State of QA Automation in DevOps: CI/CD Testing Trends from 500+ Dev Teams
What You’ll Learn:
This section offers a snapshot of the growing importance of CI/CD-friendly testing in today’s fast-paced software development environment. It highlights the evolving role of QA within the CI/CD pipeline and how teams can build an efficient QA process within 24 hours.
Value for You:
By reading this section, you’ll gain insights into why integrating quality assurance early into the CI/CD pipeline is critical for reducing testing time, improving speed-to-market, and ensuring quality at every stage of development. The benefits of an agile, continuous testing process will be clearly laid out for you to implement within your own development pipeline.
In today’s software development landscape, testing has evolved from a post-development activity into an ongoing, integrated process. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) frameworks have significantly transformed how organizations approach testing, allowing teams to catch bugs early, automate repetitive tasks, and accelerate release cycles. This shift is essential for companies looking to stay competitive, particularly in industries where the demand for frequent updates is high.
However, many organizations still struggle with integrating QA processes effectively within their CI/CD pipelines. This whitepaper will explore how businesses can efficiently implement QA automation within a CI/CD pipeline in as little as 24 hours. We will focus on automation tools, best practices, and strategies that development teams can adopt to create a seamless testing environment, reducing friction and improving software quality.
The paper will delve into various aspects of QA automation:
- Benefits and Challenges of QA Automation: A closer look at why automation is necessary for modern software teams.
- Key Tools and Frameworks: Exploring the most widely adopted tools in the industry that facilitate the CI/CD testing process.
- Practical Tips for Integration: Step-by-step advice on how to seamlessly integrate automated tests into CI/CD pipelines.
- Real-world Case Studies: Industry examples of companies that have successfully implemented CI/CD-friendly testing.
2. The Rise of QA Automation and Continuous Testing in Modern Dev Teams
What You’ll Learn:
This section delves into why QA automation is gaining traction in 2025, how it has evolved in the development world, and its increasing adoption among development teams.
Value for You:
You’ll gain insight into the rapid growth of QA automation and why it has become a priority for development teams aiming to improve their software quality, speed, and scalability.
QA automation is experiencing significant growth, especially as development teams transition from traditional software engineering practices to Agile and DevOps methodologies. The speed at which software needs to be delivered, combined with the complexity of modern applications, has pushed QA teams to move beyond manual testing to leverage automation as a strategic asset.
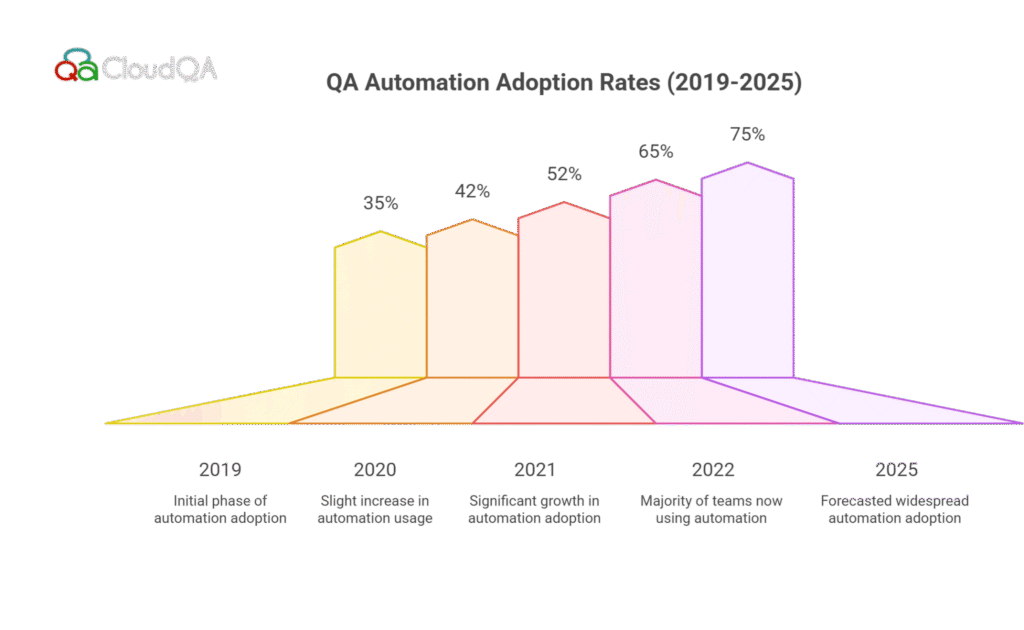
In 2025, the adoption of QA automation tools is growing at an exponential rate. Dev teams have recognized that manual testing is no longer sufficient to meet the demands of faster release cycles and complex software requirements. Automation tools like Selenium, Cypress, and JUnit allow for faster testing cycles, reduce human error, and provide better accuracy.
The main drivers behind the rise of QA automation are:
- Speed of Development: Agile methodologies and DevOps require rapid release cycles, where manual testing can no longer keep up. Automation ensures that testing is continuous and integrated into each phase of the development pipeline.
- Scalability: As software systems grow, manually executing tests becomes impractical. Automation allows testing to scale, covering more scenarios with minimal effort.
- Reduced Human Error: Automated tests run with precision, reducing the risk of human error in repetitive test execution.
- Integration into CI/CD Pipelines: Automated tests are seamlessly integrated into CI/CD pipelines, providing real-time feedback on code quality and identifying bugs early in the development cycle.
