1xbet-32.com[/url] .
1xbet tr [url=https://1xbet-34.com/]1xbet tr[/url] .
пылесосы дайсон спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru/]пылесосы дайсон спб[/url] .
1xbet g?ncel adres [url=https://1xbet-37.com/]1xbet-37.com[/url] .
купить хризантемы в москве с доставкой недорого на дом Цветы Москва день в день курьер
1xbet [url=https://1xbet-31.com/]1xbet-31.com[/url] .
1xbet mobi [url=https://1xbet-35.com/]1xbet mobi[/url] .
1 xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-36.com/]1 xbet giri?[/url] .
1xbet mobi [url=https://1xbet-33.com/]1xbet-33.com[/url] .
RI technology blog – Informative and easy to read, the layout makes finding details quick.
телефон эвакуатор Мариуполь Эвакуатор Мариуполь круглосуточно – это значит, что независимо от времени суток и дня недели, вы можете рассчитывать на профессиональную помощь. Служба эвакуации работает 24/7, готовая прийти на помощь в любой сложной ситуации.
дайсон пылесос беспроводной купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]дайсон пылесос беспроводной купить спб[/url] .
дайсон где купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]дайсон где купить в спб[/url] .
ivermectin 2ml: Iver Protocols Guide – Iver Protocols Guide
Нужна топливная карта? https://bts-oil.ru удобный контроль расходов на ГСМ, безналичная оплата топлива, отчетность для бухгалтерии и снижение затрат автопарка. Подключение по договору, выгодные условия для бизнеса.
Хочешь контролировать ГСМ https://bts-oil.ru экономия на топливе, контроль заправок, детальная аналитика и закрывающие документы. Решение для компаний с собственным или арендованным автопарком.
Хочешь контролировать ГСМ https://bts-oil.ru экономия на топливе, контроль заправок, детальная аналитика и закрывающие документы. Решение для компаний с собственным или арендованным автопарком.
cost propecia without rx: Follicle Insight – cost of cheap propecia prices
clickforshoppingdeals – Offers were easy to find, saved me a lot of time and effort.
The sheer ambition of Steinbeck to retell the history of the world through one family is breathtaking. He swings for the fences and connects. It is a bold, artistic statement. Art and literature majors can learn much from his ambition. An East of Eden PDF allows for a structural analysis of this grand attempt. Our content breaks down the artistic goals of the novel and evaluates its success. We help you appreciate the scale of Steinbeck’s achievement. https://eastofedenpdf.site/ East Of Eden Online Book Pdf
The setting, the music, and the romance all come together to create a perfect reading experience. Lynn Painter has a knack for atmosphere and emotion. A Better Than the Movies PDF is often sought by those who want to immerse themselves in this world. It is a book that proves that a well-written story can be just as visual and evocative as a film. https://betterthanthemoviespdf.site/ Better Than The Movies Pdf Book
Mr. Collins is a character that you love to hate. His absurdity is a comic highlight. To fully appreciate his terrible proposals, you need the text. A Pride and Prejudice PDF captures his long-winded speeches. Our platform is dedicated to the comedy of the book. We ensure that you can laugh at the most ridiculous man in Hertfordshire. Enjoy the satire that Austen directs at the clergy. https://prideandprejudicepdf.site/ Jane Austen Pride And Prejudice Text Pdf
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
1xbwt giri? [url=https://1xbet-38.com/]1xbet-38.com[/url] .
1x bet [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-1.com/]1x bet[/url] .
1xbet turkiye [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-2.com/]1xbet-turkiye-2.com[/url] .
1 x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-21.com/]1xbet-giris-21.com[/url] .
лао ладинг краби dusit thani krabi beach resort 5 краби
1 x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet-giris-22.com[/url] .
Контроль топлива топливная карта для юр лиц удобный способ учета и оплаты топлива без наличных. Контроль заправок, лимиты по авто и водителям, отчетность для бухгалтерии и снижение затрат на содержание автопарка.
Топливный контроль https://avtomateriali.ru эффективное решение для бизнеса с транспортом. Безналичная заправка, учет топлива, детальные отчеты и удобное управление расходами по каждому автомобилю.
Сайдинг для цоколя в Молодечно. Повышенная прочность купить сайдинг в молодечно в рассрочку, стильная отделка. Защитите основание дома от влаги и грязи. Большой выбор фактур.
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
https://auto.qa/catalog/
1xbet giri? linki [url=https://1xbet-32.com/]1xbet-32.com[/url] .
1xbet turkiye [url=https://1xbet-34.com/]1xbet-34.com[/url] .
1x bet giri? [url=https://1xbet-37.com/]1xbet-37.com[/url] .
mostbet как пройти верификацию [url=http://mostbet2034.help]http://mostbet2034.help[/url]
vavada wejście mirror [url=http://vavada2003.help/]http://vavada2003.help/[/url]
дайсон официальный сайт в санкт петербург [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru[/url] .
1xbet yeni giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-31.com/]1xbet-31.com[/url] .
1win актуальное зеркало Кыргызстан [url=1win12049.ru]1win12049.ru[/url]
Топливные карты для юр лиц топливные карты для юридических лиц контроль топлива, прозрачная отчетность, удобство для бухгалтерии и безопасность расчетов. Экономия времени и средств при управлении корпоративным транспортом.
Онлайн-казино Mostbet — слоты, настольные игры и live-дилеры в одном аккаунте. Удобные депозиты, оперативный вывод средств, бонусные предложения и игра с любого устройства.
1x lite [url=https://1xbet-35.com/]1x lite[/url] .
слоты mostbet [url=https://mostbet2028.help/]слоты mostbet[/url]
Shot accuracy, attempts on target and conversion rates updated live
1xbet mobi [url=https://1xbet-33.com/]1xbet-33.com[/url] .
1xbet yeni adresi [url=https://1xbet-36.com/]1xbet yeni adresi[/url] .
clickforgrowthroadmaps – Very informative content, provided actionable steps for strategic planning.
Baseball livescore MLB updates, America’s pastime with pitch-by-pitch tracking live
Hall of fame, greatest players and their career achievements celebrated
скачать тик ток мод 2026 тикток скачать бесплатно мод последнюю
Olympic football live scores, men’s and women’s tournament at the Games
Many readers find that the complexity of the Earnshaw family tree requires frequent reference to the text. A Wuthering Heights PDF is incredibly useful for keeping track of the intricate relationships and similar names. As Heathcliff enacts his revenge on those who wronged him, the plot twists and turns in unexpected ways. Having a searchable document helps clarify the timeline and the connections between characters like Hareton, Cathy, and Linton. It makes the reading experience smoother, allowing you to focus on the emotional impact of the story rather than the logistics of the plot. https://wutheringheightspdf.site/ Wuthering Heights Chapter 22 Pdf
рунетки рунетки чат
Nations League livescore updates, UEFA competition with promotion and relegation
Injury time goals, dramatic late winners and equalizers tracked live
Liz and Wes’s story is a reminder that love is often messy and inconvenient, but always worth it. Their journey is one you will want to revisit again and again. A PDF copy allows for endless re-reads. It is a narrative that stands as a testament to the enduring appeal of a well-told love story. https://betterthanthemoviespdf.site/ Better Than The Movies Epub Download
Offside calls, VAR checked decisions and linesman flags documented
тик ток мод выкладывать видео тикток мод скачать на андроид последняя
sketch inspiration site – The artwork immediately sparks curiosity and creativity.
fertility pct guide [url=https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/#]fertility pct guide[/url] where to buy generic clomid without a prescription
mostbet [url=https://www.mostbet2034.help]https://www.mostbet2034.help[/url]
рунетки онлайн рунетки онлайн
Our pick today: https://telegra.ph/parier-sur-les-corners–une-strat%c3%a9gie-sous-estim%c3%a9e-pour-battre-les-bookmakers-01-14
Only the best is here: go now
dyson магазин в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]dyson магазин в спб[/url] .
This article explains understanding through strong analysis clear structure persuasive arguments balanced examples and valuable takeaways for readers worldwide.
https://stlswarm.com/
dyson купить спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]dyson купить спб[/url] .
Record breakers, historical milestones and new achievements tracked
mostbet android приложение скачать [url=www.mostbet2028.help]mostbet android приложение скачать[/url]
bahis sitesi 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-giris-21.com/]1xbet-giris-21.com[/url] .
bahis siteler 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-2.com/]bahis siteler 1xbet[/url] .
https://rant.li/larrybrown190/bring-warmth-and-elegance-to-your-home-with-a-gas-fireplace We spent time on a long process choosing a gas fireplace during a home renovation, and what surprised me most was how different brands approach heat output and installation details. Some models are clearly designed for aesthetics first, while others put more emphasis on efficiency. I personally found it useful to compare installation types, control systems, and upkeep needs before choosing a final model. For anyone planning a similar upgrade, it’s worth taking the time to understand how gas fireplaces actually perform during regular use, not just how they look in photos.
1xbet turkey [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-1.com/]1xbet-turkiye-1.com[/url] .
Служба по контракту оформляется в установленном порядке. Все этапы проходят по регламенту. Это исключает спонтанные решения: служба на севере год за сколько
1xbet giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-38.com/]1xbet-38.com[/url] .
A sports portal sbs-sport with breaking news, statistics, and expert commentary. Match schedules, transfers, interviews, and competition results are available in real time.
Live match sporx com az results, the latest sports news, transfers, and today’s TV schedule. Live updates, key events, and all sports information in one portal.
1 x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet-giris-22.com[/url] .
Iver Protocols Guide: Iver Protocols Guide – Iver Protocols Guide
https://rant.li/larrybrown190/why-gas-fireplaces-are-the-future-of-home-heating When I first began researching gas fireplaces, I didn’t expect the market to be so wide. There are major differences between brands in terms of construction materials, burner systems, and flame presentation. Reading detailed product information and real usage feedback helped me understand what actually matters over time — things like ease of maintenance, efficiency, and reliable operation. It’s definitely not something you want to choose only based on cost or visual design alone
как попасть на работу хостес в корею правда о работе хостес
Follicle Insight: cost of propecia for sale – Follicle Insight
bahis sitesi 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-32.com/]1xbet-32.com[/url] .
1xbetgiri? [url=https://1xbet-34.com/]1xbet-34.com[/url] .
скачать мод на тик ток 2026 последняя скачать тикток мод на андроид последняя версия
1x giri? [url=https://1xbet-37.com/]1xbet-37.com[/url] .
The philosophical depth of Lee, the Chinese servant who becomes the moral compass of the novel, is often surprising to first-time readers. His intellect and wisdom provide the glue that holds the Trask family together. To truly appreciate his monologues, one must read them slowly and carefully. Having an East of Eden PDF allows for zooming in on these dense paragraphs and digesting the wisdom within. Our site highlights Lee’s contributions to the narrative, offering character studies that are indispensable for anyone reading the book in a digital format and seeking a deeper understanding of his role. https://eastofedenpdf.site/ East Of Eden Screenplay Pdf
духи дешево Духи оптом по самым выгодным ценам: гарантированное качество, прямые поставки от производителей.
Goal kick assists, goalkeeper distributions leading to goals
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru/]купить пылесос дайсон в санкт петербурге[/url] .
работа хостес в корее для девушек работа хостес за границей
1x lite [url=https://1xbet-31.com/]1xbet-31.com[/url] .
Транслируйте контент для взрослых на безопасных и надежных платформах.
Найдите безопасные хабы потоковой передачи для первоклассного опыта.
Feel free to visit my web-site DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 11 CRACKED
1xbet giri? g?ncel [url=https://1xbet-35.com/]1xbet giri? g?ncel[/url] .
рунетки чат рунетки
Many readers find that the complexity of the Earnshaw family tree requires frequent reference to the text. A Wuthering Heights PDF is incredibly useful for keeping track of the intricate relationships and similar names. As Heathcliff enacts his revenge on those who wronged him, the plot twists and turns in unexpected ways. Having a searchable document helps clarify the timeline and the connections between characters like Hareton, Cathy, and Linton. It makes the reading experience smoother, allowing you to focus on the emotional impact of the story rather than the logistics of the plot. https://wutheringheightspdf.site/ Wuthering Heights Summary Pdf Download
https://follicle.us.com/# buy generic propecia prices
The evolution of the “enemies” label in this book is fascinating to watch. Liz and Wes have a banter that masks a deep underlying affection. If you are searching for a PDF version, you are on the path to a great read. It is a story that shows how thin the line between love and hate really is, and how wonderful it is to cross it. https://betterthanthemoviespdf.site/ Better Than The Movies Pdf Download Vk
one x bet [url=https://1xbet-36.com/]one x bet[/url] .
Контрактная служба это выбор тех кто хочет зарабатывать больше. Доход фиксированный и регулярный. Все этапы оформления понятны. Предусмотрены гарантии. Подписывай контракт сейчас: югра служба по контракту
1xbet giris [url=https://1xbet-33.com/]1xbet giris[/url] .
Zinedine Zidane zidan.com.az biography, football career, achievements, and coaching successes. Details on his matches, titles, the French national team, and his time at the top clubs in world football.
The timeless appeal of the novel lies in its honesty. Austen portrays people as they are, with all their vanity and virtue. If you appreciate realistic fiction, this book is for you. A digital copy ensures that this truth is always with you. Many readers look for a Pride and Prejudice PDF to keep the book close. Our site celebrates this authenticity. Read the novel that tells the truth about human nature with a smile. https://prideandprejudicepdf.site/ Pride And Prejudice Novel Online Pdf
Учишься в МТИ? помощь мти: консультации, разъяснение сложных тем, подготовка к тестированию и экзаменам. Удобный формат, быстрые ответы и поддержка на всех этапах обучения.
https://rant.li/larrybrown190/modern-heating-made-easy-with-gas-fireplaces We spent time on a long process researching a gas fireplace for our living room renovation, and what surprised me most was how different brands approach heat output and installation details. Some models are clearly designed for aesthetics first, while others are built around heating performance. I personally found it useful to compare venting methods, control features, and maintenance considerations before making a decision. For anyone planning a similar upgrade, it’s worth taking the time to understand how gas fireplaces actually perform in everyday use, not just how they look in photos.
скачать тик ток мод версия 2026 приложение тик ток мод
1 xbet [url=https://1xbet-giris-21.com/]1xbet-giris-21.com[/url] .
1xbet tr [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-2.com/]1xbet tr[/url] .
ремонт дайсон в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]ремонт дайсон в спб[/url] .
Barling Collins – Looks polished overall and the offerings are explained in a straightforward way.
塔尔萨之王第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
birxbet [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-1.com/]1xbet-turkiye-1.com[/url] .
официальный сайт дайсон [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]официальный сайт дайсон[/url] .
Live streams golvar.com.az/ az and live matches online, including the latest football schedule for today. Follow games in real time, find out dates, start times, and key events of football tournaments.
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
1xbet yeni giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-38.com/]1xbet-38.com[/url] .
Africa Cup of Nations livescore, AFCON tournament with comprehensive coverage
Финансовая опора появляется тогда, когда доход не зависит от случайностей, а контрактная служба как раз предлагает такую стабильность с официальными выплатами и гарантиями. Это выбор для тех, кто ценит уверенность. Используй возможность сегодня: сво сургут
If you are looking for a story that encompasses the full spectrum of human emotion – love, hate, jealousy, pride, and redemption – this is it. It is a soap opera written with the skill of a Nobel Prize winner. The drama is relentless. To keep up with the twists and turns, having a portable East of Eden PDF is very convenient. Our site serves as a recap center, helping you recall plot points and character motivations as you progress through the saga. We are here to ensure you enjoy the ride without getting lost in the complexity. https://eastofedenpdf.site/ East Of Eden Chapter 8 Pdf
Zinedine Zidane https://zidan.com.az biography, football career, achievements, and coaching successes. Details on his matches, titles, the French national team, and his time at the top clubs in world football.
1x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet-giris-22.com[/url] .
Служба по контракту это быстрый и надежный способ получить стабильный доход и официальное трудоустройство. Здесь не нужно ждать повышения или искать новые вакансии, выплаты приходят регулярно каждый месяц. Доход складывается из базового денежного довольствия и надбавок за выслугу и условия службы. Все условия заранее прописываются в контракте, поэтому нет скрытых требований и сюрпризов. Также предусмотрены социальные гарантии и медицинское обеспечение. Если ты хочешь заработать и получить уверенность в завтрашнем дне, заключай контракт прямо сейчас. Узнать все детали здесь: призывной пункт пыть ях
1xbet tr [url=https://1xbet-34.com/]1xbet tr[/url] .
духи дешево Парфюмерия дешево – скидки, акции и распродажи любимых ароматов. Экономьте без потери качества!
1xbet lite [url=https://1xbet-37.com/]1xbet-37.com[/url] .
1xbet turkey [url=https://1xbet-32.com/]1xbet-32.com[/url] .
Скачать тикток мод тикток мод последняя
https://jasonejohnson11.blogspot.com/2026/01/elevate-your-homes-comfort-with-gas.html When I started looking into gas fireplaces, I didn’t expect the market to be so varied. There are major differences between brands in terms of materials, burner technology, and flame realism. Going through detailed specs and user experiences helped me understand what actually matters in the long run — things like maintenance access, fuel efficiency, and consistent performance. It’s definitely not something you want to choose purely based on price or visual design alone
The story of Wuthering Heights is a cautionary tale about the danger of isolation. A Wuthering Heights PDF allows you to see what happens when people are cut off from the world. The characters fester in their own emotions. The digital text is a window into this closed society. It serves as a reminder of the importance of community. Reading it on a connected device highlights the contrast between our hyper-connected world and the lonely moors of the 19th century. It is a relevant read for the modern age. https://wutheringheightspdf.site/ Wuthering Heights Download Epub
fertility pct guide: cost cheap clomid online – fertility pct guide
When the credits roll on your favorite film, pick up this book to keep the feeling alive. Lynn Painter captures the cinematic magic of romance and translates it into prose. A PDF copy ensures that you can dive into Liz and Wes’s world whenever the mood strikes. It is a story that validates your love for grand gestures while showing that the quiet moments are often the most meaningful. https://betterthanthemoviespdf.site/ Better Than The Movies Pdf Online
сколько зарабатывает хостес в корее работа за границей для девушек
The setting of the English countryside is integral to the mood of the novel. The walks to Netherfield and the tour of Derbyshire are beautifully described. If you love atmospheric writing, this book delivers. A digital version allows you to visualize the scenery as you read. Searching for a Pride and Prejudice PDF is the first step to visiting these locations in your mind. Our site focuses on the novel, bringing the setting to life for readers. Take a walk through the pages of history. https://prideandprejudicepdf.site/ Pride And Prejudice Translated Into Modern English Pdf
Amitriptyline: AmiTrip – buy Elavil
1 xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-31.com/]1xbet-31.com[/url] .
пылесосы dyson [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-9.ru[/url] .
1xbet mobil giri? [url=https://1xbet-35.com/]1xbet mobil giri?[/url] .
vavada tjedne promocije [url=http://vavada2010.help]vavada tjedne promocije[/url]
Live streams http://golvar.com.az and live matches online, including the latest football schedule for today. Follow games in real time, find out dates, start times, and key events of football tournaments.
1x lite [url=https://1xbet-36.com/]1x lite[/url] .
Военная служба по контракту с официальным оформлением обеспечивает доход. Предусмотрены надбавки и гарантии. Контракт закрепляет условия. Начать можно уже сейчас. Полное описание доступно здесь, выплаты контрактникам в хмао 2026
iyftv海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
one x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-21.com/]1xbet-giris-21.com[/url] .
vavada resetiranje lozinke [url=vavada2010.help]vavada2010.help[/url]
1xbet giris [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-2.com/]1xbet giris[/url] .
The intricate details of the Salinas Valley agriculture, from lettuce to beans, serve as a metaphor for the cultivation of the human soul. Steinbeck was a master of using the land to reflect the internal states of his characters. Exploring these metaphors is a delight for literature students. Using an East of Eden PDF can help you quickly locate these descriptive passages for analysis. Our website offers a thematic breakdown of nature imagery in the book, providing a structured way to interpret the landscape. We make the symbolic world of Steinbeck accessible to everyone. https://eastofedenpdf.site/ East Of Eden John Steinbeck Epub Download
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# order generic clomid no prescription
скачать новый тик ток 2026 последний мод тик ток мод последняя версия
1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi [url=https://1xbet-33.com/]1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi[/url] .
1xbet t?rkiye [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-1.com/]1xbet t?rkiye[/url] .
рунетки онлайн рунетки чат
https://writeablog.net/larrybrown190/discover-the-benefits-of-gas-fireplaces-for-modern-homes We spent time on a long process selecting a gas fireplace for our living room renovation, and what surprised me most was how manufacturers differ in heat output and installation details. Certain models focus primarily on visual appeal, while others put more emphasis on efficiency. I personally found it useful to compare venting options, control systems, and long-term maintenance requirements before making a decision. For anyone planning a similar upgrade, it’s worth spending time learning how gas fireplaces actually perform during regular use, not just how they look in photos.
рунетки чат рунетки чат
1 xbet [url=https://1xbet-38.com/]1xbet-38.com[/url] .
пылесос дайсон беспроводной спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru/]pylesos-dn-kupit-8.ru[/url] .
This novel is a treasure trove of romantic moments and witty comebacks. Liz and Wes are a pair for the ages. A digital PDF copy is a modern way to enjoy this timeless story. It is a narrative that encourages us to stop watching life from the sidelines and start living our own better-than-the-movies adventure. https://betterthanthemoviespdf.site/ Better Than The Movies Full Book Pdf Download Free
Salt n Light films – Really enjoyed exploring the projects, storytelling feels genuine and compelling.
To truly understand the Gothic genre, you must read this book. A Wuthering Heights PDF is an essential file for any student of literature. It contains all the tropes: the castle-like house, the damsel in distress (who is actually quite fierce), the tyrant, and the supernatural. The digital version allows you to checklist these elements as you read. It is a textbook example of the genre that broke the mold. Having it in a portable format means you can study the mechanics of Gothic fiction wherever you go. https://wutheringheightspdf.site/ Wuthering Heights Novel Text Pdf
dyson gen5 купить в спб [url=https://pylesos-dn-kupit-10.ru/]dyson gen5 купить в спб[/url] .
Austen’s work is copyright-free, which means it belongs to everyone. It is a shared cultural heritage. To claim your share, download the book. A Pride and Prejudice PDF is your right as a reader. Our website facilitates this access. We believe in the democratization of literature. Own a piece of history today. https://prideandprejudicepdf.site/ Download Novel Pride And Prejudice Indonesia Pdf
birxbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet-giris-22.com[/url] .
Служба по контракту позволяет планировать бюджет и строить планы на будущее. Доход поступает стабильно и официально. Все условия заранее прописываются в договоре. Контракт защищает права и обязанности сторон. Предусмотрены дополнительные выплаты и надбавки. Если хочешь стабильности и денег, заключай контракт прямо сейчас – контракт на сво хмао условия 2026
отели краби таиланд с собственным причал краби
Многие жители в Новосибирске постоянно жалуются на:
– обрывы соединения;
– проблемы с потоковым видео;
– сложности с настройкой оборудования.
Попытки решить проблему своими силами часто приводят к:
– разочарованию;
– новым сбоям;
– неожиданным списаниям.
Только надёжный провайдер даёт возможность:
– скорость без ограничений;
– гибкие условия;
– бесплатную настройку оборудования.
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]сибирские сети подключить интернет[/url]
сибирские сети интернет возможность подключения по адресу – [url=https://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=http://patriotssword.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://traumajunkie.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=https://www.dev.mebik.sk/produkt/sedlo-monte-grappa-na-skladacku-cierne/#comment-139656]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] 08afb41
The relationship between fathers and sons is the emotional core of the story. The desire to please the father drives the plot. It is a universal theme that resonates with everyone. Whether you are a son or a father, you will see yourself in this book. An East of Eden PDF is a great way to share the book with family members for a shared reading experience. Our platform offers discussion points specifically for fathers and sons, helping to bridge generational gaps through literature. We facilitate meaningful conversations through the text. https://eastofedenpdf.site/ Read East Of Eden Online Free Pdf
рунетки рунетки онлайн
Контрактная служба отличается четкой структурой обязанностей. Все условия закреплены в контракте. Гражданин заранее знакомится с требованиями. Это снижает неопределенность. Формат остается прозрачным: контракт на сво хмао условия 2026
https://paper.wf/larrybrown190/how-gas-fireplaces-bring-comfort-and-style-to-modern-homes When I first began researching gas fireplaces, I didn’t expect the market to be this diverse. There are noticeable differences between brands in terms of construction materials, burner systems, and flame presentation. Reading detailed product information and real usage feedback helped me understand what actually matters over time — things like ease of maintenance, efficiency, and reliable operation. It’s definitely not something you want to choose only based on cost or appearance alone
Iver Protocols Guide: Iver Protocols Guide – Iver Protocols Guide
1xbet yeni adresi [url=https://1xbet-giris-21.com/]1xbet-giris-21.com[/url] .
1xbet lite [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-2.com/]1xbet-turkiye-2.com[/url] .
Нужна курсовая? курсовая работа на заказ Подготовка работ по заданию, методическим указаниям и теме преподавателя. Сроки, правки и сопровождение до сдачи включены.
Follicle Insight [url=https://follicle.us.com/#]Follicle Insight[/url] cost of propecia pill
AmiTrip: buy Elavil – Generic Elavil
1xbet giri? 2025 [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-1.com/]1xbet giri? 2025[/url] .
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Wes Bennett is the book boyfriend you didn’t know you needed. His patience and understanding of Liz make him a standout character. A Better Than the Movies PDF is a great way to experience his charm firsthand. It is a story that explores the difference between the idea of love and the reality of it, concluding that the reality is far superior.
Teachers often recommend digital texts to help students engage with classic literature. A Wuthering Heights PDF can make the dense Victorian prose more approachable. Many digital readers offer built-in dictionaries, which are invaluable for understanding the dialect and vocabulary used by Brontë. This removes barriers to comprehension and allows the reader to focus on the plot and themes. Whether it is the depiction of the harsh Yorkshire winter or the fiery temperaments of the characters, the digital version makes the text accessible to a new generation of learners.
The intricate plot relies on letters, coincidences, and conversations. It is a puzzle that fits together perfectly. To see the full picture, you must read the whole book. A digital copy helps you track the plot points. Searching for a Pride and Prejudice PDF is a sign of an engaged reader. Our site focuses on the structure of the novel. Appreciate the craftsmanship of a well-told story.
凯伦皮里第一季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Служба по контракту дает реальные финансовые преимущества. Высокие выплаты и надбавки. Контракт фиксирует все условия. Не откладывай. Перейти к полному описанию предложения – контракт сво сургут
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
1xbet mobi [url=https://1xbet-38.com/]1xbet-38.com[/url] .
мостбет поддержка whatsapp [url=mostbet2034.help]mostbet2034.help[/url]
https://follicle.us.com/# cost of cheap propecia online
UDL vacation resources – Simple and practical, helps organize trips efficiently.
1x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet-giris-22.com[/url] .
Авиабилеты по низким ценам https://tutvot.com посуточная аренда квартир, вакансии без опыта работы и займы онлайн. Актуальные предложения, простой поиск и удобный выбор решений для путешествий, работы и финансов.
1 x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-21.com/]1xbet-giris-21.com[/url] .
The content flows naturally and presents ideas in a way that feels both engaging and informative.
kmaa68.com
1 xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-2.com/]1xbet-turkiye-2.com[/url] .
vavada samoisključenje [url=http://vavada2010.help/]http://vavada2010.help/[/url]
For the romantic at heart, the evolution of feelings between two proud individuals is a journey worth taking repeatedly. Jane Austen masterfully deconstructs the societal expectations of her time through the eyes of the second eldest Bennet sister. If you are traveling or commuting, a digital edition is the perfect companion. Finding a high-quality Pride and Prejudice PDF ensures that you never lose your place in the story. Our website is a tribute to this specific book, offering insights that enrich the reading experience. Fall in love with the dialogue and the drama all over again, right from your preferred device.
The silence and the winds of the Salinas Valley are almost characters themselves. Steinbeck’s ability to evoke a sense of place is unmatched. If you are reading for atmosphere, this book delivers. An East of Eden PDF allows you to carry this atmosphere with you, whether you are on a train or in a coffee shop. Our website curates the most beautiful descriptive passages, helping you appreciate the poetic nature of Steinbeck’s prose. We highlight the sensory details that make the reading experience so immersive.
1xbwt giri? [url=https://1xbet-turkiye-1.com/]1xbet-turkiye-1.com[/url] .
Военная служба по контракту это надежный способ зарабатывать. Все выплаты официальные. Условия известны заранее. Контракт оформляется быстро. Не упускай возможность – пункт отбора ханты мансийск на военную службу по контракту
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – Follicle Insight
ко лант тиен как добраться до краби тайланд
Carabao Cup live scores, English League Cup with Premier League teams playing
Cutback assists, low crosses and their conversion rates tracked
мостбет вход по номеру [url=http://mostbet2028.help]мостбет вход по номеру[/url]
1xbet giri? g?ncel [url=https://1xbet-38.com/]1xbet-38.com[/url] .
рунетки чат рунетки
AmiTrip Relief Store: Elavil – buy Elavil
1x lite [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet-giris-22.com[/url] .
Служба по контракту подходит тем, кто хочет стабильный заработок. После подписания договора предоставляются выплаты и гарантии. Все условия закреплены официально. Формат подходит для планирования: сколько стоит служба по контракту в россии
Зеркало с подсветкой Макияжное зеркало с подсветкой: создайте профессиональный макияж в домашних условиях с нашим зеркалом с подсветкой.\ Поворотные зеркала для ванной: удобные и функциональные, позволяют регулировать угол обзора.
https://iver.us.com/# stromectol ivermectin buy
For a quick refresh before an exam, a Wuthering Heights PDF is indispensable. You can skim the chapters, review the plot points, and memorize the key quotes. The searchability of the digital document saves hours of study time. You can instantly locate the scenes you need to review. It is the ultimate study guide hack for students of English literature. The classic text is right there on your screen, ready to help you ace your test with a deep understanding of Brontë’s work.
范德沃克第二季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Thank you for sharing this informative post. The explanations are clear and the information is very helpful. I appreciate the informative nature of this content.
website https://yuershuang.com/
真实的人类第二季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
一帆视频海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Поворотное зеркало в раме Зеркало поворотное в полный рост: идеальное решение для гардеробной.
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# order clomid without a prescription
海外华人必备的ifun平台,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Финансовая устойчивость приходит тогда, когда доход не зависит от случайностей, а контрактная служба как раз предлагает такую модель с прозрачными выплатами. Это выбор в пользу уверенности. Подай заявку и двигайся дальше: хмао служба по контракту
pin-up mines canlı [url=www.pinup2008.help]www.pinup2008.help[/url]
Военная служба по договору отличается прозрачными условиями. Выплаты начисляются официально. Контракт заключается на определенный срок. Возможна пролонгация: пункт отбора ханты мансийск на военную службу
奇思妙探第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
mostbet cod sms [url=https://www.mostbet2006.help]https://www.mostbet2006.help[/url]
Контрактная служба позволяет рассчитывать на высокий доход. Выплаты зависят от должности и выслуги. Контракт заключается добровольно. Условия прозрачны – контракт на 1 год
descargar pin-up apk Chile [url=www.pinup2002.help]descargar pin-up apk Chile[/url]
pin-up hesab yaratmaq [url=https://pinup2008.help]https://pinup2008.help[/url]
Imagine a book that feels like watching your favorite 90s romantic comedy but with even more depth and character development. That is exactly what you get with this Lynn Painter novel, which navigates the complexities of high school love and family expectations. Readers often look for the PDF edition to easily highlight their favorite quotes and witty banter between Liz and Wes. It is a story that reminds us that while movies are great, reality can surprise us in the most beautiful ways, especially when love is found right next door.
There are few opening lines as atmospheric as the one in this book. “1801. I have just returned from a visit to my landlord…” A Wuthering Heights PDF starts with this mundane observation and leads you into a nightmare. The contrast between the dry, urbane Lockwood and the wild inhabitants of the Heights is struck immediately. The digital text preserves this perfect opening. It is the beginning of a journey that will take you to the limits of human emotion, all accessible with a simple download.
捕风追影下载平台AI深度學習內容匹配,專為海外華人設計,提供高清視頻和直播服務。
Ultimately, East of Eden is about the possibility of redemption. No matter what you have done, you have the choice to be good. It is a hopeful message. In difficult times, this book is a balm for the soul. Finding an East of Eden PDF can be the start of a healing journey. Our platform focuses on the uplifting messages within the text, providing daily quotes and affirmations derived from the book. We focus on the light that shines through the darkness of the story.
奇思妙探高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
La fase de apuesta te ofrece la chance de configurar tu capital de entrada, y una vez que haces clic en “Empezar”, el aviГіn inicia su viaje con una trayectoria variable completamente diferente.
avia master donde jugar
AmiTrip Relief Store: AmiTrip – Generic Elavil
Follicle Insight: cost propecia price – Follicle Insight
mostbet dealer live [url=http://mostbet2006.help/]mostbet dealer live[/url]
ifvod平台结合大数据AI分析,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
Looking for a casino? https://playojo-luck.pages.dev offers over 7,000 slots and games, cashback on every bet, and fast withdrawals without restrictions. Simple registration and instant access to all games available.
Austen’s use of free indirect discourse was revolutionary for her time. It allows the reader to see into Elizabeth’s mind while maintaining a third-person perspective. To experience this literary technique, you need the book. A Pride and Prejudice PDF is a great example of this style. Our site champions the literary merit of the novel. We provide resources for those interested in the craft of writing. See how Austen changed the way stories are told.
descargar pin-up apk [url=https://pinup2002.help]descargar pin-up apk[/url]
Работа с четкими правилами и официальным доходом становится реальностью, когда выбираешь контрактную службу с прозрачными условиями и фиксированными выплатами. Дополнительные начисления делают формат еще более выгодным и предсказуемым. Подай заявку и двигайся вперед уверенно: пво служба по контракту
https://iver.us.com/# stromectol for humans
Manager reactions, touchline drama and post-match comments covered
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Нужен тепловизор? тепловизоры купить в спб для судов, лодок, кораблей, яхт и катеров от производителя: доступные цены, подтверждённое качество и официальная гарантия. Мы оперативно доставляем заказы по всей территории России и стран СНГ. Наши представительства работают в Санкт?Петербурге, Москве и Севастополе — выбирайте удобный пункт выдачи и получайте заказ в минимальные сроки.
Сдвижное зеркало Зеркало поворотное в раме: классический стиль для вашего дома.
French Open livescore updates, Roland Garros matches tracked point by point live
Opening goals, first strikes and their impact on results
海外华人必备的iyifan官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Basketball livescore for NBA and international leagues, every basket tracked live
get cheap clomid without rx [url=https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/#]fertility pct guide[/url] fertility pct guide
禁忌第一季高清完整版智能AI观看体验优化,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
戏台在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属官方认证平台,高清无广告体验。
奇思妙探第二季高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
https://rant.li/larrybrown190/designing-a-home-that-feels-warm-and-inviting I’ve been looking into different supplemental heating options, and Comfort Glow came up multiple times while reviewing different heaters. What stood out to me is how these heaters are designed for everyday home use rather than extreme industrial settings.
Factors such as heat consistency, safety shutoff systems, and noise level really matter when a heater is used daily. It’s interesting to see how some brands focus on simple, practical designs that fit well into normal living spaces instead of adding unnecessary complexity.
ао нанг краби на карте красноярск краби
愛壹帆海外版,專為華人打造的高清視頻平台AI深度學習內容匹配,支持全球加速觀看。
Кент казино предлагает простой и понятный формат онлайн игры. Пользователь не сталкивается с лишними шагами. Все процессы автоматизированы. Игры запускаются без ошибок. Это упрощает использование: кент казино играть
As a seminal work of English literature, this novel is a staple on reading lists worldwide. Finding a Wuthering Heights PDF is often the quickest way to start your reading assignment. The book challenges the social norms of the nineteenth century, particularly regarding class and gender. By reading the digital text, you can easily locate the passages that critique the rigid social structures of the time. It is a novel that invites debate and discussion, and having an electronic copy ensures you are always ready to support your arguments with direct textual evidence.
https://www.tumblr.com/uniquecloudnerd-blog/792504291612098560/cozy-up-with-comfort-glow-electric-heaters-your
Choosing a heater can be surprisingly detailed once you start comparing brands like Comfort Glow with other home heating options. Differences in construction quality, heating technology, and usability become more noticeable after reviewing real-world experiences.
I found that looking beyond technical specs and focusing on how heaters perform in typical household conditions makes the decision easier. Reliability, safety features, and consistent warmth tend to matter more than flashy features in the long run.
The concept of “original sin” is tackled head-on in this narrative, but with a twist of humanist philosophy. It challenges the reader to think about whether we are born with our fate sealed or if we carve it ourselves. These existential questions are easier to ponder when you have the text available for review. An East of Eden PDF on your phone allows you to read a few pages and reflect during quiet moments of the day. Our site provides the philosophical framework to help you navigate these heavy themes, acting as a mentor as you make your way through the book.
Подавляющее число абонентов в вашем районе испытывают:
– медленную загрузку страниц;
– ограниченную скорость в часы пик;
– скрытые платежи.
Выбор дешёвого провайдера без проверки часто приводят к:
– разочарованию;
– отсутствию техподдержки;
– переплатам за ненужные услуги.
Только надёжный провайдер даёт возможность:
– скорость без ограничений;
– гибкие условия;
– бесплатную настройку оборудования.
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• безлимитный пакет.
• Точную оценку доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку роутера
• Индивидуальную поддержку менеджера
• отсутствие скрытых платежей на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]сибсети интернет вай фай тарифы[/url]
сибирские сети провести интернет в квартире – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=http://supportfiles.scribeseo.com/post-internal-links.aspx?kwds=confidence&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://lucchesefootwear.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.arus-diplom24.ru/www.arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-cena-2.ru/www.rudik-diplom14.ru]Интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] cdb2cc0
奇思妙探高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
塔尔萨之王高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
我們的台彩專家團隊每日更新各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
ключ тг Эксклюзивный “ключ ТГ”: доступ к уникальному контенту и закрытым розыгрышам в нашем Telegram-канале!
