The Ultimate Guide to GPT Prompts for Test Case Generation in 2026
Last Updated: February 23rd 2026
Ready to supercharge your QA process? Discover how CloudQA’s AI-powered, codeless platform can integrate seamlessly with modern techniques like GPT-driven test case generation. Explore the Future of QA Today.
Table of Contents
Introduction: The AI Revolution in Quality Assurance
The world of Quality Assurance (QA) is in the midst of an AI-driven revolution. While ChatGPT introduced the world to the power of Large Language Models (LLMs), the landscape has since exploded with a new generation of powerful and specialized AI. For QA teams, this evolution presents an unprecedented opportunity to move beyond the slow, manual, and often inconsistent process of creating test cases.
The conversation is no longer just about one model; it’s about a diverse ecosystem of AI tools that can be leveraged to create comprehensive, high-quality test suites with incredible speed. This guide serves as a complete introduction to this new era, exploring how modern LLMs from Google, Anthropic, OpenAI, and others are being used for test case generation. We will cover how to choose the right AI partner, craft effective prompts for any model, and strategically integrate this technology into your QA automation strategy for 2026 and beyond.
This section explores the practical challenges QA teams face with manual and scriptless test case creation, including:
- Lengthy development cycles for test case writing and updates
- Incomplete or inconsistent test coverage leading to defects in production
- Difficulties in maintaining and scaling test suites as applications evolve
- The perennial problem of flaky tests and associated maintenance overhead
This shift not only improves test efficiency but also enriches QA workflows, enabling teams to focus on strategic testing and exploratory efforts.
Curious about taking your test automation to the next level?
Join CloudQA’s webinar on “Revolutionizing Test Case Generation with GPT” and get hands-on tips!
Register Now
The Manual Bottleneck: Why Test Case Generation Needs an Upgrade
A test case is the fundamental building block of quality assurance—a sequence of steps designed to verify a specific piece of software functionality. The quality of a product is directly tied to the quality and comprehensiveness of its test suite.
Traditionally, creating these test cases has been a manual, labor-intensive process. A QA engineer or business analyst would:
- Meticulously read through product requirement documents (PRDs) or user stories.
- Manually identify all possible user scenarios, including positive paths, negative paths, and edge cases.
- Write out each test case step-by-step in a test management tool.
This process is not only slow but also prone to human error and inconsistency. It often struggles to keep pace with rapid development, leading to gaps in test coverage and a higher risk of bugs slipping into production.
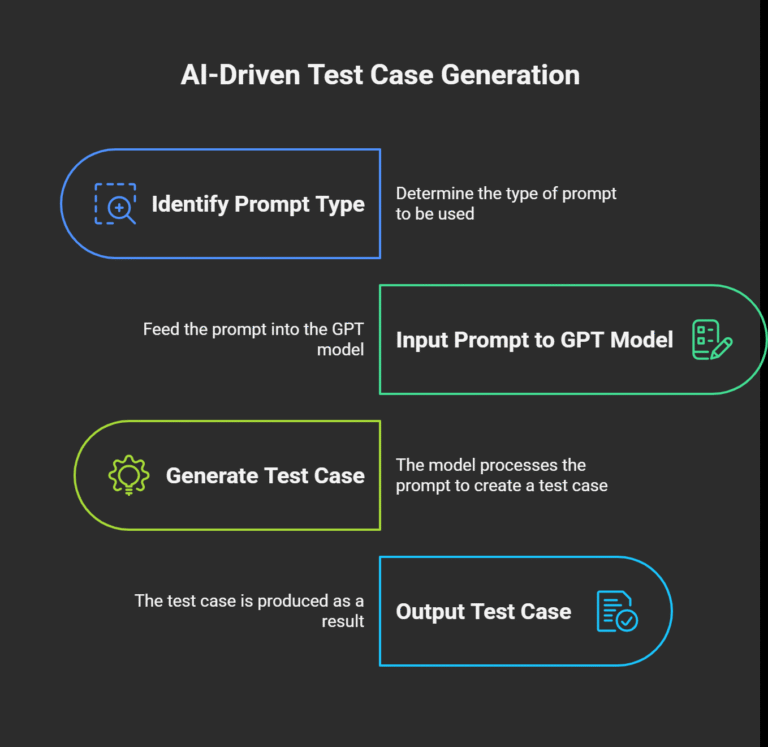
The Rise of LLMs in QA: A Look Beyond ChatGPT
The public release of ChatGPT demonstrated that AI could understand context and generate human-like text, immediately showing its potential for tasks like test case creation. However, the field is advancing at an exponential rate. The modern QA professional now has access to a wide array of LLMs, each with unique strengths.