These factors are contributing to a higher adoption rate of automation tools. According to a recent survey of over 500 dev teams, 75% of teams are using some form of automated testing, and nearly half of those teams have integrated these tools into their CI/CD pipeline for continuous testing.
Key Tools Driving Adoption:
- Selenium: Popular for UI testing, especially for web applications.
- Cypress: Gaining popularity for end-to-end testing due to its speed and ease of use.
- JUnit: A powerful tool for unit testing, particularly in Java-based applications.
- Postman & RestAssured: Widely used for API testing, ensuring that back-end services work as expected.
3. Benefits and Impact of Continuous QA Automation in CI/CD
What You’ll Learn:
In this section, we’ll explore the tangible benefits of QA automation, focusing on how it contributes to faster releases, improved accuracy, and increased productivity within development teams.
Value for You:
You will gain an understanding of how automation drives efficiency in QA processes, enhances the overall quality of software, and supports faster delivery cycles.
The integration of QA automation into modern development workflows is a game-changer. Teams leveraging automated testing tools are realizing significant advantages that improve both the development and QA processes. These benefits are driving the widespread adoption of automation tools across industries.
Here’s how QA automation is impacting development teams:
- Improved Efficiency: Automated tests run faster than manual tests and can be executed repeatedly with no additional effort, making the entire testing process more efficient. Automation eliminates time-consuming tasks such as repetitive manual test execution, enabling QA teams to focus on more strategic tasks like exploratory testing.
Example: Automated testing allows for continuous testing in the CI/CD pipeline, ensuring that bugs are caught and addressed in real-time. As a result, testing is no longer a bottleneck but an integral part of the development process.
- Better Accuracy and Reliability: Human error is reduced significantly with automated testing, leading to more accurate results. With test scripts executing exactly as designed every time, the chances of missing bugs due to oversight or fatigue are minimized. Additionally, automation tools provide consistent results, enabling teams to perform reliable testing at scale. This is especially important for regression testing where the same tests are rerun with each release.
- Enhanced Scalability: As software grows in complexity, manual testing becomes less feasible. QA automation scales seamlessly to accommodate growing test suites, covering a larger number of test cases without increasing the time or effort required. For example, with the rise of microservices, automated tests ensure that each service is thoroughly tested without impacting the overall project timeline.
- Faster Releases: With faster test execution and continuous integration, automated testing enables teams to deliver software more quickly. As development teams push new features and updates, automation ensures that existing functionality remains intact, leading to quicker release cycles and more frequent product updates.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial investment in setting up automated testing infrastructure may be significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. Automation saves time by reducing manual testing efforts, speeds up defect detection, and ultimately reduces the cost of bug fixes later in the development cycle.
Real-World Examples:
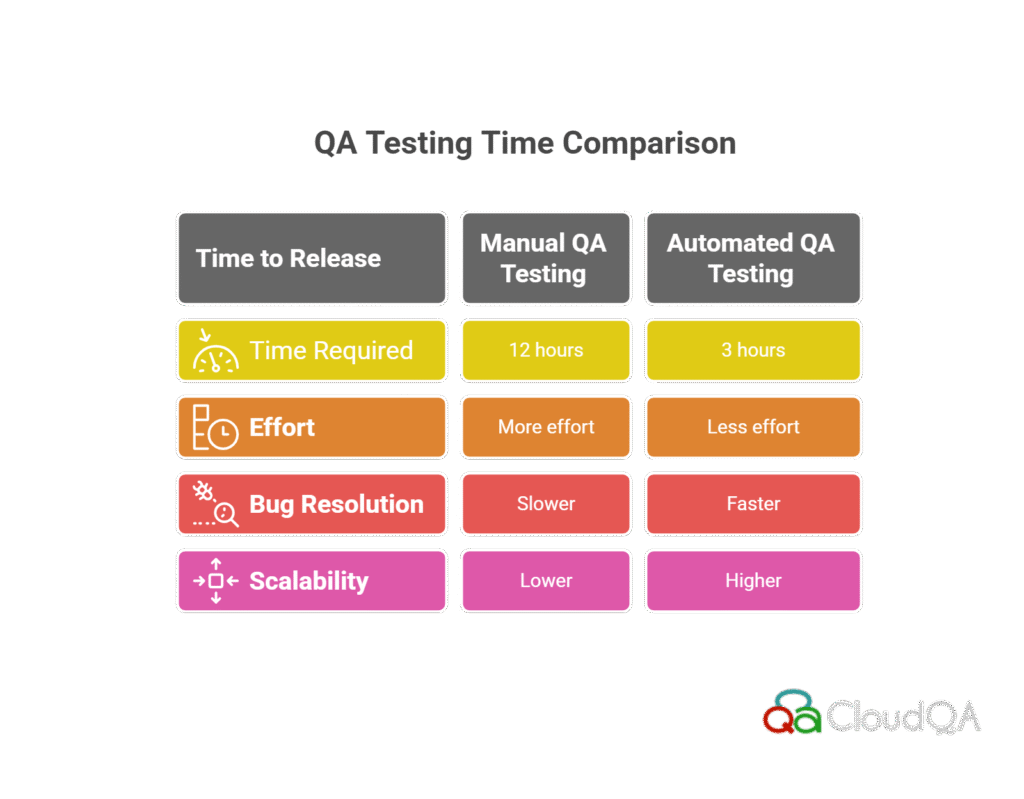
- A fintech company using Cypress for their end-to-end testing significantly reduced their testing time from 12 hours to under 3 hours per release cycle, improving the speed at which new features were delivered to customers.