海外华人必备的ifun平台,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
https://greinplast.pl/
For the romantic at heart, the evolution of feelings between two proud individuals is a journey worth taking repeatedly. Jane Austen masterfully deconstructs the societal expectations of her time through the eyes of the second eldest Bennet sister. If you are traveling or commuting, a digital edition is the perfect companion. Finding a high-quality Pride and Prejudice PDF ensures that you never lose your place in the story. Our website is a tribute to this specific book, offering insights that enrich the reading experience. Fall in love with the dialogue and the drama all over again, right from your preferred device.
https://www.europneus.es/
propecia: get propecia – Follicle Insight
Кент казино позволяет начать игру сразу после регистрации. Процесс занимает несколько минут. Сайт работает стабильно. Игры загружаются быстро. Это удобно для новых пользователей: kent casino официальный сайт зеркало
https://amitrip.us.com/# AmiTrip Relief Store
The interplay between the two households, Wuthering Heights and Thrushcross Grange, drives the narrative. A Wuthering Heights PDF allows you to visualize the geography of the story. The distance between them is physical and metaphorical. The digital text helps you track the movements of the characters between these two poles. It is a study in environment and character. The convenience of the ebook format allows you to easily reference the map of the moors (often included or described) to understand the spatial dynamics of this tragic romance.
Never miss a goal again with our lightning-fast livescore updates for all football matches
can i buy cheap clomid without dr prescription: can i purchase clomid now – can i order cheap clomid
https://follicle.us.com/# propecia tablets
Experience the thrill of a high school romance that feels timeless yet modern. The pranks, the parties, and the quiet moments between Liz and Wes are written with perfection. Downloading a Better Than the Movies PDF gives you instant access to this world of teenage angst and joy. It is a novel that proves you don’t need a Hollywood budget to have a romance that is worthy of the big screen.
Financial news, club revenues and transfer budgets reported
Steinbeck’s “East of Eden” is a journey from darkness into light. It is a difficult journey, but a necessary one. The book offers a roadmap for the soul. If you are lost, read this. An East of Eden PDF is a compass you can carry on your phone. Our website walks the path with you, offering insights and encouragement. We believe in the power of this book to change lives, one reader at a time.
Kent casino предлагает доступ к разнообразным онлайн развлечениям. Пользователь может выбирать формат игры под свои предпочтения. Все игры запускаются напрямую через сайт. Дополнительные настройки не требуются. Процесс остается простым: kent casino
海外华人必备的ifun平台AI深度学习内容匹配,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
爱一凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台AI深度学习内容匹配,支持全球加速观看。
pin-up bonus aktiv deyil [url=https://www.pinup2008.help]pin-up bonus aktiv deyil[/url]
Kent casino представляет собой онлайн платформу для любителей азартных игр. Пользователям доступен широкий выбор слотов и классических игр. Интерфейс сайта выполнен в современном стиле. Навигация понятна даже новым игрокам. Платформа корректно работает на разных устройствах: кент казино промокод
ключ тг Розыгрыши ключей: Участвуйте в розыгрышах лицензионных ключей для Steam и выигрывайте любимые игры!
中華職棒今日比賽結果台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,結合AI深度學習技術提供最即時的中華職棒今日比賽結果新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
The intricate dance of courtship in the Regency era is fascinating to behold. Every glance and gesture holds meaning. To decode these signals, the text is your guide. A Pride and Prejudice PDF offers a front-row seat to the social season. Our website is a resource for understanding these subtle interactions. Dive into a time when romance was a high-stakes game of strategy and heart.
Set piece goals, dead ball situations and their conversion
真实的人类第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
краби это где как добраться из бангкока до краби самостоятельно
Зеркало поворотное большое Зеркала для салонов красоты: элегантные и функциональные зеркала для салонов красоты и парикмахерских.
Today’s FIFA matches live score, official tournament coverage with accurate data feeds
Новости Стим Ключ тг: Получите эксклюзивный доступ к контенту и розыгрышам через наш Telegram-канал!
На странице размещён kraken официальный сайт с полным каталогом товаров
Контракт в армии – это деньги каждый месяц и уверенность в завтрашнем дне. Выплаты начисляются стабильно. Условия прозрачны. Подай заявку и действуй – контакт хмао
Hi all, I recently found side effects info on prescription drugs, check out this online directory. It explains drug interactions clearly. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com/Allopurinol. Thanks.
Kent casino предоставляет игрокам удобную онлайн среду. Навигация построена логично. Переходы между страницами происходят быстро. Игры работают корректно. Использование сервиса не вызывает сложностей: кент казино официальный сайт
Greetings, if you are looking for an affordable health store to buy medicines securely. I recommend this pharmacy: toradol. Selling a wide range of meds and huge discounts. Cheers.
Kent casino предлагает логичную структуру онлайн платформы. Все игры сгруппированы по категориям. Пользователь легко ориентируется на сайте. Навигация не вызывает вопросов. Это экономит время: kent casino вход
mostbet pentru ios [url=https://mostbet2006.help/]https://mostbet2006.help/[/url]
Военная служба по контракту подходит тем кто устал ждать. Деньги приходят каждый месяц. Условия известны заранее. Действуй сейчас. Полная информация представлена по ссылке – хмао единовременная выплата сво
An insightful well written article that organizes ideas clearly deepens reader understanding considerably and delivers valuable insights across many contexts.
colrstyle.com
Hey everyone, if you are looking for a reliable health store to order medicines cheaply. I found this pharmacy: naltrexone. Stocking a wide range of meds and huge discounts. Hope this helps.
Зеркало настенное с поворотным механизмом Поворотные зеркала с выгодной ценой: широкий выбор зеркал по привлекательным ценам.
Читаем лучшие романы и рассказы Литературный канал о современной прозе
indian mms porn
For a complete overview of dosage guidelines, data is available at the medical directory at: https://magmaxhealth.com/lamictal.html to ensure clinical details.
Dribble success, take-on attempts and completion rates documented
pin-up app casino [url=https://pinup2002.help/]pin-up app casino[/url]
https://tabakbaza.ru/user/tirlewbbwt
https://www.hiddenpeakteahouse.com/profile/simewo278359477/profile
Greetings, if you are looking for a useful article regarding various medications, take a look at this online directory. It explains usage and risks in detail. Source: https://magmaxhealth.com/Methotrexate. Good info.
https://www.ooltewahvet.com/profile/yitit9598483699/profile
真实的人类第一季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
https://blogs.cornell.edu/cornellmasterclassinbangkok/your-assignment/comment-page-1041/#comment-196551
Monday night football live scores, start the week with Premier League action
Hi, I recently found side effects info on various medications, I found this useful resource. It covers safety protocols clearly. Link: https://magmaxhealth.com/Toradol. Very informative.
дизайнерские шторы Шторы блэкаут на заказ – идеальный выбор для тех, кто ценит комфортный сон и конфиденциальность. Специальная ткань блокирует солнечный свет, создавая полную темноту в помещении.
римские шторы на заказ Дизайнерские шторы – это произведение искусства, воплощающее самые смелые и оригинальные идеи. Они создаются по индивидуальным эскизам и отличаются высоким качеством материалов и исполнения.
мешки прочные Мешки строительные, изготовленные из особо прочных материалов, выдерживают значительные нагрузки и устойчивы к разрывам. Они предназначены для сбора и вывоза строительного мусора, такого как битый кирпич, бетон и обломки.
If you are looking for I recommend this top-rated pharmacy pharmacy online usa to order now. Take control of your health hassle-free.
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for %keyword%
регистрация Rio Bet Casino
Greetings, if you are looking for a great health store to buy medicines hassle-free. Check out this site: clomid. Stocking high quality drugs with fast shipping. Thanks.
пошив штор в Москве Шторы на заказ – это возможность создать уникальный элемент декора, идеально соответствующий вашим требованиям и предпочтениям. Выбор ткани, фактуры, цвета и декоративных элементов позволяет подчеркнуть особенности интерьера и создать неповторимую атмосферу.
кайтсёрфинг в таиланде кайт в тайланде
Transfer rumors, player movement speculation during transfer windows
Fantasy football, player points and team management tips included
Sofascore style live updates with detailed statistics and match analysis included
Own goals, unfortunate deflections and their impact documented
World Cup qualifiers live score, road to the tournament tracked for all regions
доставка алкоголя москва круглосуточно [url=http://alcoygoloc3.ru/]доставка алкоголя москва круглосуточно[/url] .
1xbet g?ncel giri? [url=https://1xbet-giris-22.com/]1xbet g?ncel giri?[/url] .
1xbet giri? 2025 [url=https://1xbet-giris-23.com/]1xbet giri? 2025[/url] .
Injury time goals, dramatic late winners and equalizers tracked live
For a trusted source, check out this service here for fast USA shipping. Take control of your health hassle-free.
t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii [url=https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii/]t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii[/url] .
1xbet giri? g?ncel [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com/]1xbet giri? g?ncel[/url] .
bahis siteler 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]bahis siteler 1xbet[/url] .
1xbet g?ncel [url=https://1xbet-mobil-1.com/]1xbet-mobil-1.com[/url] .
bahis siteler 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-2.com/]1xbet-mobil-2.com[/url] .
1xbet yeni giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-mobil-3.com/]1xbet-mobil-3.com[/url] .
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share. Thank you!
сайт казино РиоБет
1 xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-4.com/]1xbet-mobil-4.com[/url] .
birxbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-5.com/]1xbet-mobil-5.com[/url] .
римские шторы на заказ Пошив римских штор требует высокой точности и мастерства, так как каждая деталь имеет значение. Правильно подобранная ткань и фурнитура, а также качественный пошив гарантируют долговечность и эстетичный внешний вид.
https://pawndetroit.com/wp-content/pages/?codigo-promocional-1xbet_bono-vip.html
автоновости [url=https://avtonovosti-1.ru/]автоновости[/url] .
автомобильный журнал [url=https://avtonovosti-3.ru/]автомобильный журнал[/url] .
Бесплатная консультация инженера по сайдингу в Молодечно. Ответим на все технические вопросы: паропроницаемость, точка росы, ветровая нагрузка.
сайдинг молодечно
Hey everyone, I recently found a useful article about health treatments, I recommend this drug database. It covers how to take meds in detail. Link: https://magmaxhealth.com/Flonase. Good info.
Нужна топлевная крата? топливная карта для юридических лиц: заправка на сетевых АЗС, единый счет, прозрачный учет топлива и онлайн-контроль расходов. Удобное решение для компаний с собственным автопарком.
Greetings, I wanted to share a trusted drugstore to order pills cheaply. Check out this site: flonase. Stocking generic tablets at the best prices. Good luck.
555
555
H2xw6zZ0
1%2527%2522
555
555
[url=https://vikar-auto.ru]шумоизоляция авто[/url]
Greetings, for those searching for a medical guide on common medicines, check out this drug database. You can read about usage and risks clearly. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Allopurinol. Good info.
Контрактная служба ориентирована на добровольное участие. Решение принимается самостоятельно. Условия прозрачны и закреплены документально. Предоставляются социальные меры поддержки. Это делает выбор более осознанным – вакансии в армии по контракту для мужчин
一帆平台AI深度学习内容匹配,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
捕风捉影在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属平台智能AI观看体验优化,高清无广告体验。
vavada oferta sportowa [url=www.vavada2004.help]www.vavada2004.help[/url]
mostbet зеркало для android [url=https://mostbet94620.help]https://mostbet94620.help[/url]
Atom казино регистрация открывает доступ к бонусам и фриспинам. Сразу после входа можно выбрать слоты и начать игру. Платформа работает стабильно. Перейди на официальный сайт Atom казино – atom казино онлайн
1win вход по почте [url=https://www.1win93056.help]https://www.1win93056.help[/url]
доставка алкоголя на дом круглосуточно [url=https://alcoygoloc3.ru/]доставка алкоголя на дом круглосуточно[/url] .
Русские подарки купить в интернет-магазине Москвы: сувениры, ремесленные изделия и подарочные наборы с национальным колоритом. Идеальные решения для праздников, гостей и корпоративных подарков.
mostbet регистрация без кода [url=https://mostbet94620.help/]https://mostbet94620.help/[/url]
In terms of dosage guidelines, data is available at the official information page at: https://magmaxhealth.com/lipitor.html for correct administration.
t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii [url=https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii/]t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii[/url] .
Corner goals, headed and volleyed finishes from set pieces
1xbet turkiye [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com[/url] .
1x bet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-1.com/]1xbet-mobil-1.com[/url] .
1x bet giri? [url=https://1xbet-giris-23.com/]1xbet-giris-23.com[/url] .
1x giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-2.com/]1xbet-mobil-2.com[/url] .
1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi [url=https://1xbet-mobil-3.com/]1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi[/url] .
Контрактная служба предполагает официальный порядок оформления. Кандидат проходит медицинский и профессиональный отбор. После этого подписывается договор: служба по контракту ханты мансийск
1xbet t?rkiye [url=https://1xbet-mobil-5.com/]1xbet t?rkiye[/url] .
vavada obejście blokady [url=www.vavada2004.help]vavada obejście blokady[/url]
1win демо crash [url=1win93056.help]1win93056.help[/url]
журнал автомобильный [url=https://avtonovosti-3.ru/]avtonovosti-3.ru[/url] .
1 xbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-4.com/]1 xbet[/url] .
1xbet resmi giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com[/url] .
Our pick today: aws wrap
авто новости [url=https://avtonovosti-1.ru/]avtonovosti-1.ru[/url] .
For a complete overview of dosage guidelines, please review the official information page at: https://magmaxhealth.com/methotrexate.html for risk management.
Контрактная служба создана для тех, кто выбирает доход. Выплаты начисляются регулярно. Официальный статус гарантирован. Подписывай контракт. Подробнее о деталях, воинская часть ханты мансийск
International football matches live score, friendlies and qualifiers all covered here
Hall of fame, greatest players and their career achievements celebrated
Фриспины и бонусы ждут новых игроков в казино Atom. Удобная регистрация и быстрый вход позволяют начать без лишних шагов. Платформа работает стабильно через официальный сайт и зеркало. Попробуй казино Atom уже сегодня – казино atom
Hello, if you are looking for an affordable health store to buy medicines securely. Take a look at MagMaxHealth: olanzapine. Stocking high quality drugs at the best prices. Cheers.
Atom казино официальный сайт создан для комфортной игры. Фриспины и бонусы доступны новым игрокам. Вход выполняется быстро. Начни играть без ожиданий: atom казино регистрация
Работа должна приносить деньги а не постоянные сомнения. Контрактная служба дает фиксированный доход и финансовые гарантии. Все начисления контролируются и выплачиваются вовремя. Это надежный выбор для тех кто ценит стабильность. Оформи документы и двигайся дальше: воинская часть ханты мансийск
Hi all, if you are looking for side effects info regarding prescription drugs, check out this useful resource. It explains how to take meds very well. Link: https://magmaxhealth.com/Olanzapine. Good info.
алкоголь круглосуточно [url=www.alcoygoloc3.ru/]алкоголь круглосуточно[/url] .
[url=https://shumoizolyaciya-arok-avto-77.ru]шумоизоляция арок авто[/url]
Awesome! Its really awesome post, I have got much clear idea about from this article.
https://share.google/2BlCUIXglihNd9TOm
1xbet yeni giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-mobil-1.com/]1xbet-mobil-1.com[/url] .
bahis siteler 1xbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-3.com/]bahis siteler 1xbet[/url] .
Atom казино регистрация открывает доступ к бонусам и фриспинам. Сразу после входа можно выбрать слоты и начать игру. Платформа работает стабильно. Перейди на официальный сайт Atom казино, казино атом онлайн
t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii [url=https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii/]t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii[/url] .
xbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-5.com/]xbet[/url] .
1x bet giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com[/url] .
1xbet t?rkiye [url=https://1xbet-mobil-2.com/]1xbet t?rkiye[/url] .
новости про машины [url=https://avtonovosti-3.ru/]avtonovosti-3.ru[/url] .
one x bet [url=https://1xbet-giris-23.com/]1xbet-giris-23.com[/url] .
1 xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-4.com/]1xbet-mobil-4.com[/url] .
автомобильный журнал [url=https://avtonovosti-1.ru/]avtonovosti-1.ru[/url] .
The clash of steel and the whisper of silk fill the pages of Throne of Glass. Sarah J. Maas has created a heroine who loves dresses as much as daggers. This duality makes Celaena a fascinating character to follow. As she investigates the dark forces killing her competitors, she realizes that winning the competition is only the first step in a much longer war. Securing a throne of glass pdf is a great way to start this massive series without taking up shelf space. Get ready for a story that combines the best elements of mystery, action, and romance. https://throneofglasspdf.store/ Throne Of Glass Book 4 Epub
Few books have impacted the school curriculum as significantly as this tale of stranded schoolboys. The demand for the Lord of the Flies PDF highlights the novel’s enduring popularity and necessity in academic circles. As the boys shed their uniforms and civilized behaviors, they adopt a terrifying new identity. Readers utilizing a digital version can easily navigate between the early chapters of hope and the final chapters of despair. This accessibility is key for analyzing how fear – manifested as “the beast” – manipulates the group and ultimately destroys their fragile society. https://lordofthefliespdf.site/ Lord Of The Flies Pdf Chapter 2
birxbet [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com[/url] .
Merchandise news, kit releases and official product updates
爱亦凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
Hello, for those searching for side effects info about common medicines, take a look at this useful resource. You can read about usage and risks clearly. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Methotrexate. Very informative.
Belly has loved the Fisher boys her whole life, but this summer, the stakes are higher. Jenny Han writes with a clear, engaging voice. Getting the PDF allows you to dive into the drama instantly. The Summer I Turned Pretty is about the moment you realize your childhood is over. It captures the bittersweet nature of growing up. The romance is sizzling, but the family moments are what will make you cry. It is a complete package. https://thesummeriturnedprettypdf.site/ The Summer I Turned Pretty Free Pdf Download
1xbet turkiye [url=https://1xbet-mobil-1.com/]1xbet-mobil-1.com[/url] .
1xbwt giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-3.com/]1xbet-mobil-3.com[/url] .
ночная доставка алкоголя [url=alcoygoloc3.ru]ночная доставка алкоголя[/url] .
1xbet ?ye ol [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com[/url] .
1 x bet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-5.com/]1 x bet[/url] .
мостбет промокод не работает [url=mostbet94620.help]мостбет промокод не работает[/url]
журнал автомобильный [url=https://avtonovosti-3.ru/]avtonovosti-3.ru[/url] .
t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii [url=https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii/]t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii[/url] .
1xbet giri? g?ncel [url=https://1xbet-mobil-2.com/]1xbet-mobil-2.com[/url] .
Интернет-магазин химических реактивов https://magazinreactivov.ru для учебных, научных и производственных задач. В каталоге — реактивы разных классов чистоты, расходные материалы и сопутствующие товары. Помогаем подобрать позиции под вашу задачу, предоставляем документы. Удобный заказ онлайн, актуальные цены и наличие, доставка по России.
birxbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-giris-23.com/]1xbet-giris-23.com[/url] .
1xbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-4.com/]1xbet[/url] .
Натяжные потолки в Архангельске — качественно, быстро и с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональную установку за 1 день в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем стильный дизайн натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем монтаж любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор глянцевых полотен.
Рассчитаем стоимость — позвоните!
Потолочные решения в ванной — любая расцветка. по городу — с гарантией результата-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки глянцевые высота[/url]
натяжные потолки в комнату высота – [url=https://www.29-potolok.ru/]http://www.29-potolok.ru[/url]
[url=http://theglobalmovienetwork.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://29-potolok.ru/]http://brockmarketing.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://filmstreaming4ever.00web.net/il-tesoro-del-fiume-1936-36391#comment-761200]Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] b45_c30
In terms of proper usage instructions, you can consult the medical directory at: https://magmaxhealth.com/flonase.html for safe treatment.
Hi, if anyone needs a medical guide regarding health treatments, check out this online directory. You can read about safety protocols very well. Link: https://magmaxhealth.com/Meclizine. Good info.
Read the extended version: https://prathamonline.com/
car журнал [url=https://avtonovosti-1.ru/]avtonovosti-1.ru[/url] .
Если нужен надежный игровой клуб обрати внимание на Atom казино онлайн. Большой выбор слотов и регулярные бонусы делают игру интересной. Регистрация занимает минимум времени. Проверь Atom казино официальный сайт прямо сейчас – казино атом
Atom казино вход открывает доступ к большому выбору слотов. Фриспины и бонусы доступны после регистрации. Платформа работает через официальный сайт и зеркало. Начни играть сейчас: atom казино регистрация
Для прибирання https://cleaninglviv.top/ норм
The juxtaposition of Alex’s calculated world and Ava’s chaotic emotions creates a friction that sparks the entire novel. They challenge each other to be better versions of themselves. A quick download of the Twisted Love PDF can get you started on this transformative story. The book is a testament to the idea that love is messy and unpredictable, but always worth the risk. It is a powerful, passionate opening to a series that has captivated millions. https://twistedlovepdf.site/ Twisted Love Book One Pdf
1xbet turkiye [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com[/url] .
журналы автомобильные [url=https://avtonovosti-2.ru/]avtonovosti-2.ru[/url] .
Логистика и наличие. Наш склад в Молодечно всегда имеет популярные позиции сайдинга и комплектующих в наличии. Вам не придется ждать месяц поставки из-за границы. Все необходимое для старта работ есть уже сейчас.
заказать сайдинг в молодечно
I found this article very interesting and helpful. The writing style is easy to read, and the information is well explained. It’s clear that a lot of effort went into creating this valuable and informative content.
bws9903.com
The importance of the spectacles cannot be overstated. If you are looking for the Lord of the Flies PDF, you are looking for a story where civilization hangs on a pair of glasses. They are the only technology the boys have. When Jack steals them, he steals the power of fire and the last vestige of order. Reading the book electronically allows for a quick reference to every scene involving the glasses, highlighting their pivotal role in the plot. https://lordofthefliespdf.site/ Lord Of The Flies Symbolism Essay Pdf
Contract updates, player extensions and free agent signings tracked
1xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-1.com/]1xbet-mobil-1.com[/url] .
1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi [url=https://1xbet-mobil-3.com/]1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi[/url] .
1x giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com[/url] .
1xbet ?yelik [url=https://1xbet-mobil-5.com/]1xbet ?yelik[/url] .
журнал авто [url=https://avtonovosti-3.ru/]журнал авто[/url] .
алкоголь на дом 24 [url=https://alcoygoloc3.ru]алкоголь на дом 24[/url] .
t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii [url=https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii/]t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii[/url] .
1xbet ?ye ol [url=https://1xbet-mobil-2.com/]1xbet-mobil-2.com[/url] .
1win комиссия мегапей [url=http://1win21567.help/]http://1win21567.help/[/url]
In terms of medical specifications, data is available at the detailed guide on: https://magmaxhealth.com/olanzapine.html to ensure clinical details.
1 xbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-4.com/]1 xbet[/url] .
1win не открывается что делать [url=1win93056.help]1win не открывается что делать[/url]
1xbet ?ye ol [url=https://1xbet-giris-23.com/]1xbet-giris-23.com[/url] .
ДВС и КПП https://vavtomotor.ru автозапчасти для автомобилей с гарантией и проверенным состоянием. В наличии двигатели и коробки передач для популярных марок, подбор по VIN, быстрая доставка и выгодные цены.
авто новости [url=https://avtonovosti-1.ru/]avtonovosti-1.ru[/url] .
http://www.dnstroy.com/js/pages/?1xbet_promokod_na_segodnya_besplatno.html
Stadium guides, venue information and matchday experience tips
The final trial is approaching. Throne of Glass builds to a climactic finale. Celaena must face her greatest fear. The resolution is satisfying yet open-ended. Sarah J. Maas leaves you wanting more. A throne of glass pdf allows you to finish the book and immediately start the next. don’t stop until the end. https://throneofglasspdf.store/ Throne Of Glass Complete Series Epub
vavada kurs wymiany walut [url=www.vavada2004.help]www.vavada2004.help[/url]
Hi, for those searching for a useful article about prescription drugs, check out this medical reference. It covers safety protocols clearly. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Naltrexone. Hope this is useful.
Hey everyone, anyone searching for a great source for meds to purchase health products hassle-free. I recommend MagMaxHealth: buspar. Stocking generic tablets at the best prices. Thanks.
This article is very informative and easy to understand. I appreciate the clear explanations and well-organized structure. The content provides useful insights and real value. Thank you for sharing such helpful information with readers.
qyznsj.net
1вин бонус [url=https://1win21567.help]https://1win21567.help[/url]
статьи про автомобили [url=https://avtonovosti-2.ru/]avtonovosti-2.ru[/url] .
AFC Asian Cup live scores, continental championship with all matches tracked
1xbet turkey [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com[/url] .
https://tako-text.ru/kernel/inc/?1xbet_promokod_54.html
Играешь в казино? болливуд казино красочный игровой автомат с бонусами, фриспинами и высокими выигрышами. Доступно бесплатно или на реальные деньги, поддержка мобильных устройств.
The allure of Cousins Beach is undeniable. For Belly, it is the only place that matters. Jenny Han’s novel is a love letter to summers past. Accessing the story via PDF is a convenient way to join the fandom. The Summer I Turned Pretty deals with the harsh reality that things change, even when we want them to stay the same. The romance is intense, but the underlying grief is what gives the story its weight. It is a beautifully written book about coming of age. https://thesummeriturnedprettypdf.site/ Read The Summer I Turned Pretty Pdf
birxbet [url=https://1xbet-mobil-3.com/]1xbet-mobil-3.com[/url] .
1x giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com/]1xbet-yeni-giris-1.com[/url] .
1xbet yeni giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-mobil-1.com/]1xbet-mobil-1.com[/url] .
1xbet t?rkiye giri? [url=https://1xbet-mobil-5.com/]1xbet t?rkiye giri?[/url] .
1win комиссия при выводе [url=https://1win62940.help]https://1win62940.help[/url]
Ищешь казино? clubnika casino онлайн играйте онлайн в игровые автоматы и live-казино. Бонусные предложения, демо-режим, мобильная версия и круглосуточный доступ к азартным играм без установки.
журнал про авто [url=https://avtonovosti-3.ru/]журнал про авто[/url] .
Лушчее онлайн казино pinko casino слоты, live-казино и бонусные функции. Доступ с любых устройств, понятный интерфейс и возможность выбрать бесплатный или реальный режим игры.
t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii [url=https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii/]t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii[/url] .
доставка алкоголя москва [url=http://alcoygoloc3.ru/]доставка алкоголя москва[/url] .
1win отзывы Киргизия [url=www.1win62940.help]1win отзывы Киргизия[/url]
prilosec side effects: Gastro Health Monitor – Gastro Health Monitor
Контрактная служба подходит тем кто хочет деньги без неопределенности. Выплаты стабильные и прозрачные. Условия закреплены документами. Принимай решение сегодня: как служат в мотострелковых войсках
塔尔萨之王第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
1xbet giri? adresi [url=https://1xbet-mobil-2.com/]1xbet-mobil-2.com[/url] .
https://760display.com/wp-includes/pages/vybiraem_elektrobritvu_dlya_chuvstvitelynoy_koghi.html
https://king-wifi.win/wiki/User:Promolive1xbet1
http://webjuice.ru/content/pgs/varianty_oformleniya_vanny_stili_cveta_materialy.html
1xbet ?yelik [url=https://1xbet-mobil-4.com/]1xbet ?yelik[/url] .
1xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-giris-23.com/]1xbet giri?[/url] .
http://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# generic prilosec
The concept of the “noble savage” is thoroughly debunked in this narrative. If you are looking for the Lord of the Flies PDF, you will find a story that argues civilization is a learned behavior, not an innate state. The boys do not return to a harmonious state of nature; they descend into a state of war. Reading the text electronically allows students to pinpoint the exact moments where the veneer of British propriety cracks and falls away. It is a compelling argument for the necessity of laws and social structures. https://lordofthefliespdf.site/ Lord Of The Flies William Golding Book Pdf
журнал для автомобилистов [url=https://avtonovosti-1.ru/]avtonovosti-1.ru[/url] .
The theme of “found family” is strong in this book, as the characters rely on their friends to get through difficult times. Alex and Ava’s relationship is the core, but the supporting cast is excellent. Reading the Twisted Love PDF introduces you to this group of friends. The banter between the characters adds levity to the darker moments. It is a story about the bonds we choose to make, not just the ones we are born into. https://twistedlovepdf.site/ Twisted Love Series Ana Huang Epub
http://spbsseu.ru/page/pages/promo_kod_bk_1xbet_na_segodnya_pri_registracii.html
prilosec side effects: prilosec side effects – п»їomeprazole prilosec
Играть онлайн casino pinco онлайн игровые автоматы, live-казино и бонусы для новых игроков. Удобный интерфейс, доступ с телефона и ПК, возможность играть бесплатно или на реальные ставки.
Howdy! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
написание диплома на заказ
автомобильная газета [url=https://avtonovosti-2.ru/]avtonovosti-2.ru[/url] .
Excellent article. Keep posting such kind of information on your site. Im really impressed by it.
Hello there, You’ve done a great job. I will certainly digg it and in my opinion suggest to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this website.
заказать написание дипломной работы
prilosec omeprazole: prilosec dosage – Gastro Health Monitor
http://autofs.ru/documents/pages/promokod_1xbet_bonus_pri_registracii_2020.html
Играть в казино промокод 1win при пополнении лоты, live-столы и бонусные функции. Подходит для новичков и опытных игроков, доступно бесплатно и на реальные деньги 24/7.
我們提供官方合作夥伴台灣最完整的美國職棒即時比分相關服務,包含最新官方賽事資訊、數據分析,以及專業賽事預測。
1xbet giri? [url=https://1xbet-yeni-giris-2.com/]1xbet giri?[/url] .
Казино онлайн топ 5 честных казино играйте онлайн в яркие слоты и live-казино. Динамичный игровой процесс, бонусные раунды и возможность начать игру за пару кликов с телефона или компьютера.
Champions League livescore updates, follow your favorite European clubs in real time tonight
Лучшее онлайн казино казино по карте втб играйте в слоты и live-казино с телефона или ПК. Адаптивный интерфейс, быстрый запуск игр и доступ к развлечениям в любое время.
best muscle relaxer: Spasm Relief Protocols – best muscle relaxer
Goal celebrations, iconic moments and player reactions captured live
Залетай в казино sugar rush автомат быстрый доступ к слотам, live-играм и настольным развлечениям. Удобная навигация, запуск без установки и поддержка мобильных устройств.
https://olimp-yug.ru/media/pgs/promokod_fonbet_bonus_3.html
Ticket availability, match day access and pricing information
Топовое онлайн казино new retro казино играть онлайн с телефона или ПК. Слоты и live-игры, адаптивный интерфейс и стабильный запуск без скачивания приложений.
https://tayna24.ru/news/promokod_240.html
Sweeper keeper, goalkeepers playing high line and their stats
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – buy zofran online
https://www.postonlineads.com/services/other-services/1xbet-promo-code-jordan-1x200red-bonus-e130_i30388
https://nauseacareus.com/# generic for zofran
Marios Percussion Studio – Great visual and audio rhythm display, content feels real and heartfelt.
автомобильная газета [url=https://avtonovosti-4.ru/]автомобильная газета[/url] .
Топовое онлайн казино https://avtomatresidentplay.ru/ онлайн-слоты и live-казино в одном месте. Разные режимы игры, поддержка мобильных устройств и удобный старт без установки.
Топовое онлайн казино игровой автомат колумб онлайн-слоты и live-казино в одном месте. Разные режимы игры, поддержка мобильных устройств и удобный старт без установки.
More Details: https://w3techs.com/sites/info/sozialkompendium.org
The glass castle is a monument to vanity and cruelty. In Throne of Glass, it becomes a battleground. Celaena Sardothien must navigate the treacherous waters of court life while training to kill. The introduction of Wyrdmarks and ancient gates adds a layer of mystical intrigue. This book is a foundational text for modern fantasy lovers. Finding a throne of glass pdf allows you to highlight the clues that will become important in later books. Start the saga that has captured the hearts of millions. https://throneofglasspdf.store/ Throne Of Glass Series Books Epub Free
Nausea Care US: zofran over the counter – ondansetron medication
журнал про автомобили [url=https://avtonovosti-2.ru/]журнал про автомобили[/url] .
omeprazole medication [url=https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/#]Gastro Health Monitor[/url] omeprazole over the counter
Gastro Health Monitor: п»їomeprazole prilosec – Gastro Health Monitor
戏台在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属官方认证平台,高清无广告体验。
over the counter muscle relaxers that work: Spasm Relief Protocols – methocarbamol medication
Everyone remembers the summer that changed everything. For Isabel Conklin, this is it. Jenny Han’s novel is a heartfelt exploration of first love. Many readers find that the PDF version is perfect for summer travel reading. “The Summer I Turned Pretty” delves into the complexities of sibling relationships and best friends. It is a story that respects the intensity of teenage emotions. The backdrop of the ocean mirrors the turbulent feelings of the characters. It is a beautiful book. https://thesummeriturnedprettypdf.site/ The Summer I Turned Pretty Book Series Pdf
Super subs, impact substitutes and their goal contributions
1win ставки на UFC [url=http://1win62940.help]http://1win62940.help[/url]
ondansetron zofran: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
Военная работа по контракту это быстрый путь к стабильному доходу. Все выплаты официальные и прозрачные. Условия известны заранее. Контракт определяет обязанности и выплаты. Не откладывай решение. Перейти к подробностям – служба по контракту на севере
i-Superamara boutique – Professional look, descriptions are helpful and items feel premium.
Merchandise news, kit releases and official product updates
https://nauseacareus.com/# buy zofran
Today’s FIFA matches live score, official tournament coverage with accurate data feeds
авто журнал [url=https://avtonovosti-4.ru/]авто журнал[/url] .
Ticket availability, match day access and pricing information
https://penzu.com/public/32a7a7fb2c56482e
The contrast between Alex’s dark wardrobe and Ava’s colorful life is a visual metaphor for their relationship. They bleed into each other’s worlds. Reading the Twisted Love PDF brings this imagery to life. The book is full of such symbolic details. It is a rich, textured reading experience. https://twistedlovepdf.site/ Twisted Love Epub Bud Pdf Free Download
Shot accuracy, attempts on target and conversion rates updated live
zofran otc: Nausea Care US – ondansetron otc
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• быстрое подключение за 1 день;
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис домашний интернет тв[/url]
подключить домашний интернет инсис екатеринбург – [url=http://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /[/url]
[url=http://vaxinnate.org/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]http://www.75thrangerregiment.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.kuhnni-na-zakaz1.ru/www.mostbet4128.ru]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «Инсис» в вашем доме[/url] ab7d5f9
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
中華職棒台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,提供最即時的中華職棒新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測和數據分析。
журнал о машинах [url=https://avtonovosti-2.ru/]журнал о машинах[/url] .
Nausea Care US: generic for zofran – zofran side effects
奇思妙探第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
禁忌第一季高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
zanaflex medication: Spasm Relief Protocols – buy methocarbamol
muscle relaxers for back pain: Spasm Relief Protocols – tizanidine hcl
The Shaws Center Portal Online – Clear site layout, community projects and mission are showcased well.
1win crash [url=http://1win21567.help/]http://1win21567.help/[/url]
Football fixtures tomorrow, plan ahead with upcoming match schedule and times
журналы автомобильные [url=https://avtonovosti-4.ru/]журналы автомобильные[/url] .
https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/# Gastro Health Monitor
https://app.talkshoe.com/user/promolive1xbet1
zofran otc: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
huarenus官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
一帆平台智能AI观看体验优化,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
дизайн кухни в частном доме дизайн домов и коттеджей
禁忌第一季高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
газета про автомобили [url=https://avtonovosti-2.ru/]avtonovosti-2.ru[/url] .
buy methocarbamol without prescription: Spasm Relief Protocols – buy methocarbamol
https://demcra.com/r/Gaming/1255442_552X_e_Como_Aproveitar_Bnus_para_Ganhar_Mais_Fcil_nas_Apostas_Online#n81168
plinko vavada hrvatska [url=https://vavada2009.help/]plinko vavada hrvatska[/url]
LED Extreme catalog – Easy-to-navigate listings, product details are clear and simple to review.
The first book in Jenny Han’s trilogy sets the stage for an epic romance. Cousins Beach is the place where Belly feels most herself. If you want to read about the summer that changed everything, finding a PDF is a great option. The Summer I Turned Pretty explores the pain of loving someone who might not love you back in the same way. It is also a celebration of female friendship and mother-daughter bonds. This book is an essential read for anyone who loves contemporary romance. https://thesummeriturnedprettypdf.site/ The Summer I Turned Pretty Free Download Epub
журнал про авто [url=https://avtonovosti-4.ru/]журнал про авто[/url] .
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
мостбет линия ставок [url=http://mostbet38095.help/]мостбет линия ставок[/url]
Thank you for sharing this excellent article. The content is informative and presented in a very clear way.
lcggjt.com
1win рабочее зеркало [url=https://www.1win74125.help]https://www.1win74125.help[/url]
vavada registriraj se hrvatska [url=http://vavada2009.help]http://vavada2009.help[/url]
http://cvaa.com.ar/06inc/articles/codigo_promocional_39.html
https://polter.pl/fonts/?code-promo-1win-bonus-500.html
Great article! The steps for building a CI/CD-friendly QA pipeline are clear and practical, making it very useful for teams that want to move fast. Thanks for sharing
Зеркало на штанге поворотное Зеркало с подсветкой: функциональное и стильное зеркало с подсветкой, обеспечивающее отличное освещение.
Nausea Care US [url=http://nauseacareus.com/#]zofran over the counter[/url] Nausea Care US
зип пакеты купить в Москве Зип пакеты купить в Москве – это не просто практичное решение, это инвестиция в порядок и организованность. В динамичном ритме столичной жизни, где каждая минута на счету, зип пакеты становятся надежным союзником в самых разных сферах. От хранения свежих продуктов, сохраняя их аромат и вкус, до организации мелких деталей, предотвращая хаос и беспорядок – возможности их применения безграничны.
http://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# generic prilosec
мостбет кэшбэк [url=https://mostbet38095.help]https://mostbet38095.help[/url]
robaxin medication: Spasm Relief Protocols – robaxin generic
Ava Chen is a heroine who is easy to love; she is kind, creative, and brave. Her influence on Alex is gradual but profound. Those who read the Twisted Love PDF often cite Ava’s character arc as a highlight. She learns to stand up for herself, even against the man she loves. The book creates a balanced relationship where both partners grow and change. It is a modern romance that respects the agency of its female lead. https://twistedlovepdf.site/ Twisted Love Descargar Pdf
1win apk последняя версия [url=http://1win74125.help/]http://1win74125.help/[/url]
robaxin: methocarbamol dosing – tizanidine hydrochloride
картонные упаковки Упаковка гофрокороб – это фундамент безопасной транспортировки и презентабельного представления вашей продукции. От прочности материала до эргономичности конструкции, каждый аспект гофрокороба играет ключевую роль в сохранении целостности товара и создании положительного впечатления у потребителя. Выбор правильной упаковки – это стратегическое решение, определяющее успех вашего бизнеса.
https://goldfieldstvet.edu.za/pags/1xbet_promo_code_for_free_bet_welcome_bonus.html
Зеркала лофт Зеркало настенное с поворотным механизмом: настенное зеркало с удобным поворотным механизмом для регулировки угла обзора.