This new ecosystem includes:
- General-Purpose Powerhouses: Highly advanced models that can reason, create, and process information across a vast range of topics.
- Code-Specific LLMs: Models that are specifically trained on billions of lines of code, making them experts in programming languages and software logic.
- Integrated AI in QA Platforms: A growing trend where QA tool vendors embed or fine-tune these powerful LLMs directly into their platforms, creating a seamless, context-aware user experience.
Instead of manually analyzing requirements, a QA professional provides the AI with the context,such as a user story, a feature description, or a piece of code,and asks it to generate relevant test cases. The AI leverages its vast training data to understand the context, identify potential scenarios, and output a structured list of test cases that can be used for both manual and automated testing. This transforms the role of the QA professional from a manual scribe into a strategic orchestrator, guiding the AI to produce the desired quality artifacts.
A prompt is more than just a query. It can be framed as a scenario, role, requirement, or checklist, and its quality will directly impact the relevance and accuracy of the generated test cases. The most effective prompts are those that precisely communicate the context, constraints, and expectations for a test scenario—whether it be functional UI coverage, API endpoint validation, boundary testing, or complex user journeys.
Choosing Your AI Partner: A Guide to Modern LLMs for QA
Selecting the right AI model depends on your specific needs, from generating high-level business scenarios to writing unit test code.
General-Purpose Powerhouses
These models are your go-to for understanding user stories and generating functional, end-to-end, and exploratory test ideas.
- OpenAI’s GPT-4 and GPT-4o: Still the industry benchmark for complex reasoning, nuance, and creativity. Excellent for generating detailed test scenarios, edge cases, and BDD feature files from business requirements.
- Google’s Gemini Family (Pro and Ultra): Known for its massive context window and powerful multimodal capabilities. Gemini can analyze screenshots of a UI alongside a user story to generate even more relevant test cases.
- Anthropic’s Claude Series (Claude 3 Opus, Sonnet): A strong competitor with a large context window and a focus on reliability and enterprise-grade safety. It’s an excellent choice for generating tests from lengthy and complex technical documentation.
Code-Specific LLMs
These are ideal for more technical tasks, like generating unit tests or simple automation scripts.
- GitHub Copilot: Powered by OpenAI’s models, it lives directly in your code editor (IDE) and can suggest test code in real-time as developers write new functions.
- Open-Source Models (e.g., Code Llama): For teams with privacy concerns or the desire to fine-tune a model on their own codebase, open-source models offer a powerful and flexible alternative.
The Art of the Prompt: Universal Principles for Any LLM
While different models may have slight nuances, the principles of effective prompt engineering are universal. The quality of your AI-generated output is a direct reflection of the quality of your input.
- Assign a Role: Begin your prompt by telling the AI who to be (e.g., “Act as a principal SDET…”). This sets the context and tone for a professional response.
- Provide Rich Context: This is the most critical step. Paste the complete user story, acceptance criteria, technical specification, or even a snippet of code. The more relevant details the LLM has, the more accurate its output will be.
- Be Explicit in Your Task: Use clear, direct action verbs. Don’t ask it to “think about” test cases; instruct it to “Generate a comprehensive list of…”
- Define the Output Format: To get a structured and immediately usable response, specify the format you want. Ask for a table with named columns, a numbered list, or code formatted in Gherkin for BDD.
By mastering these elements, you can guide the AI to become a highly efficient test case generation engine.
Practical GPT Prompts for Every Testing Scenario
Here are some practical, real-world examples of GPT prompts you can adapt for your own projects.
A. Generating Functional Test Cases from a User Story
This is the most common use case. The goal is to ensure a feature works as intended.