- A SaaS provider integrated Selenium and JUnit in their CI pipeline, enabling faster identification of bugs and improving the overall product quality. They reported a 30% reduction in post-deployment bug reports.
4. Tools and Frameworks for CI/CD Testing
Effective CI/CD testing relies on a well-chosen set of tools and frameworks that integrate seamlessly into the development pipeline. This section covers the most widely used tools in QA automation and how they integrate with CI/CD systems.
Selenium: Selenium is one of the most popular open-source tools for automating web applications. It supports various browsers and programming languages, making it highly versatile. Selenium integrates well with CI/CD pipelines, allowing teams to automate end-to-end testing for their web applications.
Cypress: Cypress is gaining popularity for end-to-end testing due to its speed and ease of use. Unlike Selenium, Cypress operates directly inside the browser, making it faster and more reliable. It is also highly compatible with modern JavaScript frameworks like React and Angular, making it ideal for web app testing in a CI/CD pipeline.
JUnit: JUnit is widely used for unit testing, particularly in Java-based applications. It is integrated into many CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing and is often used alongside tools like Jenkins and GitLab to ensure that tests are run automatically with every code commit.
Postman & RestAssured: Postman is a popular tool for API testing. It is widely used in CI/CD pipelines for testing RESTful APIs, ensuring that backend services work as expected. RestAssured is another tool for API testing, providing a simple syntax for validating HTTP requests and responses.
These tools allow teams to automate testing for different parts of their applications, from user interfaces to APIs and backend services. By integrating these tools into CI/CD pipelines, teams can ensure that testing is continuous and automated, helping to catch bugs earlier in the development cycle.
5. Common Challenges in Implementing QA Automation
What You’ll Learn:
In this section, we’ll examine the most common obstacles that organizations face when implementing or scaling QA automation. We will also discuss actionable solutions to overcome these challenges and successfully integrate automated testing into your workflows.
Value for You:
By understanding the potential pitfalls in the journey to automation, you will be better equipped to navigate them, ensuring smooth adoption and long-term success with QA automation.
While QA automation offers significant benefits, teams often encounter several challenges during implementation and scaling. Understanding these challenges and how to mitigate them is key to reaping the full benefits of automation. Below are the most common hurdles and how to overcome them:
- Tool Compatibility and Integration:
- One of the biggest hurdles in adopting QA automation is ensuring that the tools integrate seamlessly with the existing development and testing environments. Many teams struggle with compatibility between test automation frameworks and the applications being developed.
- Solution: To mitigate this, teams should focus on selecting widely supported and flexible tools, like Selenium, Cypress, or JUnit, which offer strong integrations with major CI/CD pipelines and cloud platforms. Conducting a pilot project with a selected set of tools can also help determine compatibility before a full-scale rollout.
- One of the biggest hurdles in adopting QA automation is ensuring that the tools integrate seamlessly with the existing development and testing environments. Many teams struggle with compatibility between test automation frameworks and the applications being developed.
- Lack of Skilled Professionals:
- Another challenge is the shortage of skilled professionals who can develop and maintain automated test scripts. As automation requires specialized knowledge in programming, scripting, and QA frameworks, many teams find it difficult to staff these positions, which can delay or hinder the automation process.
- Solution: Upskilling the existing QA team is a viable solution. Offering training sessions in Selenium, Cypress, or Postman for API testing can help bridge this gap. In addition, collaborating with developers to ensure automated tests are integrated into the CI/CD pipeline allows teams to share responsibility for test automation.
- Another challenge is the shortage of skilled professionals who can develop and maintain automated test scripts. As automation requires specialized knowledge in programming, scripting, and QA frameworks, many teams find it difficult to staff these positions, which can delay or hinder the automation process.
- High Initial Setup Costs:
- The initial investment in QA automation infrastructure can be significant, especially for teams moving from a manual testing approach. Costs can stem from purchasing automation tools, hiring specialized staff, and configuring test environments.
- Solution: Teams should focus on the long-term ROI that comes with QA automation. By automating repetitive tests, companies save time and reduce human errors, leading to faster development cycles and more reliable software. Open-source tools like Selenium or JUnit can reduce initial costs, while cloud-based testing platforms such as Functionize or Test.ai offer scalable options without a large upfront investment.
- The initial investment in QA automation infrastructure can be significant, especially for teams moving from a manual testing approach. Costs can stem from purchasing automation tools, hiring specialized staff, and configuring test environments.
- Resistance to Change:
- Teams may be hesitant to adopt QA automation, especially if manual testing has worked well in the past. This resistance can be particularly strong in organizations where manual testing has been entrenched for years.
- Solution: Change management practices are crucial. Building a case for automation by showcasing the tangible benefits, such as faster release cycles and fewer defects, can help shift the mindset. Starting with small, non-critical test cases and demonstrating their success can help gain buy-in for broader automation initiatives.
- Teams may be hesitant to adopt QA automation, especially if manual testing has worked well in the past. This resistance can be particularly strong in organizations where manual testing has been entrenched for years.
- Maintaining Automation Tests:
- Over time, the maintenance of automated tests can become a challenge, especially as the software evolves. Test scripts may break when new features or changes are introduced, requiring regular updates and adjustments.