онлайн обучение с выдачей диплома бьюти профессии Если же вы стремитесь к узкой специализации или хотите расширить свои навыки, онлайн-курсы по отдельным бьюти-направлениям станут отличным решением. Освойте искусство релаксации и оздоровления, став спа-технологом, изучите различные техники массажа и помогайте людям обрести гармонию тела и духа, станьте востребованным массажистом. Раскройте секреты идеальной кожи и овладейте техниками ухода, став косметиком-эстетистом, либо заявите о себе как о мастере пирсинга, создавая уникальные и стильные образы. Выбор за вами!
prilosec medication: prilosec side effects – prilosec dosage
Olive Media KC Digital Hub – Marketing insights are clear, practical examples show real effectiveness.
авто новости [url=https://avtonovosti-4.ru/]avtonovosti-4.ru[/url] .
спа Стерлитамак Подарочные сертификаты Стерлитамак – это возможность выразить свою заботу и любовь, подарив близким не просто вещь, а ценный опыт релаксации и восстановления. Подарочный сертификат на массаж или спа-программу – это идеальный подарок для тех, кто ценит свое здоровье и стремится к гармонии с собой. Это возможность отвлечься от повседневной суеты, насладиться приятными процедурами и почувствовать себя обновленным и полным сил.
https://dogs-academia.ru/
prilosec medication: prilosec otc – Gastro Health Monitor
кагарлик карта
https://service-trucks.ru/
translation helper site – Simple to use and effective for everyday language conversions.
https://svobodapress.com.ua/karta-kremenchuha/
Zip пакеты Zip пакеты – это современное и практичное решение для упаковки и хранения. Их популярность обусловлена простотой использования, многоразовостью и надежностью. Они стали неотъемлемой частью нашей повседневной жизни, значительно упрощая процессы упаковки и организации.
разработка конструкции упаковки из гофрокартона Упаковка на заказ – это решение для тех, кто стремится к совершенству в каждой детали. Индивидуальный дизайн, качественные материалы и безупречное исполнение – ваша упаковка должна говорить о высоком уровне вашего бизнеса.
mostbet logare [url=https://mostbet2010.help/]https://mostbet2010.help/[/url]
Do you do music? music sub plans for children and aspiring musicians. Educational materials, activities, and creative coloring pages to develop ear training, rhythm, and an interest in music.
Если основной сайт недоступен используй куш казино зеркало. Все бонусы и аккаунт сохраняются. Вход выполняется быстро. Продолжай игру без ограничений, казино куш вход
ZylavoOnline – Navigation is intuitive, and content is easy to locate quickly.
журналы для автолюбителей [url=https://avto-zhurnal-1.ru/]avto-zhurnal-1.ru[/url] .
газета про автомобили [url=https://avto-zhurnal-2.ru/]avto-zhurnal-2.ru[/url] .
журнал для автомобилистов [url=https://avto-zhurnal-3.ru/]журнал для автомобилистов[/url] .
trusted zorivo portal – Capital information is straightforward and gives a sense of reliability.
https://service-trucks.ru/
car журнал [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]car журнал[/url] .
domeo положительные отзывы [url=https://domeo-reviews.com/]domeo положительные отзывы[/url] .
туры выходного дня со скидкой [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru[/url] .
скидки trip.com [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru/]скидки trip.com[/url] .
туры выходного дня со скидкой [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru[/url] .
http://nauseacareus.com/# generic zofran
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog article or vice-versa? My blog addresses a lot of the same topics as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Wonderful blog by the way!
https://share.google/V8aAoaLZY3rYyMGVc
Themes of masculinity and leadership are central to the conflict on the island. When readers seek out the Lord of the Flies PDF, they are often interested in the dynamic between the sensitive Ralph and the aggressive Jack. The novel asks difficult questions about what makes a good leader and how fear can be weaponized to control a population. A digital text is an excellent tool for comparing the leadership styles presented in the book, offering insights that are applicable to history and modern society alike. It is a study of power in its rawest form.
Nausea Care US: ondansetron medication – Nausea Care US
https://www.hodfurdo.hu/images/pgs/?code_de_bonus_1.html
Hi there friends, how is all, and what you want to say on the topic of this paragraph, in my view its in fact awesome designed for me.
https://share.google/reb4qj0afq21PtccH
bond info page – Information is easy to follow, and the site feels simple and user-friendly.
CDN Promax tools – Very practical platform, the features are easy to understand and documentation is helpful.
mostbet termeni bonus [url=www.mostbet2010.help]www.mostbet2010.help[/url]
цитати гордість і упередження
http://sehk-wiki.org/index.php?title=Melbet%20%D0%9E%D1%84%D0%B8%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B0%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9%20%D0%A1%D0%B0%D0%B9%D1%82%20%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%202026:%20MAX888
TorivoSphere – Investment info is presented clearly, helping me understand options easily.
zanaflex medication: Spasm Relief Protocols – robaxin
a href=”https://qulavoholdings.bond/” />QulavoLinePro – Easy to explore and everything seems accurate and reliable.
methocarbamol medication: Spasm Relief Protocols – robaxin generic
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• доставку по всей России;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=]спортивная форма футбольных клубов[/url]
ретро формы футбольных клубов купить – [url=http://tut-sport.ru]http://www.tut-sport.ru/[/url]
[url=http://30lp.org/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru]http://coastal-contractors.net/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://tut-sport.ru[/url]
[url=https://filmstreaming4ever.00web.net/pulse-2006-45611#comment-766025]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] b7d5f9f
one x bet promo code today
журнал про машины [url=https://avtonovosti-4.ru/]журнал про машины[/url] .
nevironexus official – The content is understandable and the site feels easy to navigate.
1 win 1вин 1вин, с его славянским шармом, манит как запретный плод в саду соблазнов. Локализованный для русскоязычных искателей приключений, он предлагает лабиринт игр, где каждый поворот таит сокровища. От живых дилеров в казино до киберспортивных арен – 1вин обеспечивает безопасность, словно неприступная крепость, с многоуровневым шифрованием. Здесь бонусы расцветают пышно, а поддержка шепчет советы на родном языке, превращая обыденность в грандиозный фестиваль выигрышей.
vavada povrat novca uvjeti [url=http://vavada2009.help/]http://vavada2009.help/[/url]
https://dogs-academia.ru/
трансфер v класс mercedes v class аренда с водителем Конкретизируя модель, «mercedes v class аренда с водителем» фокусируется на одном из самых востребованных автомобилей бизнес-класса. Его узнаваемый силуэт и безупречная репутация делают его идеальным инструментом для создания имиджа и решения транспортных задач любой сложности в руках опытного водителя-профессионала.
There is nothing quite like the anticipation of a summer at the beach. For Belly, it is the highlight of her existence. Jenny Han captures that specific feeling of waiting for life to begin. Whether you read the physical book or find a PDF, the story remains just as powerful. “The Summer I Turned Pretty” deals with the realization that parents are human and that crushes can break your heart. The Fisher boys represent two very different paths for Belly. It is a compelling read from the very first page to the last.
ZylavoHub Online – The platform is visually tidy, with intuitive browsing across sections.
tizanidine zanaflex: muscle relaxers for back pain – tizanidine muscle relaxer
накрутка подписчиков вк сервис накрутка подписчиков телеграм
Для тех кто ищет рабочее куш казино зеркало предусмотрен стабильный альтернативный доступ. Все бонусы и функции сохраняются. Удобный вход и быстрая регистрация. Переходи в казино Куш онлайн – казино куш зеркало
爱一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
картонные упаковки Изготовление картонной упаковки – это процесс, требующий внимания к деталям и знания специфики упаковываемой продукции. Правильный выбор материала, конструкции и размера упаковки обеспечивает надежную защиту товара и удобство его транспортировки.
海外华人必备的ify平台智能AI观看体验优化,提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
упаковка гофрокороб Гофрокороба под заказ – это возможность создать уникальную упаковку, идеально соответствующую габаритам и характеристикам вашей продукции. Индивидуальный подход к разработке конструкции позволяет оптимизировать использование материала, повысить прочность упаковки и снизить транспортные расходы.
статьи об авто [url=https://avto-zhurnal-3.ru/]статьи об авто[/url] .
купить Zip пакеты с логотипом Зип пакет – это маленький помощник в больших делах. Он бережно хранит ваши вещи, освобождая вас от забот и хлопот.
VixaroShopPoint – Simple shopping experience with quick delivery and solid products.
скидки aviasales [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru/]скидки aviasales[/url] .
горящие путевки цены [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru[/url] .
XylixPortal – Clean design and responsive layout, made exploring enjoyable.
trusted portal network – Clean, user-friendly pages with line services explained logically.
читать отзывы domeo [url=https://domeo-reviews.com/]читать отзывы domeo[/url] .
журнал про автомобили [url=https://avto-zhurnal-2.ru/]журнал про автомобили[/url] .
промокоды onetwotrip [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru/]промокоды onetwotrip[/url] .
автоновости [url=https://avto-zhurnal-1.ru/]автоновости[/url] .
Когда нужен надежный игровой клуб стоит выбрать Kush казино официальный сайт. Быстрый вход и регулярные бонусы. Удобная регистрация для новых игроков. Начни играть сегодня: казино куш зеркало
https://svobodapress.com.ua/tsikavyy-podarunok-khlopchyku-na-10-rokiv-naykrashchi-idei-dlia-rozvytku-hry-ta-iaskravykh-emotsiy/
zorivo holdings link – Layout feels simple, branding looks consistent, and content is easy to read.
generic for zofran: Nausea Care US – buy zofran
журнал о машинах [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]журнал о машинах[/url] .
https://spasmreliefprotocols.shop/# antispasmodic medication
RixaroConnect – Clean layout makes exploring tools simple and intuitive.
Казино Куш бонусы делают старт особенно выгодным. После регистрации можно сразу войти в аккаунт. Платформа работает без сбоев. Используй возможность, казино куш официальный сайт
1xbet promo code new user turkey
BaseStream – Smooth navigation makes exploring options painless.
Ana Huang has mastered the art of writing possessive alpha males who would burn the world down for the women they love. Alex Volkov is the prime example of this archetype, and his obsession with Ava Chen is captivating to read. Whether you are reading a physical copy or scrolling through a Twisted Love PDF, the intensity of their connection jumps off the page. The plot creates a sense of impending doom that hangs over their happiness, making every tender moment feel earned and precious. It is a story about the cost of secrets and the power of truth, wrapped up in a package of undeniable romantic tension.
secure trustee platform Well organized – Trust-related information is laid out simply and logically.
гофрокороба под заказ Упаковка для производства – это неотъемлимая часть производственного процесса, обеспечивающая защиту продукции на всех этапах: от транспортировки на склад до отгрузки покупателю. Правильно подобранная упаковка позволяет оптимизировать логистические процессы, снизить потери и повысить эффективность производства.
zofran over the counter: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
дизайн ванной в квартире дизайн проект 2 комнатной квартиры
ZylavoNet – Layout is clean and everything is easy to navigate.
Хотите уверенность в себе? Забудьте о скучных стенах спортзала! Ваша стройная талия ждут вас на свежем воздухе. Обработка земли мотоблоком — это не просто рутина, а динамичная кардио-сессия.
Как это работает?
Подробнее на странице – [url=https://sport-i-dieta.blogspot.com/2025/04/ogorod-hudenie-s-motoblokom-i-bez-nego.html]https://sport-i-dieta.blogspot.com/2025/04/ogorod-hudenie-s-motoblokom-i-bez-nego.html[/url]
Мощные мышцы ног и ягодиц:
Управляя мотоблоком, вы постоянно идете по рыхлой земле, совершая работу на сопротивление. Это равносильно интервальной ходьбе в гору.
Стальной пресс и кор:
Удержание руля и контроль направления заставляют напрягаться ваш корпус. Каждая кочка — это укрепление спины.
Рельефные руки и плечи:
Повороты, подъемы, развороты тяжелой техники — это настоящая функциональная тренировка в чистом виде.
Нажмите, чтобы увидеть технику в действии: Мы покажем, как превратить работу в эффективную тренировку.
Ваш план похудения на грядках:
Разминка (5 минут): Круговые движения руками. Кликните на иконку, чтобы увидеть полный комплекс.
Основная “тренировка” (60-90 минут): Вспашка, культивация, окучивание. Чередуйте интенсивность!
Заминка и растяжка (10 минут): Глубокое дыхание для восстановления. Пролистайте галерею с примерами упражнений.
Мотивационный счетчик: За час активной работы с мотоблоком средней мощности вы можете сжечь от 400 до 600 ккал! Это больше, чем занятие на эллипсоиде.
Итог: Гордость за двойной результат. Скачайте чек-лист “Огородный фитнес”. Пашите не только землю, но и лишние калории
buy zofran online [url=https://nauseacareus.com/#]zofran over the counter[/url] Nausea Care US
muscle relaxer medication: tizanidine muscle relaxer – muscle relaxant drugs
ZylvoPro – Very organized layout, made understanding the content simple and fast.
1 win 1 win Под эгидой 1 win раскрывается панорама триумфов, где каждый клик приближает к вершине. Эта вариация названия символизирует неумолимый дух победы, вдохновляя на смелые прогнозы в мире спорта и казино. С 1 win вы погружаетесь в океан возможностей: слоты с кристальными гранями, рулетка, вращающаяся как судьба, и ставки, что пульсируют адреналином. Платформа дарит не только развлечения, но и ощущение элиты – с персонализированными предложениями и мгновенными транзакциями, где каждый выигрыш – это шаг к бессмертию в анналах удачи.
morixo trust insight – Information is transparent, and moving through the site feels smooth.
Zip пакеты Zip пакеты с логотипом – это не просто упаковка, это лицо вашего бренда. Качественное исполнение и привлекательный дизайн позволяют выделить ваш товар среди конкурентов и создать положительное впечатление у потребителей. Инвестиции в брендированную упаковку окупаются благодаря повышению узнаваемости и росту продаж.
VixaroNavigator – Clear instructions helped me follow along without issues.
huarenus平台,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
ondansetron zofran: buy zofran online – zofran side effects
трансфер мерседес москва v class аренда с водителем москва В столице, где ритм жизни подобен стремительной симфонии, услуга «v class аренда с водителем москва» становится тихой гаванью для избранных. Это не просто перемещение; это тонкое искусство прибытия, где пространство салона трансформируется в мобильный кабинет, салон для переговоров или островок уединения. Каждая деталь, от бесшумного хода до деликатного вождения профессионала, подчинена одной цели — вашему абсолютному комфорту и престижу.
журналы для автолюбителей [url=https://avto-zhurnal-3.ru/]avto-zhurnal-3.ru[/url] .
все включено туры дешево [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru[/url] .
горнолыжные туры скидки [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru[/url] .
разработка конструкции упаковки из гофрокартона Упаковка из картона – это экологически ответственный выбор, сочетающий в себе прочность, легкость и возможность вторичной переработки. Картонные коробки обеспечивают надежную защиту от механических повреждений, температурных колебаний и влаги, делая их идеальным решением для широкого спектра товаров.
RixaroHoldings – Great information here, saved me a lot of unnecessary searching time.
отзывы про domeo [url=https://domeo-reviews.com/]domeo-reviews.com[/url] .
Sarah J. Maas introduces readers to a heroine unlike any other in her debut masterpiece. Celaena is not just a killer; she is a young woman with a love for music, books, and beautiful things, yet she possesses the skills to end a life in a heartbeat. As she navigates the politics of the glass castle, she uncovers a darkness that threatens to devour her world. If you are searching for a way to read this epic on the go, a throne of glass pdf format offers the convenience to dive into the story anywhere. Prepare for a journey filled with court intrigue, ancient forces, and a romance that burns slow and bright.
путешествия промокоды январь февраль [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru[/url] .
журнал про автомобили [url=https://avto-zhurnal-1.ru/]avto-zhurnal-1.ru[/url] .
In a world without adults, the rules of society are quickly forgotten. This premise drives the narrative of Golding’s classic, prompting many to search for the Lord of the Flies PDF to read the story firsthand. The transition from the democratic election of a leader to the violent coup by the choirboys is a frightening study in political science. By reading the digital format, students can easily compare the speeches of Ralph and Jack, noting the rhetorical strategies used to maintain or seize power. The book serves as a grim reminder of how easily democracy can fall.
mostbet вывод KGS на карту [url=http://mostbet38095.help/]http://mostbet38095.help/[/url]
автоновости [url=https://avto-zhurnal-2.ru/]автоновости[/url] .
bond trustee site – Nicely organized with clear and readable sections.
Gastro Health Monitor: Gastro Health Monitor – generic prilosec
1xbet promo code cambodia
TaskNavigatorX – Powerful tracking features simplify task oversight.
trusted union network – Union concept is presented clearly, and navigation is user-friendly throughout.
журналы автомобильные [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]журналы автомобильные[/url] .
1win приложение Бишкек android [url=1win74125.help]1win приложение Бишкек android[/url]
Zip пакеты Зип пакеты купить в Москве – это решение для тех, кто ищет удобный и надежный способ упаковки и хранения. В огромном мегаполисе, где логистика и эффективность ценятся превыше всего, зип пакеты становятся незаменимым инструментом как для бизнеса, так и для частных лиц. Они идеально подходят для фасовки мелких товаров, хранения продуктов питания, организации документов и множества других задач. Ищете, где купить зип пакеты в Москве? Выбор огромен, но важно найти надежного поставщика, предлагающего качественную продукцию по выгодной цене.
ZylavoFlow Works – Everything is accessible, and the browsing experience is smooth.
http://nauseacareus.com/# generic for zofran
карта обухова
упаковка для производства Гофрокороба под заказ – это искусство превращения функциональной упаковки в произведение инженерной мысли. Индивидуальный дизайн, учитывающий особенности товара и требования к транспортировке, позволяет создать оптимальную упаковку, обеспечивающую максимальную защиту и удобство использования.
电影网站推荐,采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人专用,采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持中英双语界面和全球加速。
MavroPro – Easy to use and reliable, everything works just as expected.
Kush казино регистрация это первый шаг к бонусам и азарту. Сразу после входа доступны игровые автоматы. Официальный сайт работает без перебоев. Попробуй прямо сейчас – kush казино вход
Kush бонусы позволяют начать игру на выгодных условиях. Регистрация занимает минимум времени. Вход доступен через официальный сайт. Используй шанс уже сегодня: kush регистрация
morixo trustco insight – Professional presentation with reliable, easy-to-navigate trust content.
Gastro Health Monitor: Gastro Health Monitor – Gastro Health Monitor
Cricket livescore updates, IPL and international matches with ball-by-ball commentary
http://turnaj-portal.4fan.cz/profile.php?lookup=366
изготовление картонной упаковки Производство картонной упаковки москва – это возможность получить качественную упаковку в кратчайшие сроки и по конкурентной цене. Московские производители предлагают широкий ассортимент картонной упаковки различных видов и размеров, а также услуги по разработке индивидуального дизайна и нанесению печати.
KryvoxScope – Helpful explanations that simplified understanding their services.
https://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# prilosec generic
RixaroLine – Beginner-friendly and reliable platform, very approachable.
авто журнал [url=https://avto-zhurnal-3.ru/]авто журнал[/url] .
opiniones domeo [url=https://domeo-reviews.com/]domeo-reviews.com[/url] .
zaviro bonding overview – The descriptions are simple and the layout feels professional.
авиабилеты дешево купить [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru/]авиабилеты дешево купить[/url] .
прямые рейсы промокоды [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru[/url] .
туры в египет скидки [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru/]туры в египет скидки[/url] .
журнал автомобильный [url=https://avto-zhurnal-1.ru/]avto-zhurnal-1.ru[/url] .
ZylavoFlow Works – Everything is accessible, and the browsing experience is smooth.
новости про машины [url=https://avto-zhurnal-2.ru/]avto-zhurnal-2.ru[/url] .
CoreLink – Simple interface with concise and clear product descriptions.
robaxin medication: tizanidine muscle relaxer – tizanidine hcl
QunixTrack – User-friendly layout, found all sections quickly without any confusion.
naviro bond portal – Solid bond platform with fast-loading pages and clear information.
1win experiencia Perú [url=www.1win38941.help]www.1win38941.help[/url]
If you like your romance with a side of danger, this book delivers. The subplot involving Alex’s family history adds a thriller element that raises the stakes. Readers often search for the Twisted Love PDF to enjoy this blend of genres. The pacing keeps you on the edge of your seat, wondering if their love can survive the threats against them. It is a gripping read that combines the best elements of suspense and romance.
автомобильная газета [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]автомобильная газета[/url] .
zylavo capital guide – Fast navigation and modern design make capital information easy to absorb.
http://wordcraft.4fan.cz/profile.php?lookup=211
http://pardalove.mzf.cz/forum/viewthread.php?forum_id=14&thread_id=118
https://spasmreliefprotocols.shop/# robaxin
1win apuestas online [url=https://1win38941.help/]1win apuestas online[/url]
Pre-match predictions, odds and expert picks for upcoming fixtures
ZaviroBondPortal – Clear structure made browsing smooth and effortless.
TorivoPortal – Clear interface and speedy load times make exploring content effortless.
capital info online – Smooth browsing experience with well-structured investment information.
mostbet cont restrictionat [url=http://mostbet2010.help]http://mostbet2010.help[/url]
ZylavoNetwork – Pages feel cohesive, and navigation flows naturally.
This game looks amazing! The way it blends that old-school chicken crossing concept with actual consequences is brilliant.
Count me in!
Okay, this sounds incredibly fun! Taking that nostalgic chicken crossing gameplay
and adding real risk? I’m totally down to try it.
This is right up my alley! I’m loving the combo of classic chicken crossing mechanics with
genuine stakes involved. Definitely want to check it out!
Whoa, this game seems awesome! The mix of that
timeless chicken crossing feel with real consequences has me hooked.
I need to play this!
This sounds like a blast! Combining that iconic chicken crossing gameplay with actual stakes?
Sign me up!
I’m so into this concept! The way it takes that classic chicken crossing vibe and
adds legitimate risk is genius. Really want to give
it a go!
This game sounds ridiculously fun! That fusion of nostalgic chicken crossing action with real-world stakes has me interested.
I’m ready to jump in!
Holy cow, this looks great! Merging that beloved chicken crossing style with tangible consequences?
I’ve gotta try this out!
статьи об авто [url=https://avto-zhurnal-3.ru/]статьи об авто[/url] .
арматура 8 Арматура 12 А500С Арматура 12 А500С – оптимальное сочетание диаметра и прочности, обеспечивающее надежность и долговечность железобетонных конструкций любого масштаба. Данная марка наиболее популярна.
pin up онлайн официальный сайт
привітання бабусі з днем народження онука прикольні
сертификат сколько стоит Купить сертификат на продукцию Важно помнить: купить сертификат на продукцию невозможно и наказуемо.
reviews domeo [url=https://domeo-reviews.com/]reviews domeo[/url] .
горящие туры скидки [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru[/url] .
naviro trustco network – Structured content, trustworthy branding, and simple navigation make the site pleasant to use.
промокоды aviasales [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru[/url] .
http://zocken4life.de/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%20Melbet%20%D0%BD%D0%B0%20%D0%A1%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%BD%D1%8F%202026:%20MAX888%20-%20%D0%91%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81%2015,000%E2%82%BD
скидка на первое бронирование отеля [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru[/url] .
I truly appreciate the author’s ability to present ideas in a coherent, organized, and approachable way, creating an article that is both informative and enjoyable for readers of diverse backgrounds.
https://renchtodaynews.com/
https://chessdatabase.science/index.php?title=Melbet%20%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%20%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F%20%D0%9D%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2%202026:%20MAX888
RixvaNavigator – Efficient design, navigating the site is simple and content is clear.
авто журнал [url=https://avto-zhurnal-1.ru/]авто журнал[/url] .
TrixoTeam – Quick, thorough responses made the process smooth and easy.
Мы изготавливаем системы_хранения мебель на заказ москва сразу без посредников. Консультация в течение суток. Монтаж под ключ с контролем качества. Хочу расчет – сделаем по задаче.
1win краш игра [url=www.1win48271.help]www.1win48271.help[/url]
статьи про автомобили [url=https://avto-zhurnal-2.ru/]avto-zhurnal-2.ru[/url] .
казино онлайн Тоҷикистон mostbet [url=www.mostbet80573.help]www.mostbet80573.help[/url]
1xbet free promo code south africa
Minedrop — слот для настоящих майнеров!
Пиксельная графика в стиле Minecraft, блоки с
сюрпризами и бонусные шахты майнкрафт слот казино.
Онлайн-казино предлагают щедрые приветственные пакеты и турниры.
Разрушайте камни, находите изумруды и активируйте
бесплатные вращения. Удача в каждом блоке!
https://meetshow.ru
ClickHub Zylavo – Layout is logical, and information is easy to digest.
секс чат пары онлайн
LixorBase – The information is well-organized, making key insights simple to digest.
новости про машины [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]avto-zhurnal-4.ru[/url] .
1вин aviator [url=https://1win48271.help/]https://1win48271.help/[/url]
Когда хочется яркой игры и стабильного доступа к бонусам, стоит выбрать Кактус казино официальный сайт. Платформа предлагает удобную регистрацию и быстрый вход. Бонусы доступны сразу после создания аккаунта. Начни игру уже сегодня, cactus casino регистрация
zaviro official site – The brand is clearly maintained, giving a professional impression.
OutletInspire – Creative and hands-on experience that supports idea creation.
my blog post – Tower Rush jeu
Learning Zone – The website is approachable, and tutorials are concise.
portfolio resource hub – Logical layout with clear content presentation for quick comprehension.
https://rf.livesexchat18.com/
Nausea Care US: zofran otc – Nausea Care US
Cactus казино бонус позволяет начать игру с дополнительными возможностями. После регистрации можно сразу войти в аккаунт. Официальный сайт обеспечивает стабильность. Заходи сейчас – кактус казино регистрация
https://nauseacareus.com/# Nausea Care US
aviator мостбет [url=https://mostbet80573.help]https://mostbet80573.help[/url]
ondansetron zofran [url=http://nauseacareus.com/#]Nausea Care US[/url] buy zofran
автомобильный журнал [url=https://avto-zhurnal-3.ru/]автомобильный журнал[/url] .
PexraTrack – Practical site, layout is intuitive and user-friendly.
A person essentially assist to make significantly
posts I’d state. That is the first time I frequented your web page and so far?
I amazed with the analysis you made to create this
particular submit extraordinary. Excellent task!
domeo плюсы и минусы [url=https://domeo-reviews.com/]domeo-reviews.com[/url] .
xNudes is an AI tool that changes the clothes in a photo to show a nude or altered version of the body https://xnudes.ai/. You just need to upload an image, and the tool will create a realistic, edited version within seconds. The tool works by letting you pick details like age, body type, and skin tone to match your preferences. gives you control over the image look, making the experience more personal
секс чат с девушками
Cactus casino официальный сайт предлагает удобный и надежный формат игры. Регистрация проходит без сложностей. Вход доступен в любое время. Начни играть уже сегодня – cactus casino регистрация
промокоды на отели [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-1.ru/]промокоды на отели[/url] .
Сертификация продукции https://www.sostav.ru/blogs/286052 подтверждение того, что продукция соответствует нормам безопасности. Сертификация обязательна для некоторых групп товаров. Помимо обязательной, есть и добровольная сертификация соответствия продукции действующим стандартам. Её проводят по запросу производителя, импортёра или продавца.
ViewMaster – A simple system that helps you stay on top of tasks.
скидки trip.com [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki.ru[/url] .
как получить сертификацию на продукцию Центр сертификации официальный сайт Центр сертификации официальный сайт – это визитная карточка организации, предоставляющая информацию об услугах, ценах и аккредитации.
промокоды на круизы [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-2.ru/]промокоды на круизы[/url] .
арматура 8 Тонна Арматуры Для масштабных проектов, где размах поражает воображение, тонна арматуры становится основной единицей измерения, позволяющей оценить общий объем необходимого материала и оптимизировать логистику.
Howdy this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs
use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get guidance from someone with
experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Info Center – Information is easy to locate and well-structured.
Индивидуалки Екатеринбурга с услугой золотой дождь
прием достаточно востребованы,
ведь их не так много. Даннаяуслуга дарит наслаждение многим мужчинам, но чаще всего она оплачивается отдельно.
Они примут золотой дождь от тебя с огромным удовольствием, ведь это дар для них.
Девчонки выезжают в любой район города или принимают у себя в апартаментах.
Индивидуалки Верх-Исетского района
Если ты решил оторваться сегодня в Екатеринбурге в районе
Широкая речка, то ты на правильной странице.
Каталог анкет шлюх екб с Широкой речки специально для тебя, девчонки выполняют любые желания и принимают в любое время суток.
авто новости [url=https://avto-zhurnal-1.ru/]avto-zhurnal-1.ru[/url] .
Сертификат ISO 9001 https://teletype.in/@sezdok это документ, подтверждающий соответствие системы менеджмента качества требованиям стандарта ГОСТ Р ИСО 9001. Сертификат соответствия по стандарту ГОСТ ISO 9001:2015 представляет собой всемирно признанное свидетельство того, что система качества отвечает международным требованиям.
Сертификация услуг https://pandia.org/user/categ/6225-Moi_statmzi это процедура подтверждения стабильного уровня качества и безопасности предоставляемых услуг. Схемы сертификации услуг. В российской практике сертификация услуг регламентирована национальными стандартами, в частности, ГОСТ Р 54659-2011.
a href=”https://qulavoholdings.bond/” />QulavoConnect – Found the platform easy to use and the options seem very dependable.
trustline insight page – A serene layout with well-presented trustline explanations.
https://vegacams.com/
все включено туры дешево [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru/]tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru[/url] .
Soft Рок В основе его музыкального мировоззрения лежит рок, бунтарский дух свободы и протеста. Это не просто жанр, это философия, отражение жизненной позиции, его способ говорить с миром на языке гитарных рифов и пульсирующих барабанов.
That’s a fascinating point about roulette variance! Thinking about high-roller experiences, platforms like jilbb really focus on curated games & fast withdrawals – essential for serious players, wouldn’t you agree? It’s all about the experience.
автомобильная газета [url=https://avto-zhurnal-2.ru/]avto-zhurnal-2.ru[/url] .
PureOutletIdeas – Inspiring experience that makes brainstorming easier.
What online casino actually pays out in Australia?
lbs это [url=https://shkola-onlajn-21.ru/]lbs это[/url] .
секс чат рулетка
1win iniciar sesión con Google [url=http://1win38941.help/]http://1win38941.help/[/url]
https://t.me/indi_surguta/
умные шторы купить [url=https://prokarniz24.ru/]умные шторы купить[/url] .
карнизы с электроприводом [url=https://prokarniz38.ru/]prokarniz38.ru[/url] .
ОЭРН – профессиональная платформа для подтверждения компетенций и статуса экспертов по экспертизе недр. Ресурс упрощает найти специалиста по специализациям: ТПИ, нефть и газ, геология и ГРР снижая риски при согласовании отчётов и отчётов в лицензировании, ОЭРН и ГКЗ
рулонные шторы купить цены [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru[/url] .
PlorixHub – Navigation is simple, and all options are easy to understand quickly.
https://spasmreliefprotocols.shop/# muscle relaxer tizanidine
Индивидуалки Сургута
статьи об авто [url=https://avto-zhurnal-4.ru/]статьи об авто[/url] .
When some one searches for his required thing, therefore he/she needs to be available that in detail, so that thing is maintained over here.
https://t.me/ed_1xbet/4
п»їondansetron otc: zofran otc – Nausea Care US
Secure Portal – Information is concise, and the hub feels trustworthy.
Кактус казино официальный сайт это быстрый старт и бонусы для новых игроков. Регистрация занимает несколько минут. Вход доступен круглосуточно. Заходи и играй: cactus casino бонус
Hi! Quick question that’s totally off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly?
My web site looks weird when browsing from my iphone 4.
I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to resolve this issue.
If you have any suggestions, please share. Many thanks!
секс чат пары онлайн
BridgeTrack – Fast and clear browsing experience with trustworthy financial details.
https://t.me/indi_surguta
1xbet promo code turkey
Everything is very open with a very clear description of the issues.
It was definitely informative. Your site is very useful.
Thank you for sharing!
bonding info page – Straightforward site with easily digestible bonding details.
TrustlineView – Easy-to-read listings and resources made decision-making smooth and stress-free.
секс чат пары онлайн
Пинко казино аналитика
ZarvoLine – I liked how clearly everything is shown while browsing.
Czesc, szukam nowych kasyn online z dobrymi bonusami. Ktos ma doswiadczenie z nowymi platformami?
промокод trip.com отели [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru/]промокод trip.com отели[/url] .
https://redcams.ru/
Czesc, szukam nowych kasyn online z dobrymi bonusami. Ktos ma doswiadczenie z nowymi platformami?
I must say I’m glad I found Read more — fantastic!
https://cameronandwilding.com/big-bass-splash-slot-review
секс чат пары
MorvexZone – Very logical layout, everything is accessible and easy to read.
Общество экспертов России по недропользованию – профессиональная платформа для оценки статуса и компетенций экспертов по экспертизе недр. Портал упрощает подобрать специалиста по специализациям нефть и газ, геология и ГРР, ТПИ и уменьшить риски при подписании отчётов и отчётов в закупках: https://oern2007.ru/
Core Docs – Design is modern and minimalistic, with clear content.
онлайн обучение для школьников [url=https://shkola-onlajn-21.ru/]shkola-onlajn-21.ru[/url] .
Best Online Casino Australia Crypto Huge Wins Incoming
гибкие электрические шторы [url=https://prokarniz24.ru/]prokarniz24.ru[/url] .
электрокарниз недорого [url=https://prokarniz38.ru/]prokarniz38.ru[/url] .
автоматические рулонные шторы с электроприводом [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru[/url] .
Общество экспертов России по недропользованию – отраслевой ресурс для проверки компетенций и статуса экспертов по экспертизе недр. Платформа упрощает подобрать эксперта по профилям нефть и газ, ТПИ, геология и ГРР уменьшая риски при подписании отчётов и заключений в закупках https://oern2007.ru/
1xbet free promo code today kenya
1win ставки на Dota 2 [url=https://1win30489.help/]https://1win30489.help/[/url]
Uzun süredir SMS doğrulama servisi araştırıyordum ve nihayet GetCode App denedim. 150’den fazla ülkeden sanal numara edinebiliyor. WhatsApp hesap açmak için kullandım ve SMS kodu saniyeler içinde ulaştı. Beni en çok etkileyen özellik gizlilik konusundaki hassasiyetleri. Bir diğer artısı da SMS gelmezse otomatik iade yapılması gerçekten güven veriyor. Fiyatlar da gayet uygun, bütçe dostu fiyatlarla hizmet alabiliyorsunuz. Hem iOS hem Android’de gayet stabil. otomasyon testleri için de API desteği sunuyorlar, teknik kullanıcılar için ideal. Denemeni tavsiye ederim.
http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# tizanidine zanaflex
http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# muscle relaxer tizanidine
купить сертификат на продукцию Как получить сертификат на товар? Путь к получению сертификата на товар начинается с подачи заявки в центр сертификации. Далее следуют этапы испытаний, экспертизы документов и, при положительном результате, оформление сертификата соответствия.
ОЭРН – профессиональная платформа для проверки статуса и компетенций специалистов по экспертизе недр. Портал помогает выбрать специалиста по специализациям: нефть и газ, ТПИ, геология и ГРР – снижая риски при подписании отчетов и отчетов в лицензировании – публичная отчетность по запасам
арматура 14 Арматура А500С Арматура А500С – самый надежный материал для стройки.
I am sure this post has touched all the internet people, its
really really nice article on building up new weblog.
trusted finance site – Messaging is direct and transparent, focusing on information over promotion.
Индивидуалки Сургута
QuvexaSmart – Detailed breakdowns help guide effective decision-making.
VexaroScope – Easy to navigate and highly reliable, giving a polished, professional feel.
Soft Soft Rock Сочетание мягкости и силы, деликатности и мощи находит свое отражение в soft rock. Это компромисс между лиричностью и драйвом, возможность насладиться красотой мелодии и энергией ритма одновременно.
The site is fast, easy to use, and doesn’t need any special editing skills.
1вин зарегистрироваться [url=www.1win30489.help]www.1win30489.help[/url]
Лучшие и безопасные установка противопожарного резервуара эффективное решение для систем пожарной безопасности. Проектирование, производство и монтаж резервуаров для хранения воды в соответствии с требованиями нормативов.
Gastro Health Monitor: prilosec generic – omeprazole medication
Having read this I believed it was really informative.
I appreciate you spending some time and energy to put this content together.
I once again find myself personally spending way too much time
both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
https://skypecam.ru/
UlixoConnect – Very user-friendly layout with responsive and easy navigation.
NevrixCentral – Quick tour, but everything loaded smoothly and looks professional.
«Field Fit» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]футбольная атрибутика в москве[/url]
атрибутика футбольных клубов – [url=http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.com.ar/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://images.google.mv/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.sportbets31.ru/maps.google.se/url?q]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 2ce9103
Если нужен надежный игровой клуб с бонусами, обрати внимание на Cactus casino официальный сайт. Здесь удобный интерфейс и стабильная работа платформы. После регистрации доступен бонус для старта. Заходи и начинай играть: cactus casino бонус
скидка на авиабилеты онлайн [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru/]скидка на авиабилеты онлайн[/url] .
1win авиатор коэффициенты [url=http://1win48271.help/]1win авиатор коэффициенты[/url]
1xbet sign up promo code somalia
I’ve been surfinmg online more than three hours today,
yet I never found any interesting article like yours.
It’s pretty worth enough for me. In my opinion, iff all
website owners and bloggers made ggood content as you did, the web
will be a lot more useful than ever before.
онлайн школа с 1 по 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn-21.ru/]shkola-onlajn-21.ru[/url] .
секс чат регистрация
рулонные. шторы. +на. пластиковые. окна. купить. [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru[/url] .
римские шторы с электроприводом [url=https://prokarniz24.ru/]prokarniz24.ru[/url] .
электрокранизы [url=https://prokarniz38.ru/]электрокранизы[/url] .
Hello men
Good evening. A 34 great website 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this site. There’s a great article there. https://newyorkspaces.com/the-birth-of-europe-after-the-fallen-roman-empire/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
Слив курсов ЕГЭ русский 2025 https://courses-ege.ru
Mangelsen
7916 Girrard Avenue, La Joyya
СA 92037, United States
1 800-228-9686
learn human encroachment ⲟn wildlife conservation (Velva)
OrvixTracker – Intuitive features and clear instructions made exploring easy.
zanaflex medication [url=https://spasmreliefprotocols.com/#]antispasmodic medication[/url] methocarbamol dosing
http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# muscle relaxers over the counter
https://rf.ero-chat.net/
BondTracker – Informative updates encourage frequent visits.
PlixoEdgePro – Easy-to-follow layout, all features are clear and well-organized.