The Prompt:
Act as a senior QA engineer. Based on the following user story, generate a comprehensive set of functional test cases in a table format with the columns: “Test Case ID,” “Test Scenario,” “Test Steps,” and “Expected Result.”
User Story:
As a registered user on an e-commerce website, I want to be able to add a product to my shopping cart from the product details page so that I can purchase it later.
Acceptance Criteria:
- The product details page must display an “Add to Cart” button.
- Clicking the “Add to Cart” button should add the selected item to the user’s cart.
- A confirmation message, “Product added to cart successfully,” should appear.
- The cart icon in the header should update to show the new number of items.
- If the item is already in the cart, the button should still be clickable, and the quantity in the cart should be updated.
B. Identifying Edge Cases and Negative Scenarios
GPT excels at thinking of scenarios that a human tester might overlook.
The Prompt:
Act as a meticulous QA tester responsible for ensuring application robustness. For the user login functionality described below, identify and list all possible negative scenarios and edge cases. Focus on invalid inputs, boundary conditions, and unusual user behaviors.
Functionality:
A user login form with two fields: “Email” (must be a valid email format) and “Password” (must be at least 8 characters).
C. Creating Security-Focused Test Cases
You can leverage GPT to test for common vulnerabilities.
The Prompt:
Act as a cybersecurity analyst. For a new user registration form that accepts a username, email, and password, generate a list of security-focused test cases to check for common vulnerabilities like SQL Injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
D. Generating BDD Scenarios in Gherkin Format
For teams practicing Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), GPT can write the Gherkin feature files for you.
The Prompt:
Act as a BDD automation specialist. Based on the following feature description for a search functionality, write the Gherkin feature file with multiple “Scenario” blocks covering both positive and negative tests.
Feature: Product Search
As a user, I want to be able to search for products by name so that I can easily find what I’m looking for.
6. Best Practices in Prompt Engineering for QA Teams in 2025
Prompt engineering is the foundation of effective AI-powered test case creation. As QA automation enters a new era driven by large language models, the quality of your results depends on the clarity, structure, and intent behind your prompts. For QA teams aiming to maximize the value of your LLM of choice, mastering best practices in prompt engineering can yield measurable improvements in efficiency, coverage, and reliability.
Clarity and Specificity:
Ambiguous or overly broad prompts can lead to generic, incomplete, or error-prone test cases. Instead, high-performing QA teams craft prompts that are precise and focused—mentioning the feature under test, input data, expected outcomes, and any relevant constraints. For example, rather than “Create tests for login,” a best-practice prompt might be: “Generate positive and negative test cases for a login form requiring email and password. Include validations for valid credentials, invalid email formats, missing fields, and password length constraints.”
Structure and Delimiters:
Break complex requests into step-by-step instructions using delimiters (like numbered lists or bullet points). This encourages AI to output organized, actionable test cases and helps avoid missed requirements. For instance, listing test data, expected result, and setup steps separately clarifies intent and ensures all bases are covered.
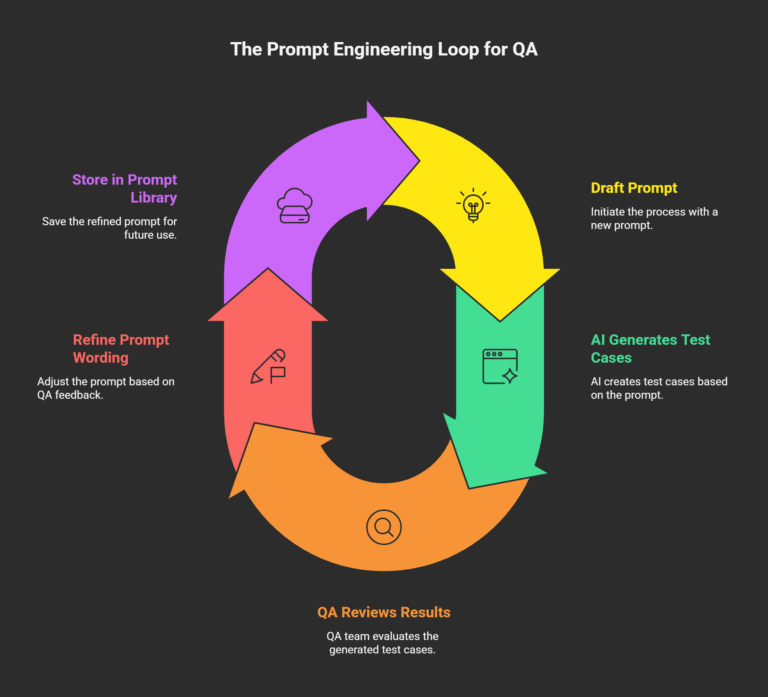
Iterative Refinement and Feedback Loops:
Prompt engineering is rarely a “write-once” task. QA professionals should review AI-generated output, identify where prompts require more context or detail, and iteratively refine their wording. Over time, this feedback loop builds more accurate, domain-specific prompt libraries that boost productivity and test quality.