- Over time, the maintenance of automated tests can become a challenge, especially as the software evolves. Test scripts may break when new features or changes are introduced, requiring regular updates and adjustments.
Solution: To maintain a healthy test suite, teams should focus on creating modular, reusable test scripts and versioning the tests in sync with the application code. Automation tools like Cypress allow easy maintenance of tests through their ability to auto-sync with the latest application code and handle UI changes effectively.
5. The Role of AI and Machine Learning in QA Automation
What You’ll Learn:
In this section, we will explore how AI and machine learning are transforming the landscape of QA automation. We will cover the integration of intelligent testing processes, predictive testing, and how these innovations are enhancing the quality and efficiency of automated tests.
Value for You:
AI and ML are not just buzzwords—they’re driving real change in QA automation. By the end of this section, you will understand the specific ways in which these technologies can improve test accuracy, speed, and adaptability, helping to future-proof your testing strategy.
AI and machine learning are increasingly playing a pivotal role in automating testing tasks that were previously time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale. Here’s how AI/ML are reshaping QA automation:
- Automating Intelligent Testing Processes:
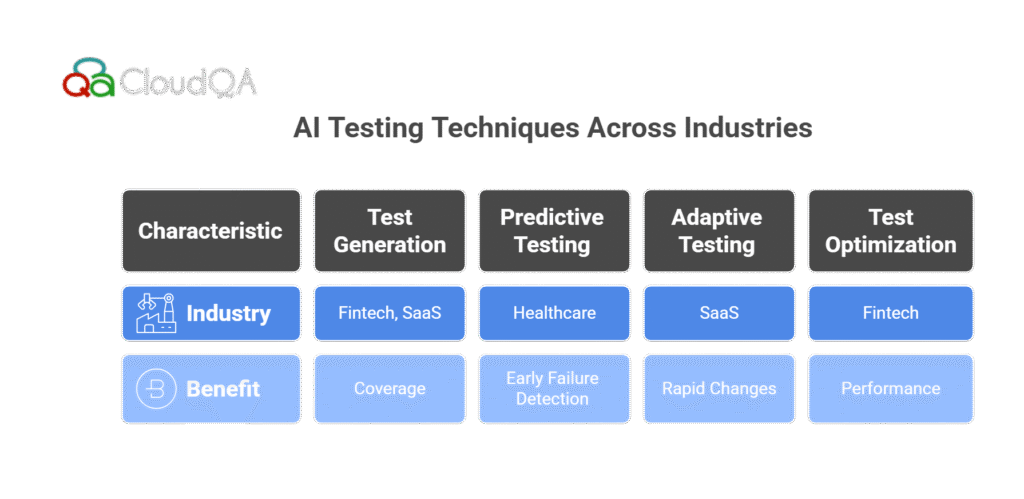
- AI-powered tools are capable of automatically generating test scripts by learning from the application’s behavior and user interactions. This reduces the time spent on manual test script creation and ensures that tests cover a wide range of scenarios.
- Example: Tools like Test.ai use AI to automatically generate tests based on user behavior patterns, identifying potential gaps in test coverage that might have been missed by human testers.
- AI-powered tools are capable of automatically generating test scripts by learning from the application’s behavior and user interactions. This reduces the time spent on manual test script creation and ensures that tests cover a wide range of scenarios.
- Predictive Testing:
- Machine learning models can analyze historical test data and predict future failures, enabling QA teams to focus on the areas most likely to encounter issues. This form of proactive testing enhances the efficiency of QA teams and reduces the need for redundant tests.
- Example: AI-based predictive analytics can analyze previous bug reports and user feedback, helping to predict which areas of an application are most prone to errors based on the current development trends.
- Machine learning models can analyze historical test data and predict future failures, enabling QA teams to focus on the areas most likely to encounter issues. This form of proactive testing enhances the efficiency of QA teams and reduces the need for redundant tests.
- Adaptive Testing:
- ML can enable adaptive testing, where the system learns over time to adapt test cases based on changes in the codebase. This ensures continuous coverage of new and modified features without the need to manually update tests.
- Example: Cypress integrates AI/ML to dynamically adjust test cases based on changes made in the code, ensuring tests are always up to date with the latest build.
- ML can enable adaptive testing, where the system learns over time to adapt test cases based on changes in the codebase. This ensures continuous coverage of new and modified features without the need to manually update tests.
- Automating Test Optimization:
- ML models can optimize test execution by selecting the most relevant tests to run, based on code changes or past test results. This is especially useful in large projects with complex codebases.
- Example: Tools like Functionize use machine learning to prioritize tests based on the likelihood of failure, optimizing test execution and reducing test run times.
- ML models can optimize test execution by selecting the most relevant tests to run, based on code changes or past test results. This is especially useful in large projects with complex codebases.
- Improved Test Data Generation:
- AI can generate realistic and diverse test data, which is crucial for testing edge cases, validating boundary conditions, and covering all possible user scenarios.
- Example: Test.ai leverages AI to generate test data based on user interactions and historical data, ensuring comprehensive testing without manual data creation.
- AI can generate realistic and diverse test data, which is crucial for testing edge cases, validating boundary conditions, and covering all possible user scenarios.
6. Best Practices for Implementing QA Automation in CI/CD Pipelines
Implementing QA automation in CI/CD pipelines requires careful planning and best practices. This section provides actionable insights into how to optimize your QA pipeline for faster, more reliable testing.