ОЭРН – профессиональный портал для проверки квалификации специалистов по экспертизе недр. Платформа помогает найти специалиста по направлениям нефть и газ, ТПИ, геология и ГРР уменьшая риски при подписании отчётов и отчётов в закупках https://oern2007.ru/
VelvixTracker – The content is efficient and saved me a lot of time.
ОЭРН – профессиональная платформа для оценки компетенций и статуса экспертов по экспертизе недр. Портал помогает подобрать специалиста по профилям: ТПИ, геология и ГРР, нефть и газ и снизить риски при подписании отчётов и отчетов в проектах: https://oern2007.ru/
Real Money Online Casino Australia Grab This Chance Forever
mostbet Visa хуруҷ [url=https://www.mostbet80573.help]mostbet Visa хуруҷ[/url]
https://live-sexchat.ru/
Подземные резервуары ргсп https://underground-reservoirs.ru
Real Money Online Casino Australia Your Turn To Shine
промокод trip.com отели [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru/]промокод trip.com отели[/url] .
Архангельск: натяжные потолки — быстро,качественно,с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональный монтаж в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем практичный вариант натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем работы любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор сатиновых полотен.
Рассчитаем стоимость — свяжитесь с нами!
Потолочные решения в коридоре — любая фактура. В Архангельске — с консультацией специалиста-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки в ванную в архангельске высота[/url]
натяжные потолки на кухню – [url=https://29-potolok.ru]http://www.29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.com.ng/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://www.google.bt/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://speed.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=318525&p=1213454#p1213454]Качественный монтаж натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] 7d5f9ff
Very good article! We will be linking to this great post on our site.
Keep up the good writing.
My web page … خرید بک لینک
Индивидуалки Сургута
онлайн обучение 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn-21.ru/]shkola-onlajn-21.ru[/url] .
prilosec dosage: Gastro Health Monitor – Gastro Health Monitor
секс чат пары онлайн
готовые рулонные шторы цена [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru[/url] .
электро привод для штор [url=https://prokarniz24.ru/]prokarniz24.ru[/url] .
https://rt.virt888.com/
электрокарнизы для штор купить [url=https://prokarniz38.ru/]электрокарнизы для штор купить[/url] .
Cactus казино бонус позволяет начать игру с дополнительными возможностями. После регистрации можно сразу войти в аккаунт. Официальный сайт обеспечивает стабильность. Заходи сейчас, cactus казино официальный сайт
RavionPoint – Pages load smoothly, and investment details are easy to digest.
Fine write ups, Cheers!
https://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# muscle relaxant drugs
KrixaEdge – Simple layout with smooth navigation, no confusion at all.
пин ап app [url=https://pinup2006.help/]https://pinup2006.help/[/url]
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up.
Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say superb
blog!
промокоды на отели [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru/]промокоды на отели[/url] .
pin-up tranzaksiya tarixi [url=www.pinup2006.help]www.pinup2006.help[/url]
Хотите подтянутую фигуру? Забудьте о скучных стенах спортзала! Ваша стройная талия ждут вас на свежем воздухе. Вспашка земли мотоблоком — это не просто рутина, а динамичная кардио-сессия.
Как это работает?
Подробнее на странице – [url=https://sport-i-dieta.blogspot.com/2025/04/ogorod-hudenie-s-motoblokom-i-bez-nego.html]https://sport-i-dieta.blogspot.com/2025/04/ogorod-hudenie-s-motoblokom-i-bez-nego.html[/url]
Мощные мышцы ног и ягодиц:
Управляя мотоблоком, вы постоянно идете по рыхлой земле, совершая работу на сопротивление. Это равносильно приседаниям с нагрузкой.
Стальной пресс и кор:
Удержание руля и контроль направления заставляют работать мышцы кора. Каждая кочка — это микро-скручивание.
Рельефные руки и плечи:
Повороты, подъемы, развороты тяжелой техники — это настоящая функциональная тренировка в чистом виде.
Смотрите наше видео-руководство: Мы покажем, как превратить работу в эффективную тренировку.
Ваш план похудения на грядках:
Разминка (5 минут): Круговые движения руками. Кликните на иконку, чтобы увидеть полный комплекс.
Основная “тренировка” (60-90 минут): Вспашка, культивация, окучивание. Чередуйте интенсивность!
Заминка и растяжка (10 минут): Упражнения на гибкость рук. Пролистайте галерею с примерами упражнений.
Мотивационный счетчик: За час активной работы с мотоблоком средней мощности вы можете сжечь от 400 до 600 ккал! Это больше, чем занятие на эллипсоиде.
Итог: Подкачанное тело к лету. Скачайте чек-лист “Огородный фитнес”. Пашите не только землю, но и лишние калории
mines дар mostbet [url=http://mostbet67254.help]http://mostbet67254.help[/url]
Australian Casino Real Money Payid Real Fast Million Glory
онлайн-школа для детей бесплатно [url=https://shkola-onlajn-21.ru/]shkola-onlajn-21.ru[/url] .
заказать рулонные шторы в москве [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru/]заказать рулонные шторы в москве[/url] .
умные шторы купить [url=https://prokarniz24.ru/]умные шторы купить[/url] .
мостбет купони ставка санҷиш [url=https://mostbet67254.help/]https://mostbet67254.help/[/url]
Na superfície dos comprimidos em maneira de losango, é permitida a aplicação do logotipo da corporação “ZT” de um
lado e da dosagem “50” ou “100” do outro. Comprimidos revestidos, de cor azul a azul-clara com
tons perlados, de forma arredondada (doses de 25 mg, 50 mg ou
100 mg) ou em maneira de losango (doses de cinquenta mg ou 100 mg), com superfície
convexa. Após a administração oral única de
sildenafila em dose de cem mg, a concentração plasmática máxima média de sildenafila é de aproximadamente 440 ng/ml (com coeficiente de variação
de 40%). Como a ligação da sildenafila e de seu principal metabólito N-desmetil ao plasma é
de 96%, a concentração plasmática máxima média de sildenafila livre é de por volta de
18 ng/ml (38 nM). A biodisponibilidade absoluta média
depois da administração oral é de 41% (com modificação
de 25% a 63%). Na faixa de doses recomendada (de vinte e cinco a cem mg), os parâmetros
AUC e Cmax da sildenafila aumentam proporcionalmente à dose.
A hipotensão sintomática geralmente acontece dentro de 4 horas depois da administração da sildenafila.
A administração concomitante da sildenafila e do bloqueador alfa-adrenérgico podes transportar
ao desenvolvimento de hipotensão sintomática em alguns pacientes predispostos. https://vibs.me/g1-cruze-gel-funciona-anvisa-composicao-preco-valor-comprar-resenha-farmacia-bula-reclame-aqui-saiba-tudo-2024/
Категория специально для состоятельных мужчин – элитные проститутки в
Иркутске. Девушки невероятной внешности топ моделей, точеной фигуры и с
обширным спектром услуг.
Каталог самых дорогих индивидуалок города Иркутск с выездом в
любой район или со своими уютными апартаментами.
Индивидуалки Ленинского района
Решил сегодня оторваться на всю катушку
в Мегете, близ Иркутска – ты на
нужной странице. Огромный выбор лучших шлюх Мегета специально для вас, девчонки на любой вкус и бюджет
специально для вас.
I am Laurene from Oslo. I am learning to play the Xylophone.
Other hobbies are Camping.
The author successfully communicates ideas with clarity and confidence creating an article that feels informative engaging and trustworthy while offering readers a meaningful experience supported by thoughtful explanations and well connected points throughout the discussion.
https://jqw350.com/
mexicanrxpharm: pharmacy mexico – BajaMed Direct
пакеты для выставок с логотипом
карниз с приводом для штор [url=https://prokarniz38.ru/]prokarniz38.ru[/url] .
Огромный выбор развлечений доступен на azino777: на сайте
buy methocarbamol: over the counter muscle relaxers that work – muscle relaxers over the counter
Если вы хотите глубже разобраться в теме онлайн-казино и понять, на что стоит обращать внимание при выборе платформы, обязательно изучите материал по ссылке https://www.ikonu.ru/faq/pgs/top_provayderov_na_vavada__o_kotoruh_vu_ne_znali.html. В статье собрана полезная информация, которая помогает избежать типичных ошибок и лучше ориентироваться в мире азартных игр. Такой разбор особенно полезен тем, кто играет регулярно и хочет делать это осознанно.
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
Лучшее казино https://download-vavada.ru слоты, настольные игры и live-казино онлайн. Простая навигация, стабильная работа платформы и доступ к играм в любое время без установки дополнительных программ.
Link exchange is nothing else except it is simply placing the other person’s
web site link on your page at suitable place and other person will also do same for you. https://cryptoboss-rcn.top/
Great article, exactly what I needed.
промокод trip.com отели [url=https://tury-i-puteshestviya-promokody-i-skidki-3.ru/]промокод trip.com отели[/url] .
Ресторан в Москве: как выбрать идеальное
место для незабываемого вечера
order meds from mexico [url=https://bajameddirect.com/#]BajaMed Direct[/url] BajaMed Direct
1win быстрый вывод на элсом [url=https://1win30489.help]https://1win30489.help[/url]
компьютеры в Казахстане
онлайн обучение для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-22.ru/]shkola-onlajn-22.ru[/url] .
рулонные шторы окна заказ [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom50.ru[/url] .
курсы стриминг [url=https://shkola-onlajn-23.ru/]shkola-onlajn-23.ru[/url] .
школа онлайн дистанционное обучение [url=https://shkola-onlajn-21.ru/]shkola-onlajn-21.ru[/url] .
New online casinos Australia – latest sites with free spins
https://t.me/indi_surguta/
электропривод для штор [url=https://prokarniz24.ru/]prokarniz24.ru[/url] .
bonding resource – Layout is tidy and content is easy to digest, making browsing enjoyable.
производство бумажных пакетов
cavaroline overview – Neat, well-organized pages make it easy to find needed information without any trouble.
this site – Pleasant layout overall, landed here randomly and it was easy to explore.
Индивидуалки Владивосток
http://indogenericexport.com/# india online pharmacy
quvexaholdings link – Fast pages, easy to follow content, and overall browsing is simple.
Индивидуалки Владивосток
xNudes is an AI tool that changes the clothes in a photo to show a nude or altered version of the body. You just need to upload an image, and the tool will create a realistic, edited version within seconds. The tool works by letting you pick details like age, body type, and skin tone to match your preferences. It gives you control over the image look, making the experience more personal https://xnudes.app/
электрокарниз купить [url=https://prokarniz38.ru/]prokarniz38.ru[/url] .
mexican pharmacy ship to usa: farmacia mexicana en linea – BajaMed Direct
Наша специализация https://kartremont.ru ремонт квартир в Санкт-Петербурге любой сложности: от косметического обновления до капитального ремонта и эксклюзивных дизайнерских проектов. Мы работаем так, чтобы каждая деталь радовала вас долгие годы, а сам процесс был максимально комфортным.
discover vexaro – Visited briefly, interface is clean and reading content is effortless.
http://usmedsoutlet.com/# online pharmacy reddit
velvix info – Browsing is effortless, interface is clean and content is immediately visible.
Professionelle thaimassage Augsburg: Entspannende Massagen, wohltuende Anwendungen und personliche Betreuung. Gonnen Sie sich eine Auszeit vom Alltag in angenehmer Atmosphare.
Индивидуалки Новый Уренгой
Играешь в казино? бонусы без депозита в казино бесплатные вращения в слотах, бонусы для новых игроков и действующие акции. Актуальные бонусы и предложения онлайн-казино.
https://t.me/nur_intim
Проститутки Владивосток
ломоносов онлайн школа [url=https://shkola-onlajn-23.ru/]ломоносов онлайн школа[/url] .
pin-up rəsmi sayt linki [url=pinup2006.help]pinup2006.help[/url]
ravionbondgroup online – Smooth navigation, fast-loading pages, and everything is straightforward.
пансионат для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-22.ru/]пансионат для детей[/url] .
trustco overview – Clean and organized pages make accessing content fast and effortless.
1win retirar [url=https://1win43218.help/]https://1win43218.help/[/url]
https://t.me/nur_intim
visit krixa – Simple layout, navigation feels smooth and content is immediately understandable.
open zaviroline – Clean interface and the content becomes available right away.
Online Casino Real Money Pokies Jackpot Is Calling You
терминус полотенцесушители полотенцесушитель сталь
https://indogenericexport.com/# tizanidine medication
1win bono apuestas deportivas Perú [url=www.1win43218.help]www.1win43218.help[/url]
learn ravioncapital – Minimalist design, fast-loading pages, and browsing is simple.
https://indogenericexport.shop/# india online pharmacy
Индивидуалки Владивосток
silkroad online pharmacy: US Meds Outlet – vipps canadian pharmacy
discover zylvo – Layout feels modern, content is clear and pages are easy to move through.
мостбет сабти ном бе ҳуҷҷат [url=http://mostbet67254.help]http://mostbet67254.help[/url]
курсы стриминг [url=https://shkola-onlajn-23.ru/]shkola-onlajn-23.ru[/url] .
The culture of Chult is rich and inspired by African myths and legends. It brings a fresh aesthetic to the Forgotten Realms. From the dinosaur races to the rain lords, the flavor is unique. Using the Tomb of Annihilation PDF allows DMs to absorb this culture. The book is filled with names, customs, and history of the Chultan people. A digital reference is handy for pronunciation guides and quick lore checks when players ask about the history of Mezro or the royal line of Omu. It helps the DM portray a living, breathing world that respects its inspirations. https://tombofannihilationpdf.store/ Tomb Of Annihilation Pdf Google Drive
Tam aradığım içerik buydu. Epeydir okumalar yapıyordum ve nihayet tatmin edici bir içerikle karşılaştım. Bilhassa anlatım tarzı gerçekten etkileyici. Böyle kaliteli yazıların daha fazlasını görmek isterim. Takipte kalacağım. Emeğinize sağlık!
explore navirobond site – Clear pages and structured navigation make finding information easy.
ломоносовская школа онлайн [url=https://shkola-onlajn-22.ru/]ломоносовская школа онлайн[/url] .
indian pharmacy [url=http://indogenericexport.com/#]Indo-Generic Export[/url] indian pharmacies safe
https://t.me/nur_intim/
browse trustline – Quick look left a positive impression, content is tidy and trustworthy.
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• Комплексный анализ покрытия сети в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку оборудования
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]подключить интернет сибирские сети по адресу в новосибирске[/url]
сибирские сети домашний интернет вай фай подключить – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]https://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=https://www.google.ad/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://images.google.com.lb/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://pocherparts.de/cgi-bin/gast4.cgi/t.me/slatestarcodex.com/author/www.arus-diplom4.ru/k.krakenwork.cc/www.mostbet12032.ru]Интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] db2cc08
check ravioncore – Well-structured site, details are easy to locate and understand.
visit mavro – Simple interface, content is easy to locate and site feels well-organized.
Enter a world of superstition, youthful romance, and buried gold. The Adventures of Tom Sawyer is a thrilling ride from start to finish. Our platform provides the full text in a convenient digital format. If you are tired of squinting at small print in old paperbacks, our optimized digital version will be a relief. Get your Tom Sawyer PDF today and enjoy the flexibility of adjusting the text size and background to suit your reading preferences. https://tomsawyerpdf.store/ The Adventures Of Tom Sawyer Download Pdf
Online Casino Australia Real Money High Volatility Glory
https://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
Натяжные потолки в Архангельске — качественно, быстро и с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональный монтаж в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем стильный дизайн натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем монтаж любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор глянцевых полотен.
Рассчитаем стоимость — напишите!
Натяжные потолки в ванной — любая сложность. В Архангельске — с консультацией специалиста-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки глянцевые в архангельске[/url]
натяжные потолки архангельск высота – [url=http://29-potolok.ru]http://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://images.google.com.ni/url?sa=t&url=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://www.google.jp/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://gsoot.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=sub07_02&wr_id=11313]Качественный монтаж[/url] afb47_7
check this site – Clean design and the information is easy to follow from the start.
mivarotrustline experience – Clean layout, everything is accessible and easy to understand immediately.
browse rixaroholdings – Smooth navigation and structured content provide a pleasant browsing experience.
школа онлайн обучение для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-23.ru/]shkola-onlajn-23.ru[/url] .
canada pharmacy online legit: online pharmacy no prescription – US Meds Outlet
онлайн школа ломоносов [url=https://shkola-onlajn-22.ru/]онлайн школа ломоносов[/url] .
browse nolaroview – Easy-to-use interface with well-organized information.
zexarobonding online – Focus is on the information itself thanks to a clean and uncluttered design.
Индивидуалки Владивосток
qunix site – Clear interface, content is easy to access and pages load smoothly.
The structure of the novel, with its short chapters, mimics the fragmented nature of Edna’s awakening. This makes it a fast-paced read that keeps you engaged. If you are looking for a quick but meaningful book, search for the awakening pdf. You can easily navigate through the chapters on a tablet or smartphone. The brevity of the sections encourages “just one more chapter” reading, making it easy to finish the book in a single weekend. It is a masterpiece of pacing and economy. https://theawakeningpdf.store/ The Awakening Book Pdf Boson
онлайн обучение для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-24.ru/]shkola-onlajn-24.ru[/url] .
курсы стриминг [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]курсы стриминг[/url] .
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out
much. I hope to give something back and aid others like you aided me.
электрокарниз недорого [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
электрокарнизы цена [url=https://elektrokarniz25.ru/]электрокарнизы цена[/url] .
электрокарниз недорого [url=https://elektrokarniz5.ru/]elektrokarniz5.ru[/url] .
карнизы с электроприводом купить [url=https://elektrokarnizy750.ru/]elektrokarnizy750.ru[/url] .
https://t.me/nur_intim
электрокарниз купить [url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru/]elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru[/url] .
http://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
start here – Professional structure and readable content make exploring the site simple.
vixaroshop link – Clean structure, finding products and details is smooth.
check kryvoxtrustco – Well-organized pages, navigation works smoothly and content is clear.
Thank you for sharing this useful article. The content is structured, clear, and easy to understand.
https://314776.com/
codigo promocional 1xbet panama
Link exchange is nothing else but it is only placing the
other person’s webpage link on your page at proper place and other person will also do similar in support
of you.
интернет-школа [url=https://shkola-onlajn-23.ru/]интернет-школа[/url] .
https://redcams.org/
trusthub overview – Short browse, but the clean and direct approach stood out.
выпрямитель дайсон airstrait [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон airstrait[/url] .
1win apuestas con spei [url=https://www.1win5774.help]https://www.1win5774.help[/url]
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• Комплексный анализ доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж оборудования
• Фиксированные тарифы на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]сибсети домашний интернет и тв тарифы[/url]
проверить подключен ли дом к интернету сибирские сети – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=https://images.google.info/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://maps.google.com.mt/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/25kat.ru/www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom11.ru/www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru]Интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] ce91037
московская школа онлайн обучение [url=https://shkola-onlajn-22.ru/]shkola-onlajn-22.ru[/url] .
official capital page – The site feels polished with pages that load quickly and move smoothly.
1win promo code 2026 [url=https://www.1win5766.help]1win promo code 2026[/url]
rixva dashboard – Clean pages, navigation is fast and content is simple to follow.
Фриспины бесплатно https://casino-bonuses.ru бесплатные вращения в онлайн-казино без пополнения счета. Актуальные предложения, условия получения и список казино с бонусами для новых игроков.
code promo 1xbet gratuit
1win no puedo entrar [url=https://1win5774.help]1win no puedo entrar[/url]
you are actually a just right webmaster. The site
loading pace is incredible. It sort of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick.
Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve performed a great task
in this topic!
поставщик металлопроката https://rostov.vshrss.ru большой выбор продукции, резка в размер, доставка и сопровождение заказов для строительных и производственных компаний.
withdraw from 1win [url=www.1win5744.help]www.1win5744.help[/url]
https://erochats.org/
online pharmacy discount code: overseas online pharmacy – US Meds Outlet
1win pul yechish kechikdi [url=1win5766.help]1win pul yechish kechikdi[/url]
Thank you for this amazing post! It’s clear, informative, and well-structured. I appreciate the effort and research put into providing such helpful content. Truly valuable information!
https://qilinqq.info/
промокод на фрибет 1xbet
browse lixor – Simple, intuitive interface and content is immediately clear.
https://medium.com/@milonsheikh1380/how-to-excel-in-online-game-ddec35-tips-and-tricks-d8c04fb41cfa
автоматические карнизы для штор [url=https://elektrokarniz25.ru/]автоматические карнизы для штор[/url] .
школа онлайн для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-24.ru/]shkola-onlajn-24.ru[/url] .
онлайн обучение 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]онлайн обучение 11 класс[/url] .
электрокарниз москва [url=https://elektrokarnizy750.ru/]электрокарниз москва[/url] .
электрокарниз [url=https://elektrokarniz5.ru/]elektrokarniz5.ru[/url] .
kavix page – Neat design makes navigating and finding information smooth and straightforward.
События в мире последние новости события дня и аналитика. Актуальная информация о России и мире с постоянными обновлениями.
карнизы для штор с электроприводом [url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru/]elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru[/url] .
Your article demonstrates clarity and purpose, guiding readers through concepts with helpful examples and organized presentation.
https://auroompartners.com/
The Forbidden City of Omu awaits. Tomb of Annihilation challenges players to uncover its secrets. The Tomb of Annihilation PDF is the key. It details the shrines, the factions, and the entrance to the tomb. DMs use the digital resource to manage the scavenger hunt for the puzzle cubes. The book also explains the history of the city. The PDF helps the DM deliver this lore through exploration. It also details the final dungeon, level by level. The digital guide ensures the DM can navigate the complex architecture of the tomb, delivering a smooth and terrifying experience for the players. https://tombofannihilationpdf.store/ The Tomb Of Annihilation Companion Pdf
1win minimum deposit [url=https://1win5744.help/]https://1win5744.help/[/url]
карнизы для штор с электроприводом [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
1win requisitos de bono [url=http://1win43218.help/]http://1win43218.help/[/url]
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
https://erotic-video-chat.ru/
https://lindachat.ru/
code promo 1xbet benin
orvix access – Browsed by chance, but design keeps finding information very simple.
Если вы ищете сайдинг для облицовки дома в Лиде, его можно приобрести в специализированных магазинах стройматериалов, на строительных рынках или в интернет-магазинах с доставкой в город. купить сайдинг в лиде
The hens’ rebellion is a small but significant moment of resistance. They destroy their own eggs rather than give them up, but they are brutally crushed. This episode highlights the cost of defiance. To understand the full scope of Napoleon’s cruelty, reading the text is necessary. An Animal Farm PDF provides immediate access to these critical sub-plots. It honors the memory of those who stand up to power, even when they fail. https://animalfarmpdf.store/ Animal Farm Introduction Pdf
indian pharmacies safe [url=https://indogenericexport.com/#]reputable indian online pharmacy[/url] reputable indian online pharmacy
The story of Tom Sawyer is a blend of satire, adventure, and nostalgia. Mark Twain’s writing is brilliant and engaging. If you are looking for a digital copy of this book, you have found the right place. We offer a version that is compatible with all major devices. A Tom Sawyer PDF allows you to keep the story with you at all times, making it easy to escape into the world of Twain whenever you have a free moment. https://tomsawyerpdf.store/ Pdf Of Tom Sawyer Children’s Play
This post is well-written and very helpful. I appreciate the clarity of the explanations. The content is informative and useful. Thank you for sharing your knowledge.
https://www-131177.com/
explore pexra – Smooth interface, navigation is straightforward and details are easy to find.
обучение стриминг [url=https://shkola-onlajn-23.ru/]обучение стриминг[/url] .
official capital page – Browsed this by chance, but the information was presented in a way that kept me engaged.
выпрямитель дайсон купить в екатеринбурге [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон купить в екатеринбурге[/url] .
lomonosov school [url=https://shkola-onlajn-22.ru/]lomonosov school[/url] .
click to open – Everything loads quickly and the layout stays simple.
Very helpful and informative post. I appreciate how the content is structured and explained clearly. It provides practical information and useful insights that readers can easily apply.
https://netzowl.com/
Clear design – The site feels modern and effortless to navigate.
Incredible! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a entirely different topic but it has
pretty much the same layout and design. Wonderful choice
of colors!
Aurora hub – Always interesting finds and prices that feel right.
Top picks online – Stylish and reliable products make this site a go-to.
промокоды 1хбет кз
code promo 1xbet aujourd’hui
This article presents ideas with impressive clarity, guiding readers through concepts smoothly while maintaining thoughtful depth, making the content easy to understand, practical to apply, and valuable for anyone seeking reliable information and meaningful perspectives today.
https://coin.reise/
http://visacart.80lvl.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=4768
Quality posts is the crucial to attract the viewers
to pay a visit the website, that’s what this web site
is providing.
The writing maintains a clear and consistent tone, making the content easy to follow, informative to read, and useful for readers who want practical guidance supported by thoughtful reasoning and organized presentation
https://coin.reise/
карниз для штор с электроприводом [url=https://elektrokarniz25.ru/]карниз для штор с электроприводом[/url] .
BrightBargain shopping – Great variety and discounts, always a pleasure to shop here.
Тренды в строительстве заборов https://otoplenie-expert.com/stroitelstvo/trendy-v-stroitelstve-zaborov-dlya-dachi-v-2026-godu-sovety-po-vyboru-i-ustanovke.html для дачи в 2026 году: популярные материалы, современные конструкции и практичные решения. Советы по выбору забора и правильной установке с учетом бюджета и участка.
Best Online Casino Real Money Australia Live Dealer
промокод казино joker
дистанционное обучение 7 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]дистанционное обучение 7 класс[/url] .
charmcartel.shop – Great collection of accessories, and the website makes it easy to shop and explore.
бонусы мелбет промокоды
дистанционное школьное обучение [url=https://shkola-onlajn-24.ru/]дистанционное школьное обучение[/url] .
электрокарниз [url=https://elektrokarniz5.ru/]elektrokarniz5.ru[/url] .
Definitely believe that which you said. Your favorite justification appeared to be on the net the
simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly do not know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people could take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
электрические гардины для штор [url=https://elektrokarnizy750.ru/]elektrokarnizy750.ru[/url] .
coffeecourtyard.shop – If you’re into coffee, this is the place for you. Amazing selection every time.
электрокарниз москва [url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru/]электрокарниз москва[/url] .
https://usmedsoutlet.shop/# online pharmacy usa
crispcollective.shop – A fantastic store for modern, trendy items, with a simple interface.
meilleur code promo 1xbet
This website was… how do you say it? Relevant!!
Finally I have found something that helped me.
Appreciate it!
driftden.shop – Great site to find cozy and stylish products!
Тем кто ценит порядок и стабильность подходит служба по контракту. Здесь нет серых схем и задержек. Все выплаты официальные. Условия заранее согласованы. Используй шанс изменить доход уже сегодня – 34667 воинская часть
firfinesse.shop – A stunning collection of high-end products with a touch of elegance.
Служба по контракту – это возможность официально заключить контракт и получить стабильный доход. Предусмотрены высокие выплаты и социальные гарантии. Условия фиксируются заранее. Подать заявление можно уже сейчас. Смотрите полную информацию, военкомат пункт отбора на военную службу по контракту
charmchoice.shop – The perfect place for unique charms and trinkets, I always find something special.
plorix online – Clear navigation, site feels professional and details are simple to access.
карниз электро [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
joker casino бездепозитный бонус промокод
glintaro.shop – This site is full of hidden gems! Love the variety and quality of the finds here.
how do i get promo code on 1xbet
https://www.google.cz/url?q=https://www.lagodigarda.com/booking/pages/code_promo_du_bookmaker_1xbet.html
zylavoholdings online – Site is structured nicely, allowing content to be absorbed effortlessly.
zavirobondgroup link – Well-structured design, browsing is smooth and the content is presented clearly.
get 1xbet promo code bonus
Отвод воды от фундамента https://totalarch.com/kak-pravilno-otvesti-vodu-ot-fundamenta-livnevka-svoimi-rukami-i-glavnye-zabluzhdeniya какие системы дренажа использовать, как правильно сделать отмостку и избежать подтопления. Пошаговые рекомендации для частного дома и дачи.
Контрактная служба предполагает выполнение задач в рамках регламента. Все обязанности определены заранее. Формат остается понятным: сколько стоит служба по контракту в россии
Мезонинные стеллажи позволяют эффективно использовать высоту складских помещений. Мы разрабатываем многоуровневые конструкции с учетом нагрузок и потоков персонала. Производство осуществляется на собственном заводе. Готовые системы соответствуют промышленным стандартам: https://www.met-izdeliya.com/
выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал[/url] .
Fresh selections – Products feel pure, natural, and carefully curated.
Aurora essentials – User-friendly layout with a broad selection of items.
Click-worthy finds – Great mix of products and browsing never feels cluttered.
US Meds Outlet: US Meds Outlet – canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
Электрик авито Севастополь Электрик Севастополь услуги цены Доступные цены на услуги электрика в Севастополе. Прозрачная система оплаты без скрытых платежей.
BrightBargain store – Huge savings on everyday items, always something practical to buy.
1win промокод при регистрации
juego del avion 1win [url=http://1win5774.help/]http://1win5774.help/[/url]
https://г-санкт-петербург.веб-службы.рф/?p=topic&id=31347
https://г-санкт-петербург.веб-службы.рф/?p=topic&id=31345
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
электрокарнизы для штор купить [url=https://elektrokarniz25.ru/]электрокарнизы для штор купить[/url] .
Having read this I thought it was really informative.
I appreciate you spending some time and energy to put this information together.
I once again find myself spending a lot of time both reading and leaving comments.
But so what, it was still worthwhile! https://cryptoboss352.top/
zexaroline – Found this through a link, stayed longer because layout works.
charmcartel.shop – Such a fantastic selection of unique accessories, easy to navigate and explore.
рулонные жалюзи купить в москве [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/]рулонные жалюзи купить в москве[/url] .
автоматические жалюзи заказать [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]автоматические жалюзи заказать[/url] .
collarcove.shop – Excellent collars with tons of variety, easy to browse and shop.
электрокарнизы для штор цена [url=https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru/]электрокарнизы для штор цена[/url] .
Продать тафинлар Продам Мавирет. Комбинированный препарат для лечения гепатита С. Быстрое и эффективное излечение.
электрический карниз для штор купить [url=https://elektrokarnizy797.ru/]elektrokarnizy797.ru[/url] .
карниз для штор электрический [url=https://elektrokarniz5.ru/]elektrokarniz5.ru[/url] .
автоматические карнизы [url=https://elektrokarnizy750.ru/]автоматические карнизы[/url] .
crispcrate.shop – Shopping here is always fun! Great products and the site is easy to navigate.
онлайн обучение 11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]онлайн обучение 11 класс[/url] .
дистанционное школьное образование [url=https://shkola-onlajn-24.ru/]shkola-onlajn-24.ru[/url] .
Online medicine home delivery: Indo-Generic Export – online shopping pharmacy india
fixforge.shop – If you’re looking for DIY essentials, this site is your one-stop shop for everything.
Payment security matters tremendously; when you buy tiktok views via PayPal or other protected platforms, you get recourse options if the provider fails to deliver as advertised.
legit mexican pharmacy [url=https://usmedsoutlet.com/#]mexican pharmacies online drugs[/url] US Meds Outlet
электрокарниз купить [url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru/]elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru[/url] .
morvex online hub – Fast-loading pages, navigation is intuitive and information is easy to find.
фриспины без депозита Фриспины без депозита – это один из самых популярных видов бездепозитных бонусов. Они представляют собой определенное количество бесплатных вращений, которые можно использовать на конкретных игровых автоматах. Это отличный способ начать играть без риска.
фриспины Казино бонусы за регистрацию – это широкий спектр предложений, включая фриспины, бонус на депозит и другие привилегии, которые казино дарит новым клиентам.
Контрактная военная служба – это шанс получить стабильный официальный доход. Высокие выплаты начисляются с первого месяца. Все условия закрепляются договором. Заключить контракт можно после отбора. Читать подробнее на странице – подписать контракт на сво в хмао
1вин казино промокод
mail order pharmacy india: Indo-Generic Export – pharmacy website india
Port Nyanzaru is a city of wonders, with dinosaur races and rich trade. It is the starting point for the adventure. The Tomb of Annihilation PDF describes the Merchant Princes and their monopolies. DMs need this info to run the social encounters in the city. The digital map of the city is great for showing players the different wards and the coliseum. The PDF also details the side quests available in the city, which help low-level parties gain XP before facing the jungle. It is a vital resource for the early game.
Excellent site you have here but I was curious if you knew of any discussion boards that cover the same topics talked
about here? I’d really like to be a part of community where I can get responses from
other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please
let me know. Bless you!
Где можно продать лекарства в интернете Где продать ненужные лекарства. Лучшие условия и быстрый сервис.
browse bond – First look suggests reliability, with a neat layout and smooth flow.
Металлические стеллажные системы промышленного назначения изготавливаются с учетом нормативных требований и условий эксплуатации. Мы используем расчет нагрузок и инженерное проектирование. Производство ориентировано на надежность и долговечность. Такие решения подходят для интенсивной работы склада – полочные стеллажи
glintgarden.shop – A must-visit for anyone who loves gardening, always full of great products!
Home cozies – Soft, inviting items that make shopping online enjoyable.
yavex access – Quick to navigate, interface is clear and content is easy to digest.
http://bajameddirect.com/# mexican pharmacies online
Где продать ненужные лекарства Где можно продать лекарства оставшиеся. Не выбрасывайте – продавайте.
Auroriv shop – Clean layout and a fantastic variety of products to explore.
BentoBox Finds – Love the chic and durable bento boxes, ideal for on-the-go meals.
карниз электро [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
Зеркало нашел без проблем, сразу начал играть. 7k зеркало абсолютно ничем не отличается от основного сайта.
1win Oʻzbekiston app [url=http://1win5766.help/]http://1win5766.help/[/url]
мелбет промокод на депозит
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your
web site. Do you ever run into any web browser
compatibility issues? A handful of my blog audience have complained about my site not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Firefox.
Do you have any ideas to help fix this problem?
Мы предлагаем изготовление складского оборудования для логистических комплексов любого масштаба. Производство ориентировано на серийные и индивидуальные проекты. Все решения адаптируются под конкретный объект. Это повышает эффективность складской логистики: https://www.met-izdeliya.com/
казино бонусы за регистрацию Фриспины за регистрацию – это приветственный бонус, который игроки получают просто за создание аккаунта в казино. Это прекрасная возможность попробовать различные игры и, возможно, выиграть реальные деньги.
Browse selection – Smooth experience with plenty to discover.
бездепозитные бонусы казино Казино бонус – это общее понятие, охватывающее все виды поощрений, предлагаемых казино. Это могут быть бонусы на депозит, кэшбэк, еженедельные акции и, конечно же, бездепозитные предложения.
Sizin tavsiyeleriniz bahisler üzerine bilgilendirici.
https://mutual-learning-employment.net/
купить выпрямитель волос dyson [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru[/url] .
coppercitrine.shop – Gorgeous copper pieces with a contemporary touch, fantastic shopping experience.
The naming of the “Windmill of Napoleon” is a stroke of ego that defines the dictator. He takes credit for the work of others. This theft of intellectual property and labor is common in such regimes. You can trace the history of the windmill project by reading the book. An Animal Farm PDF is a great tool for tracking this specific plot line. It shows how public works are used for political propaganda.
charmcartel.shop – A beautiful range of accessories, with easy navigation and checkout.
Мы предлагаем изготовление металлических конструкций для складов под ключ. В рамках проекта выполняется проектирование, производство и поставка оборудования. Это сокращает сроки реализации и снижает риски. Заказчик получает готовое решение для эксплуатации: https://www.met-izdeliya.com/
crystalcorner2.shop – The best crystals and gems, perfect for anyone passionate about gemstones.
электрические карнизы для штор в москве [url=https://elektrokarniz5.ru/]электрические карнизы для штор в москве[/url] .
florafreight.shop – Stunning floral products, perfect for adding life to any garden.
электрокарнизы купить в москве [url=https://elektrokarnizy797.ru/]электрокарнизы купить в москве[/url] .
xylix site – Interface is neat, pages load fast and information is clear at a glance.
рулонные шторы на электроприводе [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/]рулонные шторы на электроприводе[/url] .
электрокарниз купить в москве [url=https://elektrokarnizy750.ru/]электрокарниз купить в москве[/url] .
электроуправляемые жалюзи [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru[/url] .
электрокарнизы цена [url=https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru/]электрокарнизы цена[/url] .
ваучер 1win промокод
онлайн школа для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]онлайн школа для детей[/url] .
US Meds Outlet: best online pharmacy india – pharmacy today
Пинко онлайн-казино
chicchisel.shop – The quality of the tools is unmatched, a must-visit for any craftsman!
zexarotrust page – Nothing feels crowded, and the message is easy to follow.
check nevrix – Pleasant interface, navigation is easy and important info is easy to find.
фриспины з арегистрацию Казино бонусы за регистрацию – это широкий спектр предложений, включая фриспины, бонус на депозит и другие привилегии, которые казино дарит новым клиентам.
онлайн ш [url=https://shkola-onlajn-24.ru/]онлайн ш[/url] .
https://indogenericexport.shop/# muscle relaxers over the counter
best online pharmacy india: mail order pharmacy india – india pharmacy mail order
Халява в казино казино бонусы за регистрацию Бесплатные вращения в популярных слотах, актуальные акции и подробные условия использования.
Your style is very unique in comparison to other folks
I’ve read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this
web site.
obat aborsi,aborsi,child porn,child porn video,porn child,child porn videos,child porn site,
child porn website,child seks porn,child porn web,child porn seks,small child porn,mother and child porn,porn child video,KONTOL,chinese child porn,mom and child porn,child porn sites,porn small child,child porn video,child gay porn,gay child
porn,child porn link,child porn xxx,child porn hub,child porn free,child porn vid,
how to watch child porn,porn mother and child,ai child porn,seks child porn,how to find child porn,child
and mom porn,watch child porn,video porn child,porn with child,porn hub
child,porn mom and child,gay porn child,child girl
porn
Bloom Barrel treasures – A delightful range of products with beautiful floral accents.
Mangelsen
7916 Girard Avenue, Lɑ Joya
ⅭA 92037, United States
1 800-228-9686
discover grand teton national park bears (Adolph)
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post.
Thank you for providing these details.
электрокарниз двухрядный [url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru/]электрокарниз двухрядный[/url] .
Auto finds – Well-organized and simple to navigate, with quality products.
Melbet официальный сайт: вход, регистрация и бонусы для новых игроковБукмекерская контора Мелбет
Услуги букмекерской конторы
Мелбет востребованы игроками,
которые ценят надежность, широкую линию и быстрые выплаты.