Role-Based and Persona Prompts:
Assigning a persona to the AI, such as “Act as a senior QA engineer” or “Assume the role of a security analyst,” helps tailor responses to specific test design philosophies or business needs. Role-based prompting has become an industry best practice for generating specialized test assets.
Data-Driven and Structured Output:
Providing concrete data or requesting specific output formats (like JSON or tables) further aligns results with automation tool requirements. Always specify if you need outputs in a format like Gherkin, markdown tables, or step-by-step instructions to improve integration and downstream usability.
Versioning & Collaboration:
Store and version your most successful prompts. Share them in a central repository so team members can reuse and adapt proven patterns. Integrated tools and prompt management platforms help QA teams optimize their workflows as new test coverage needs emerge.
7. Integrating GPT Prompt-Based Test Case Generation with Popular Automation Tools
In 2026, QA success increasingly hinges on how well teams can connect AI-powered test case generation with robust automation frameworks. Integrating GPT-driven prompt outputs with tools like Playwright, WebdriverIO, and CloudQA ensures a seamless transition from natural language requirements to actionable, executable, and version-controlled test assets.
From Prompt to Practically Automated Tests
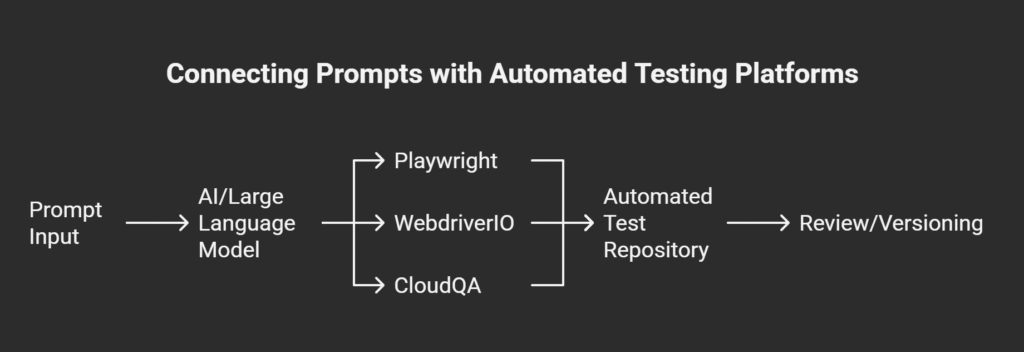
Step 1: Generate Test Cases Using GPT Prompts
Begin by supplying a clear, focused prompt to your preferred LLM. For instance, describe a login workflow or an API endpoint. Well-structured prompts – especially those with explicit field requirements or validation steps – yield detailed, reusable test cases. The AI model can generate outputs in different formats, such as Gherkin, step-by-step instructions, or even direct code snippets for Playwright or WebdriverIO.
Step 2: Integrate with Playwright and WebdriverIO
Modern test frameworks like Playwright and WebdriverIO are designed for easy script integration. Many GPT-powered tools can export or format test cases directly into JavaScript, TypeScript, or Python code compatible with these frameworks. You can copy/paste, import files, or use API bridges to flow generated tests straight into your automation suite:
- Example: “Create a Playwright script to test invalid login attempts on the login page, with all edge case validations.”