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): TDD is a development practice where tests are written before the code itself. This ensures that tests are always aligned with the code, reducing the risk of bugs and improving the quality of the software from the beginning. When combined with CI/CD, TDD ensures that tests are run continuously, catching errors early in the development process.
- Regression Testing: Regression testing is essential to ensure that new code changes do not introduce new bugs. In CI/CD pipelines, automated regression tests can be run every time code is committed, providing immediate feedback to developers. This ensures that issues are identified and fixed quickly, preventing bugs from reaching production.
- Version Control and Parallel Testing: Version control is critical for maintaining test quality and managing changes in the codebase. By using version control systems like Git, teams can track changes in test scripts and ensure that they are always up to date with the latest application code. Parallel testing allows teams to run tests across multiple environments simultaneously, reducing test execution time and increasing coverage.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuous testing is not just about running automated tests; it’s also about monitoring the results in real time. Tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab allow teams to continuously monitor test results and receive instant feedback when tests fail. This enables teams to fix issues before they become major problems, improving the overall quality of the
7. The Future of QA Automation: Key Trends and Predictions
What You’ll Learn:
In this section, we will explore the upcoming trends in QA automation, focusing on emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, and low-code/no-code tools. We will also discuss the role of predictive testing and continuous testing in shaping the future of software quality assurance.
Value for You:
This section will provide you with a glimpse into the future of QA automation. By understanding the trends and technologies on the horizon, you can position your team and organization to adopt the best practices that will drive efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration into Automation:
- AI and ML are poised to transform QA automation by enabling more intelligent, adaptable testing processes. These technologies will allow for better prediction of potential failures, reducing the time spent on repetitive tests and improving the accuracy of test results.
- Example: In the future, AI will not only generate tests but also evaluate the effectiveness of these tests by learning from past results. This will lead to self-optimizing test suites that can adapt to code changes without human intervention.
- Impact: Expect smarter testing tools that analyze test outcomes, identify patterns in failed tests, and suggest fixes or optimizations to the test scripts.
- AI and ML are poised to transform QA automation by enabling more intelligent, adaptable testing processes. These technologies will allow for better prediction of potential failures, reducing the time spent on repetitive tests and improving the accuracy of test results.
- Predictive Testing and Test Automation:
- Predictive testing is set to become one of the most powerful features of future QA automation. With the help of machine learning, QA teams will be able to predict which areas of the application are most likely to encounter issues. This will help teams focus on high-risk areas and perform tests even before a bug appears.
- Example: Predictive models could be used to determine which parts of the application code should be tested after each new commit based on past failures, user feedback, or new feature updates.
- Impact: Reduced testing time, fewer redundant tests, and faster identification of high-priority issues.
- Predictive testing is set to become one of the most powerful features of future QA automation. With the help of machine learning, QA teams will be able to predict which areas of the application are most likely to encounter issues. This will help teams focus on high-risk areas and perform tests even before a bug appears.
- Low-Code/No-Code Automation Tools:
- Low-code/no-code platforms are democratizing test automation by allowing non-technical users to create automated tests. This enables more people within a development team—such as business analysts and product managers—to contribute to QA efforts, speeding up the overall process and increasing collaboration.
- Example: Platforms like Cypress and Testim are evolving to offer no-code/low-code interfaces, allowing testers and product managers to create automated test cases through intuitive drag-and-drop functionality.
- Low-code/no-code platforms are democratizing test automation by allowing non-technical users to create automated tests. This enables more people within a development team—such as business analysts and product managers—to contribute to QA efforts, speeding up the overall process and increasing collaboration.
Impact: Wider adoption of automated testing across teams, faster onboarding for non-developers, and a reduction in bottlenecks.
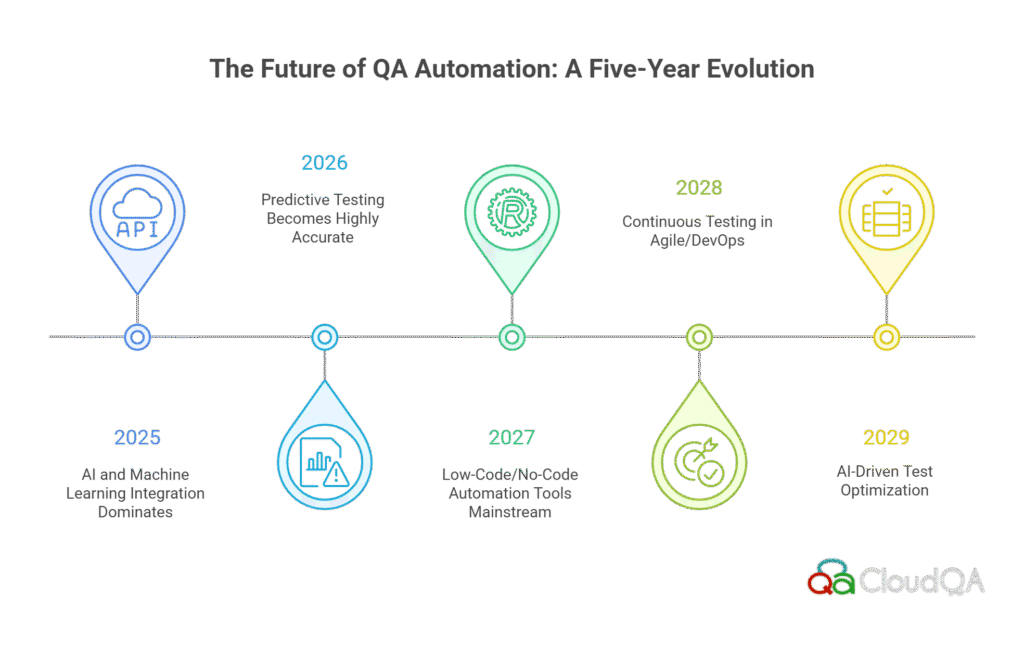
- Continuous Testing and Agile DevOps:
- With the rise of continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, continuous testing is becoming essential. Future QA practices will be tightly integrated into these pipelines, allowing for automated testing with every build, every deployment, and every commit. This ensures quality is maintained throughout the development lifecycle.