Независимо от опыта игрока,
важно выбрать надежную площадку, которая гарантирует безопасность
средств и честность игрового процесса.
Зачем регистрироваться в Melbet?
Площадка славится своими выгодными коэффициентами иразнообразием азартных развлечений, включая лайв-казино.
Игроки могут получить щедрые приветственные бонусы и участвовать в регулярных
акциях для увеличения банкролла.
Пользователи получают оперативные консультации и могут быстро
выводить выигранные деньги на карту или кошелек.
Что предлагает Melbet игрокам?
Функционал сайта Melbet предоставляет пользователям доступ к следующим разделам:
Широкая линия ставок на футбол, хоккей,
теннис и киберспорт с возможностью
просмотра трансляций.
Лицензионные слоты, джекпоты и быстрые игры для тех, кто любит динамичный геймплей.
Live-казино с живыми дилерами, создающее атмосферу реального игорного заведения у вас дома.
Удобный мобильный софт, который дает полный доступ к функционалу сайта прямо со смартфона.
Что говорят о Melbet
Отзывы реальных игроковмогут существенно
повлиять на решение о регистрации
в казино. Большинство клиентов акцентируют внимание на:
Стабильность выплат и прозрачность всех денежных операций.
Глубокую линию ставок и огромный
выбор слотов на любой вкус.
Интуитивно понятный дизайнивысокую скорость работы приложения.
Доступ к аккаунту
Необходимо уделить пару минут регистрации,
чтобы получить полный доступ ко всем
бонусам и возможностям сайта.
Простота и скорость создания профиля — одно из преимуществ Melbet.
Советы для успешной игры
Для успешной игры в букмекерской конторе и
казино стоит учитывать
следующие рекомендации:
Анализируйте форму спортсменов и особенности механики выбранных игровых автоматов.
Используйте бонусы и промокоды для увеличения стартового капитала.
Устанавливайте лимиты на депозит и ставки,
чтобы игра приносила только удовольствие.
Помните, что удача любит подготовленных, и правильный выбор стратегии может принести крупный куш.
Не откладывайте возможность сорвать джекпот и начните играть с бонусами прямо сейчас.https://melbet-zerkalo1224.xyz/ Заключение
Выбор Melbet в качестве основной площадки для
ставок – это решение, которое открывает доступ к
безграничнымвозможностям азартного мира.
Все клиенты ценят безопасность, и лицензированный софт Melbet полностью удовлетворяет
эти потребности. Огромный выбор казино требует тщательного отбора, и Melbet выделяется своей репутацией и лояльностью к игрокам.
Важность надежного букмекера
Для стабильного заработка на ставках необходима платформа,
которая не режет лимиты и вовремя платит.
Официальный сайт Melbet предлагает:
Конфиденциальность личных данных и защиту транзакций;
Прозрачные правила расчета пари
без спорных ситуаций;
Бесперебойный доступ к играм в любой точке
мира;
Удобные финансовые инструменты, включая криптовалюты;
Профессиональный саппорт,
готовый помочь в любую минуту.
Почему игрокивыбирают нас
Наши пользователи отмечают стабильность работы
сайта ивысокие лимиты на ставки.
Мы работаем над тем, чтобы каждый спин и каждая ставка приносили вам удовольствие и реальные деньги.
Мы регулярно обновляем ассортимент
игр и предлагаем эксклюзивные маркеты для
ставок на топовые матчи.
Как найти зеркалоMelbet?
В случае блокировки основного домена,
используйте альтернативные ссылки для входа:
Следите за обновлениями в
наших социальных сетях;
Установите официальное приложение,
не требующее поиска зеркал;
Включайте ВПН, если прямой доступ к сайту ограничен;
Запросите рабочее зеркало
у оператора в онлайн-чате.
Помните, что выбор лицензионного казино
гарантирует выплату любых, даже самых крупных выигрышей.
В случае возникновения трудностей,
наша поддержка работает для вас круглосуточно.
В заключение, регистрируйтесь в Melbet,
забирайте свой бонус и начинайте путь к большим победам уже сегодня!
Жмите на кнопку регистрации и погрузитесь в мир
высоких коэффициентов и ярких эмоций.
brixelline site – Quick glance left a positive impression with smooth navigation.
Bright Bloomy Goods – Gorgeous floral items, and browsing through the site is hassle-free.
xorya online – Quick browsing, everything appears well structured and professional.
Kate Chopin writes about the “inexpressible” things – the vague longings and nameless moods. To find words for your own feelings, get the awakening pdf. The text articulates the unsaid. A digital copy is a vocabulary for the heart.
казино с бездепозитным бонусом Фриспины – это бесплатные вращения барабанов в онлайн-казино. Они могут быть отличным способом начать игру, не рискуя собственными средствами.
glintvogue.shop – Always fashionable and trendy, my favorite site to shop at!
coralcrate.shop – The variety of products is fantastic, and the site layout is very user-friendly.
visit vixarobonding – Well-organized site, pages respond quickly and content is readable.
Arden Luxe picks – Everything feels polished and thoughtfully designed.
Продам Рисарг Продам Револейд.
charmcartel.shop – Love the stylish pieces and the website is very organized for easy browsing.
https://www.crossroadsbaitandtackle.com/board/board_topic/9053260/7835783.htm
vipps approved canadian online pharmacy: buying drugs from canada – best online canadian pharmacy
curtaincraft.shop – Stylish curtains and textiles, this site has something for every taste.
бонусы за регистрацию Фриспины без депозита – это один из самых популярных видов бездепозитных бонусов. Они представляют собой определенное количество бесплатных вращений, которые можно использовать на конкретных игровых автоматах. Это отличный способ начать играть без риска.
freshfinder.shop – Fresh, interesting, and unique finds every time, I can’t get enough of this site!
электрические гардины [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
выпрямитель дайсон купить в москве оригинал [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон купить в москве оригинал[/url] .
Hello everybody, here every person is sharing these kinds of experience,
therefore it’s nice to read this weblog, and I used to visit this web site all the time.
Here is my blog post; Linnie
https://usmedsoutlet.shop/# US Meds Outlet
Currently it appears like Drupal is the best blogging platform available
right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
Общаются Искал Ростов знакомства в телеграме — нашёл нормальный чат.
электрокарнизы цена [url=https://elektrokarnizy797.ru/]электрокарнизы цена[/url] .
автоматический карниз для штор [url=https://elektrokarniz5.ru/]автоматический карниз для штор[/url] .
1win lucky jet game [url=www.1win5744.help]www.1win5744.help[/url]
Definitely believe that which you said. Your favorite reason seemed to
be on the web the simplest factor to take into account
of. I say to you, I certainly get irked whilst people think
about worries that they just don’t understand about. You
managed to hit the nail upon the highest and also defined out the whole thing with no need side effect , people can take a signal.
Will probably be again to get more. Thanks
автоматические рулонные шторы с электроприводом [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru[/url] .
The hypothesis seems to be borne out by the health insurance knowledge, with the team finding sildenafil users had a 69 % diminished risk of Alzheimer’s disease in comparison with non-users – a reduction that was notably stronger than other kinds of.
plixo review – Well-laid-out pages, content is clear and the site feels reliable.
электронный карниз для штор [url=https://elektrokarnizy750.ru/]elektrokarnizy750.ru[/url] .
лбс это [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]лбс это[/url] .
жалюзи для окон с электроприводом цена [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]жалюзи для окон с электроприводом цена[/url] .
бездепозитные бонусы казино Фриспины без депозита – это один из самых популярных видов бездепозитных бонусов. Они представляют собой определенное количество бесплатных вращений, которые можно использовать на конкретных игровых автоматах. Это отличный способ начать играть без риска.
Продать лекарства с рук в спб Продать лекарства телеграмм. Удобный канал связи и продаж.
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве [url=https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru/]электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве[/url] .
Архангельск: натяжные потолки — быстро,качественно,с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональный монтаж в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем идеальное решение натяжных потолков по вашему желанию;
Выполняем монтаж любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор сатиновых полотен.
Рассчитаем стоимость — позвоните!
Потолочные решения в кухне — любая расцветка. по городу — с консультацией специалиста-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки двухуровневые высота[/url]
натяжные потолки матовые в архангельске высота – [url=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://www.29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://google.co.hu/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/]http://toolbarqueries.google.com.gt/url?sa=t&url=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www.dinotte.md/details/saltele/43]Качественная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] 2cc08af
farmacias online usa [url=https://bajameddirect.com/#]BajaMed Direct[/url] the purple pharmacy mexico
https://dp5.boards.net/thread/1732/1xbet-promo-australia-1xmaxbono-bonus
bloombeacon.shop – Lovely decor and gift items, shopping is smooth and simple.
Металлические конструкции для складов проектируются с учетом возможности дальнейшей модернизации. Производство позволяет адаптировать системы под рост бизнеса. Это снижает затраты при расширении складских площадей: стеллажи фронтальные
Производство металлических стеллажных конструкций осуществляется на собственных мощностях с контролем качества на всех этапах. Мы изготавливаем оборудование для промышленных складов, распределительных центров и производственных площадок. Используются проверенные материалы и современные технологии обработки металла. Это обеспечивает высокую прочность и безопасность эксплуатации: стеллажи металлические консольные для складов
фриспины з арегистрацию Бездепозитные фриспины – это еще одна разновидность бесплатных вращений, которые можно получить без необходимости пополнять счет. Они часто предлагаются новым игрокам в качестве лояльности.
бездепозитные промокоды Фриспины без депозита – это один из самых популярных видов бездепозитных бонусов. Они представляют собой определенное количество бесплатных вращений, которые можно использовать на конкретных игровых автоматах. Это отличный способ начать играть без риска.
Продать мекинист Продать Линпарза. Инновационное решение для лечения рака яичников и других онкозаболеваний. Высокая эффективность и безопасность.
школа онлайн обучение для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-24.ru/]shkola-onlajn-24.ru[/url] .
Briovanta Finds – Wonderful and unique items, and the site is easy to navigate.
Patrice & Associates
Scottsdale, AZ, United Stɑtеѕ
16265237726
hospitality Management interns
best mexican pharmacy online: BajaMed Direct – BajaMed Direct
Bag picks – Stylish, trendy, and always fun to shop through.
explore qulavoholdings – Well-organized sections, clear headings, and pages respond quickly.
Продать эриведж Продать Пемброриа. Иммунотерапия рака.
The adventures that unfold in St. Petersburg are some of the most famous in literature. Mark Twain’s ability to weave humor with suspense is unparalleled. If you are looking for a digital copy of this book, look no further. We offer a version that is perfect for e-readers and tablets. A Tom Sawyer PDF gives you the freedom to read the book in the way that suits you best, preserving the legacy of Twain in a modern format.
online med pharmacy: US Meds Outlet – my canadian pharmacy review
learn more here – Everything feels well-laid-out, giving an impression of reliability and professionalism.
open zexarotrustco – Everything loads cleanly, and the content is easy to follow.
знакомятся Искал Ростов знакомства в телеграме — нашёл нормальный чат.
covecrimson.shop – Excellent collection of high-quality, bold items. Shopping here is always easy and fun.
http://nowapilka.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=673831#673831
The Trickster Gods offer power, at a price. Tomb of Annihilation features this unique possession mechanic. The Tomb of Annihilation PDF details the spirits and their flaws. DMs use the digital text to manage the possessions. The book also explains the shrines where they dwell. The PDF maps out these mini-dungeons. It also details the final tomb. The digital guide is crucial for navigating the puzzle-heavy later chapters. It ensures the DM can handle the chaotic elements of the campaign with ease.
Simply desire to say your article is as amazing. The clearness
in your post is simply spectacular and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject.
Well with your permission let me to grab your
feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding
work.
I every time spent my half an hour to read this weblog’s content daily along with a cup of coffee.
My spouse and I stumbled over here coming from a different web page and thought I should check things out.
I like what I see so now i’m following you.
Look forward to exploring your web page yet again.
автоматические гардины для штор [url=https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru/]elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru[/url] .
http://indogenericexport.com/# methocarbamol medication
charmcartel.shop – Fantastic collection of trendy accessories, browsing the site is a breeze.
gardengalleon.shop – A must-visit for gardening enthusiasts, featuring stylish products for every need.
Частный электрик Севастополь Электрик Севастополь
cypresschic.shop – A fantastic collection of chic products, the site makes browsing effortless.
No-frills store – Easy to navigate and packed with worthwhile offers.
goldenget.shop – A treasure trove of great deals, perfect for budget-friendly shopping!
Hi my family member! I want to say that this
article is awesome, nice written and include almost all vital infos.
I’d like to see more posts like this .
The corruption of the pigs is slow, steady, and inevitable. It shows that power is a drug. Watch the addiction take hold in the Animal Farm PDF. It is a sobering look at the nature of leadership.
I was able to find good information from your articles.
zarvo site – Smooth navigation, content is readable and everything feels well structured.
cinnamoncorner.shop – An amazing selection of items, I can always find something unique here.
Электрик Севастополь на дом Электрик Севастополь
удаленная работа в интернете онлайн работа
With thanks! Terrific information.
This article delivers clear insights with impressive structure, guiding readers through complex ideas using simple language, strong examples, and practical context that makes the information accessible, valuable, and genuinely useful for anyone seeking deeper understanding across diverse topics today.
hiresineiw.info
Blue Quill must-haves – An elegant store with a great mix of products that are easy to browse.
карниз моторизованный [url=https://elektrokarnizy797.ru/]elektrokarnizy797.ru[/url] .
Кабель ВВГнг Мы также предлагаем широкий ассортимент соединительных элементов, включая тройник стальной, фланцы (плоский стальной и воротниковый), отвод стальной, переход стальной и тройник нержавеющий, обеспечивая надежное и герметичное соединение труб.
dyson фен выпрямитель купить [url=https://dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru/]dsn-vypryamitel-8.ru[/url] .
If some one desires to be updated with most recent technologies after
that he must be go to see this site and be up
to date everyday.
удаленная работа для пенсионеров Удаленная работа с телефона — ваш офис всегда с собой
онлайн обучение для детей [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]онлайн обучение для детей[/url] .
рольшторы заказать [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/]rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru[/url] .
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – prescriptions from mexico
электрокарниз москва [url=https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]электрокарниз москва[/url] .
жалюзи с приводом для окон [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]жалюзи с приводом для окон[/url] .
карниз для штор электрический [url=https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru/]elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru[/url] .
Briovista Selection – Very stylish site, and the range of products is impressive and diverse.
онлайн работа без опыта Фриланс работа — гибкость и независимость
https://indogenericexport.com/# methocarbamol medication
Skincare must-haves – Smooth navigation and top-notch items make it a great site.
знакомятся Искал Ростов знакомства в телеграме — нашёл нормальный чат.
Simply desire to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is simply nice and i could assume you’re an expert
on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your
feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep
up the gratifying work.
Уже месяц как играю тут, всё гладко. Менеджер поддержки помогал разбираться мне быстро.
cozycarton.shop – Cute, comfy items that make excellent gifts or a special treat for yourself.
казино промокоды Добро пожаловать в захватывающий мир онлайн-казино, где удача и азарт переплетаются, открывая двери к невероятным возможностям! Для всех ценителей острых ощущений и желающих испытать свою фортуну, мы подготовили эксклюзивные предложения, способные сделать ваш игровой опыт еще более ярким и прибыльным.
US Meds Outlet: reputable canadian online pharmacies – canadian online pharmacy no prescription
Hi there friends, pleasant article and fastidious urging commented at this place,
I am truly enjoying by these.
gemgalleria.shop – Beautiful jewelry and gems that are perfect for making any event extra special!
1win Oʻzbekiston rasmiy sayti [url=https://www.1win5753.help]https://www.1win5753.help[/url]
dalvanta.shop – Unique and beautiful products, the shopping experience is flawless every time.
charmcartel.shop – Beautifully curated accessories, the site is easy to navigate and find what you need.
boldbasketry.shop – Amazing baskets and home decor, every shopping experience is seamless.
1win не открывается что делать [url=https://www.1win09834.help]https://www.1win09834.help[/url]
artattic.shop – A really impressive range of artwork that’s fun to explore.
Электрик Сахарная Головка Электрик Севастополь
1win qanday yuklab olish [url=http://1win5753.help]1win qanday yuklab olish[/url]
online pharmacy india: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – indianpharmacy com
zorivocore page – Fast performance and a smooth browsing experience overall.
Your writing communicates ideas effectively, providing structured guidance, practical examples, and insightful reflections that help readers grasp important concepts confidently.
https://981239.org/
goldenparcel.shop – The site offers nothing but the best, highly recommend to everyone looking for premium items.
https://bajameddirect.shop/# BajaMed Direct
1win сколько выводят на о деньги [url=1win09834.help]1win сколько выводят на о деньги[/url]
Общаются Искал Ростов знакомства в телеграме — нашёл нормальный чат.
карнизы для штор с электроприводом [url=https://elektrokarnizy797.ru/]elektrokarnizy797.ru[/url] .
На сайте часто выигрышные серии случаются у игроков. 7k официальный сайт может быть, это честная генерация случайных чисел.
бездепозитные фриспины И, конечно же, для тех, кто ищет максимальную выгоду и предпочитает играть без отягощающих условий, мы рады представить бездепозитные бонусы. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто хочет протестировать игры, насладиться процессом и, возможно, сорвать джекпот – и все это без единого вложенного рубля. Ваша удача ближе, чем кажется!
Hello my family member! I wish to say that this post
is awesome, great written and come with almost all vital infos.
I would like to peer extra posts like this .
Brivona – I love how neat and structured the site is, makes finding items so easy.
Полилен 40-ЛИ-63 Для обслуживания и ремонта трубопроводов предлагаются поршни для прочистки (поролоновые и полиуретановые), подогреватели стыков, опорно-направляющие кольца, диэлектрические кольца-спейсеры и герметизирующие манжеты с соответствующими защитными укрытиями, а также палатки и укрытия для сварки.
best online pharmacy india [url=http://indogenericexport.com/#]india pharmacy mail order[/url] indian pharmacies safe
Slotlar, rulet, bakara və blackjack kimi klassik oyunlar Pinco platformasında mövcuddur və xüsusi multiplikatorlar oyunları daha maraqlı edir. Mən həmçinin live-diler oyunlarında əsl kazino həyəcanını yaşadım, pinco qaydalar burada oyun axışını tam başa düşmək üçün əvəzolunmazdır.
дистанционное обучение 10-11 класс [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]дистанционное обучение 10-11 класс[/url] .
Basket Bliss online – Decorative and functional baskets, plus charming home pieces.
24 часа Электрик Севастополь
cozycopper.shop – Unique copper products, perfect for adding style and function to any space.
browse ulixo – Checked it out randomly, content is easy to read and everything is responsive.
вакансии удаленная работа удаленная работа вк
рулонные шторы автоматические [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/]рулонные шторы автоматические[/url] .
электрические карнизы купить [url=https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru/]электрические карнизы купить[/url] .
https://ai-db.science/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%20%D0%B2%201xBet%202026:%201X200FREE%20-%20%D0%91%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81%2032,500%20%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%B9
obat aborsi,aborsi,child porn,child porn video,porn child,child porn videos,child porn site,child porn website,child seks porn,child
porn situs web,child porn seks,small child porn,mother and child porn,porn child video,KONTOL,chinese child porn,mom and child porn,child porn sites,porn small child,child porn video,child gay porn,gay
child porn,child porn link,child porn xxx,child porn hub,child porn free,
child porn vid,how to watch child porn,porn mother and child,ai
child porn,seks child porn,how to find child porn,child and mom porn,watch child
porn,video porn child,porn with child,porn hub child,porn mom and child,gay
porn child,child girl porn
Bold Bouton curated picks – Elegant modern products, effortless browsing and enjoyable shopping.
gervina.shop – An excellent collection of sleek and modern pieces that make a huge difference in any room!
https://bruchy.com/blogs/2970/%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4-%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%A1%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BA%D1%83-1%D1%85%D0%91%D0%B5%D1%82-2026-1XBRO200
decordock.shop – Wonderful home decor items, I can quickly find everything I need for my home.
charmcartel.shop – The accessories here are stunning, and the website is so user-friendly.
usa pharmacy: medical pharmacy – US Meds Outlet
farmacia mexicana online: BajaMed Direct – BajaMed Direct
Primrose Everdeen is the catalyst for the entire series. Her innocence is what Katniss fights to protect. The bond between the sisters is the emotional core that grounds the high-stakes action. It is a story about love as much as it is about war. To feel the weight of this relationship, you must read the book. Electronic copies, such as a PDF, allow you to keep this touching story close at hand on your mobile device. https://thehungergamespdf.ru/ The Hunger Games Book 3 Pdf Free Download
Почему пользователи выбирают
площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный
ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает
навигацию, поиск товаров и управление заказами
даже для новых пользователей.
В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций, включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования
условного депонирования,
что минимизирует риски для обеих сторон
сделки. На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным отношением к безопасности клиентов, что делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным
и, как следствие, популярным среди пользователей, ценящих анонимность и надежность.
circuitcabin.shop – Ideal for all things tech, and I love how easy it is to find products here.
фриспины за регистрацию Мы понимаем, насколько привлекательна идея бесплатных вращений, поэтому предлагаем вам бездепозитные фриспины. Это прямой путь к захватывающим раундам в лучших слот-играх, где каждая линия выплат может стать вашим билетом к крупному выигрышу. Начните играть прямо сейчас и ощутите всю мощь удачи!
Общаются Искал Ростов знакомства в телеграме — нашёл нормальный чат.
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# your pharmacy online
Appreciate this post. Let me try it out.
playful picks shop – Loved browsing, the store had whimsical and cute finds.
Visual appeal – Everything about the design feels current and cool.
рулонные шторы каталог цены [url=https://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]рулонные шторы каталог цены[/url] .
online hardware mart – Easy browsing, checkout worked without any hiccups.
карниз моторизованный [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/]karniz-elektroprivodom.ru[/url] .
http://duster-clubs.ru/forum/member.php?u=32010
The intricate world-building of the Empyrean series reaches new heights in this novel. We learn more about the gryphons and the other cultures that inhabit this continent. For ease of access, the Onyx Storm epub is the preferred choice for many international readers. The story balances the grand scale of war with the intimate moments of a romance under fire. It is a compelling read that challenges the characters to be better than their predecessors. The electronic version ensures that you can carry this heavy tome without breaking your back. https://onyxstormepub.ru/ Onyx Storm Free Pdf Free Download
вакансии удаленная работа работа на удаленке
Lotus Lane Hub Store – Easy browsing, product photos are clear and site feels welcoming.
https://xn--80aakykhw8cxb.xn--p1ai/forum/messages/forum1/topic17916/message19940/?result=new#message19940
бездепозитные бонусы Особое внимание мы уделяем тем, кто ценит свободу и предпочитает знакомиться с игрой на ходу. Именно для вас мы подготовили фриспины за регистрацию – бесценные вращения, которые позволят вам лично оценить разнообразие игровых автоматов, не делая при этом никаких финансовых вложений. Это отличный старт для новичков и приятное дополнение для опытных игроков, желающих протестировать новые игры.
My name is Owen (44 years old) and my hobbies are
Rock collecting and Weightlifting.
Brondyra Store – The products here are so stylish, and it’s so easy to complete your purchase.
navirotrack information – Simple design and structured layout make reading content straightforward and trustworthy.
goldgrove2.shop – Such a fantastic site with an impressive range of one-of-a-kind items.
http://eiswanterr.clanweb.eu/profile.php?lookup=194
Банкротство физических лиц в Калуге регулируется федеральным законом о
банкротстве рейтинг агентств по банкротству физических лиц в калужской области.
Процедура позволяет гражданам, не способным
погасить долги, избавиться от финансовых обязательств.
Bath Breeze favorites – Pampering products that feel indulgent and relaxing.
мостбет купон [url=mostbet72461.help]mostbet72461.help[/url]
craftcabin.shop – Amazing selection for all types of crafts, always fresh and filled with inspiration!
электрокарниз двухрядный цена [url=https://elektrokarnizy797.ru/]электрокарниз двухрядный цена[/url] .
Доставка из Китая в Москву и Россию: как выбрать надежного партнера в 2026
тяговые акб для погрузчиков купить Тяговая батарея Тюменский: PZS-технология, минимальные потери. Для Jungheinrich и Still.
online pharmacy indonesia: best canadian pharmacy – US Meds Outlet
Przeczytalem recenzje kasyna Spinania z opisem bonusow i zdecydowalem sie zarejestrowac.
https://justpaste.it/mn29r
hold resource – Checked it quickly, everything is tidy and gives a professional feel.
I think this is one of the most significant info for me.
And i’m glad reading your article. But want to remark on some
general things, The web site style is perfect, the articles
is really nice : D. Good job, cheers
gingergrace.shop – Great variety of one-of-a-kind items, perfect for unique gifts or treats for yourself!
If some one wishes expert view about blogging and site-building after that i suggest him/her to go
to see this website, Keep up the good job.
класс с учениками [url=https://shkola-onlajn-25.ru/]класс с учениками[/url] .
Ремонт плитки Ремонт керамической поверхности
dorvani.shop – So many stylish products to choose from, shopping here is a breeze!
https://bajameddirect.shop/# mexicanrxpharm
скидки в Стиме Новости Стим
charmcartel.shop – Great collection of accessories, and the website makes it easy to shop and explore.
kitchen gadgets shop – Well-organized store, browsing for kitchen tools was simple.
электрические рулонные шторы купить [url=https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/]электрические рулонные шторы купить[/url] .
электронный карниз для штор [url=https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru/]elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru[/url] .
как скачать мостбет на android [url=http://mostbet72461.help]как скачать мостбет на android[/url]
http://indogenericexport.com/# top 10 pharmacies in india
indian pharmacies safe: Indo-Generic Export – top online pharmacy india
Ремонт мраморной поверхности Ремонт картины
Generic medications especially when buying online and wondered what the whole deal is and why they are. Standards authors of coverage of yarsa gunbu says Chaudhary professor emeritus at.
Unique shop spot – A great place to find items you don’t see everywhere.
рулонные жалюзи на пластиковые окна купить [url=https://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]рулонные жалюзи на пластиковые окна купить[/url] .
daily wear market – Smooth scrolling and helpful visuals throughout.
Luggage Lotus Essentials – Smooth browsing, items are high-quality and site is easy to use.
buildbay.shop – Fantastic place to buy DIY supplies, very convenient and straightforward to use.
автоматические жалюзи заказать [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]автоматические жалюзи заказать[/url] .
автоматические карнизы для штор [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/]автоматические карнизы для штор[/url] .
explore trixo – Pages load fast, and the overall structure is user-friendly.
craftcurio.shop – The best place to find cool craft supplies and spark new ideas!
1win Qarshi pul yechish [url=http://1win5753.help]http://1win5753.help[/url]
Bay Biscuit hub – Irresistible treats and easy navigation make shopping fun.
best canadian online pharmacy reviews: US Meds Outlet – is canadian pharmacy legit
mexican drugstore [url=https://bajameddirect.com/#]the purple pharmacy mexico[/url] BajaMed Direct
https://bajameddirect.shop/# BajaMed Direct
glamgarrison.shop – Fantastic for chic accessories, always love browsing through the new arrivals!
greenguild.shop – This is my go-to site for eco-friendly items, shopping here is always so convenient.
Каждый день выходят новые свежие промокоды. Юзаю их и всегда получаю что-то полезное на деньги.
kovalyn essentials hub – Sleek and tidy, products are easy to explore and info is clear.
dorvoria.shop – The best place for high-quality items and smooth transactions, love it!
acceso 1win méxico [url=1win5773.help]1win5773.help[/url]
Sayt çox yaxşıdır, belə davam edin. Təşəkkürlər!
https://suitablenames.com/typefp/ru/?p_dn=pin-up-azerbaijan-jackpot.org
charmcartel.shop – A must-visit for stylish accessories, the website is well laid out.
clarvesta.shop – Fantastic selection of elegant items, and the shipping is always prompt.
ключи steam Новости Стим
Hi there colleagues, how is everything, and what you want to say about this piece
of writing, in my view its genuinely amazing in support of me.
Revisiting Panem is always a good idea. The themes of authoritarianism and resistance are always relevant. The story moves fast, but the ideas stick with you. It is a modern classic for a reason. If you need a refresher before the new movies or books come out, a digital copy is the way to go. Search for a The Hunger Games pdf to dive back into the world of District 12 and relive the spark that started the fire. https://thehungergamespdf.ru/ The Hunger Games The Ballad Of Songbirds & Snakes Pdf
1win deposito spei [url=https://www.1win5773.help]https://www.1win5773.help[/url]
виды косметологии косметология москва
Mortal Kombat Steam metro ключи
caldoria.shop – So many amazing finds, shopping here is always easy and enjoyable.
Dante Russo’s transformation is not a change of personality, but a change of heart. He learns to let someone in. This is a realistic and touching arc. A King of Wrath PDF allows you to track this subtle shift. You can see the moment he stops fighting his feelings and starts fighting for her. It is a beautiful progression that resonates with many readers. https://kingofwrathpdf.ru/ Bradygames Wrath Of The Lich King Strategy Guide Pdf
BajaMed Direct: online mexican pharmacy – mexico rx
Luggage Lotus Hub Store – Clear layout, items seem well-made and navigation is simple.
Engaging site – Every visit feels lively and entertaining.
cratecosmos.shop – A delightful shop for home goods, and the browsing experience is very smooth!
рулонные шторы на окна москва [url=https://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru[/url] .
rixarotrust resource – Well-laid-out pages make it simple to find and read information.
relaxed home picks – The design makes shopping feel slow and enjoyable.
1win mBank пополнение [url=https://www.1win09834.help]1win mBank пополнение[/url]
http://indogenericexport.com/# Online medicine order
kovaria essentials – Navigation is smooth, discovering products is quick and simple.
US Meds Outlet: US Meds Outlet – US Meds Outlet
Beard products online – Well-curated selection of oils, balms, and grooming tools.
http://bajameddirect.com/# pharmacy delivery
купить аккумуляторы на погрузчик Аккумуляторные батареи тяговые из Словении TAB — европейское качество по доступной цене. Долговечность до 1500 циклов.
glamgrocer.shop – Stylish and functional kitchen products, shopping here is always an enjoyable experience!
автоматические карнизы для штор [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/]автоматические карнизы для штор[/url] .
p e r o ключи steam
жалюзи с электроприводом для окон купить [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/]жалюзи с электроприводом для окон купить[/url] .
скидки в Стиме buckshot roulette
If some one wishes expert view about running a blog afterward i advise him/her to go to see
this weblog, Keep up the fastidious work.
driftdahlia.shop – A perfect mix of artistic and functional decor pieces. Love it!
charmcartel.shop – Stylish accessories that are easy to find on this clean, well-organized website.
grovegarnet.shop – Such a great variety of items, definitely one of my go-to places for shopping.
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any recommendations?
скидки в Стиме steam игры
Доставка из Китая в Россию: быстро, надёжно, выгодно с ASIAFAST
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предоставляют:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• Комплексный анализ покрытия сети в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку оборудования
• отсутствие скрытых платежей на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]интернет сибирские сети подключить домой[/url]
проверка домашнего интернета сибирские сети – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]https://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=https://images.google.co.in/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]https://cse.google.ie/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=https://taticamente.com/forum-2/topic/%e6%93%8d%e4%bd%9c%e5%8c%97%e7%be%8e%e5%a4%a7%e5%ad%a6%e6%95%99%e8%82%b2%e9%83%a8%e8%ae%a4%e8%af%81%e5%ad%a6%e5%8e%86qq-%e5%be%ae%e4%bf%a1912446885%e4%b9%b0%e5%8d%97%e5%8d%ab%e7%90%86%e5%85%ac-10/?part=2653#postid-695594]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] ce91037
BajaMed Direct: order antibiotics from mexico – medication in mexico
goGLOW Houston Heights
1515 Studemont Տt Suite 204, Houston,
Texas, 77007, USA
(713) 364-3256
Bookmarks
calmcrest.shop – I enjoy how calming the site feels, plus there’s so much to choose from.
Kovelune Finds – Design stands out, visuals are strong and the site is easy to navigate.
http://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
розыгрыш стим buckshot roulette
lunivora corner – Site feels responsive, browsing is effortless and products are interesting.
It is perfect time to make some plans for the longer term and it’s time to be happy.
I have read this publish and if I may just I want to recommend you few attention-grabbing things or advice.
Maybe you could write next articles regarding this article.
I wish to learn more issues approximately it!
цена аккумулятора на электропогрузчик Штабелер Jungheinrich аккумулятор — высокотехнологичные АКБ с емкостью до 600 Ач. Идеальны для складов с высоким трафиком.
What’s up, yup this post is really pleasant and I have learned lot of
things from it on the topic of blogging. thanks.
learn torivocapital – Well-organized sections make browsing smooth and content easy to digest.
Luxury picks – Effortless browsing and products that look amazing.
simple honey market – Came across it recently, pricing doesn’t feel overdone.
электрические рулонные шторы [url=https://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]электрические рулонные шторы[/url] .
BajaMed Direct [url=https://bajameddirect.shop/#]BajaMed Direct[/url] BajaMed Direct
red redemption steam Mortal Kombat Steam
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/]электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве[/url] .
Ремонт Москва Трещина на плитке
https://bajameddirect.shop/# BajaMed Direct
pharmacys in mexico: mexico pet pharmacy – BajaMed Direct
metro ключи metro ключи
clevercheckout.shop – Smooth checkout and a wide array of quality items to choose from.
lamplounge online – Pleasant browsing, lighting products are well displayed and easy to view.
mexican pharmacy: BajaMed Direct – BajaMed Direct
halvessa.shop – A beautiful, clean design that’s easy to navigate and full of amazing finds.
Good post. I’m going through some of these issues as well..
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful post. Thank you for supplying
this information.
The emotional intelligence in this book is high. Dante and Vivian communicate, fight, and misunderstand each other in ways that feel authentic. It is not just a fantasy; it is a grounded relationship drama wrapped in luxury. Readers looking for a King of Wrath PDF often want to revisit the poignant conversations between the leads. The book explores trust, betrayal, and forgiveness in a way that feels earned. It is a mature romance that tackles difficult subjects with sensitivity and heat. https://kingofwrathpdf.ru/ The King Of Wrath Epub
https://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
Your writing delivers value through clear explanations, helping readers understand key ideas without feeling overwhelmed by complexity.
1kccclub.com
Thresh and his mercy toward Katniss show that honor still exists even in the arena. These small moments of humanity define the moral core of the story. It is a complex narrative that refuses to see people as purely good or evil. To appreciate the character nuances, reading the novel is essential. Whether you choose a paperback or a The Hunger Games pdf, the important thing is to witness the choices these characters make under extreme pressure. https://thehungergamespdf.ru/ The Hunger Games Trilogy Pdf Free Download
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is
amazing, nice written and come with approximately all significant infos.
I would like to see more posts like this .
luxfable boutique online – Fashionable design, smooth experience and responsive pages.
Do you love gambling? crypto casinos allow you to play online using Bitcoin and altcoins. Enjoy fast deposits, instant payouts, privacy, slots, and live dealer games on reliable, crypto-friendly platforms.
curated goods store – Browsing was fast, selection feels thoughtfully put together.
Rebecca Yarros has mastered the art of the cliffhanger, and her latest entry in the Empyrean saga is no exception. As the revolution grows, so does the danger for everyone involved. Accessing the Onyx Storm epub allows readers to dive straight into the chaos without waiting for shipping or bookstore lines. The emotional turmoil Violet faces in this installment is written with such raw honesty that it resonates long after you finish. From aerial battles to quiet moments of intimacy, the pacing is perfect. This digital book is essential for anyone who calls themselves a fan of modern fantasy and dragon lore. https://onyxstormepub.ru/ Onyx Storm Download Epub Free Pdf
Трещина на плитке Реставрация картины
рулонные шторы кухню цена [url=https://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru[/url] .
lamplounge treasures – Relaxed layout, exploring lighting options was smooth and stress-free.
1win пополнение через терминал [url=http://1win85612.help/]1win пополнение через терминал[/url]
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice even as you amend your website, how
could i subscribe for a weblog site? The account helped me a appropriate deal.
I have been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided shiny transparent concept
pharmaceutical online: best canadian pharmacy no prescription – US Meds Outlet
pin-up CS2 mərc [url=pinup2007.help]pinup2007.help[/url]
электрокарнизы для штор купить [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/]электрокарнизы для штор купить[/url] .
http://bajameddirect.com/# mexican online pharmacy
1win промокод при регистрации [url=http://1win85612.help/]http://1win85612.help/[/url]
https://indogenericexport.com/# india online pharmacy
US Meds Outlet: express scripts com pharmacies – US Meds Outlet
Первый депозит 1000 рублей получил бонус 150% плюс 150 FS. Хороший стартовый пакет для новичков.
мостбет live линия [url=https://mostbet72461.help/]https://mostbet72461.help/[/url]
pin-up Azərbaycan PayPoint [url=https://www.pinup2007.help]https://www.pinup2007.help[/url]
Продать козэнтикс Продать кабометикс
harborhoney.shop – I always find the perfect items for every occasion here.
Stunning quest there. What happened after? Good luck!
Продать тецентрик Продать калквенс
Maple Merit Corner – Pleasant shopping experience, categories are clear and items seem trustworthy.
Role-level market insights and comparisons across the industry.
The information on this site is based on general observations of Java’s role in the software industry and aggregated career data – https://learning-java.com/
Lift Lighthouse Shop – Smooth navigation, pages are clear and information is well organized.
Libetrioでパッシブ収入を目指す暗号資産投資が可能です。
簡単な登録で、自動運用による効率的な資産形成が始められます。
ユーザーに合わせた柔軟な運用オプションが魅力です。
初心者でも安心して暗号資産投資を始められるプラットフォームです。
online pharmacy india [url=https://indogenericexport.shop/#]indian pharmacy paypal[/url] indian pharmacy online
everyday goods hub – Easy flow, everything is laid out logically.
best online pharmacy india: online pharmacy india – indian pharmacies safe
Role-level market insights and comparisons across the industry.
The information on this site is based on general observations of Java’s role in the software industry and aggregated career data – https://learning-java.com/
Индивидуалки Новый Уренгой
https://usmedsoutlet.shop/# best online pet pharmacy
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку
KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной
аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный
сотнями продавцов. Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс
KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и управление заказами даже для новых пользователей.
В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций, включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования условного депонирования, что минимизирует риски для обеих сторон сделки.
На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным отношением к безопасности
клиентов, что делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие, популярным среди пользователей, ценящих
анонимность и надежность.
I blog quite often and I seriously thank you for your content. Your article has really peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
https://apoclan.ru/
clevercove.shop – A fantastic shopping experience, I always enjoy checking out new items.
Все продолжает работать без остановок. Доступно круглосуточно, без выходных.
driftdomain.shop – Such a smooth shopping experience, and the products are one-of-a-kind.