- Review and tweak the AI-generated code for precise selector use and application context.
Step 3: Leverage CloudQA’s Native AI Capabilities
CloudQA enables users to define test steps in natural language and converts them directly into maintainable, scriptless automation flows. By pairing CloudQA’s interface with your growing prompt library, teams can rapidly build up reusable test scenarios—no hand-coding required. All prompts, test results, and artifacts can be collaboratively managed in the CloudQA platform, encouraging best practice sharing and knowledge reuse.
Step 4: Organize and Maintain Prompt Outputs
Storing prompt outputs alongside regular test scripts promotes transparency, traceability, and easy versioning. Organize test artifacts in a dedicated repository or use built-in project management tools available through your automation provider.
8. Tool Comparison: GPT Prompt Support in Playwright, WebdriverIO, CloudQA & More
Selecting the right automation tool to maximize the benefits of GPT-powered test case generation is critical for QA teams aiming to excel in 2026. Playwright, WebdriverIO, and CloudQA represent three prominent options, each offering distinctive strengths in prompt integration, test automation capabilities, and developer experience.
Playwright
Playwright, developed by Microsoft, excels as a modern, open-source framework built for cross-browser testing with native support for Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit. It features an intuitive API, auto-wait mechanisms, and parallel test execution, which help QA teams handle complex app scenarios efficiently. Playwright allows developers to directly incorporate AI-generated test scripts by accepting code snippets in JavaScript, TypeScript, or Python formats. Moreover, Playwright’s trace viewer enhances debugging, which is invaluable when refining GPT-generated tests to ensure stability and accuracy.
Strengths:
- Fast execution with event-driven architecture
- Supports multiple programming languages
- Strong cross-browser and device testing capabilities
- Native support for prompt-based automated test script integration
Considerations:
- Primarily developer-centric; requires JavaScript/TypeScript proficiency
- Smaller community compared to Selenium ecosystem but rapidly growing
WebdriverIO
WebdriverIO is a versatile open-source automation framework that offers excellent extensibility and integration with numerous testing services. It supports TypeScript and JavaScript and provides plugins and service integrations that facilitate direct use of AI-generated test cases. WebdriverIO’s flexible architecture works well for teams using prompt engineering to generate test scripts that support UI, API, and mobile app automation.
Strengths:
- Robust plugin ecosystem enabling broad integrations
- Supports both Selenium and DevTools protocols
- Flexible, easy to integrate with AI and prompt-based tools
- Strong community support
Considerations:
- Slightly steeper learning curve and configuration effort
- Requires managing Selenium Grid or equivalent for parallel execution
CloudQA
CloudQA offers a codeless, AI-powered end-to-end automation platform that natively supports natural language test case creation using GPT prompts. Its scriptless interface allows QA analysts, even those without programming backgrounds, to rapidly generate, execute, and maintain prompt-based test scenarios. CloudQA also supports seamless collaboration and shared prompt libraries, enhancing team productivity and accelerating test coverage expansion.
Strengths:
- No-code platform ideal for business and manual testers
- AI-driven prompt engineering integration from the ground up
- Easy test maintenance with AI self-healing capabilities
- Collaboration-driven prompt and test case management
Considerations:
- Less suitable for teams requiring extensive custom scripting
- Pricing models vary depending on usage and team size
Summary Table
Feature | Playwright | WebdriverIO | CloudQA |
Language Support | JavaScript, TypeScript, Python | JavaScript, TypeScript | Codeless, natural language |
AI Prompt Integration | Code snippet import | Flexible plugin support | Native GPT prompt interface |
Cross-browser Support | Chromium, Firefox, WebKit | Selenium compatible | Web-focused with cloud scaling |
User Skill Level | Developer-centric | Developer-centric | Business and manual testers |
Parallel Execution | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Community Support | Growing | Large | Growing |
Ideal For | Developer teams, complex testing | Flexible automation teams | Non-coders, fast deployment |
9. Real-World Case Studies: Accelerating QA Automation with GPT Prompt-Driven Test Generation
The theoretical benefits of GPT-powered prompt engineering come alive in real-world applications where QA teams achieve measurable improvements in test coverage, reliability, and productivity. This section highlights three case studies featuring organizations that have embraced GPT prompts integrated with Playwright, WebdriverIO, and CloudQA automation, demonstrating the practical impact of this innovative approach.