- Example: As part of the DevOps lifecycle, continuous testing will run automatically every time there is a code update. Tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab will support the seamless integration of automated tests to check for regressions, bugs, and performance issues.
- Impact: Real-time feedback on every code change, ensuring that bugs are detected early and fixed quickly, reducing the cost and time spent on quality assurance in later stages.
- With the rise of continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, continuous testing is becoming essential. Future QA practices will be tightly integrated into these pipelines, allowing for automated testing with every build, every deployment, and every commit. This ensures quality is maintained throughout the development lifecycle.
- The Role of AI-Driven Test Optimization:
- In the near future, AI will not only automate test execution but also optimize test suites. AI will help prioritize tests based on real-time usage data, past failures, and business priorities. This ensures that only the most critical tests are executed, which is particularly important in large systems.
- Example: An AI system could analyze historical testing data, flag areas prone to errors, and dynamically adjust the testing coverage based on real-time code changes or production data.
- Impact: Optimized testing processes that are faster, more reliable, and better suited to real-world user interactions.
- In the near future, AI will not only automate test execution but also optimize test suites. AI will help prioritize tests based on real-time usage data, past failures, and business priorities. This ensures that only the most critical tests are executed, which is particularly important in large systems.
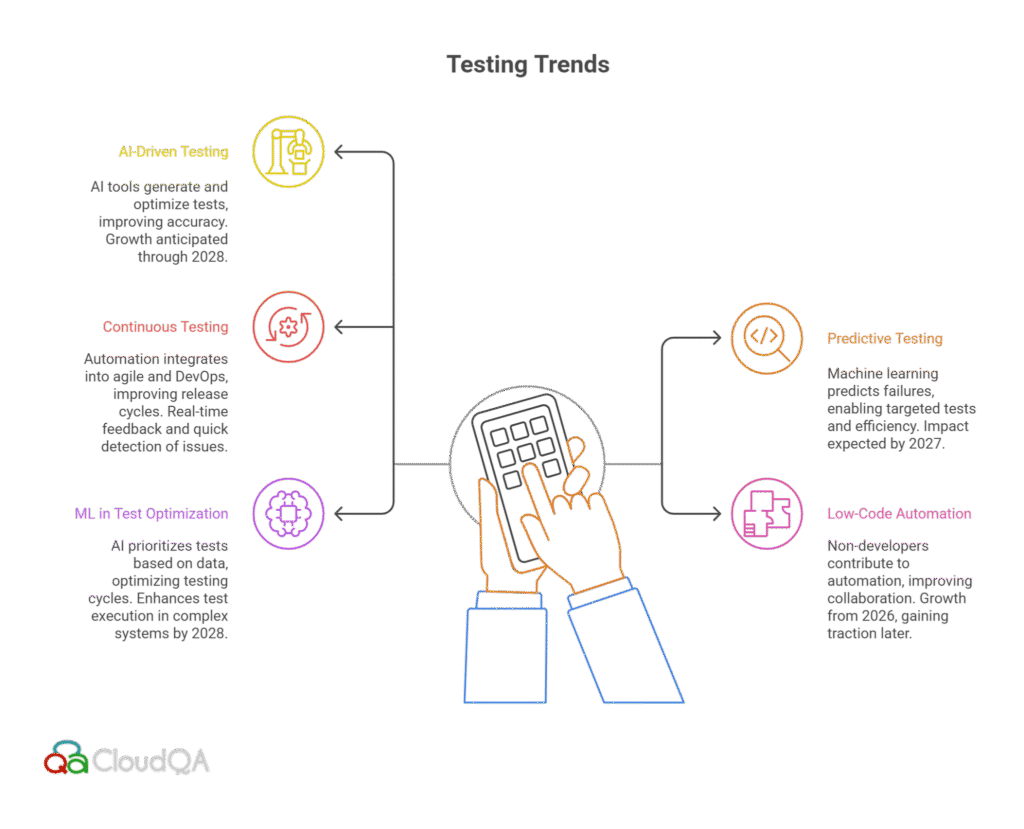
8. Case Studies and Industry Applications
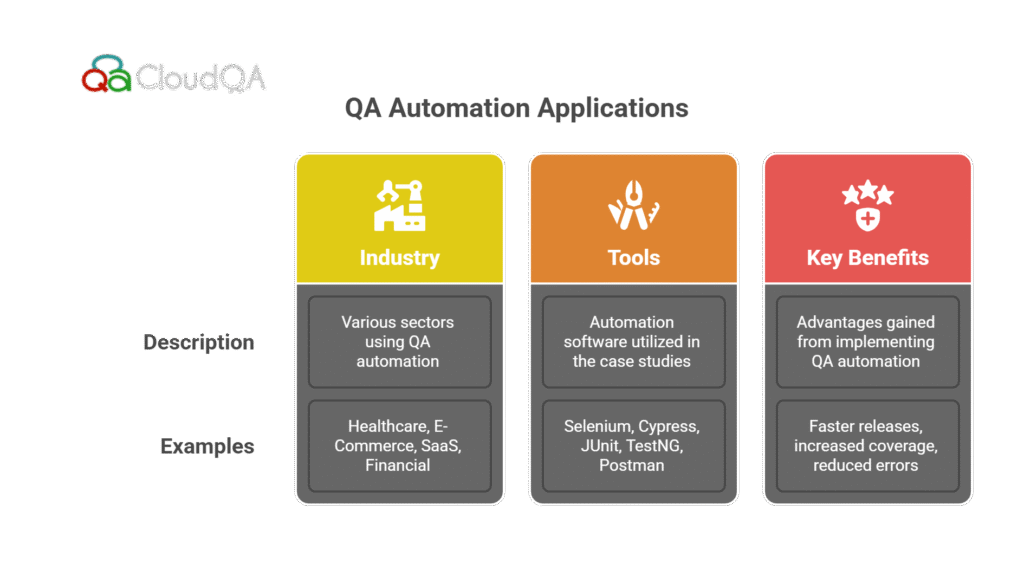
This section highlights how various organizations across different industries have successfully implemented QA automation in their CI/CD pipelines, leading to faster releases, improved software quality, and better customer satisfaction.