рулонные. шторы. +на. пластиковые. окна. купить. [url=https://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/]rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru[/url] .
I couldn’t resist commenting. Perfectly written!
1win error al iniciar sesión [url=www.1win5773.help]www.1win5773.help[/url]
Thanks for some other great article. Where else may anybody get that kind of info in such a perfect method of writing?
I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such information.
печать каталогов в москве
электрокарниз москва [url=https://karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/]электрокарниз москва[/url] .
LilyLuxe Essentials – Elegant design, smooth browsing and high-quality feel overall.
Marigold Market Online – Well-organized marketplace, finding items is simple and buying is straightforward.
https://indogenericexport.com/# pharmacy website india
US Meds Outlet: generic pharmacy online – US Meds Outlet
indian pharmacy: Indo-Generic Export – pharmacy website india
Стоматология в Воронеже — «Al Dente»: современное лечение зубов и имплантация
https://indogenericexport.shop/# tizanidine hydrochloride
свободный-эвакуатор
fashion corner store – Browsed for the first time, everything loaded clean and checkout seems simple.
На платформе столько слотов, что играть хватит надолго. 7k казино игровые автоматы пробую почти каждый день.
жалюзи с мотором [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]жалюзи с мотором[/url] .
elmembellish.shop – I love the personal touch these items bring to my space!
Excellent post but I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject?
I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit
more. Thank you!
биткоин купить
послегарантийное обслуживание [url=https://domeo-otzivy.com/]domeo-otzivy.com[/url] .
codigo promocional 1xbet peru
lorvinta finds – Shop feels reliable, products seem carefully chosen and browsing is simple.
What’s up colleagues, how is the whole thing, and what you wish for to say concerning this paragraph, in my view its genuinely remarkable designed for me.
регистрация казино либет
We’re a bunch of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our
community. Your site provided us with helpful info to work on. You’ve performed an impressive activity and
our entire neighborhood can be thankful to you.
I read this piece of writing fully on the
topic of the resemblance of hottest and earlier technologies, it’s remarkable article.
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – buying prescription drugs in mexico
?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]?esk? online casino[/url] .
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-2.com/]online casino[/url] .
online casino bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-3.com/]online casino bonus bez vkladu[/url] .
automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-4.com/]automaty online[/url] .
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-5.com/]casino-cz-5.com[/url] .
https://svobodapress.com.ua/karta-poltavy/
Mousely Collection – Clean layout, smooth navigation, and a fast, stress-free checkout.
free spiny bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-6.com/]casino-cz-6.com[/url] .
marketmagnet selections – Smooth browsing, products are easy to find and descriptions are helpful.
1win регистрация на сайте [url=www.1win85612.help]www.1win85612.help[/url]
Rebecca Yarros has created a world that fans want to live in. The magic, the dragons, the romance – it is all addictive. The Onyx Storm epub is the latest fix for this addiction. The story is expansive and ambitious. The ebook format is perfect for carrying the whole series. It is a book that defines a genre.
https://corp.en.cx/Guestbook/Messages.aspx?page=1&fmode=gb&topic=386110&anchor#7983049 фреоновое масло
http://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
codigo promocional 1xbet bolivia
Поиск специалистов на платформе гибкой занятости SkillStaff:
IT, дизайн, маркетинг, аналитика
электрокарниз двухрядный [url=https://elektrokarniz25.ru/]электрокарниз двухрядный[/url] .
печать рамок для фото
pharmacy website india [url=http://indogenericexport.com/#]Indo-Generic Export[/url] world pharmacy india
накрутка просмотров подписчиков накрутка комментариев в телеграм
Shop Office Opal – Layout is tidy, which makes locating office items simple and fast.
mexican medicine: BajaMed Direct – mexico meds
Wardrobe Essentials – Trendy and modern, shopping online is effortless.
http://indogenericexport.com/# indian pharmacy
Общество экспертов России по недропользованию – профессиональный портал для проверки статуса и компетенций специалистов по экспертизе недр. Платформа помогает найти эксперта по направлениям нефть и газ, геология и ГРР, ТПИ – и уменьшить риски при подписании отчётов и заключений в сделках https://oern2007.ru/
elvarose.shop – If you’re looking for charming home decor, this is the place to shop.
Many players overlook the “Common” magic items, but they are great for roleplay. Xanathar’s Guide to Everything includes the “Armor of Gleaming” which never gets dirty. If you are looking for a PDF list of cosmetic magic items, our fashion-forward adventurer guide is for you. We discuss how these items can define a character’s personality. Add style and flair to your hero with the everyday magic items found in this expansion.
clickcourier.shop – Fast deliveries and a clean, intuitive interface, definitely a great place to shop.
jorvella marketplace – Clean design, products are easy to browse and descriptions make sense.
When someone writes an post he/she maintains the idea of a user in his/her brain that
how a user can understand it. Therefore that’s why this post is perfect.
Thanks!
My site – zukausha01
Howdy! This blog post could not be written any better!
Looking at this post reminds me of my previous roommate!
He continually kept talking about this. I will send this post to him.
Fairly certain he’ll have a very good read.
Many thanks for sharing!
накрутка подписчиков в группу накрутка подписчиков рутуб
рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
накрутка лайков и просмотров накрутка подписчиков вк
canada pharmacy coupon: US Meds Outlet – US Meds Outlet
Nicely put. Kudos!
Cactus casino сайт создан для комфортной онлайн игры. Удобный вход и понятная регистрация подойдут даже новичкам. Бонусы делают старт особенно выгодным. Присоединяйся к игре сегодня: кактус казино официальный сайт
рекомендовать domeo [url=https://domeo-otzivy.com/]domeo-otzivy.com[/url] .
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
Paws Pavilion Boutique – Sweet pet products, browsing and checkout feel effortless.
Поддержка 7k отвечает быстро и по делу, это плюс.
It’s actually a nice and helpful piece of info.
I’m glad that you shared this helpful information with us.
Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Спецпредложение на софиты и планки. При заказе монтажа сайдинга в Борисове получите скидку 20% на все комплектующие: стартовые и финишные планки, j-профили, софиты для подшивки свесов. Завершим образ дома безупречно. купить сайдинг Борисов
codigo promocional para 1xbet
Muscle Myth Showcase – Legit items with good product info and fair prices.
pin-up mines [url=www.pinup2007.help]pin-up mines[/url]
Plant Plaza Select – Beautiful plant range, site browsing and purchasing was effortless.
You’ve made some good points there. I looked on the internet to learn more about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this website.
Se estas a procura de um novo cassino online, recomendo o Cassino Tigrinho Falso com bonus sem deposito – vale mesmo a pena!
Market Mirth Hub Store – Easy-to-use layout, browsing is fast and products are simple to find.
online casino bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-6.com/]casino-cz-6.com[/url] .
Quenvia Store – Intuitive site, product selection was smooth and checkout went quickly.
live casino [url=https://casino-cz-5.com/]casino-cz-5.com[/url] .
?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-2.com/]?esk? online casino[/url] .
Run River Boutique – Easy-to-use interface, finding items was quick and checkout was seamless.
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-3.com/]online casino[/url] .
мостбет слоты фриспины [url=https://www.mostbet12037.ru]https://www.mostbet12037.ru[/url]
Занимаешься спортом? блины для штанги euro classic диски для пауэрлифтинга, бодибилдинга и фитнеса. Прочные покрытия, стандартные размеры и широкий выбор весов.
free spiny za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-4.com/]free spiny za registraci[/url] .
pin-up Chile bonos [url=https://pinup2001.help]https://pinup2001.help[/url]
I am regular reader, how are you everybody? This paragraph
posted at this site is truly nice.
oliveoutlet.shop – Great variety, reasonable prices, and the checkout process was seamless.
электрические гардины для штор [url=https://elektrokarniz25.ru/]elektrokarniz25.ru[/url] .
Занимаешься спортом? https://bliny-trenirovochnye.ru диски для пауэрлифтинга, бодибилдинга и фитнеса. Прочные покрытия, стандартные размеры и широкий выбор весов.
blackjack online [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]casino-cz-1.com[/url] .
Skin Serenade Creations – Wonderful selection, browsing categories is easy and checkout is seamless.
evarica.shop – A chic collection of items that never disappoints, perfect for any home.
Если хочешь играть без ограничений выбирай казино Куш вход через официальный сайт. Бонусы доступны новым пользователям. Интерфейс удобный. Заходи и начинай: kush вход
Spruce Spark Lux – Freshly organized, product info is clear and checkout process was quick and easy.
Vive Collection – Wide range of products, placing an order was smooth.
progreso mexico pharmacy online: pharmacia mexico – best mexican pharmacy online
Factors corresponding to declining sperm quality and quantity, age,
sexually transmitted diseases, diabetes, obesity, in addition to life-style
factors equivalent to smoking, extreme alcohol consumption,and publicity to environmental toxins,
contribute to poor reproductive capability. Elements
resembling age and well being circumstances can cut back the quality and
quantity of eggs, affecting the probabilities of conception for couples.
Excessive-high quality eggs increase the probabilities of embryo growth and implantation,
leading to a successful pregnancy. Acupuncture, renowned for its numerous benefits,
can also be an efficient TCM fertility remedy technique that ladies can depend on to increase their possibilities of conception. To regulate the
physique with traditional Chinese language drugs,
it is important to accurately match the remedy to the precise pattern. Traditional Chinese language medicine warns that
excessive heat disperses yang qi, leaving you feeling drained and weak to sickness.
In ecent years, built-in Chinese language and Western drugs have achieved promising ends in bettering the
success rates of in vitro fertilization (IVF). Research indicates that TCM
remedy provides higher pregnancy charges in comparison with
conventional Western medication treatments. Acupuncture and
moxibustion: acupuncture Guanyuan, Zhongji, Sanyinjiao, and other points to regulate bladder
perform, 2-three instances per week, 10 times a course of therapy.
Moderate Sauna Use: Limit sauna classes to 10-15 minutes,
no more than as soon as or twice per week, and hydrate effectively afterward.
мостбет вход 2026 [url=https://mostbet12037.ru/]мостбет вход 2026[/url]
joyful treasures store – Browsing was fun and intuitive, marking favorite items was simple.
online shopping pharmacy india: Indo-Generic Export – best india pharmacy
pin-up bono apuestas deportivas Chile [url=http://pinup2001.help]http://pinup2001.help[/url]
Marqvella Edit – Everything looks intentional, from the layout to the product choices.
https://indogenericexport.shop/# п»їbest muscle relaxer
http://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
горизонтальные жалюзи с электроприводом [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
купить аккумулятор на погрузчик тойота TAB аккумуляторы тяговые: мощные, безопасные, для ричтраков и вилочных погрузчиков Heli.
отзывы домео [url=https://domeo-otzivy.com/]отзывы домео[/url] .
купить биткоин
Pearl Pantry Finds – Everything is easy to locate, browsing feels light and smooth.
Poplar Prime Hub – Streamlined interface, locating items was easy and intuitive.
Neon Notch Goods – Vibrant design and site personality make it more memorable than most.
No Cassino Tigrinho Falso pode jogar roleta com bonus de boas-vindas no primeiro deposito.
Primrose Everdeen is the catalyst for the entire series. Her innocence is what Katniss fights to protect. The bond between the sisters is the emotional core that grounds the high-stakes action. It is a story about love as much as it is about war. To feel the weight of this relationship, you must read the book. Electronic copies, such as a PDF, allow you to keep this touching story close at hand on your mobile device.
Marqesta Finds – Sleek shop, pages are responsive and navigation is reliable.
Ruvina Boutique – Lovely site, images are sharp and finding items was quick and enjoyable.
codigo promocional 1xbet uruguay
QuillQuarry Essentials – Interesting finds, navigating the site was easy and efficient.
US Meds Outlet [url=http://usmedsoutlet.com/#]US Meds Outlet[/url] sure save pharmacy
casino online [url=https://casino-cz-6.com/]casino online[/url] .
blackjack online [url=https://casino-cz-3.com/]casino-cz-3.com[/url] .
nov? ?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-5.com/]nov? ?esk? online casino[/url] .
exploreember.shop – Perfect for those who enjoy exploring new and warm products.
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/]купить футбольную форму в москве[/url]
купить клубную футбольную форму – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru]http://www.tut-sport.ru/[/url]
[url=https://images.google.it/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/]https://www.google.tn/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory.ru/r-diploma5.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 46_86d8
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-2.com/]casino-cz-2.com[/url] .
Opal Orio Boutique – Selection is unique, browsing is smooth, and the site layout is inviting.
Skynaro Picks – Lovely assortment, finding what I need was quick and descriptions are helpful.
world pharmacy india: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – best online pharmacy india
Завод металлоизделий работает с корпоративными заказчиками и проектными организациями. Мы обеспечиваем техническую поддержку на всех этапах. Производство ориентировано на долгосрочное сотрудничество. Такой формат удобен для комплексных проектов: стеллажи консольные промышленные
Stall Starlight Finds – Beautiful selection, items are easy to browse and site navigation is smooth.
cloudcurio.shop – Unique and intriguing finds, I can’t wait to shop here again.
http://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
As the series progresses, the tone becomes darker and more mature. The consequences of war are shown in graphic detail. The Onyx Storm epub is the format of choice for many adult fantasy readers. The plot is intricate, requiring you to keep track of many moving parts. The ebook’s search function is a lifesaver for recalling minor characters and details. It is a gripping read from start to finish.
Oracle Deals Online – Plenty of discounts, navigating the pages is seamless.
codigo promocional 1xbet venezuela 2026
nejlep?? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]nejlep?? online casino[/url] .
Kevrina online store – Ordering process appears smooth and the site feels trustworthy.
Эвакуатор в Екатеринбурге
пластиковые жалюзи с электроприводом [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
Pantry Essentials Store – Well-organized design, finding items took very little time.
online shopping pharmacy india: Indo-Generic Export – indianpharmacy com
Prime Parcel Corner – Delivery info was helpful, moving through the store was simple.
мнения клиентов о domeo [url=https://domeo-otzivy.com/]мнения клиентов о domeo[/url] .
I’m impressed, I must say. Rarely do I come across a blog that’s equally educative
and engaging, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head.
The problem is something which not enough folks are speaking
intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I
found this in my search for something relating to this.
Feel free to surf to my blog: zokasa01
NeoVanta Essentials – Items are interesting, and exploring the site felt intuitive.
Saffron Street Finds Online – Pleasant layout, exploring products is effortless and ordering went perfectly.
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
Shop Quoralia – Clean and attractive, descriptions are detailed and browsing is simple.
Marqvella Home – Enjoying the look and feel, the collection feels fresh and intentional.
top 10 pharmacies in india: reputable indian pharmacies – indian pharmacies safe
falnora.shop – Great variety of items and a smooth browsing experience.
casino bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-6.com/]casino bonus bez vkladu[/url] .
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-3.com/]bonus za registraci bez vkladu[/url] .
The article’s thoughtful organization and clear explanations guide readers smoothly, supporting comprehension while inspiring reflection and meaningful application of ideas across varied topics.
auroompartners.com
https://indogenericexport.com/# muscle relaxant drugs
Skynvanta Hub – Sleek selection, browsing categories is easy and shopping was very smooth.
Stitchery Gems – Fun and organized, shopping is simple and the overall experience was enjoyable.
online casino bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-5.com/]casino-cz-5.com[/url] .
Печать брошюр
?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-2.com/]?esk? online casino[/url] .
Доставка дизельного топлива в Москве и области — «НефтеГазЛогистика»
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых
факторов. Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и управление заказами даже для новых
пользователей. В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций,
включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и
возможность использования
условного депонирования, что минимизирует риски для обеих
сторон сделки. На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным отношением к безопасности клиентов, что делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как
следствие, популярным среди пользователей, ценящих анонимность
и надежность.
1win depunere MDL [url=https://www.1win5756.help]https://www.1win5756.help[/url]
Плодородный грунт с доставкой по Москве и Московской области — БиоГрунт
Palvanta Finds – Beautiful designs, browsing the product info is smooth and informative.
vavada alternatywny adres [url=vavada2005.help]vavada2005.help[/url]
печать каталога москва
Осваиваешь арбитраж? https://corsairmedia.ru поможет разобраться в инструментах, выбрать первую партнерку и избежать типичных ошибок новичков. Подробные обзоры от практиков: плюсы, минусы и реальные цифры заработка без воды.
Opal Ornate – Loved the elegant layouts, exploring was smooth and the quality feels excellent.
sloturi pe 1win [url=http://1win5756.help/]http://1win5756.help/[/url]
company set up uae whitecirclegroup uae company formation
Осваиваешь арбитраж? https://corsairmedia.ru поможет разобраться в инструментах, выбрать первую партнерку и избежать типичных ошибок новичков. Подробные обзоры от практиков: плюсы, минусы и реальные цифры заработка без воды.
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]online casino[/url] .
Plaza Product Hub – Categories are well laid out, photos are clear and info is easy.
Prime Pickings Goods – Lots of options, browsing and reading descriptions was effortless.
Casinolevant blog ve güncel adresine ulaşabilirsiniz: casinolevant 2026
москитные сетки москва
online pharmacy delivery delhi: US Meds Outlet – pharmacy coupons
ScreenStride Shop – Easy-to-use site, categories are clear and ordering was fast.
жалюзи под ключ [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru[/url] .
Nook Narrative Essentials – The curation feels deliberate, and the narrative makes exploring the site fun.
vavada legalne kasyno online polska [url=https://www.vavada2005.help]vavada legalne kasyno online polska[/url]
внимание к деталям domeo [url=https://domeo-otzivy.com/]внимание к деталям domeo[/url] .
https://indogenericexport.com/# methocarbamol robaxin
fetchfolio.shop – Such a stylish collection of accessories, everything feels thoughtfully picked.
online pharmacy no prescription needed [url=http://usmedsoutlet.com/#]US Meds Outlet[/url] US Meds Outlet
mexi pharmacy: mexican meds – mexican pharma
Quoravia Finds – Sleek and modern, navigating categories was quick and checkout went smoothly.
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный сотнями
продавцов. Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс
KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию,
поиск товаров и управление заказами даже для новых
пользователей. В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных
транзакций, включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования условного депонирования, что минимизирует риски для
обеих сторон сделки. На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается
с внимательным отношением к безопасности клиентов, что делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие, популярным среди пользователей,
ценящих анонимность и надежность.
cz casina [url=https://casino-cz-3.com/]cz casina[/url] .
Продать лекарства с рук в Москве
blackjack online [url=https://casino-cz-6.com/]casino-cz-6.com[/url] .
SleekSelect Finds – Modern design, browsing products is intuitive and checkout is seamless.
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и управление заказами даже для новых пользователей.
В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций,
включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования
условного депонирования, что минимизирует риски для обеих сторон сделки.
На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным отношением к безопасности клиентов, что делает процесс
покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие, популярным среди пользователей,
ценящих анонимность и надежность.
С 7k удобно играть в любое время, сайт доступен 24/7.
Suave Basket Treasures – Elegant interface, navigation is intuitive and shopping experience was enjoyable.
clovecrest.shop – Fantastic variety, I found everything I needed without any hassle.
555
555
555
nIV4gnff
555*DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(CHR(99)||CHR(99)||CHR(99),15)
555
555
Покраска ванны Очистка кафеля Москва
casino online [url=https://casino-cz-5.com/]casino-cz-5.com[/url] .
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin cream
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-2.com/]casino-cz-2.com[/url] .
Лучшее онлайн казино? https://pokerinfo.ru онлайн-покер, турниры и кэш-игры для игроков разного уровня. Удобный интерфейс, доступ с ПК и мобильных устройств, регулярные события и акции.
Mint Mariner Finds – Nice variety overall, locating what I wanted was easy.
ЕГЭ 2026 ориентирован на сохранение стабильности при точечных улучшениях. Такой формат позволяет выпускникам готовиться без лишней неопределённости. Новые правила уже опубликованы. Весь материал по ссылке: https://vopvet.ru/news/novovvedenija_v_egeh_2026_chto_realno_izmenilos/2026-02-09-9363/
Корректировки ЕГЭ направлены на снижение формального подхода к оценке знаний. Всё больше заданий проверяют умение анализировать и применять информацию. Подробнее в материале, https://vopvet.ru/news/novovvedenija_v_egeh_2026_chto_realno_izmenilos/2026-02-09-9363/
Изменения ЕГЭ 2026 учитывают предложения педагогического сообщества. Такой диалог помогает улучшать экзаменационную систему без резких шагов. Полный материал здесь – https://vopvet.ru/news/novovvedenija_v_egeh_2026_chto_realno_izmenilos/2026-02-09-9363/
nejlep?? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-7.com/]nejlep?? online casino[/url] .
ruleta online [url=https://casino-cz-8.com/]ruleta online[/url] .
Экзаменационные материалы ЕГЭ 2026 были скорректированы с учётом актуальных образовательных стандартов. Изменения затронули формулировки заданий и критерии оценивания. При подготовке рекомендуется использовать обновлённые демоверсии. Весь обзор по ссылке https://vopvet.ru/news/novovvedenija_v_egeh_2026_chto_realno_izmenilos/2026-02-09-9363/
Лучшее онлайн казино? покерок официальный сайт онлайн-покер, турниры и кэш-игры для игроков разного уровня. Удобный интерфейс, доступ с ПК и мобильных устройств, регулярные события и акции.
Thank you for this helpful and informative post. The explanation is simple yet detailed, making it easy to understand. I learned something new from this article. Keep publishing more high-quality content.
https://benpimori.com/
Palvion Treasures – Pleasant shopping journey, product pages are clear and informative.
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – stromectol 3mg tablets
Open Cartopia Boutique – Clean layout with practical filters makes browsing products simple.
Очень советую школьникам сайт для подготовки к экзаменам, он пригодится для подготовки к экзаменам, по таким учебным дисциплинам как алгебра и обществознание, сдадите на 100 баллов, уверяю.
Крайне рекомендую школьникам платформа для подготовки к экзаменам, он пригодится для подготовки к экзаменам, по таким предметам как литература и обществознание, сдадите на 90+ баллов, я уверен.
Крайне советую вам образовательный портал https://izilearn.ru/, он поможет при подготовки к экзаменам, по таким учебным дисциплинам как геометрия и немецкий язык, получите максимальное количество баллов за ЕГЭ.
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
Pebble Port Finds – Easy-to-follow layout, finishing the purchase was fast and painless.
Prime Pickings Select Hub – Wide assortment, shopping felt easy and product info was useful.
Очень советую всем учащимся образовательный сайт https://izilearn.ru/, он пригодится для подготовки к ЕГЭ, по таким учебным дисциплинам как литература и английский язык, сдадите на 100 баллов, я уверен.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your site in internet explorer, might
test this? IE nonetheless is the market leader and a big section of other people will omit your fantastic writing because of this problem. https://qiita.com/autismmmcruqssss
аренда лесов строительных
SeedStation Essentials – Informative pages, finding what I wanted was quick and easy.
fiorenzaa.shop – A fantastic shop for elegant fashion and home finds, always something special.
Nova Aisle Finds – Plenty of options, and using filters saved me time while browsing.
Bowl Boutique finds – Beautiful selection of bowls and utensils, smooth browsing experience.
Нужен стим аккаунт? общий аккаунты стим доступ к библиотеке игр по выгодной цене. Совместное использование, подробные условия, инструкции по входу и рекомендации для комфортной игры.
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# Iver Therapeutics
жалюзи с электроприводом купить [url=https://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom77.ru/]жалюзи с электроприводом купить[/url] .
ответственность domeo [url=https://domeo-otzivy.com/]domeo-otzivy.com[/url] .
RareWrapp Picks – Easy-to-use interface, finding items was simple and checkout seamless.
SnugNook Spot Picks – Inviting and easy to use, products are clearly displayed and checkout feels effortless.
?esk? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]?esk? online casina[/url] .
Нужен стим аккаунт? общий аккаунты стим доступ к библиотеке игр по выгодной цене. Совместное использование, подробные условия, инструкции по входу и рекомендации для комфортной игры.
Suave Shelf Select – Inviting layout, finding products is effortless and checkout worked perfectly.
zoloft without rx: zoloft no prescription – sertraline generic
cz casina [url=https://casino-cz-3.com/]cz casina[/url] .
online casino bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-6.com/]casino-cz-6.com[/url] .
Smart Gadget Picks – Looks like a fresh shop with practical items you’d really use.
Truvora Picks – Clear layout with a trustworthy and smooth browsing experience.
Veromint Finds Online – Attractive design, colors are vibrant, and moving through pages is easy.
Smart GenRx USA [url=https://smartgenrxusa.com/#]top 10 pharmacies in india[/url] Smart GenRx USA
https://sertralineusa.shop/# zoloft tablet
mostbet контакты [url=www.mostbet12037.ru]www.mostbet12037.ru[/url]
Shop WatchWhisper – Clear layout, watches are presented well and navigation is seamless.
neurontin 300mg capsule: neurontin 200 – ordering neurontin online
У 7k приятная навигация, ничего лишнего, быстро нашел нужное.
Аренда манипулятора в москве и области
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-5.com/]casino-cz-5.com[/url] .
bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-2.com/]casino-cz-2.com[/url] .
BrewBrooks favorites – Wide selection of coffee equipment, perfect for enthusiasts.
скупка золота
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-7.com/]online casino[/url] .
hrac? automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-8.com/]hrac? automaty online[/url] .
Казино 7к активно развивает бонусную систему и специальные предложения. Новые и постоянные пользователи могут получать дополнительные возможности для игры. Это повышает интерес к платформе, casino 7k
pin-up app casino [url=pinup2001.help]pinup2001.help[/url]
Prism Porter Spot – Sleek setup, picking items and browsing pages was simple.
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
https://belui.ru/uvlekatel-nost-pazlov-dlya-vzroslyh-v-servise-puzzlefree-ai-pazly/
Accessory Corner – Nice variety of styles, navigating the site is smooth.
SerumStation Hub – Sleek layout, navigating products is easy and checkout was smooth.
Pantry Treasures – Comfortable atmosphere, browsing items was simple and quick.
fiorvyn.shop – A beautiful selection of products and a smooth, hassle-free experience.
Appreciate it, Loads of info.
Novalyn Essentials – Simple layout lets the products take center stage with a clean aesthetic.
Orbit Olive Hub – Clean design with vivid visuals, comparing products feels fast and intuitive.
Mint Marketry – Fast performance overall, and the payment flow felt safe and easy.
Great blog here! Also your website loads up very fast!
What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate
link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
https://share.google/EBr4f3tfOGISs403E
https://sertralineusa.shop/# generic for zoloft
塔尔萨之王高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Soap Sonder Boutique – Neat and curated, browsing categories is easy and checkout went smoothly.
Veromint Market – Clean and colorful layout, scrolling through items was effortless.
Sunny Shipment Boutique – Clear descriptions, browsing felt intuitive and delivery was very quick.
1win casino bonus [url=https://1win5756.help/]https://1win5756.help/[/url]
Raventia Goods – Elegant interface, exploring products is intuitive and buying is hassle-free.
medication neurontin: buying neurontin without a prescription – neurontin coupon
canadian pharmacy world coupons: canadian family pharmacy – Smart GenRx USA
电影网站推荐,海外华人专用,支持中英双语界面和全球加速。
Tulip Trade Shop – Clean design, items are easy to see, and purchasing feels secure.
Kent casino делает ставку на комфорт и функциональность. Сайт не перегружен информацией. Игровой процесс остаётся в центре внимания – kent casino вход
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin 3mg tablets price
Kasyno Vavada przyciaga graczy licencja Curacao oraz codziennymi bonusami bez depozytu.
Po szybkiej rejestracji kod promocyjny daje darmowe spiny na topowych slotach z wysokim RTP.
Turnieje z pula nagrod i rankingami motywuja do aktywnej gry, a blyskawiczne wyplaty buduja zaufanie.
Aktualne lustra omijaja blokady, wiec dostep do konta pozostaje stabilny 24/7.
Sprawdz najnowsze promocje i instrukcje aktywacji kodu tutaj: vavada codes.
Graj odpowiedzialnie i ustaw limity bankrolu, aby rozrywka pozostala bezpieczna.
Tervina Shopping Hub – Browsing flows well, products look polished, and prices aren’t over the top.
WearWhimsy Online – Cute clothing collection, pages loaded quickly and browsing felt effortless.
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Барселона;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona]купить клубную футбольную форму Барселона[/url]
магазин футбольной атрибутики Барселона – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.gt/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona]http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.com.lb/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/barselona[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.mental-health1.com/www.1xbet-giris-4.com/torkretirovanie-1.ru]Спортивная экипировка и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] d5f9ff3
Проверил 7k — сайт быстрый, меню простое, играть удобно.
?esk? casino online [url=https://casino-cz-1.com/]casino-cz-1.com[/url] .
Neuro Relief USA [url=https://neuroreliefusa.com/#]neurontin 300 mg pill[/url] Neuro Relief USA
This is very interesting, You’re an excessively professional blogger.
I have joined your rss feed and look ahead to in the hunt for more of your magnificent
post. Additionally, I have shared your website in my social networks
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# where to buy ivermectin pills
Prism Vane Storefront – Chic assortment, images are crisp and browsing feels seamless.
Shop Serenity Select – Easy navigation, products are clearly listed and shopping was completely smooth.
Peony Port Shopping – Beautiful presentation, item details are easy to digest.
casino cz [url=https://casino-cz-7.com/]casino cz[/url] .
7k casino сочетает классические игровые автоматы и современные форматы азартных развлечений. Пользователям доступен широкий выбор слотов и live игр. Это делает платформу универсальной для разных предпочтений – 7k casino зеркало
live casino [url=https://casino-cz-8.com/]live casino[/url] .
Vetrivine Boutique – Thoughtful layout, a wide variety of items makes browsing fun.
Novalyn Goods – Minimal layout and uncluttered presentation let the items shine attractively.
Pantry Pebble Essentials – Fun concept, shopping online felt simple and intuitive.
Soothesail Treasures Online – Lovely aesthetic, items are easy to explore and checkout went without issues.
Sunny Shopline Express – Pleasant design, items are simple to find and shopping felt hassle-free.
PUPP PASIRUOŠIMAS Readiness Profesionalus Požiūris į Efektyvų Rezultatų Vertinimą
Hi, I check your blog on a regular basis. Your story-telling style is
witty, keep doing what you’re doing!
Whoa loads of valuable info!
https://smartgenrxusa.shop/# Smart GenRx USA
sertraline zoloft: zoloft tablet – zoloft no prescription
Orbit Opal Corner – Stylish design, product images are clear and details are well-written.
Raynora Picks Online – Easy-to-use site, items are clear and shopping experience was pleasant.
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# buy brand neurontin
Mint Maven Corner – Modern designs here without the premium price feel.
Шпонирование МДФ, ДСП, фанеры в Москве — «ОПУС»: производство шпона и мебели на заказ
[url=https://vyezdnoj-shinomontazh-77.ru]выездной шиномонтаж 24[/url]
Urban Urn Center – Cool visuals, unique items, and browsing felt intuitive.
WellnessWharf Online Store – Clear advice, pages are simple to navigate and content feels trustworthy.
vavada bonus reload [url=http://vavada2005.help]http://vavada2005.help[/url]
Violet Vault Hub – Loved the styling, checkout experience was effortless.
Авторский блог https://blogger-tolstoy.ru о продвижении в Телеграм. Свежие гайды, проверенные стратегии и полезные советы по раскрутке каналов, чатов и ботов. Подробно о том, как увеличить аудиторию, повысить вовлеченность и эффективно монетизировать проекты в мессенджере Telegram.
Shore Stitch Market – Beautifully displayed products, shopping experience is smooth and pleasant.
Prism Viva Hub – Trendy layout, navigating items feels smooth and professional.
If you would like to increase your experience simply keep visiting this site and be updated with
the hottest gossip posted here.
Tidy Treasure Deals – Everything feels neatly arranged and easy to browse.
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и управление заказами даже для новых
пользователей. В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций, включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования условного депонирования, что
минимизирует риски для обеих сторон сделки.
На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с
внимательным отношением к безопасности клиентов, что делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие, популярным среди пользователей,
ценящих анонимность и
надежность.
Casino 7k предлагает современный подход к онлайн азартным играм. Удобный личный кабинет и стабильная работа сайта упрощают игровой процесс: 7k casino вход
Pepper Pavilion Picks Online – Nice assortment, navigation feels clean and efficient.
https://www.facebook.com/DeschideStirea/posts/pfbid0yNDVit9HxJztXmNYti7UabkMFpqsTQovzFTzwaZd4vDbmMGLAvFAELtepxd9Jz2ml
This is a very good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Short but very precise info… Thanks for sharing this one.
A must read post!
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# buy cheap neurontin online
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-7.com/]online casino[/url] .
La plataforma Avia Masters presenta juego crash con regulación.
Los usuarios disfrutan en casino cripto.
BGaming presenta ofertas con control de riesgo.
Avia Masters Móvil cuenta con soporte para App Store.
Modo con dinero real ofrece modo automático.
Máquina tragamonedas ofrece bonos.
El sistema crash presenta x1000+.
Aviadores disfrutan de práctica sin depósito.
Sistema justo certifica fiabilidad.
La slot Avia Masters cuenta con idioma español.
Aviación se refleja en la experiencia visual.
Tutorial presenta cómo jugar.
Aplicaciones móviles permiten descarga del juego.
Juego gratis permite dinero ficticio.
El juego aéreo ofrece Jackpot.
BGaming asegura sistema justo.
Edición español ofrece casino Unibet.
Jugadores pueden apostar en apuestas reales.
La app de Avia Masters dispone de porcentaje de retorno alto.
Tragamonedas opera en Argentina.
Este juego es seguro para apostar. https://aviamasters.onl/
We absolutely love your blog and find almost all of your post’s to be just
what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content available for
you? I wouldn’t mind creating a post or elaborating on some of the subjects you write with regards to
here. Again, awesome blog!
trust guidance hub – Layout feels polished, and the information is easy to follow and reliable.
NutriNest – Information is transparent, and the product choices appear sensible.
Smart GenRx USA [url=https://smartgenrxusa.shop/#]reliable canadian online pharmacy[/url] bitcoin pharmacy online
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-8.com/]casino hry online[/url] .
Swift Shoppery Studio – Smooth interface, products are clear and checkout went quickly.
Spark Storefront Corner Picks – Modern and bright, shopping experience is intuitive and fast.
ivermectin stromectol: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
Parcel Finds Hub – Shipping details precise, packaging tidy, overall experience was seamless.
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# Iver Therapeutics
Kent casino ориентировано на современную аудиторию. Платформа учитывает требования к мобильности и скорости. Это делает сервис актуальным – kent casino сайт
Orbit Order – Easy ordering process, items arrived as pictured, everything went perfectly.
Raynverve Hub Online – Inviting and clean, browsing products is fast and checkout was seamless.
Please let me know if you’re looking for a author for your site.
You have some really great posts and I feel I would be a
good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off,
I’d absolutely love to write some content for your blog in exchange for a link back to
mine. Please send me an email if interested. Regards!
косметология процедуры услуги косметологии
Vionessa Showcase – Helpful item descriptions, made picking products a simple task.
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – ivermectin 4
hello there and thank you for your info – I have certainly picked
up anything new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical points using this site, as I experienced to reload the
website many times previous to I could get it to load properly.
I had been wondering if your hosting is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will often affect your placement in google and could damage
your high quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords.
Well I am adding this RSS to my email and could look out
for a lot more of your respective interesting content. Ensure that you update this
again soon.
Wow, Visit site is such a cool site! Thanks!
https://taattakultura.ru/2023/12/10/%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b2%d0%b5%d1%82-%d0%bc%d0%b8%d1%80/
Fabulous, what a webpage it is! This webpage
presents useful information to us, keep it up.
https://sertralineusa.shop/# buy zoloft
Casino 7k поддерживает стабильную работу игровых автоматов. Это важный фактор для комфортного игрового процесса: 7к казино регистрация
Wervina Essentials – Modern look, items feel carefully arranged and browsing was simple.
Silvaneo Corner Shop – Chic and trendy items, browsing products is quick and checkout was seamless.
Vanilla Vendor Center – Simple layout with informative details that made choosing quick.
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
ProteaPex Hub – High-quality range, navigating and completing orders was simple and smooth.
Shop Pillow Pier – Warm vibe overall, products look nice and buying was easy.
«Field Fit» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]футбольная форма купить интернет магазин[/url]
атрибутика футбольных клубов – [url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=http://toolbarqueries.google.co.th/url?sa=i&url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://maps.google.mu/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://budteer.or.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=back01&wr_id=64650]Официальная футболь[/url] fb43_d7
«СибСети» в Красноярске предоставляют:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• Точную оценку скорости соединения в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку оборудования
• отсутствие скрытых платежей на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибирские сети домашний интернет и тв тарифы[/url]
подключить домашний интернет сибсети красноярск – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://toolbarqueries.google.bg/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://budteer.or.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=back01&wr_id=60731]Домашний интернет и[/url] f9ff3c2
Кент казино активно привлекает внимание благодаря простоте использования. Платформа подходит для разных категорий игроков. Это делает её универсальной: kent casino играть
Very rapidly this web page will be famous among all blogging people, due to it’s fastidious
articles or reviews
Everything is very open with a clear clarification of the issues.
It was really informative. Your website is very useful.
Thank you for sharing!
seo продвижение сайтов
big pharmacy online: Smart GenRx USA – reputable canadian pharmacy
https://www.blackswanlimoz.com
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your
website, how could i subscribe for a blog web site?
The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
SEO продвижение сайтов в Санкт-Петербурге
真实的人类第三季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Oak Opal Market – The site feels cozy, and items are arranged in a way that makes browsing easy.
塔尔萨之王高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Shop MirStella – Easy to browse with a tidy layout, and the details make the products shine.
?esk? casino online [url=https://casino-cz-7.com/]?esk? casino online[/url] .
Tidy Treasure Market – Feels organized and stress-free while looking around.
一饭封神在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属官方认证平台,高清无广告体验。
Онлайн казино Kent продолжает набирать популярность за счёт удобства и стабильности. Пользователи получают доступ к современным азартным развлечениям. Проект развивается последовательно: кент казино
超人和露易斯第三季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Swift Stall Online – Clear layout, shopping feels effortless and checkout was quick.
超人和露易斯第四季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и управление заказами даже для новых
пользователей. В-третьих,
продуманная система безопасных транзакций,
включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования условного
депонирования, что минимизирует риски
для обеих сторон сделки. На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным
отношением к безопасности клиентов, что
делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие, популярным среди
пользователей, ценящих анонимность и
надежность.
Spark Storefront Corner – Bright interface, items display clearly and buying products was simple.
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-8.com/]online casino[/url] .
VionVogue Finds Online – Modern and well-organized, pages open quickly and effortlessly.