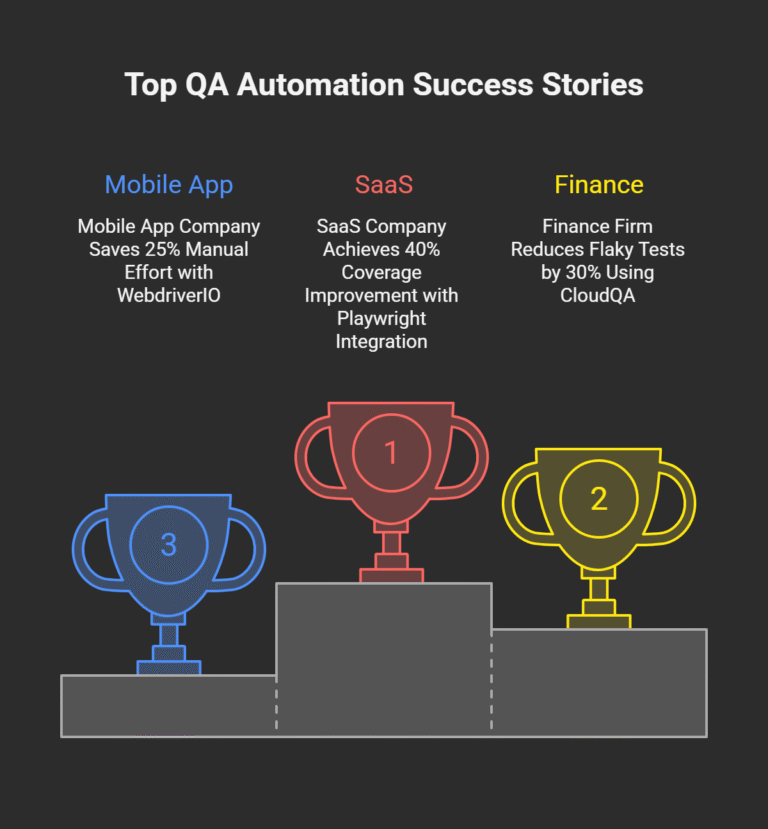
Case Study 1: SaaS Company Boosts Test Coverage and Developer Confidence
A fast-growing SaaS provider struggled with maintaining comprehensive regression suites as their application rapidly evolved. By adopting GPT prompt engineering, their QA team generated over 50 reusable test case prompts tailored for API and UI scenarios. Automating test case creation with Playwright scripts enabled a 35% increase in test coverage and reduced manual scripting time by 60%. The prompts ensured consistent and detailed test cases across releases, helping developers catch bugs earlier and improve release stability.
Case Study 2: Reducing Flaky Tests with Iterative Prompt Refinement
A financial services firm faced significant challenges with flaky UI tests causing false positives and slowing deployments. Using CloudQA’s AI-driven platform, the team harnessed GPT prompts with role-based scenarios to systematically generate robust, context-aware test cases. They implemented iterative prompt refinement cycles that cut flaky test rates by 45%, resulting in less downtime and smoother CI automation. Prompt versioning and collaboration features enabled quick sharing of best practices across the QA team.
Case Study 3: Expanding Mobile and Cross-Browser Coverage
A mobile app developer needed a scalable approach to test on multiple devices and browsers but had limited automation expertise. By leveraging WebdriverIO with GPT prompt-based test case generation, their team developed a library of data-driven and device-specific prompts. This enabled broad test case creation for diverse user interactions and edge conditions with minimal scripting. The result was a 50% reduction in manual test effort and faster release cycles without compromising user experience quality.