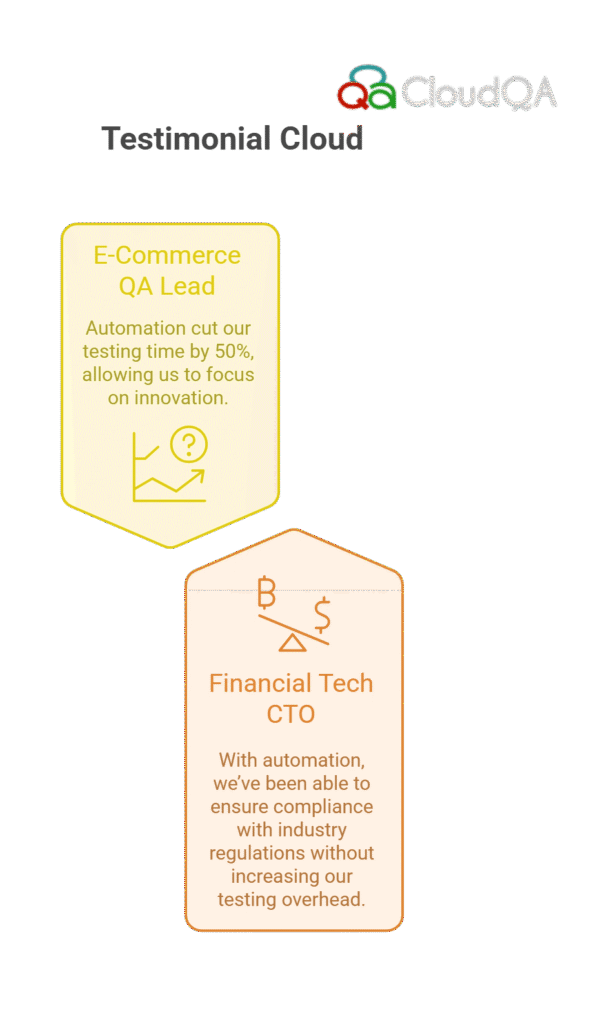
- Healthcare Industry: A healthcare provider automated their regression testing using Selenium and JUnit, reducing testing time by 40% and improving the accuracy of patient record validation. This allowed for quicker updates to their patient management system without compromising the quality of service.
- E-Commerce Industry: An e-commerce platform adopted Cypress for end-to-end testing, automating key user journeys like checkout and payment processing. By integrating Cypress into their CI/CD pipeline, they reduced test execution time by 50%, enabling more frequent releases and better customer satisfaction.
- SaaS Industry: A SaaS company used TestNG and Jenkins to automate their regression tests, reducing manual testing efforts by 70%. This allowed the team to focus on critical functionalities and accelerate the release of new features.
- Financial Industry: A financial tech company automated API testing with Postman, ensuring that their app remained compliant with industry regulations. By running automated tests on every update, they were able to maintain compliance and reduce the risk of errors in financial transactions.