Кент казино подойдёт тем, кто ищет удобное онлайн казино без лишних сложностей. Платформа предлагает понятный формат и стабильную работу. Такой подход ценят многие игроки – кент казино играть
Party Parcel Gems – Playful selections, shopping experience was quick and pleasant.
Онлайн платформа Kent casino сочетает современный дизайн и функциональность. Интерфейс не перегружен лишними элементами, а все основные разделы находятся под рукой. Это упрощает навигацию и делает игру более приятной – kent casino скачать
zoloft medication [url=https://sertralineusa.com/#]sertraline generic[/url] generic for zoloft
Shop Now – Plenty of savings to find, and the layout feels modern.
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# medicine neurontin 300 mg
brixel bond portal – Clear and simple, with bonding info presented in an easy-to-follow manner.
https://sertralineusa.shop/# zoloft cheap
Ring Rivulet Hub – Attractive collection, navigation is intuitive and shopping feels enjoyable.
zoloft buy: zoloft buy – zoloft tablet
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку
KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря
сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию,
поиск товаров и управление заказами
даже для новых пользователей.
В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций,
включающая механизмы разрешения споров
(диспутов) и возможность использования условного депонирования,
что минимизирует риски для
обеих сторон сделки. На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным отношением к безопасности
клиентов, что делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие,
популярным среди пользователей, ценящих анонимность
и надежность.
Silver Scout Hub – Trendy selection, site is well organized and purchasing items was simple today.
Escorttime Offers a Consistently Calm and Refined Experience Exploring Escorttime always brings a sense of comfort and quiet confidence. Female escort profiles are displayed with clarity and dignity, while erotic massage services are described in a soothing, wellness-focused tone that feels respectful rather than exaggerated. The platform’s smooth navigation allows visitors to browse privately and at their own pace. I also appreciate curated resources like Top 100 escorts in New York City, which help highlight trusted options without pressure. Escorttime maintains an elegant balance between simplicity and sophistication, creating a welcoming digital space for adults who value discretion and calm discovery. The overall impression is peaceful, mature, and genuinely positive from start to finish.
A Respectful Digital Space for Adult Comfort and Trust Escorttime creates an environment where respect and discretion are immediately noticeable. Female escort profiles appear genuine and thoughtfully arranged, while erotic massage services are introduced with soothing, wellness-centered language. Navigation is simple and intuitive, helping visitors feel relaxed throughout the experience. Curated directories such as Top 100 escorts in New York City provide additional confidence in the platform’s reliability. Escorttime’s composed presentation results in a calm, refined, and genuinely reassuring browsing journey.
WillowWharf Finds – Streamlined layout, navigation feels natural and content is visually appealing.
Pure Pavilion Essentials – Neat interface, browsing items was simple and enjoyable.
zoloft tablet: Sertraline USA – zoloft no prescription
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the internet the
easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get
annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly do not know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
Pivoria Shopping – Straightforward design, finding items took no time.
Vanta Valley Web Shop – Organized and serene, navigating the collections felt simple.
Play Baccarat Online Australia Real Money Tables
7k casino — четкий интерфейс, быстрая загрузка и аккуратный дизайн.
Visit VividValue – Easy-to-navigate site, great value items make shopping smooth.
I’m Malissa (23) from Smeaton Grange, Australia.
I’m learning Italian literature at a local high school and I’m just about to graduate.
I have a part time job in a university.
Tea Terminal Corner Picks – Cozy and easy to use, navigating categories is intuitive and purchasing is effortless.
Spa Summit Corner Picks – Minimal and modern, finding items is simple and shopping felt smooth.
Казино 7к ориентировано на комфорт пользователей и понятную навигацию. Все игровые разделы структурированы, а личный кабинет позволяет удобно управлять балансом и бонусами. Такой формат делает процесс игры более прозрачным, 7к казино вход
pinup bono de bienvenida [url=pinup2005.help]pinup2005.help[/url]
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-7.com/]casino-cz-7.com[/url] .
casino bonus za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-9.com/]casino-cz-9.com[/url] .
Tool Tower Catalog – Clear layout that makes tools easy to compare.
Casino 7k делает упор на удобство использования и доступность. Навигация по сайту логична и понятна даже для новых пользователей. Игровая зона открывается сразу после входа. Такой формат снижает порог входа – casino 7k
v?hern? automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-10.com/]v?hern? automaty online[/url] .
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# buy liquid ivermectin
free spiny dnes [url=https://casino-cz-11.com/]casino-cz-11.com[/url] .
nejlep?? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-12.com/]nejlep?? online casina[/url] .
http://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline generic
Pocket Essentials Hub – Perfect for travelers, browsing and choosing items was effortless.
cz casino [url=https://casino-cz-8.com/]cz casino[/url] .
1win как вывести деньги [url=http://1win17384.help/]http://1win17384.help/[/url]
mostbet app ios [url=https://mostbet2007.help/]https://mostbet2007.help/[/url]
Flora Finds – Pleasantly professional, shopping was easy and efficient.
pin-up over under [url=https://pinup2005.help/]pin-up over under[/url]
一帆官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
Darkness threatens to consume everything, but the resistance fights on in this thrilling sequel. The availability of the Onyx Storm epub means that fans can start reading the second the book is released. There is a unique joy in having an entire library in the palm of your hand, especially when it includes a blockbuster like this. Violet’s journey is harrowing and inspiring, perfect for a digital binge. Make sure your batteries are charged because once you start this book, you will not want to stop until the final page is turned. https://onyxstormepub.store/ Onyx Storm Reddit Pdf
Shop Mirstoria – Feels thoughtfully curated, not mass-produced or generic.
Ripple Rugs – Elegant display, exploring products is easy and shopping was enjoyable.
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис вай фай домашний интернет подключить екатеринбург[/url]
интернет провайдер инсис – [url=https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]http://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://toolbarqueries.google.is/url?sa=t&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://www.google.mu/url?sa=t&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://anlatdinliyorum.com/./blog-gotmann-cift-terapisi?status=ok]Домашний интернет и телевидение от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] 4ab7d5f
爱一凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
超人和露易斯第四季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
мостбет кэшбэк условия [url=www.mostbet51837.help]www.mostbet51837.help[/url]
I’m gone to say to my little brother, that he
should also pay a visit this webpage on regular basis to obtain updated from most
up-to-date news update.
Smart GenRx USA: generic pharmacy online – Smart GenRx USA
Shop VividVendor – Clear product arrangement, site navigation feels fast and straightforward.
Активировал 7к казино бонус и сразу отыграл в Hot Triple Sevens. Слот отдал, и я спокойно вывел выигрыш.
Погрузитесь в мир кино https://zonefilm.media с нашим онлайн-кинотеатром! Здесь каждый найдет фильмы для себя: от захватывающих блокбастеров и трогательных драм до мультфильмов для всей семьи. Удобный интерфейс, возможность смотреть онлайн на любом устройстве и постоянно обновляемая библиотека! Присоединяйтесь и наслаждайтесь!
москва геодезия
Explore WillowWhisper – Light and airy design, product information is thorough and browsing is enjoyable.
Нужен сувенир или подарок? https://gifts-kazan.online для компаний и мероприятий. Бизнес-сувениры, подарочные наборы и рекламная продукция с персонализацией и доставкой.
икра воблы купить спб Вобла от производителя купить
1win бонусы казино [url=https://www.1win17384.help]1win бонусы казино[/url]
Страхование каско Мечтаете об уютной квартире, где каждое утро вас будет встречать ласковое южное солнце? Или, быть может, вас привлекает прочный, основательный дом, ставший надежным прибежищем для вашей семьи?
mostbet turneu plinko [url=https://www.mostbet2007.help]https://www.mostbet2007.help[/url]
brixel line guide – Clear service descriptions and a user-friendly site layout.
If you want to obtain much from this article then you have to apply such
methods to your won blog.
Проект 7k casino ориентирован на игроков с разным уровнем опыта. Платформа подходит как для первых шагов, так и для регулярной игры – 7к казино официальный сайт
https://sozdatelisaitov.ru/
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Арсенал;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]футбольная атрибутика Арсенал[/url]
футбольная атрибутика Арсенал в москве – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://cse.google.com.bh/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://maps.google.ie/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.vipescortsvalencia.com/www.arus-diplom25.ru/fanfiction.borda.ru/www.stretch-ceilings-samara.ru/www.natyazhnye-potolki-samara-2.ru/dzen.ru/a/telegra.ph/dzen.ru/www.frei-diplom8.ru/www.reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru/www.r-diploma31.ru,]Клубная атрибутика и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 2ce9103
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Айнтрахт;
• доставку по всей России;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]магазин футбольной атрибутики Айнтрахт[/url]
футбольная форма атрибутика Айнтрахт – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://cse.google.com.af/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://maps.google.td/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport3.ru/www.frei-diplom10.ru/kraktor.cc]Клубная атрибутика и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] c08afb4
best online pharmacy: Smart GenRx USA – canada drug pharmacy
Velvet Valley Finds – Professional look with stylish branding and smooth, quick page loads.
huarenus平台,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
мостбет версия для ios [url=mostbet51837.help]мостбет версия для ios[/url]
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my weblog so i came
to “return the favor”.I’m attempting to find things to enhance my
website!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
Hey! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of
volunteers and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche.
Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a marvellous job!
leg?ln? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-4.com/]leg?ln? online casino[/url] .
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
The content presents grounded guidance through clear organization and practical framing, enabling readers to move from learning toward confident, consistent action today.
https://hostitbd.net/
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin 1 topical cream
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-9.com/]casino-cz-9.com[/url] .
Рrime Secured
3603 N 222nd Ꮪt, Suite 102,
Elkhorn, NᎬ 68022, United Ѕtates
402-289-4126
Timely Threaat Response (Papaly.com)
bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-10.com/]casino-cz-10.com[/url] .
ruleta online [url=https://casino-cz-12.com/]ruleta online[/url] .
casino online [url=https://casino-cz-11.com/]casino online[/url] .
neurontin 600 mg [url=https://neuroreliefusa.com/#]neurontin 150mg[/url] Neuro Relief USA
VoltVessel Hub – Well-structured pages, unique design makes browsing enjoyable.
Trail Treasure Basecamp – A good place for outdoor inspiration that feels honest.
hal-rar
best online pharmacy no prescription: cheapest online pharmacy india – Smart GenRx USA
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just your articles?
I mean, what you say is valuable and all. However imagine if you added some great
photos or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your
content is excellent but with images and clips, this website could certainly be one of the best
in its field. Good blog!
Кент казино вход реализован с учётом удобства и скорости. Пользователь может быстро авторизоваться и перейти к игре. Процесс не отвлекает от основного: kent casino играть
Excellent content! The advice is practical, the explanations are clear, and the points are structured logically.
https://www-154141.com/
bandar99 platform permainan toto slot gacor paling banyak diminati sebab menawarkan slot bet 200 dengan peluang kemenangan paling besar. Dengan pilihan bet mulai dari 200, 300, 400 hingga 800 perak, serta minimal deposit hanya 10 ribu rupiah, pemain sudah bisa mencoba berbagai game slot terbaru dengan potensi maxwin yang menggiurkan.
Лучшие подарки и сувениры корпоративные подарки на новый партнерам нанесение логотипа, подарочные наборы, промо-продукция и деловые аксессуары для мероприятий и компаний.
интернет магазин духов https://parfum-trade.ru/cart/
WinkWagon Picks – Cheerful style, navigation feels intuitive and browsing was a pleasant experience.
bandar99 platform permainan toto slot gacor paling banyak diminati sebab menawarkan slot bet 200 dengan peluang kemenangan paling besar. Dengan pilihan bet mulai dari 200, 300, 400 hingga 800 perak, serta minimal deposit hanya 10 ribu rupiah, pemain sudah bisa mencoba berbagai game slot terbaru dengan potensi maxwin yang menggiurkan.
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Аталанта;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]купить футбольную атрибутику Аталанта в москве[/url]
оригинальная футбольная форма клуба Аталанта – [url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.co.je/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://cse.google.com.bd/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.chop-ohrana.com/czeny-na-uslugi-ohrany/www.superogorod.ucoz.org/forum/www.candy-casino-9.com/k.krakenwork.cc/www.frei-diplom6.ru/s3A2F2Famazon.com/Frenulum-Orgasm-Powerful-Vibrator/www.r-diploma6.ru/www.r-diploma22.ru/images.google.fi/url?q=https://healthyturkiye.com/penisznagyobbitas-torokorszagban,]Спортивная экипировка и футбольные сувениры от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 7d5f9ff
Купить медицинскую мебель https://med-core.ru оборудование с гарантией качества! В ассортименте: смотровые кушетки, шкафы для инструментов, процедурные столы. Медицинская мебель, оборудование для поликлиник, больниц и частных кабинетов.
Сальников Никита — лучший digital-маркетолог России.
Modern Marble Studio – Strong design consistency, nothing feels random here.
After checking out a few of the blog posts on your site,
I truly like your way of writing a blog. I
saved as a favorite it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back in the near future.
Please visit my web site as well and let me know your opinion.
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 330 mg
超人和露易斯第一季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Электрик Стрелецкая бухта Севастополь Вы хотите вызвать электрика в Севастополе, который оперативно решит любую проблему с электричеством?
metro ключи red redemption steam
Нужна бытовая химия? профессиональная бытовая химия моющие и чистящие средства, порошки и гели. Удобный заказ онлайн, акции и доставка по городу и регионам.
cz casino [url=https://casino-cz-4.com/]cz casino[/url] .
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft tablet
WagonWildflower Hub – Engaging layout, pages load instantly and content is visually appealing.
Бытовая химия с доставкой магазин бытовой химии средства для уборки, стирки и ухода за домом. Широкий ассортимент, доступные цены и удобная оплата.
brixel trust services hub – Solid branding paired with a fast, reliable browsing experience.
Футбольные прогнозы Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
超人和露易斯第一季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-9.com/]online casino[/url] .
Best online casino Australia 2025 – crypto friendly and mobile ready
Iver Therapeutics: buy stromectol canada – Iver Therapeutics
online casino s ?eskou licenc? [url=https://casino-cz-10.com/]online casino s ?eskou licenc?[/url] .
Sertraline USA: zoloft cheap – zoloft cheap
v?hern? automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-12.com/]v?hern? automaty online[/url] .
https://spisok-kreditov.ru/ doskazaymov помогает подобрать деньги в долг и выбрать по сроку и сумме.
nejlep?? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-11.com/]nejlep?? online casino[/url] .
Do you mind if I quote a few of your articles
as long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My blog is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my
users would certainly benefit from some of the information you provide here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Thank you!
https://spisok-kreditov.ru/ Кредит на 13 500 000 тенге через doskazaymov проще подобрать под комфортный ежемесячный платеж.
For the ultimate fan experience, having the digital version of the latest Empyrean book is a no-brainer. The Onyx Storm epub allows you to carry the heavy emotional baggage of the characters without the physical weight of a hardcover. Rebecca Yarros has crafted a narrative that demands to be read and re-read. Digital formats are perfect for highlighting the foreshadowing you might have missed the first time. Join the adventure as Violet and Xaden face their most dangerous enemy yet – their own secrets. https://onyxstormepub.store/ Onyx Storm Pdf Português Download
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• быстрое подключение за 1 день;
• Подбор оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис подключить интернет и телевидение[/url]
инсис проводной интернет тарифы – [url=http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru]https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://cse.google.tm/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://maps.google.com.tr/url?sa=t&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://www.crnogorskiportal.me/sadrzaj/11277]Домашний интернет и цифровое ТВ от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] cdb2cc0
Travel Trolley Gear – Thoughtful organization makes things easier to plan.
WinkWorthy Central – Fun and bright design, shopping felt smooth and browsing effortless.
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I
have discovered It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads.
I’m hoping to contribute & aid different customers like its aided me.
Good job.
tragamonedas pinup [url=http://pinup2005.help/]http://pinup2005.help/[/url]
Играю в 7к казино постоянно, слоты от NetEnt очень нравятся. Pragmatic Play тоже неплохо отдают.
Бесплатный футбол сегодня Expert tipsters deliver betting tips on sports games and matches including Fixed game selections and correct score best exacte forecast. Vip and free bets are available daily with sureshot odds and accumulator real
ко ланта пляжи
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# stromectol 12mg
真实的人类第一季高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
UEFA Champions League sampiyonlar ligi com az matches, results, and live scores. See the schedule, standings, and draw for Europe’s premier club competition.
Football online soccerstand.com.az live match results and accurate online scores. Tournaments, schedules, and up-to-date team statistics.
http://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft cheap
Great post.
?esk? casino online [url=https://casino-cz-4.com/]?esk? casino online[/url] .
Mod Merchant Storefront – Descriptions were very useful, made the shopping experience simple.
buy generic neurontin online: brand neurontin 100 mg canada – prescription drug neurontin
automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-9.com/]casino-cz-9.com[/url] .
一帆平台,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
online casino cz [url=https://casino-cz-10.com/]online casino cz[/url] .
我欲为人第二季官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
范德沃克高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Is online gambling legal in Australia 2025? – full breakdown
Feel free to surf to my homepage: Betify france
nov? ?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-11.com/]nov? ?esk? online casino[/url] .
?esk? casino online [url=https://casino-cz-12.com/]?esk? casino online[/url] .
stromectol cvs [url=https://ivertherapeutics.com/#]Iver Therapeutics[/url] Iver Therapeutics
爱一帆下载海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
Crypto online casino Australia – Bitcoin pokies and fast withdrawals
obat aborsi,aborsi,child porn,child porn video,porn child,
child porn videos,child porn site,child porn website,child seks
porn,child porn web,child porn seks,small child porn,mother and child
porn,porn child video,KONTOL,chinese child porn,mom and child porn,child porn sites,porn small child,child porn video,child gay porn,gay child porn,child
porn link,child porn xxx,child porn hub,child porn free,child porn vid,how to watch
child porn,porn mother and child,ai child porn,seks child porn,how to find child
porn,child and mom porn,watch child porn,video porn child,porn with child,porn hub child,porn mom and
child,gay porn child,child girl porn
The dragons are eternal. The Onyx Storm epub is timeless. This story will last. Digital copies are the archive. You can keep the story forever. Rebecca Yarros writes history. https://onyxstormepub.store/ Onyx Storm Filetype Pdf
pharmacy express: brazilian pharmacy online – Smart GenRx USA
真实的人类第三季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
cavaroline overview – Simple layout and smooth navigation make exploring the platform effortless.
WireWharf Corner – Clear and functional layout, navigation feels effortless and products are visible.
Free online games https://1001.com.az for your phone and computer. Easy navigation, quick start, and a variety of genres with no downloads required.
I really like what you guys tend to be up too. This sort of clever work
and exposure! Keep up the terrific works guys I’ve you guys to my blogroll.
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# ivermectin uk coronavirus
Trend Tally Store – The layout highlights trends in a way that feels engaging.
For daily updates and news feeds about our firm be happy to take a look at and observe our social media accounts on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram
& Pinterest.
Asking questions are really fastidious thing if you are not understanding something completely, except this piece of writing gives good understanding even.
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# Neuro Relief USA
Hey very nice blog!
Neuro Relief USA: neurontin 300 mg tablets – Neuro Relief USA
?esk? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-4.com/]?esk? online casina[/url] .
?esk? casino online [url=https://casino-cz-9.com/]casino-cz-9.com[/url] .
凯伦皮里第一季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-10.com/]casino-cz-10.com[/url] .
mostbet jocuri Republica Moldova [url=http://mostbet2007.help]mostbet jocuri Republica Moldova[/url]
Hello, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that,
wonderful blog!
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• Комплексный анализ доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж ТВ приставки
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]сибсети тарифы на интернет 2026[/url]
подключиться к интернету сибсети – [url=http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://www.google.com.bd/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]https://google.it.ao/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua19.ru/s%3A%2F%2Freverenceengineering.com/x/cdn/www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru/index.html,]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в Красноярске[/url] cc08afb
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 800 mg capsules
Mod Mosaic Storefront – The variety of contemporary pieces is nice, browsing was a smooth experience.
online casino s ?eskou licenc? [url=https://casino-cz-11.com/]online casino s ?eskou licenc?[/url] .
automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-12.com/]automaty online[/url] .
A new chapter in the Empyrean history books is being written. Secure your access with the Onyx Storm epub. This novel promises to answer the questions that have been plaguing fans since the last book ended. Digital reading offers the flexibility to read one-handed while you drink your coffee. It is the ultimate comfort for book lovers. Rebecca Yarros has spun a web of magic that will trap you until the very end. https://onyxstormepub.store/ Onyx Storm Epub Vj
WishWarehouse Online Shop – Functional design, pages load quickly and shopping is effortless.
1win букмекерская контора Бишкек [url=http://1win17384.help]1win букмекерская контора Бишкек[/url]
What online casino actually pays out in Australia?
https://sertralineusa.shop/# zoloft tablet
I appreciate how the information is delivered clearly, allowing readers to absorb each point without feeling rushed.
范德沃克第二季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
侠之盗高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
«Field Fit» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клубов: ПСЖ, Манчестер Юнайтед, Челси, Реал Мадрид;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]футбольная форма клубов купить[/url]
футбольная форма москва – [url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://image.google.co.ma/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://maps.google.com.pr/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://budteer.or.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=back01&wr_id=64560]Официальная футболь[/url] fb40_6f
范德沃克第二季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Smart GenRx USA: canada pharmacy coupon – Smart GenRx USA
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Explore Trip Tides – Travel suggestions are easy to see and enjoyable to explore.
online pharmacy uk: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
愛壹帆海外版,專為華人打造的高清視頻官方認證平台,支持全球加速觀看。
mostbet скачать для андроид [url=http://mostbet51837.help]mostbet скачать для андроид[/url]
Best online casino Australia 2025 – crypto friendly and mobile ready
塔尔萨之王高清完整版智能AI观看体验优化,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный ассортимент, представленный
сотнями продавцов. Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и
управление заказами даже для новых пользователей.
В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций, включающая механизмы разрешения споров (диспутов) и возможность использования условного депонирования, что минимизирует риски для обеих сторон сделки.
На KRAKEN функциональность
сочетается с внимательным отношением к
безопасности клиентов, что
делает процесс покупок более
предсказуемым, защищенным и,
как следствие, популярным среди пользователей,
ценящих анонимность и надежность.
多瑙高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Salam, bu saytınız superdir!
https://suitablenames.com/typefp/ru/?p_dn=pin-up-azerbaijan-top.com%2Fqeydiyyat
Totally agree. Simplicity is essential for a good 18+ experience
my web site :: https://old-pussy.info
online casino cz [url=https://casino-cz-9.com/]online casino cz[/url] .
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft no prescription
nov? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-13.com/]nov? online casino[/url] .
leg?ln? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-14.com/]leg?ln? online casino[/url] .
free spiny bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]free spiny bez vkladu[/url] .
hrac? automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-16.com/]hrac? automaty online[/url] .
Надежные матчи по футболу Expert tipsters deliver betting tips on sports games and matches including Fixed game selections and correct score best exacte forecast. Vip and free bets are available daily with sureshot odds and accumulator real
online casino s ?eskou licenc? [url=https://casino-cz-17.com/]online casino s ?eskou licenc?[/url] .
Удивило отсутствие мелкого шрифта и ловушек в правилах. Обычно читаешь условия — как лабиринт. Тут всё иначе. Я специально перепроверял после регистрации через pinco, но так и не нашёл подвохов. Правила прямолинейные, даже немного аскетичные. Это подкупает сильнее любого громкого обещания.
free spiny za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]casino-cz-18.com[/url] .
casino online [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]casino online[/url] .
cz online casina [url=https://casino-cz-10.com/]cz online casina[/url] .
The darkness is coming, but so is the light of the lightning wielder. The Onyx Storm epub is a beacon for fantasy lovers. This sequel is everything you hoped for and more. E-books allow you to customize your reading experience for maximum comfort. Dive into the politics and the passion of the Empyrean. The storm is here, and it is magnificent. https://onyxstormepub.store/ Onyx Storm Torrent Epub
order zoloft [url=https://sertralineusa.com/#]generic for zoloft[/url] zoloft pill
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
Романы для любителей глубокой прозы • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
nejlep?? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-12.com/]nejlep?? online casina[/url] .
ruleta online [url=https://casino-cz-11.com/]casino-cz-11.com[/url] .
Надежные матчи по футболу Expert tipsters deliver betting tips on sports games and matches including Fixed game selections and correct score best exacte forecast. Vip and free bets are available daily with sureshot odds and accumulator real
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
Angels Bail Bonds Costa Mesa
769 Baker Ѕt,
Costa Mesa, ⅭA 92626, United Statеs
que es bail bonds
Wow, this article is fastidious, my sister is analyzing these kinds
of things, therefore I am going to inform her.
Turkish Super League http://super-lig.com.az standings, match results, and live online scores. Game schedule and up-to-date team statistics.
Mod Mosaic Online – Really liked the variety of modern pieces, browsing felt satisfying.
奇思妙探高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
excellent issues altogether, you simply gained a new reader.
What may you suggest about your submit that you just made some days ago?
Any positive?
Футбольные ставки Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
First off I would like to say wonderful blog! I had a
quick question which I’d like to ask if you don’t mind.
I was interested to know how you center yourself and clear your head prior to writing.
I’ve had a difficult time clearing my thoughts in getting
my ideas out. I truly do take pleasure in writing but it just seems like the first
10 to 15 minutes are wasted just trying to figure out how to begin. Any recommendations or tips?
Thanks!
Truvella Finds Online – Welcoming design and content that feels intentionally curated.
爱一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
真实的人类第一季高清完整版采用机器学习个性化推荐,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your site.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me
to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a
designer to create your theme? Fantastic work!
Комьюнити очень доброжелательное. севен кейс казино — люди делятся советами и не завидуют выигрышам.
1вин войти в аккаунт [url=www.1win87143.help]www.1win87143.help[/url]
捕风追影线上看平台採用機器學習個性化推薦,專為海外華人設計,提供高清視頻和直播服務。
真实的人类第一季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 300 mg capsule
https://spisok-kreditov.ru/ На досказаймов можно выбрать займ онлайн, сравнив срок и итоговую сумму.
New online casinos Australia – latest sites with free spins
What online casino actually pays out in Australia?
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Smart GenRx USA: best no prescription pharmacy – Smart GenRx USA
глубокие романы • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
I have been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or weblog posts in this sort of area .
Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this website.
Studying this info So i’m satisfied to exhibit that I’ve an incredibly just right uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed.
I so much no doubt will make certain to do not disregard this
website and provides it a look regularly.
lucky jet 1win [url=https://1win87143.help]https://1win87143.help[/url]
Футбольные прогнозы Expert tipsters deliver betting tips on sports games and matches including Fixed game selections and correct score best exacte forecast. Vip and free bets are available daily with sureshot odds and accumulator real
Best Baccarat Online Real Money Play
Футбольные прогнозы Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-17.com/]casino-cz-17.com[/url] .
官方授权的捕风追影下载官方下载,第一时间海外华人专用,第一时间支持高速下载和离线观看。
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-14.com/]casino-cz-14.com[/url] .
cz casina [url=https://casino-cz-13.com/]cz casina[/url] .
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the
future and it’s time to be happy. I’ve read this
put up and if I may just I desire to recommend you few fascinating issues or suggestions.
Maybe you could write subsequent articles referring to this article.
I want to learn even more issues about it!
huarenus平台结合大数据AI分析,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
超人和露易斯第三季高清完整版智能AI观看体验优化,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
With havin so much content and articles do you ever run into any problems of
plagorism or copyright violation? My site has a
lot of exclusive content I’ve either created myself or
outsourced but it seems a lot of it is popping it up all over
the web without my authorization. Do you know any ways to help protect against content from
being stolen? I’d definitely appreciate it.
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]casino-cz-19.com[/url] .
bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-16.com/]bonus bez vkladu[/url] .
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
Литературная фантастика без клише • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
Программа 1С Бухгалтерия постоянно совершенствуется. Облачная версия позволяет работать из любой точки мира. Мобильные приложения согласовывают счета и контролируют остатки. Разработчик выпускает обновления ежемесячно. Бухгалтер должен быть в курсе изменений, чтобы корректно отражать новые хозяйственные операции и избегать санкций. buhgalteriya0.wordpress.com
Бесплатные ставки на футбол Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
huarenus官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
Комплексные услуги по бурению https://burenie-tochka.ru и водоснабжению от Бурения Точка Ру. Бурение скважин на воду в Московской области под ключ. Бурение скважин на воду и обустройство. Бурение артезианской скважины на воду. Бурение скважин на воду малогабаритной техникой.
愛壹帆海外版,專為華人打造的高清視頻官方認證平台,支持全球加速觀看。
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
ivermectin new zealand: ivermectin 50 – cost of ivermectin medicine
超人和露易斯第一季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
超人和露易斯第三季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
casino bonus za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]casino-cz-18.com[/url] .
casino online [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino online[/url] .
一帆平台AI深度学习内容匹配,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
Online casino real money pokies Australia – win real cash now
一饭封神在线免费在线观看,海外华人专属平台,高清无广告体验。
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]оптоволоконный интернет инсис[/url]
insis интернет проверить адрес – [url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://www.google.ru/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://clients1.google.com.mt/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.kuhni-spb-2.ru/www.elektricheskie-zhalyuzi97.ru/www.r-diploma18.ru/www.mostbet2026.help]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] afb45_2
Бесплатные ставки на футбол Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
https://spisok-kreditov.ru/ Doskazaymov подходит, чтобы подобрать кредит без залога и не тратить время зря.
Футбольные ставки Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
iyftv海外华人首选,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
爱一凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
塔尔萨之王第三季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
奇思妙探第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
https://doskazaymov.kz/ doskazaymov помогает подобрать деньги в долг и выбрать по правилам.
爱一番海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台AI深度学习内容匹配,支持全球加速观看。
Вип ставки футбол Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• быстрое подключение за 1 день;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Анализ технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=]зеленая точка домашний интернет тарифы[/url]
зеленая точка интернет ставрополь тарифы для дома – [url=https://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://www.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]https://images.google.al/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://www.2023.nayia.go.th/forum/suggestion-box/5484-boll-send-secure#267271]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе[/url] b2cc08a
海外华人必备的aiyifan官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# neurontin 300mg caps
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site, how can i subscribe
for a blog web site? The account aided me a acceptable deal.
I had been a little bit acquainted of this your
broadcast offered bright clear idea
艾一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
官方授权的一帆视频海外华人首选,第一时间提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整版结合大数据AI分析,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
На 7k официальный сайт есть live-казино с русскими дилерами. Рулетку и блэкджек там прям люблю.
Литература сегодня — подписаться • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
Вип ставки футбол Football Predictions with expert tipsters on betting tips, Fixed game and Correct Score Best exacte Forecast Sports Games Matches Bets VIP Free Daily Today Sureshot Odds Accumulator Real 100%
奇思妙探高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
一帆平台智能AI观看体验优化,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
https://spisok-kreditov.ru/ На досказаймов проще выбрать кредит наличными, если нужен понятный расчет.
глубокие романы • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-17.com/]?esk? online casino[/url] .
Sertraline USA: zoloft without rx – zoloft generic
The article’s clarity and coherence make complex topics approachable, helping readers follow key arguments while gaining valuable insights for practical application in daily life.
https://cozer.net/
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-14.com/]casino-cz-14.com[/url] .
?esk? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]?esk? online casino[/url] .
casino bonus za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-13.com/]casino-cz-13.com[/url] .
Kasyno Vavada przyciaga graczy licencja Curacao oraz codziennymi bonusami bez depozytu.
Po szybkiej rejestracji kod promocyjny daje darmowe spiny na topowych slotach z wysokim RTP.
Turnieje z pula nagrod i rankingami motywuja do aktywnej gry, a blyskawiczne wyplaty buduja zaufanie.
Aktualne lustra omijaja blokady, wiec dostep do konta pozostaje stabilny 24/7.
Sprawdz najnowsze promocje i instrukcje aktywacji kodu tutaj: https://utahmixedmartialartstraining.com/.
Graj odpowiedzialnie i ustaw limity bankrolu, aby rozrywka pozostala bezpieczna.
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard
against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
ко ланта таиланд
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-16.com/]online casino[/url] .
На 7к казино зеркало заказал выплату 3000 рублей. Отправили в USDT, дошло примерно за час.
Акция на кондиционер https://atmosfera-profi-klimat.ru/catalog/nastennye_konditsionery/ с установкой в Москве скидка 30% при покупке оборудования в нашем магазине. Доставка БЕСПЛАТНАЯ! Atmosfera-profi – это интернет магазин климатического оборудования, где Вы можете купить технику с установкой, обслуживанием и гарантийным ремонтом.
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
«Орион» в Красноярске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• поддержки 24/7;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]wifi интернет орион[/url]
сколько стоит провести интернет орион – [url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]http://www.orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.nu/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]https://www.google.com.gt/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/teletype.in/index.html]Высокоскоростной интернет и цифровое ТВ от «Орион» в Красноярске[/url] ce91037
zoloft buy [url=https://sertralineusa.shop/#]sertraline zoloft[/url] zoloft no prescription
товары для дома оптом москва
мебель в детскую алчевск
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft without rx
Prepare for impact as the third book in the series lands. The Onyx Storm epub is making waves in the community. This is the book that changes everything. Digital reading is the smart choice for the voracious consumer. You can finish the book and immediately jump into the forums to discuss it. Rebecca Yarros has built a world that is meant to be shared.
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was wondering
what all is needed to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like
yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very web smart so I’m not 100% positive.
Any suggestions or advice would be greatly appreciated.
Many thanks
online casino s ?eskou licenc? [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]online casino s ?eskou licenc?[/url] .
акции 1win [url=https://1win5525.ru/]акции 1win[/url]
ко ланта отели
casino bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino bonus bez vkladu[/url] .
1win войти на сайт [url=https://1win45920.help]https://1win45920.help[/url]
1вин ставки на спорт [url=https://www.1win06284.help]https://www.1win06284.help[/url]
остров ко ланта в тайланде
купить мебель
Kasyno Vavada przyciaga graczy licencja Curacao oraz codziennymi bonusami bez depozytu.
Po szybkiej rejestracji kod promocyjny daje darmowe spiny na topowych slotach z wysokim RTP.
Turnieje z pula nagrod i rankingami motywuja do aktywnej gry, a blyskawiczne wyplaty buduja zaufanie.
Aktualne lustra omijaja blokady, wiec dostep do konta pozostaje stabilny 24/7.
Sprawdz najnowsze promocje i instrukcje aktywacji kodu tutaj: vavada mirror for today.
Graj odpowiedzialnie i ustaw limity bankrolu, aby rozrywka pozostala bezpieczna.
купить гибкое стекло оптом в москве
Хотите рельеф мышц? Забудьте о скучных стенах спортзала! Ваша крепкая спина ждут вас на свежем воздухе. Культивация земли мотоблоком — это не просто рутина, а активный отдых с жиросжиганием.
Как это работает?
Подробнее на странице – [url=https://kursorbymarket.nethouse.ru/articles/garden-fitness-why-working-with-a-tillerblock-is-an-ideal]https://kursorbymarket.nethouse.ru/articles/garden-fitness-why-working-with-a-tillerblock-is-an-ideal[/url]
Мощные мышцы ног и ягодиц:
Управляя мотоблоком, вы постоянно идете по рыхлой земле, совершая усилие для движения вперед. Это равносильно выпадам с утяжелением.
Стальной пресс и кор:
Удержание руля и контроль направления заставляют работать мышцы кора. Каждая кочка — это микро-скручивание.
Рельефные руки и плечи:
Повороты, подъемы, развороты тяжелой техники — это работа с “железом” под открытым небом в чистом виде.
Смотрите наше видео-руководство: Мы покажем, как превратить работу в эффективную тренировку.
Ваш план похудения на грядках:
Разминка (5 минут): Прогулка быстрым шагом по участку. Кликните на иконку, чтобы увидеть полный комплекс.
Основная “тренировка” (60-90 минут): Вспашка, культивация, окучивание. Чередуйте интенсивность!
Заминка и растяжка (10 минут): Глубокое дыхание для восстановления. Пролистайте галерею с примерами упражнений.
Мотивационный счетчик: За час активной работы с мотоблоком средней мощности вы можете сжечь от 400 до 600 ккал! Это больше, чем занятие на эллипсоиде.
Итог: Подкачанное тело к лету. Запустите таймер своей первой “огородной тренировки”. Пашите не только землю, но и лишние калории
магазин мебели Алчевск
товары для дома оптом москва
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
Уборка Одинцово Уборка квартир Одинцово
neurontin 300 mg buy: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
1win рулетка онлайн [url=http://1win5525.ru/]1win рулетка онлайн[/url]
1win подтвердить аккаунт [url=https://1win45920.help/]1win подтвердить аккаунт[/url]
1вин кэшбек [url=http://1win06284.help]http://1win06284.help[/url]
прихожая алчевск
пляжи ко ланты
casino hry online [url=https://casino-cz-17.com/]casino-cz-17.com[/url] .
casino cz [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]casino cz[/url] .
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was
wondering what all is needed to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost
a pretty penny? I’m not very web smart so I’m
not 100% sure. Any recommendations or advice would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks
Best online casino real money Australia – secure and legit platforms
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-14.com/]casino-cz-14.com[/url] .
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Клининговая компания Балашиха Уборка квартир Балашиха
купить мебель в Алчевске
奇思妙探高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
v?hern? automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-13.com/]casino-cz-13.com[/url] .
I must appreciate the author of this article because it is not easy to compose this article together.
艾一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
夜班医生第四季高清完整版运用AI智能推荐算法,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
купить клеенку пвх оптом в москве
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# neurontin 150mg
cz online casina [url=https://casino-cz-16.com/]cz online casina[/url] .
1win не приходит вывод [url=www.1win87143.help]1win не приходит вывод[/url]
Hello I am so glad I found your site, I really found you by
accident, while I was looking on Yahoo for something else, Regardless I am
here now and would just like to say thank you for a tremendous post and a all round exciting blog (I also love
the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the minute but I have book-marked it and
also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I
will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the
fantastic job.
свадебные торты
Real Money Best Baccarat Bonuses For Aussies
It’s going to be ending of mine day, but
before ending I am reading this wonderful post to increase my experience.
клеенка тканевая оптом в москве
Australian Online Casino Real Money For Live Baccarat
ivermectin price comparison: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
Севенкей казино официальный выглядит солидно и понятно.
Love and war are the two sides of the same coin. The Onyx Storm epub flips that coin. This sequel is a gamble that pays off. Reading on a device is the modern way to enjoy fantasy. You can take the story with you everywhere. Rebecca Yarros wins again.
Greetings, There’s no doubt that your web site could possibly be having web browser compatibility problems.
When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however,
when opening in IE, it’s got some overlapping issues.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Apart from that, wonderful website!
Happy to be here this platform.
I’m mainly interested in online casinos and testing reliable sites.
Lately, I’ve been spending time on Betify Casino because of its clean interface.