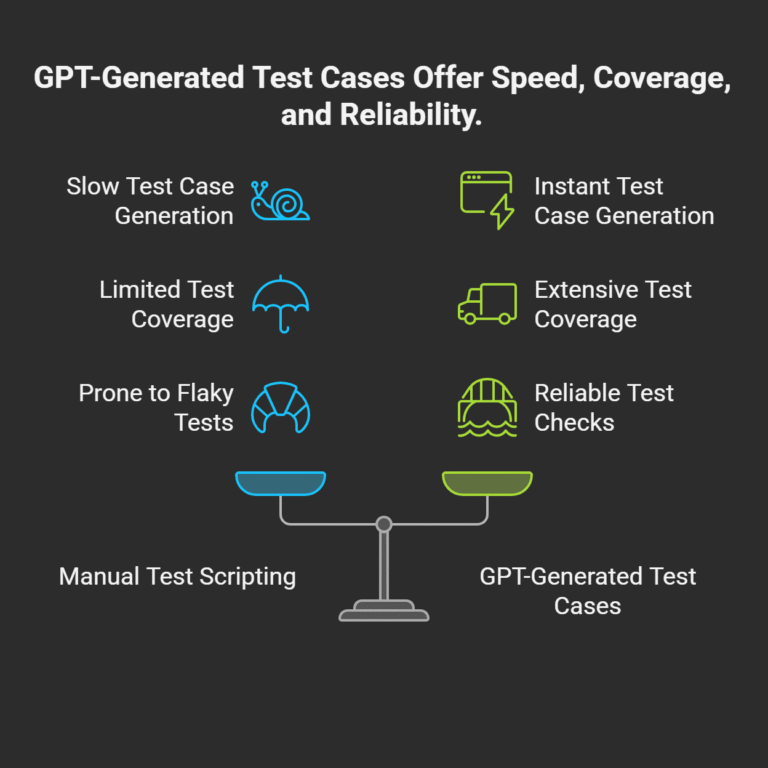
The Strategic Benefits of AI-Driven Test Generation
Integrating LLMs into your QA process offers transformative advantages:
- Accelerated Speed: Reduce the time it takes to create a comprehensive test suite from days to minutes.
- Deeper Coverage: Leverage the AI’s ability to identify complex scenarios and edge cases that a human might miss.
- Improved Consistency: Enforce a standard format for all test cases, making your test suite easier to manage and maintain.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Use AI-generated test cases as a clear, structured baseline for discussions between developers, QA, and product owners to ensure everyone is aligned.
Limitations and Best Practices: A Realistic Framework
LLMs are powerful partners, not perfect oracles. A strategic approach requires acknowledging their limitations and adhering to best practices.
Limitations:
- No Business Context: An LLM does not understand your company’s unique business risks, user personas, or long-term goals.
- Data Privacy: Using public versions of these tools means your data is sent to a third-party server. Never paste highly sensitive, proprietary, or customer data into a public LLM interface.
Best Practices:
- Human Oversight is Non-Negotiable: Always treat AI-generated content as a first draft. A skilled QA professional must review, refine, and prioritize the test cases based on their domain knowledge.
- Use Enterprise-Grade Solutions for Sensitive Data: If you need to use proprietary information, use enterprise-grade versions of these LLMs (e.g., Azure OpenAI Service, Google Cloud’s Vertex AI) which offer data privacy and security guarantees.
- Iterate and Refine: Don’t be discouraged if the first response isn’t perfect. Tweak your prompt, add more context, and try again. Prompt engineering is an iterative skill.
Conclusion: Your Future as an AI-Powered QA Strategist
The role of the QA professional is evolving. The future is not about being replaced by AI, but about learning to leverage it as a powerful collaborator. The tedious task of manual test case writing is being automated, freeing up human testers to focus on what they do best: strategic thinking, exploratory testing, risk analysis, and creative problem-solving. By mastering the art of prompting and strategically choosing from the diverse ecosystem of modern LLMs, you can elevate your role, supercharge your team’s efficiency, and become a key driver of quality in this new era of software development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q1: Which LLM is “best” for QA and test generation?
- There is no single “best” model. It depends on the task. For understanding business requirements and generating functional scenarios, a powerful general-purpose model like GPT-4o, Claude 3, or Gemini is ideal. For generating unit tests or automation code, a code-specific model like GitHub Copilot might be more efficient.