Key Takeaways
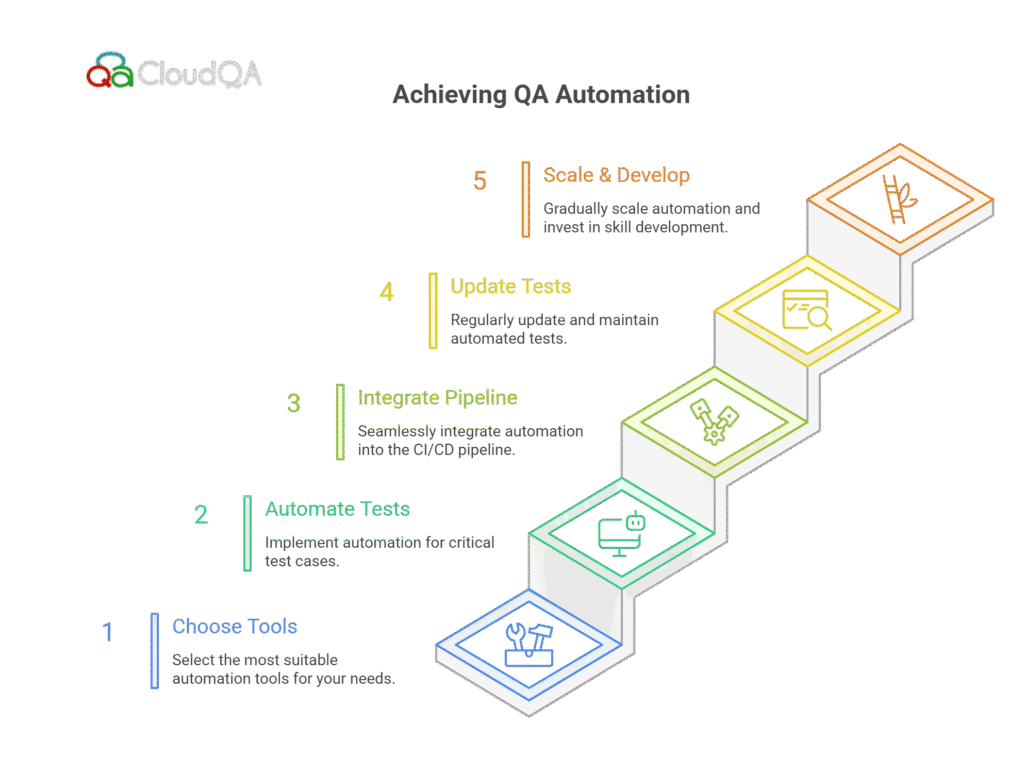
In conclusion, QA automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for modern software development. By implementing a robust CI/CD-friendly testing pipeline, teams can enhance software quality, reduce testing time, and ensure faster releases. The integration of automation tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Jenkins into CI/CD pipelines ensures continuous testing and early bug detection, which ultimately leads to improved product quality and faster time-to-market.
Key takeaways:
- QA automation has become essential for modern software development.
- Integrating automation into CI/CD pipelines improves testing speed and accuracy.
- Automation tools like Selenium, Cypress, and JUnit play a key role in streamlining testing processes.
- Best practices like TDD, regression testing, and version control are critical for successful implementation.
- Real-world case studies demonstrate the benefits of QA automation across various industries.
By following the practices outlined in this paper, development teams can build a more efficient and reliable QA pipeline that supports continuous integration and delivery.
Bibliography
- Srinivasan, R. (2024). “The State of QA Automation: Trends and Impact Across Industries”. Quality Assurance Review, Vol. 7(2). Available at: https://example.com.
- Zhang, H., Chen, L. (2023). “QA Automation in Agile DevOps: Trends and Case Studies”. DevOps Today. Available at: https://example.com.
- Kaur, S., & Singh, J. (2023). “Quality Assurance Challenges in AI Applications: A Survey”. IEEE Xplore. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10111755.
- TechCrunch. (2023). “How AI is Shaping the Future of QA Automation”. Available at: https://techcrunch.com.
- Functionize. (2024). “Intelligent Test Automation Powered by AI”. Available at: https://www.functionize.com.
- Forrester Research. (2023). “Automation in QA: Trends and Impact”. Available at: https://www.forrester.com.
- Test.ai. (2024). “AI-Powered Testing for Mobile Apps”. Available at: https://test.ai/resources/whitepapers.
- Gartner, Inc. (2024). “Emerging Tech: AI Engineering and Quality Assurance Trends”. Available at: https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/emerging-technologies-and-the-future-of-ai-engineering.
- Leong, D. (2023). “The Future of Test Automation: AI, Machine Learning, and Beyond”. Tech Trends. Available at: https://www.techtrends.com.
- Jenkins (2024). “Continuous Testing and CI/CD Integration”. Available at: https://www.jenkins.io.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is QA Automation, and why is it important?
- Brief explanation of QA automation and its role in the software development lifecycle.
- How does CI/CD testing improve development speed?
- Explaining how CI/CD pipelines enable continuous testing and faster feedback loops, leading to more efficient development cycles.
- How can AI enhance QA automation?
- Exploring how AI and machine learning are used to improve test prediction, automation, and error detection.
- What are the main challenges in implementing QA automation?
- A brief overview of common obstacles such as tool compatibility, high initial costs, and lack of skilled professionals.
- What are some tools commonly used in QA automation?
- A list of popular tools like Selenium, Cypress, JUnit, and their respective use cases in CI/CD pipelines.
- What is predictive testing, and how does it help in QA?
- Explanation of predictive testing and how it helps QA teams focus on the areas most likely to experience issues.
- How do I start implementing QA automation in my team?
- Practical tips for getting started with QA automation, including training, tool selection, and integrating automation into the CI/CD pipeline.
- What impact does QA automation have on product quality?
- Discuss how automation leads to better product quality by reducing human errors, increasing test coverage, and speeding up the testing process.
- How do you maintain automated tests as software evolves?
- Methods for keeping automated tests up-to-date with software changes, such as version control, modular scripts, and regular updates.
- What is the future of QA automation?
- A glimpse into the future of QA automation, focusing on trends like AI-powered testing, continuous testing, and low-code/no-code tools.
- What is QA Automation, and why is it important?