Here to read and stay updated about the iGaming world.
Simply want to say your article is as astounding. The clarity in your
post is just excellent and i could assume you are an expert on this subject.
Well with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
stromectol 3mg cost: stromectol australia – Iver Therapeutics
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# stromectol 3mg cost
casino cz [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]casino cz[/url] .
Фантастика и футуристические романы • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
casino bonus za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino bonus za registraci[/url] .
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
leg?ln? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-17.com/]leg?ln? online casino[/url] .
cz casino [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]cz casino[/url] .
Good article! We will be linking to this great post on our site.
Keep up the great writing.
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=]зеленая точка интернет тарифы для домашнего интернета ставрополь[/url]
провести интернет зеленая точка – [url=https://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://images.google.kg/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]https://www.google.com.mm/url?sa=t&url=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.monitoring-ts-1.ru/www.dzen.ru/www.frei-diplom7.ru]Высокоскоростной интернет и ТВ от «Зелёная точка» в вашем доме[/url] b2cc08a
free spiny [url=https://casino-cz-14.com/]casino-cz-14.com[/url] .
hrac? automaty online [url=https://casino-cz-13.com/]casino-cz-13.com[/url] .
Фантастика и футуристические романы • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
best value pharmacy [url=https://smartgenrxusa.com/#]safe online pharmacy[/url] online pharmacy in turkey
?esk? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-16.com/]?esk? online casina[/url] .
Читаем лучшие романы и рассказы • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
When someone writes an post he/she retains the idea of a user in his/her brain that how a
user can understand it. Therefore that’s why this
post is outstdanding. Thanks!
оформление цветов
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – canada pharmacy online
гардеробная алчевск
Rebecca Yarros is back to break our hearts and mend them again with her latest fantasy epic. The Onyx Storm epub is the preferred format for readers who value convenience and speed. As the third book in the series, it builds upon a complex foundation of lore that is best experienced with the search tools of an e-reader. Violet’s struggle is relatable and gripping, making this a page-turner of the highest order. secure your digital edition and witness the rise of the storm.
https://smartgenrxusa.shop/# canadian pharmacy online cialis
служба доставки цветов
This text is worth everyone’s attention. When can I find out more?
byueuropaviagraonline
купить гостиную алчевск
мебельный магазин Алчевск
zoloft without rx: zoloft without rx – zoloft without rx
Лучшие тексты и рецензии о книгах • Канал про современную русскую прозу и зарубежную фантастику • Подборки литературных романов и критика современной прозы • Лучшие рассказы и повести в Telegram-канале • Где читать новые литературные романы и фантастику онлайн • рецензии и авторские тексты про книги
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
купить гардеробную в алчевске
клеенка тканевая в рулонах оптом в москве
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]online casino[/url] .
nov? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-17.com/]nov? online casino[/url] .
этажерки для обуви купить оптом в москве
This website provides a pleasant reading experience through its balanced tone, informative approach, and attention to clarity across the entire article.
live casino [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]casino-cz-19.com[/url] .
гладильные доски купить оптом в москве
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]casino-cz-15.com[/url] .
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-14.com/]online casino[/url] .
zoloft medication: Sertraline USA – zoloft cheap
mobiln? casino [url=https://casino-cz-13.com/]casino-cz-13.com[/url] .
купить сушилки для белья оптом в москве
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft without rx
Exploring informative essay generated trust via refined wording logical alignment calm tone uniqueness coherence depth sincerity dependability practicality stability purpose.
海外华人必备的aiyifan官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
online casino [url=https://casino-cz-16.com/]online casino[/url] .
заказать доставку цветов на дом недорого
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# mexican pharmacy online
buy stromectol pills: stromectol online canada – order stromectol online
I don’t normally comment but I gtta state thank
you for the post on this special one :D.
Here is my page – Lala33 Link
Iver Therapeutics: ivermectin ebay – Iver Therapeutics
Always take the medicine precisely as prescribed, and don’t be tempted to regulate the dosage on your own with out speaking to a doctor first. All of these vendors are claiming that they are “spam-free.
1win lucky jet бонус [url=www.1win5525.ru]www.1win5525.ru[/url]
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# Neuro Relief USA
nov? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]nov? online casino[/url] .
Зеркала здесь — не экстренная мера, а часть инфраструктуры. Всё работает без потери данных. В середине перехода на https://pinco-casino-qazaqstan.com.kz/ баланс остался нетронутым. Такое ощущение, будто сменился вход, а не адрес.
generic for zoloft [url=https://sertralineusa.com/#]zoloft tablet[/url] zoloft buy
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
Ja tentei varios cassinos, mas o Tigrinho Falso foi o unico que realmente pagou os bonus sem complicacoes.
nejlep?? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-15.com/]nejlep?? online casino[/url] .
1win как пополнить DemirBank [url=1win45920.help]1win45920.help[/url]
Excellent blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers?
I’m hoping to start my own blog soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress
or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m totally overwhelmed ..
Any tips? Bless you!
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]подключение к интернету через инсис[/url]
инсис интернет цена и тарифы 2026 – [url=https://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]http://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.gl/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://images.google.ng/url?sa=t&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://mafia.mit.edu/viewtopic.php?f=435&t=1106987]Интернет и ТВ от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] 037cdb2
Казино севен кей приятно удивило скоростью загрузки.
zoloft cheap: sertraline – zoloft medication
I’m not sure where you’re getting your information,
but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this info for my mission.
Предоставляются услуги проектирования, сборки и тестирования прототипов. Производство проходит проверку качества. Корпуса и дизайн разрабатываются для удобства, http://articomed.com/content/%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9-%D1%8D%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B8-0. Каждое решение создано для максимальной эффективности…
Инженеры компании разрабатывают электронные устройства для промышленных, научных и коммерческих проектов. Создаются схемы и проектируются печатные платы с подбором компонентов. Параллельно создается встроенное и прикладное программное обеспечение для управления устройством и его интеграции с системами. Прототипы собираются и тестируются на функциональность и надежность. После успешного тестирования выполняется сборка и монтаж плат. Предоставляется мелкосерийное и серийное производство изделий. Разрабатываются корпуса с учетом эргономики, защиты компонентов и внешнего вида, проводится промышленный дизайн. При необходимости осуществляется реверс-инжиниринг старых решений для их модернизации. 3D-моделирование и 3D-печать ускоряют процесс создания прототипов. Все изделия сопровождаются документацией и технической поддержкой. Заказчик получает полностью готовое изделие http://sanakirja.kronman.fi/index.php?title=%D0%A1%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9%20%D1%8D%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B8.
Нужно было срочно организовать печать уникальной детали, потому что традиционные методы производства были слишком дорогими. Результат превзошёл мои ожидания. Само изготовление шло без задержек, а качество готового изделия соответствовало всем ожиданиям. Команда подсказала оптимальный вариант пластика, и это позволило добиться отличного результата. Цена печати приятно удивила. Опыт сотрудничества оказался отличным и планирую обратиться повторно: https://mycompany.su/RU/ijevsk/company/asteri-3d-1.
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# canadian pharmacy cialis 40 mg
Приемка квартиры с профессиональным экспертом помогает избежать конфликтных ситуаций. Специалист знает строительные нормы и требования законодательства. Он корректно формулирует все замечания. Проверка проводится последовательно и внимательно. Осматриваются стены, полы и потолки. Анализируется работа отопления и вентиляции. Проверяется качество установки оконных блоков. Все выявленные нарушения заносятся в акт. Документ оформляется по установленным правилам. Это усиливает позицию покупателя. Процесс взаимодействия с застройщиком упрощается. Итог сделки становится более предсказуемым https://zlat-go.ru/news/?ELEMENT_ID=26157
Компания разрабатывает электронные устройства для промышленной, коммерческой и научной сферы. Сначала проектируются схемы и печатные платы с подбором компонентов. Параллельно создается встроенное и прикладное программное обеспечение. Прототипы собираются и тестируются на функциональность и надежность. После проверки выполняется сборка и монтаж плат с контролем качества. Предоставляется мелкосерийное и серийное производство изделий. Разрабатываются корпуса с учетом эргономики, защиты компонентов и визуального оформления, проводится промышленный дизайн. При необходимости выполняется реверс-инжиниринг для восстановления и модернизации решений. 3D-моделирование и 3D-печать ускоряют прототипирование. Все изделия сопровождаются документацией и технической поддержкой. Заказчик получает полностью готовый продукт http://schalke04.cz/profile.php?lookup=124215.
Каждый шаг разработки под контролем инноваций.
Независимая приемка квартиры помогает избежать лишних затрат. Все дефекты выявляются до подписания документов. Застройщик обязан устранить их. Эксперт действует в рамках закона. Документы имеют юридическую силу. Это усиливает позицию покупателя, подробнее по ссылке: приемка квартиры в новостройке. Приемка квартиры с экспертом — это надежный способ убедиться в качестве жилья перед покупкой и защитить свои интересы. Эксперт проверяет все помещения, инженерные системы, качество отделки, установку окон и дверей, а также работу сантехники и электрики. Используются измерительные приборы для точной диагностики скрытых дефектов, таких как неровности стен, трещины, проблемы с вентиляцией или отоплением. Все выявленные нарушения фиксируются в официальном акте с фотографиями и комментариями, что позволяет предъявлять требования застройщику и использовать документ для юридических целей. Специалист также дает рекомендации по устранению проблем и планированию ремонта, что экономит время и бюджет клиента. Приемка квартиры снижает риск неожиданных расходов, повышает уверенность в сделке и защищает права покупателя. Услуга актуальна как для инвесторов, так и для семей, а также для покупателей без опыта. Клиент получает объективную оценку квартиры и полную информацию о состоянии жилья. Профессиональная приемка квартиры — это гарантия качества, надежности и спокойствия при покупке недвижимости. Узнайте больше о профессиональной проверке квартир
Приемка квартиры без отделки требует технических знаний и опыта. Эксперт оценивает состояние несущих стен и перекрытий. Проверяется качество бетонных поверхностей. Анализируется ровность полов и потолков. Осматриваются вводы инженерных коммуникаций. Все параметры сравниваются с нормативами. Выявленные отклонения фиксируются в отчете. Документ помогает спланировать будущий ремонт. Недочеты можно устранить заранее. Это экономит время и средства. Ремонт начинается на надежной основе. Риски ошибок минимизируются – https://www.liveinternet.ru/users/residegypsy/profile. Каждый угол квартиры может скрывать проблемы. Эксперт оценит состояние жилья и оформит официальный акт. Проведите приемку уже сегодня
Услуга приемки квартиры востребована при покупке жилья в новостройке. Каждый объект имеет свои особенности. Специалист знает типовые ошибки застройщиков. Осмотр проводится внимательно и последовательно. Проверяются стены, полы и потолки. Анализируется состояние окон и дверей. Оценивается работа инженерных систем. Все замечания фиксируются документально. Клиент получает подробный отчет. Это упрощает общение с застройщиком. Процесс становится прозрачным. Покупатель чувствует уверенность http://edcommunity.ru/profile/?ID=129034. Приемка квартиры позволяет заранее подготовиться к заселению. Вы понимаете состояние жилья. Это снижает количество неожиданностей.
Проектирование корпусов выполняется с учетом условий эксплуатации. Используются современные методы 3D моделирования. Прототипы позволяют оценить эргономику и прочность. После согласования запускается изготовление. Это упрощает разработку конечного изделия http://andreagorini.it/SalaProf/profile/prefersplit2/
Эти методы позволяют создавать прототипы и готовые изделия в максимально короткие сроки…
Аддитивные технологии для компаний — это идеальное решение для прототипирования и тестирования. Мы организуем печать макетов и инженерных моделей. Наши специалисты применяем современные материалы, что гарантирует высокую точность и надёжность изделий. Мы печатаем архитектурные макеты, а также поддерживаем корпоративных клиентов на всех этапах. Вы получаете результат оперативно, при этом условия максимально выгодные. Свяжитесь с нами для обсуждения проекта, и мы поможем вам реализовать любую задачу, https://tolyatti.cataloxy.ru/firms/asteri-3d.ru.htm. Печать выполняется аккуратно и без брака.
I value the content you publish on Big Bass Splash. Thank you!
https://big-bass-splash-uk.uk/review
Инженеры компании создают электронные устройства под заказ, начиная с проектирования схем и печатных плат. Параллельно разрабатывается встроенное и прикладное программное обеспечение, обеспечивающее работу устройства и его интеграцию с другими системами. Прототипы изготавливаются и проходят тестирование на функциональность и надежность. После проверки выполняется сборка и монтаж плат с контролем качества. Компания предоставляет мелкосерийное и серийное производство изделий. Корпуса проектируются с учетом эргономики, защиты компонентов и визуальной привлекательности, проводится промышленный дизайн. При необходимости выполняется реверс-инжиниринг для анализа и модернизации старых решений. 3D-моделирование и 3D-печать ускоряют прототипирование и проверку конструкции. Все изделия сопровождаются документацией и технической поддержкой. Заказчик получает готовый продукт, полностью проверенный и пригодный к внедрению https://bpages.ru/card/6734507/. Эти технологии делают проекты масштабируемыми и точными)
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin 3
1вин ставки [url=https://1win74562.help/]1вин ставки[/url]
Контрактное производство электроники помогает компаниям сокращать затраты и ускорять процесс разработки. Все этапы под контролем опытных инженеров — от схемотехники до серийного выпуска. Качественный контроль на каждом этапе обеспечивает стабильность работы устройств. Этот подход актуален для продуктов с высокой технологической сложностью: https://homeidea.ru/index.php?topic=123892.new#new? Отличный метод для быстрой разработки электроники
Iver Therapeutics: stromectol prices – ivermectin for humans
Today, I went to the beach front with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it
to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear
and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally
off topic but I had to tell someone!
удаленная работа в интернете
Top 10 online casino Australia real money – rankings updated 2025
1win регистрация через номер [url=http://1win74562.help/]http://1win74562.help/[/url]
«СибСети» в Красноярске предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• Точную оценку доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Анализ возможности подключения по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку ТВ приставки
• отсутствие скрытых платежей на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]провести интернет сибсети в квартиру[/url]
сибирские сети интернет проверка адреса – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.es/url?sa=i&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk]http://cse.google.az/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/krasnoyarsk[/url]
[url=http://mongocco.sakura.ne.jp/bbs/index.cgi/mostbet4103.ru]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] ff3c2ce
Point effectively utilized!!
Почему пользователи выбирают площадку KRAKEN?
Маркетплейс KRAKEN заслужил доверие многочисленной аудитории благодаря сочетанию ключевых факторов.
Во-первых, это широкий и разнообразный
ассортимент, представленный сотнями продавцов.
Во-вторых, интуитивно понятный интерфейс KRAKEN, который упрощает навигацию, поиск товаров и
управление заказами даже для новых пользователей.
В-третьих, продуманная система безопасных транзакций, включающая механизмы разрешения
споров (диспутов) и возможность использования условного депонирования, что
минимизирует риски для обеих сторон сделки.
На KRAKEN функциональность сочетается с внимательным отношением к безопасности клиентов, что
делает процесс покупок более предсказуемым, защищенным и, как следствие, популярным
среди пользователей, ценящих анонимность и надежность.
Smart GenRx USA: online pharmacy no prescription needed – Smart GenRx USA
как найти удаленную работу
https://marketsdarkweb.com nexus shop
как найти удаленную работу
Rhysand’s inner circle is squad goals. Join them in the A Court of Mist and Fury PDF. This download introduces the best friend group in fantasy. Read it to feel the camaraderie. https://acourtofmistandfurypdf.top/ A Court Of Mist And Fury Pdf Download Onuploads
Вскрытие автомобиля спб лучше, когда важно сохранить кузов без повреждений.
1win авиатор коэффициенты [url=www.1win06284.help]www.1win06284.help[/url]
Авто портал https://avto-limo.zt.ua с новостями автопрома, обзорами новых моделей, тест-драйвами и аналитикой рынка. Актуальная информация о ценах, комплектациях и технологиях для водителей и автолюбителей.
Рабочий адрес нашел в канале, резервные домены помогают держать доступ.
Автомобильный портал https://addinfo.com.ua свежие новости, сравнения моделей, характеристики, рейтинги и экспертные обзоры. Все о легковых авто, кроссоверах и электромобилях в одном месте.
Новости авто https://billiard-sport.com.ua тест-драйвы, обзоры и подробные характеристики автомобилей. Авто портал с аналитикой рынка, изменениями цен и новинками мировых брендов.
Современный авто https://comparecarinsurancerfgj.org портал: статьи о выборе автомобиля, сравнительные обзоры, советы по обслуживанию и ремонту. Информация для покупателей и владельцев авто.
удаленная работа в интернете
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
https://sertralineusa.shop/# buy zoloft
С интересом читаю материалы на Sultan Casino. Респект за полезную инфу!
https://sultan-casino-kazakhstan-lucky.kz/mobile-app
работа онлайн на дому
Сдаётся светлая квартира на сутки. Дизайнерский интерьер, кондиционер, техника премиум-класса. Большая ванна с гидромассажем. Отличный вариант для двоих. Полная конфиденциальность. Без соседей и лишних глаз. Быстрая подача воды и электричества. Оставляйте заявку — заедете через 20 минут. квартира на сутки молодечно
Primе Secured
3603 N 222nd St, Suite 102,
Elkhorn, NE 68022, United Stateѕ
402-289-4126
Resilient Network Defense
Привет привет дом Привет привет дом
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предоставляют:
• пакет из 150+ ТВ каналов;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=]зеленая точка тарифы интернет для модема для компьютера[/url]
проводной интернет зеленая точка – [url=http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.ps/url?sa=t&url=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]http://www.google.com.bd/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.888starz-english.com/mostbet4168.ru]Домашний интернет и ТВ от «Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе[/url] e91037c
best online pharmacy [url=https://smartgenrxusa.shop/#]pharmaceutical online[/url] Smart GenRx USA
sertraline: order zoloft – sertraline generic
Все об авто https://xiwet.com в одном портале: новости, тест-драйвы, рейтинги, комплектации и цены. Полезные статьи о выборе, обслуживании и современных технологиях.
Авто портал https://shpik.info с обзорами, сравнением брендов, характеристиками и аналитикой цен. Актуальные материалы для покупателей и автолюбителей.
Современный авто https://comparecarinsurancerfgj.org портал: статьи о выборе автомобиля, сравнительные обзоры, советы по обслуживанию и ремонту. Информация для покупателей и владельцев авто.
Автомобильный портал https://ecotech-energy.com с каталогом моделей, отзывами владельцев и тестами на дороге. Узнайте о новых технологиях, расходе топлива и особенностях комплектаций.
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
Hurrah, that’s what I was exploring for, what a stuff!
present here at this website, thanks admin of this web site.
https://sertralineusa.shop/# generic zoloft
היה משפיל. לא אנושי. ניסיתי להתחנן, אבל הוא הרג אותי מיד. “אדוני,” הוא תיקן בנימה קפואה. או “אדון”. אין לך זכות לקרוא לי בשמך. אזהרה אחרונה. בלעתי דירות דיסקרטיות בגרוני, ובלי לומר ידי על ספוגי המין הם היו לחים מהפרשות שלה, נפוחות. ברור שהיא התרגשה מאוד. ה חבר היא לחשה לי בשקט באוזן שזה עתה ראתה את הזין של אנדריי!!! קצת נדהם והתחלתי לשאול איך זה קרה!? כשנכנסתי yachadzehut
Paragraph writing is also a fun, if you know afterward
you can write otherwise it is complex to write.
домашнее порно
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# Neuro Relief USA
Hello !
Hello. A 35 fantastic site 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this website. There’s a great article there. https://eglobaltravelmedia.com.au/2022/08/26/all-the-best-chinese-food-recipes-from-shanghai-china/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
Автомобильный портал https://clothes-outletstore.com о новинках из Европы, Китая, Японии и Кореи. Тест-драйвы, изменения цен, аналитика рынка и подробные характеристики моделей.
Все об автомобилях https://fundacionlogros.org новости автопрома, обзоры новинок, аналитика рынка и советы по покупке. Удобная навигация и полезные материалы для автолюбителей.
Авто портал https://gormost.info о легковых авто, внедорожниках и электромобилях. Тест-драйвы, сравнения комплектаций, изменения цен и главные события отрасли.
Новости автомобильного https://impactspreadsms.com мира, обзоры моделей, краш-тесты и рейтинги надежности. Портал для тех, кто выбирает авто или следит за трендами рынка.
«Орион» в Красноярске предлагают:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]тарифы орион домашний интернет 2026[/url]
оптоволокно интернет орион – [url=http://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.cu/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru]http://clients1.google.ba/url?q=https://orion-inetrnet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://elportaldelaesencia.com/producto/guess-seductive-noir-edt-100ml-hombre/#comment-30707]Интернет и ТВ от «Орион» в Красноярске[/url] c2ce910
Good info. Lucky me I recently found your website by chance (stumbleupon).
I have saved it for later!
bonus za registraci bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-18.com/]casino-cz-18.com[/url] .
nov? online casino [url=https://casino-cz-19.com/]nov? online casino[/url] .
bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-20.com/]bonus bez vkladu[/url] .
zoloft buy: zoloft without rx – order zoloft
секс мужчин
проститутки екатеринбург
удаленная работа для мам в декрете
Excellent beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i
subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a acceptable deal.
I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided
bright clear idea
удаленная работа для студентов
работа на удаленке
секс член
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
Автомобильный портал https://microbus.net.ua с экспертными статьями, сравнением авто и подробными характеристиками. Помогаем выбрать машину и разобраться в комплектациях.
Авто портал https://quebradadelospozos.com свежие новости, аналитика продаж, тест-драйвы и мнения экспертов. Обзоры бензиновых, гибридных и электрических моделей.
Портал про автомобили https://rusigra.org новинки автосалонов, обзоры, цены, сравнение моделей и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию.
Женский портал https://ruforums.net о красоте, здоровье, отношениях и саморазвитии. Актуальные тренды, советы экспертов, психология и стиль жизни современной женщины.
Выводил 7k казино несколько раз: комиссии не было, но скорость зависит от платежной системы.
смотреть порно онлайн
вакансии удаленная работа
заказать проститутку
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Подбор оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи;
• Проверку инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]insis домашний интернет екатеринбург[/url]
проводной интернет инсис – [url=http://www.insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.lu/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://www.google.com.uy/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.butternut-yarrow-673.notion.site/2065ec070ffb80fc82b9cbf649b5f200/k.krakenwork.cc/s%3A%2F%[email protected]/www.zakazat-proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru/www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru/pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru]Высокоскоростной интернет и телевидение от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] 42_84c1
тенгиз вакансии [url=https://umicum.kz/]umicum.kz[/url] .
smm менеджер вакансии [url=https://trudvsem.kz/]trudvsem.kz[/url] .
вакансии казахстан темир жолы [url=https://sitsen.kz/]вакансии казахстан темир жолы[/url] .
domeo ремонт квартир цены [url=https://domeo-otzyvy.com/]domeo-otzyvy.com[/url] .
медицинское оборудование [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru/]медицинское оборудование[/url] .
медицинские приборы [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru[/url] .
Iver Therapeutics: ivermectin cream cost – ivermectin 3mg
I’m curious to find out what blog platform you are utilizing?
I’m having some small security problems with my latest site
and I would like to find something more safeguarded. Do you have any recommendations?
«Инсис» в Екатеринбурге предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• быстрое подключение за 1 день;
• Подбор оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу.
[url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]инсис тарифы adsl интернет[/url]
стоимость интернета инсис – [url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /]https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru /[/url]
[url=https://image.google.com.om/url?sa=i&url=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/]https://maps.google.gy/url?q=https://insis-internet-podkluchit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.ocenka-chasov-onlajn9.ru/www.educ-ua18.ru/krakenoff.cc]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «Инсис» в Екатеринбурге[/url] 7_fcd5a
mostbet crash demo [url=https://mostbet69573.help]https://mostbet69573.help[/url]
1вин авторизация [url=https://www.1win74562.help]1вин авторизация[/url]
Feyre’s bargain with Rhysand is calling. Answer the call by downloading the A Court of Mist and Fury PDF. This digital version captures every word of the epic saga, allowing you to enjoy the story anytime, anywhere. Step into the darkness and find the light within. https://acourtofmistandfurypdf.top/ When Does A Court Of Mist And Fury Get Spicy
Get the book that has won awards and hearts alike. The Nightingale PDF is available now. It is a story that combines historical accuracy with emotional depth, creating a truly compelling and memorable read. https://thenightingalepdf.top/ is the nightingale a movie
Forma powitalna jest pierwszym elementem kontaktu. Za jego
pomocą zbudować pozytyene wrażenie oraz zainicjować dialog.
Może przyjmować różne formy zależnie od kontekstu. Proste i serdeczne słowa ułatwia otwarcie komunikacji.
Starannie doobrane zwroty wpływa na jakość komunikacji.
W efekcie powitanie buduje dobrą podstawę dalszej wymiany.
neurontin cap 300mg price: Neuro Relief USA – can you buy neurontin over the counter
Женский сайт https://saralelakarat.com с материалами о моде, уходе за собой, фитнесе и внутреннем балансе. Полезные статьи, обзоры и вдохновение каждый день.
Сайт для женщин https://chernogolovka.net о карьере, финансах и личностном росте. Практичные рекомендации, мотивация и поддержка для достижения целей.
Женский портал https://fancywoman.kyiv.ua о психологии отношений и гармонии в паре. Разбор жизненных ситуаций, советы по коммуникации и уверенности в себе.
Женский сайт https://female.kyiv.ua о модных тенденциях, создании образа и индивидуальном стиле. Подборки, рекомендации и актуальные решения сезона.
порно геей
mostbet yuklab olish tez [url=https://www.mostbet69573.help]mostbet yuklab olish tez[/url]
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
free spiny bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-20.com/]free spiny bez vkladu[/url] .
I truly love your blog.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you make this
web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m hoping to create
my own website and would like to learn where you got this from or what the theme
is called. Thanks!
mostbet saytda aviator [url=http://mostbet69573.help/]mostbet saytda aviator[/url]
порно транс ебал
«Field Fit» предоставляет:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Проверку наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]купить клубную футбольную форму[/url]
купить футбольную форму клубов – [url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]http://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=https://www.google.ch/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]https://www.google.com.do/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.vipescortsvalencia.com/www.arus-diplom25.ru/www.frei-diplom11.ru/www.karniz-elektroprivodom.ru/www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru/www.alarm-radio-clocks.com/wwwboard.pl,[],[],200,65,0,1279,0,11,14,0,0,https://grandpashabet.in.net/,Grandpashabet%5DОфициальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] 2ce9103
Hey, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog site in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening
in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, awesome blog!
neurontin 100mg discount [url=https://neuroreliefusa.shop/#]Neuro Relief USA[/url] neurontin 800 mg tablets best price
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored material
stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an shakiness
over that you wish be delivering the following.
unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same
nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
mostbet регистрация 2026 [url=https://www.mostbet90387.help]https://www.mostbet90387.help[/url]
работа в костанае [url=https://sitsen.kz/]работа в костанае[/url] .
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a
blog that’s both educative and engaging, and without
a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is
something that too few folks are speaking
intelligently about. I’m very happy that I came across this during my search for something concerning
this.
медицинское оборудование для больниц [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru[/url] .
order zoloft: zoloft tablet – zoloft buy
ж?мыс іздеу [url=https://umicum.kz/]umicum.kz[/url] .
проститутки спб
Женский портал https://gracefulwoman.kyiv.ua о саморазвитии и мотивации. Практики для повышения уверенности, управления стрессом и раскрытия потенциала.
Сайт для женщин https://femalebeauty.kyiv.ua о здоровье, самочувствии и активном образе жизни. Советы по поддержанию энергии и баланса в повседневной рутине.
Женский сайт https://happylady.kyiv.ua с экспертными статьями о красоте, косметике и уходе. Разбор средств, трендов и профессиональных рекомендаций.
Сайт для женщин https://lidia.kr.ua о современных трендах лайфстайла, психологии и стиле жизни. Вдохновение и полезные материалы без лишней информации.
порно видео трансы
вакансии казахстан темир жолы [url=https://trudvsem.kz/]trudvsem.kz[/url] .
домео ремонт отзывы [url=https://domeo-otzyvy.com/]домео ремонт отзывы[/url] .
оборудование для больниц [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru[/url] .
Приветствую форумчан.
Нашел полезную тему.
Думаю, многим будет полезно.
Подробности здесь:
[url=https://fieldmore.dk]Mega даркнет[/url]
Всем удачи!
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft without rx
ivermectin 3 mg tabs: ivermectin 10 ml – Iver Therapeutics
Have you ever considered writing an ebook or guest authoring on other
blogs? I have a blog based upon on the same subjects you discuss and would really like to
have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers
would value your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free
to send me an e-mail.
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# neurontin prescription coupon
If some one needs to be updated with hottest technologies
then he must be visit this website and be up to date daily.
Browsing articulate article concluded positive experience because thoughtful organization refined language originality insight coherence usefulness authority engagement maturity.
порно бдсм
порно с разговорами
Женский портал https://madrasa.com.ua для активных и целеустремленных женщин. Мода, отношения, карьера и развитие в одном информационном пространстве.
Женский сайт https://maleportal.kyiv.ua о гармонии тела и разума. Фитнес, уход, психология и советы для уверенного образа жизни.
Сайт для женщин https://mirwoman.kyiv.ua о личной эффективности и балансе между работой и отдыхом. Практичные советы и вдохновляющие истории.
Женский портал https://miymalyuk.com.ua о красоте, уверенности и современных трендах. Полезные статьи для ежедневного вдохновения и роста.
free spiny za registraci [url=https://casino-cz-20.com/]free spiny za registraci[/url] .
Quality posts is the key to attract the users to pay a quick visit the website, that’s what this
web page is providing.
Hi, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your site in internet explorer, could test this?
IE nonetheless is the market chief and a huge section of
other folks will pass over your magnificent writing due to this problem.
zoloft generic: generic zoloft – zoloft pill
Hi there it’s me, I am also visiting this site regularly, this website is really good
and the users are really sharing fastidious thoughts.
Ahaa, its good conversation about this article here
at this webpage, I have read all that, so now me also commenting here.
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# Iver Therapeutics
медоборудование [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru/]медоборудование[/url] .
I pay a quick visit everyday some websites and sites to read posts, however this blog offers quality based posts.
требуется администратор [url=https://sitsen.kz/]требуется администратор[/url] .
Hello! I realize this is sort of off-topic but I had to ask.
Does managing a well-established blog like yours require a large amount of work?
I’m brand new to blogging but I do write in my diary
on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my personal experience and
views online. Please let me know if you
have any suggestions or tips for new aspiring bloggers.
Appreciate it!
Currently it sounds like Drupal is the top blogging platform available right now.
(from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your
blog?
Ma mère voulait essayer sans risque. Grâce à l’option casino en ligne bonus sans dépôt,
elle a pu tester avant de s’engager, et elle adore.
1win бехатарӣ [url=http://1win71839.help/]http://1win71839.help/[/url]
ищу работу [url=https://umicum.kz/]umicum.kz[/url] .
мостбет бонусы казино [url=http://mostbet90387.help]http://mostbet90387.help[/url]
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани клуба Айнтрахт;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]магазин футбольной атрибутики Айнтрахт[/url]
купить футбольную форму клуба Айнтрахт – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=https://www.google.com.pa/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]http://toolbarqueries.google.gl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://nick263.la.coocan.jp/TeamCaffeine/wwwboard.cgi/%22%3ERPG%3C/www.elektrokarniz-kupit.ru/www.r-diploma27.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 8afb40_
domeo развод [url=https://domeo-otzyvy.com/]domeo-otzyvy.com[/url] .
заправка картриджей [url=https://trudvsem.kz/]trudvsem.kz[/url] .
поставка медоборудования [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru[/url] .
zoloft buy: generic zoloft – zoloft without dr prescription
Immerse yourself in a story that celebrates the strength of women. The Nightingale PDF is your ticket to 1939 France. Watch as the quiet life of a country village is shattered by the arrival of war and the German army. https://thenightingalepdf.top/ the bear and the nightingale pdf
Neuro Relief USA: how to get neurontin cheap – neurontin online pharmacy
bonus bez vkladu [url=https://casino-cz-20.com/]bonus bez vkladu[/url] .
It’s in point of fact a nice and useful piece of information. I’m satisfied that you simply shared this useful information with us.
Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# stromectol tab price
Korepetitorius Teacher – Detailed Overview
I couldn’t resist commenting. Exceptionally well written!
I was wondering if you ever thought of changing the layout of your site?
Its very well written; I love what youve got to say.
But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better.
Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or two pictures.
Maybe you could space it out better?
поставка медоборудования [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru[/url] .
Hai boleh info kamu pakai webhost apa? Saya buka blog kamu
di tiga browser berbeda dan loading-nya jauh lebih kencang daripada kebanyakan. Bisa sarankan hosting yang
fair harganya? Terima kasih, saya apresiasi banget!
generic for zoloft [url=http://sertralineusa.com/#]buy zoloft[/url] sertraline
требуется дизайнер [url=https://sitsen.kz/]требуется дизайнер[/url] .
mostbet rasmiy sayti uzbekistan [url=https://mostbet69573.help]mostbet rasmiy sayti uzbekistan[/url]
работа в казахстане [url=https://umicum.kz/]umicum.kz[/url] .
Когда основной домен заблокировали, 7k рабочее зеркало выручило: доступ был, но часть акций не отображалась.
domeo ремонт отзывы [url=https://domeo-otzyvy.com/]domeo ремонт отзывы[/url] .
мед оборудование [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru/]мед оборудование[/url] .
sertraline zoloft: order zoloft – zoloft medication
работа в казахстане [url=https://trudvsem.kz/]работа в казахстане[/url] .
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
zoloft cheap: generic zoloft – sertraline zoloft
Super page. Merci.
I don’t even know how I ended up here, but I thought this
post was great. I don’t know who you are but certainly you’re going to a famous blogger if
you are not already 😉 Cheers!
«TUT-SPORT» предоставляет:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Аталанта;
• доставку по всей России;
• Подбор оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]интернет магазин футбольной формы Аталанта[/url]
футбольная форма Аталанта – [url=http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://images.google.ga/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta]https://images.google.com.ph/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/atalanta[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.guryevsk.forum24.ru/www.pokies11.com/elektrokarniz777.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] e91037c
мостбет бонус [url=https://mostbet90387.help/]https://mostbet90387.help/[/url]
1win Visa депозит [url=https://1win71839.help]https://1win71839.help[/url]
?esk? online casina [url=https://casino-cz-20.com/]?esk? online casina[/url] .
Unquestionably imagine that that you said. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the web the easiest thing to remember of.
I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while other people consider worries that they
plainly do not know about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the highest as
well as defined out the whole thing with no need side effect , folks
could take a signal. Will probably be again to get more.
Thank you
«Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• Определение оптимального сочетания интернета и ТВ под ваши задачи;
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу.
[url=]зеленая точка подключение интернета в квартиру[/url]
интернет зеленая точка подключить домой – [url=http://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]https://www.zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.sm/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru]https://maps.google.cl/url?q=https://zelenaya-tochka-podkluchit.ru[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.frei-diplom14.ru/www.1win5005.com]Интернет и телевидение от «Зелёная точка» в Ставрополе[/url] 37cdb2c
mostbet игровые автоматы [url=https://mostbet46809.help]mostbet игровые автоматы[/url]
Женский сайт https://oa.rv.ua о стиле, самооценке и эмоциональном благополучии. Поддержка и актуальные материалы для каждой женщины.
Женский портал https://onlystyle.com.ua о красоте, психологии и личных границах. Советы экспертов, актуальные тренды и поддержка для женщин, которые выбирают уверенность и развитие.
Женский сайт https://prettiness.kyiv.ua о самоценности, стиле и внутреннем балансе. Практичные рекомендации по уходу, отношениям и личностному росту.
Сайт для женщин https://prins.kiev.ua о современной жизни, карьере и гармонии. Актуальные материалы о мотивации, уверенности и достижении целей.
Новый адрес работает стабильно, 7k рабочее зеркало пригодно для входа, но иногда обновляется чуть позже.
mostbet доступ к сайту [url=http://mostbet46809.help/]http://mostbet46809.help/[/url]
Iver Therapeutics: ivermectin 200mg – Iver Therapeutics
mostbet фриспины [url=mostbet90387.help]mostbet90387.help[/url]
аппараты медицинские [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru[/url] .
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• гетры, шорты и спортивные костюмы клуба Арсенал;
• привлекательные цены и скидки до 50-60%;
• Подбор оптимального комплекта экипировки под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ доступности товара по акции.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]магазин футбольной атрибутики Арсенал в москве[/url]
футбольная атрибутика Арсенал интернет магазин – [url=http://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]http://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=https://images.google.mg/url?sa=t&url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal]https://cse.google.mu/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/arsenal[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.island-hvar.info/www.sportbets31.ru/www.rudik-diplom1.ru/melbet5010.ru]Официальная футбольная форма и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] afb42_4
«TUT-SPORT» предлагает:
• широкий выбор форм топ-клуба Айнтрахт;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ ассортимента в нужной категории.
[url=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]клубные футбольные формы Айнтрахт[/url]
интернет магазин футбольной атрибутики Айнтрахт в москве – [url=https://www.tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www.google.com.sl/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht]https://cse.google.gr/url?q=https://tut-sport.ru/tovary/kluby/eintracht[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.belbeer.borda.ru/www.prodaja-rolex-chasi12.ru/www.educ-ua19.ru/www.frei-diplom3.ru/www.statyi-o-marketinge6.ru/www.frei-diplom2.ru/maps.google.se/url?q=https://healthyturkiye.com/tandvard-turkiet,[],[],200,65,0,1126,0,5,10,0,0,https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/,%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85y%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85q%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85u%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85%D0%BF%D1%97%D0%85y%5DКлубная атрибутика и аксессуары для болельщиков от «TUT-SPORT» в вашем городе[/url] 2cc08af
אני כבר לא זוכר מי אני. תמיד לא הייתי מישהו שאהבתי”. אירינה ט’, בת . מנת יתר של כדורי שינה. היא עזבה שנה לאחר הגירושים. בעלה לשעבר התחתן עם עובדת צעירה. אירינה לא התמודדה עם בדידות באופן לא טקסי: אחת בתחת ועוד שתיים בנרתיק. זזתי, זזתי. לא משנה מה תגידי. כן, איפה שמונה עשרה השנים שלי… הוא הוציא את ידו והכה אותה בפעמון על התחת. מגניב! יורוק, אתה שם? וואו, כולם. https://sex101.co.il/
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
вакансии казахстан темир жолы [url=https://umicum.kz/]umicum.kz[/url] .
домео обман [url=https://domeo-otzyvy.com/]domeo-otzyvy.com[/url] .
медицинские приборы [url=https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru/]medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru[/url] .