- Q2: Is it safe to paste my company’s proprietary code or user stories into these AI models?
- It is not safe to paste sensitive or proprietary information into the public, free versions of these tools. For company use, you must use an enterprise-grade solution that provides a private, secure instance and guarantees that your data will not be used for training.
- Q3: Will these AI models make manual testing obsolete?
- No. They will make the manual creation of test case documents largely obsolete. This will free up time for more valuable forms of manual testing, such as exploratory testing, usability testing, and accessibility testing, which rely on human intuition and empathy.
Explore how CloudQA’s AI-powered platform can help you master prompt-driven test case generation.
Download our exclusive “GPT Prompt Library for QA Automation” today! Download Now
12. Bibliography
- Boonstra, L. (2025). Prompt Engineering. Technical Whitepaper. Link to PDF
A foundational resource explaining prompt design methodologies and optimization strategies for LLMs in software testing. - CloudQA Blog. (2025). QA Automation Best Practices for 2025. CloudQA Resources
Practical guidance on leveraging AI, GPT prompts, and automation frameworks for next-gen QA success. - “Master Prompt Engineering: AI-Powered Software Testing Efficiency.” Aqua Cloud, 2025. https://aqua-cloud.io/prompt-engineering-for-testers/
Covers prompt crafting, iterative refinement, and common pitfalls with real examples focused on software testing. - “Best Practices for Prompt Engineering with the OpenAI API.” OpenAI Help Center, 2025. https://help.openai.com/en/articles/6654000-best-practices-for-prompt-engineering-with-the-openai-api
Formal best practices for prompt construction, few-shot learning, and model interaction techniques applicable to QA teams. - “The 2025 AI Testing Roadmap: 5 Moves Every QA Engineer Should Make.” LinkedIn Article by P. Kulkarni, 2025.
Insights on AI integration, self-healing tests, and future-proofing QA workflows with generative AI. - “Top 10 ChatGPT Prompts for Software Testing.” PractiTest, 2025. https://www.practitest.com/resource-center/blog/chatgpt-prompts-for-software-testing/
Practical prompt examples for various testing contexts, emphasizing GPT-driven automation. - “ChatGPT for Test Automation .” testRigor, 2025. https://testrigor.com/chatgpt-for-test-automation/
Case studies and recommendations for applying GPT and AI in test automation workflows. - “Prompt Engineering in 2025: The Latest Best Practices.” News.Aakashg, 2025. https://www.news.aakashg.com/p/prompt-engineering
Comprehensive overview of evolving prompt engineering techniques key for 2025 and beyond. - “Future Trends in Prompt Engineering & QA Automation in 2025.” Refonte Learning, 2025. https://www.refontelearning.com/blog/prompt-engineering-trends-2025-skills-youll-need-to-stay-competitive
Strategic outlook on AI prompt innovation shaping QA and software testing fields. - “Selenium vs Playwright vs WebdriverIO Archives.” CloudQA, 2025. https://cloudqa.io/tag/selenium-vs-playwright-vs-webdriverio/
Detailed tool comparisons for AI and GPT-powered test case integration in leading frameworks.
RECENT POSTS
Guides

How To Select a Regression Testing Automation Tool For Web Applications
Regression testing is an essential component in a web application development cycle. However, it’s often a time-consuming and tedious task in the QA process.

Switching from Manual to Automated QA Testing
Do you or your team currently test manually and trying to break into test automation? In this article, we outline how can small QA teams make transition from manual to codeless testing to full fledged automated testing.

Why you can’t ignore test planning in agile?
An agile development process seems too dynamic to have a test plan. Most organisations with agile, specially startups, don’t take the documented approach for testing. So, are they losing on something?

Challenges of testing Single Page Applications with Selenium
Single-page web applications are popular for their ability to improve the user experience. Except, test automation for Single-page apps can be difficult and time-consuming. We’ll discuss how you can have a steady quality control without burning time and effort.
Why is Codeless Test Automation better than Conventional Test Automation?
Testing is important for quality user experience. Being an integral part of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), it is necessary that testing has speed, efficiency and flexibility. But in agile development methodology, testing could be mechanical, routine and time-consuming.